Orange County, Virginia
Orange County is a county located in the Central Piedmont region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. At the 2010 census, the population was 33,481.[3] Its county seat is Orange.[4]
Orange County | |
|---|---|
 Orange County Courthouse
ex image size = 200px | |
 Seal | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Virginia | |
 Virginia's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 38°14′N 78°01′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1734[1] |
| Named for | Prince William III of Orange |
| Seat | Orange |
| Largest town | Orange |
| Area | |
| • Total | 343 sq mi (890 km2) |
| • Land | 341 sq mi (880 km2) |
| • Water | 2.5 sq mi (6 km2) 0.7% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 33,481 |
| • Estimate (2018)[2] | 36,644 |
| • Density | 98/sq mi (38/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 7th |
| Website | orangecountyva |
Orange County includes Montpelier, the 2,700-acre (1,100 ha) estate of James Madison, the 4th President of the United States and often known as the "Father of the Constitution". The county celebrated its 275th anniversary in 2009.[5]
History
The area was inhabited for thousands of years by various cultures of indigenous peoples. At the time of European encounter, the Ontponea, a sub-group of the Siouan-speaking Manahoac tribe, lived in this Piedmont area.[6]
The first European settlement in what was to become Orange County was Germanna, formed when Governor Alexander Spotswood settled 12 immigrant families from Westphalia, Germany, there in 1714; a total of 42 people. Orange County, as a legal entity, was created in August 1734 when the Virginia House of Burgesses adopted An Act for Dividing Spotsylvania County. Unlike other counties whose boundaries had ended at the Blue Ridge Mountains, Orange was bounded on the west "by the utmost limits of Virginia" which, at that time, stretched to the Mississippi River and the Great Lakes. The colony of Virginia claimed the land, but very little of it had yet been occupied by any English. For this reason, some contend that Orange County was at one time the largest county that ever existed.[7] This situation lasted only four years; in 1738 most of the western tract was split off into Augusta County. The expansiveness of the county boundaries was to encourage settlement further westward as well as to contend against the French claim to the Ohio Valley region.[8]
No battles of the American Revolution were fought in Orange County. However, two companies of 50 men each were recruited from Orange County to the Culpeper Minutemen. One was led by Col. Lawrence Taliaferro. In December 1775, this company fought in the Battle of Great Bridge[9] Orange County's Committee of Safety was also active in providing money, salt, horses, guns, beef, and other supplies to Continental forces.[10]
Orange County prospered with the development of several railroad routes through Orange and Gordonsville in the 1840s and 1850s. They succeeded the plank road between Fredericksburg and Orange, which connected with two important roads: the Richmond Road between the state capital and the Shenandoah Valley (which passed through Louisa) and a stagecoach route to Charlottesville and points south. The Orange and Alexandria Railroad and Virginia Central Railroad helped foster a diversified agricultural economy in Orange County, bringing produce and timber to markets in Richmond, Washington D.C., and Norfolk as well as more industrial products. The final adjustment of the county's boundaries occurred in 1838 when Greene County was created from the western portion of Orange. The Town of Orange was legally established in 1834 (officially becoming a town in 1872) and had already served as the county seat for nearly a century; Gordonsville officially achieved town status in 1870.[8]
During the Civil War, the towns of Orange and Gordonsville continued as important railroad hubs and hospital centers for the Confederacy. Confederate military companies recruited from the county included three companies of the 13th Virginia Infantry, the Gordonsville Grays, two artillery companies, one cavalry company (the Orange Rangers), and many soldiers in the 7th Virginia Infantry, Wise Artillery and 6th Virginia Cavalry. General Robert E. Lee often rode through the county and wintered the Army of Northern Virginia in Orange County during 1863–64, the Rapidan River becoming a defensive line.[11] Cavalry raids against the railroad supply lines occurred, including several at Rapidan on the border with Culpeper County. Troops often crossed the Rapidan River at Germanna Ford near Locust Grove. After Fredericksburg fell to Union forces, Mosby's Rangers were formed and conducted some operations (as well as recovered from wounds) in Orange County; Mosby himself was once captured while waiting for a train in Beaverdam in Hanover County for travel through Orange County. The 1863 Battle of Mine Run and the 1864 Battle of the Wilderness both occurred in eastern Orange County, as Union troops drove toward the Confederacy's capital. The latter became a significant turning point in the war.
Following Virginia's readmission to the Union in 1870, the railroads were rebuilt (many being consolidated into the Chesapeake and Ohio Railroad after 1868). The county was also divided into Barbour, Madison, Taylor, and Gordon townships, named after important pre-war citizens.[12] The agricultural economy resumed despite the loss of slave labor (6,111 slaves had lived in the county in 1860, valued at $1.5 million),[13] with more livestock and dairy farming both because such required less physical labor and because the railroads could deliver those agricultural products to larger markets relatively quickly and cheaply. Virginia Governor James L. Kemper (1874-1878) moved from Madison County to near Orange as his term ended. Agriculture and manufacturing continued to expand into the twentieth century, with a peak of 1279 farms and 20 manufacturing companies located within the county as of 1929. A manufacturing survey taken during the Great Depression noted that Orange County's economy remained relatively healthy due to its accessibility.[8] The county's population fluctuated following the Civil War up through the 1930s. From that point forward, the population continued to grow steadily, representing an almost 300% increase through the 2010 Census.
In 1991, the Virginia Landmarks Register designated approximately 31,200 acres (126 km2) in the county's western portion as the Madison-Barbour Rural Historic District. The largest such district in the Commonwealth includes James Madison's Montpelier, James Barbour's Thomas Jefferson-designed Barboursville mansion (now in ruins), several plantations, portions of the Monticello Viticultural Area, as well as numerous individual sites listed on the National Register.[14] The Gordonsville Historic District was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1984, the Rapidan Historic District in 1987, and the Orange Commercial Historic District added to the NRHP in 1999.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 343 square miles (890 km2), of which 341 square miles (880 km2) is land and 2.5 square miles (6.5 km2) (0.7%) is water.[15] The terrain is characterized by rolling hills, generally increasing in altitude and slope as they continue westward toward the Blue Ridge Mountains. The highest point is Cowherd Mountain at 1,196 ft (345 m), approximately 2.5 miles (4 km) northwest of Gordonsville.[16]
Orange County lies within the watersheds of both the Rappahannock River and the York River, both of which drain into the Chesapeake Bay.[17]
Adjacent counties
- Madison County – northwest
- Culpeper County – north
- Spotsylvania County – east
- Louisa County – south
- Albemarle County – southwest
- Greene County – west
Waterbodies
- The Rapidan River defines the northern boundary of the county
- Lake Orange – a 124-acre public lake southeast of the Town of Orange
- The 500-acre Main Lake in Lake of the Woods
Nationally protected areas
- The Wilderness Battlefield in the eastern portion of the county lies within the Fredericksburg & Spotsylvania National Military Park
Transportation
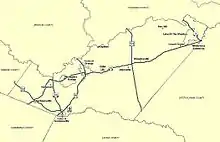
Airports
- Orange County Airport (OMH)
- Gordonsville Airport (GVE)
Public transportation
- The Town of Orange Transit (TOOT) provides bus service around and between the towns of Orange and Gordonsville
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 9,921 | — | |
| 1800 | 11,449 | 15.4% | |
| 1810 | 12,323 | 7.6% | |
| 1820 | 12,913 | 4.8% | |
| 1830 | 14,637 | 13.4% | |
| 1840 | 9,125 | −37.7% | |
| 1850 | 10,067 | 10.3% | |
| 1860 | 10,851 | 7.8% | |
| 1870 | 10,396 | −4.2% | |
| 1880 | 13,052 | 25.5% | |
| 1890 | 12,814 | −1.8% | |
| 1900 | 12,571 | −1.9% | |
| 1910 | 13,486 | 7.3% | |
| 1920 | 13,320 | −1.2% | |
| 1930 | 12,070 | −9.4% | |
| 1940 | 12,649 | 4.8% | |
| 1950 | 12,755 | 0.8% | |
| 1960 | 12,900 | 1.1% | |
| 1970 | 13,792 | 6.9% | |
| 1980 | 18,063 | 31.0% | |
| 1990 | 21,421 | 18.6% | |
| 2000 | 25,881 | 20.8% | |
| 2010 | 33,481 | 29.4% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 37,051 | [18] | 10.7% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[19] 1790-1960[20] 1900-1990[21] 1990-2000[22] | |||
At the 2010 census[23] there were 33,481 people, 12,895 households (14,616 total housing units) and 9,342 families residing in the county. The county experienced a population increase of 29%, or 7,600 people, since the 2000 census. This ties with Louisa County as the 11th fastest growing county in the commonwealth, and one of the fastest outside of Northern Virginia. The racial makeup of the county was 82.4% White, 12.7% Black or African American, 0.3% Native American, 0.7% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 1.4% from other races, and 2.4% from two or more races. 3.4% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
Of the 12,895 households, 27.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 56.8% were married couples living together, 10.9% had a female householder with no husband present, and 27.6% were non-families. Out of the total number of households, 32.6% housed someone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.55 and the average family size was 2.97.
The age distribution of the population was 22.9% under the age of 18, 6.7% from 18 to 24, 10.7% from 25 to 44, 28.5% from 45 to 64, and 18.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 42.6 years. For every 100 females there were 96 males.
The median household income was $56,837 and the median family income was $65,195. The per capita income was $26,820 and approximately 11.5% of the population was below the poverty line. Orange County had the 9th longest mean travel time to work (37 minutes)[24] out of 132 Virginia localities polled. The median home value was $238,500.
Education

Primary and secondary education is provided by Orange County Public Schools,[25] whose current (as of April 2019) superintendent is Dr. Cecil Snead .[26] The school board is represented by five elected officials, one from each district, whose terms run for three years.
List of previous superintendents.
Dr. Dennis Kellison 1996-
Dr. Dave Baker
William Crawford 2005- Nov 2008
Roy Walton (interim)
Dr. Robert Grimesey xxxx-2014
Dr Brenda Tanner 2014- current
Primary schools
- Gordon-Barbour Elementary
- Lightfoot Elementary
- Locust Grove Elementary
- Locust Grove Primary
- Orange Elementary
- Unionville Elementary
Secondary schools
- Locust Grove Middle
- Prospect Heights Middle
- Orange County High School
Post-secondary
Germanna Community College maintains a 65,000 ft2 (6,000 m2) facility on a 100-acre campus in Locust Grove which houses the college's Nursing and Allied Health programs. The facility, as part of the Virginia Community College System, includes classrooms, laboratories, faculty offices, a wellness center, student lounge and bookstore, as well as trails throughout the surrounding woodlands. Due to the growing demand for nursing and health professionals, in August 2013, the college has planned for expansion of the campus.[27]
Issues
In October 2014, 33% of the county-run schools failed to meet state accreditation levels resulting in a warning being issued by the Virginia Department of Education.[28] If the schools in question, Lightfoot, Unionville, and Prospect Heights, failed to meet accreditation levels for three consecutive years their accreditation would be denied. County residents paid $51,564,565.00 in taxes for educational operating expenses in 2015,[29] an increase of 11% ($5,684,921.00) in four years.
The former location of the Locust Grove Middle School was abandoned in 2011 after a new school was built less than two miles away. In 2013, plans were underway[30] to return the students to the original location due to what was referred to as cohabitation issues at the new school and a projected "boom" of approximately 20 third graders. This perceived increase was actually a return to prior attendance levels due to an anomalous single year decrease.[31] The initial cost to taxpayers to reopen the school was estimated at over $611,000.
Government
Federal
The county is part of Virginia's 7th congressional district and is represented by Congresswoman Abigail Spanberger.[32][33] It is represented by Bryce Reeves (R) in the 17th district of the Virginia State Senate, and by Ed Scott (R) in the 30th district of the Virginia House of Delegates.
Since 1952, the county has leaned Republican in national elections. Republican congressmen have won every contest and averaged 67% of the vote. Republican presidential candidates have averaged 55% of the vote, and the last Democratic presidential nominee to carry Orange County was Harry S. Truman in 1948.[34] Republican senatorial candidates typically garnered 56% of the county vote until the electorate swung in favor of Democratic candidates in 2008 and 2012 with an average of 57% of the vote, then back to Republican candidates in 2014 with 60% of the vote.[35]
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 59.9% 12,426 | 38.5% 7,995 | 1.6% 321 |
| 2016 | 60.9% 10,521 | 34.5% 5,957 | 4.6% 789 |
| 2012 | 56.5% 9,244 | 42.0% 6,870 | 1.5% 240 |
| 2008 | 53.8% 8,506 | 45.0% 7,107 | 1.2% 188 |
| 2004 | 59.9% 7,749 | 38.8% 5,015 | 1.3% 164 |
| 2000 | 57.2% 5,991 | 39.4% 4,126 | 3.5% 366 |
| 1996 | 49.8% 4,435 | 40.3% 3,590 | 9.9% 883 |
| 1992 | 45.6% 4,092 | 37.3% 3,348 | 17.0% 1,526 |
| 1988 | 61.6% 4,319 | 37.0% 2,592 | 1.5% 104 |
| 1984 | 65.7% 4,483 | 33.5% 2,285 | 0.8% 53 |
| 1980 | 54.9% 3,381 | 39.3% 2,420 | 5.8% 357 |
| 1976 | 49.4% 2,549 | 44.7% 2,309 | 5.9% 303 |
| 1972 | 71.3% 2,758 | 26.7% 1,032 | 2.0% 79 |
| 1968 | 47.2% 1,727 | 24.0% 879 | 28.8% 1,055 |
| 1964 | 51.3% 1,595 | 48.5% 1,508 | 0.1% 4 |
| 1960 | 54.3% 1,413 | 42.6% 1,108 | 3.2% 82 |
| 1956 | 53.6% 1,344 | 31.6% 794 | 14.8% 372 |
| 1952 | 62.2% 1,525 | 37.3% 916 | 0.5% 12 |
| 1948 | 39.2% 726 | 46.2% 856 | 14.6% 270 |
| 1944 | 36.6% 694 | 63.2% 1,199 | 0.2% 3 |
| 1940 | 26.4% 464 | 72.9% 1,283 | 0.7% 12 |
| 1936 | 24.6% 402 | 75.0% 1,227 | 0.4% 7 |
| 1932 | 19.7% 309 | 80.0% 1,253 | 0.3% 5 |
| 1928 | 46.4% 732 | 53.6% 846 | |
| 1924 | 17.0% 181 | 78.1% 834 | 5.0% 53 |
| 1920 | 26.4% 258 | 73.5% 718 | 0.1% 1 |
| 1916 | 20.0% 153 | 79.6% 608 | 0.4% 3 |
| 1912 | 11.4% 87 | 80.9% 619 | 7.7% 59 |
Local
Locally, the county is represented by the five-person Orange County Board of Supervisors, each of whom is elected from their respective districts; there are no at-large members. Board members serve four-year staggered terms and appoint district representatives to the Planning Commission, Board of Zoning Appeals, and the Economic Development Authority, among others. Administratively, the county operates under a council-manager form of government.
Taxation
Between 2006 and 2011, the county increased its property tax revenue by 25.2%, increased its personal property tax revenue by 30.4%, while simultaneously decreasing merchants capital tax revenue by -0.5%. Forecasts for 2012-2014 include additional increases of another 3.9% in property tax revenue, increases of 27.5% in personal property tax, and a further decrease of 0.9% in merchants capital tax.[37] During the previous 8-year period, property tax collections increased 29.1%, personal property tax collections increased 57.9%, and merchants capital taxes decreased by 1.4%.[38]
Crime
In November 2017, there was one registered sex offender living in Orange County.[39]
On 6 April 2014, George Toombs, a 10-year-old boy, was shot and killed.[40] The suspect in the case was scheduled to appear in court on murder charges on 15 February 2015.[41] The boys' mother was also charged with felony child neglect.[42]
While extremely rare in the county, a second fatal shooting occurred on 29 June 2014 in Gordonsville resulting in the death of Clyde Johnson.[43]
On 12 April 2012, 84-year-old James Weaver was bludgeoned to death in his home by a Louisa County man who used to do work around Weaver's home.[44]
On 10 September 2010, 19-year-old Samantha Clarke disappeared from her Orange home. Her disappearance remains unsolved.[45]
Orange County Sheriff's office maintained 36 sworn officers in 2012. The Town of Orange had 15 sworn officers and the Town of Gordonsville five. In 2012, the incident rate for the county was 1.6%, for the town of Orange 6.1%, and the Town of Gordonsville 3.4%.[46]
Economy
Orange County businesses generated over $200 billion in taxable sales in 2012. The top five industries by taxable sales, as classified by the NAICS, were food and beverage stores, food services and drinking places, gasoline stations, general merchandise dealers and motor vehicle and parts dealers. The top five industries by employment were local government, retail trade, manufacturing, accommodations and food services, and wholesale trade. In July 201), the top five private-sector employers are Dogwood Village, Macmillan Publishing Solutions, Battlefield Farms Inc., American Woodmark Corp. and Aerojet Rocketdyne. However, small businesses were the predominant employer type, with 65% of all Orange County businesses employing four or fewer workers.
Agriculture is an important part of the county's economy, of which nursery, greenhouse, floriculture and sod (NAICS category) represent the largest sector. Orange County is Virginia's top producer in this market sector. The equestrian and forestry industries are also large sectors within the agricultural economy of the county. In addition, tourism (particularly related to history, wine and agritourism) is a significant and growing portion of the economy.
Unemployment over the years has remained considerably below the United States average and slightly above that of Virginia. Recent studies show a 6% unemployment rate, which is the second highest rate in the region.[47] The highest-paid industry in Orange County in 2012 was finance and insurance, followed by pProfessional/scientific/technical services, educational services and transportation/warehousing. The highest-paid was accommodations/food services, followed by arts/entertainment/recreation, health care/social assistance and retail trade. The average weekly wage across all industries was $671.[48]
Wine
Portions of Orange County lie within the Monticello Viticultural Area. Four wineries are located within the county: Barboursville Vineyards, Horton Vineyards, Chateau MerrillAnne[49] and the Reynard Florence Vineyard. In 2012, Orange County contained 214 acres (868 short tons) worth of wine grape production, which was the third highest of all counties in the state. Tonnage of grapes produced and acreage devoted to production in the county has risen 60% and 72%, respectively, since 2004. This is representative of the growing wine industry in Virginia, which contributed a total of $747 billion to the state economy in 2010.[50]
Development issues


In September 2008, Wal-Mart submitted an application for a special use permit to build a 141,000-square-foot (13,100 m2) Supercenter store less than a quarter of a mile from the National Park Service boundary of the Wilderness Battlefield. It was to be situated on a 52-acre (210,000 m2) tract just north of the Route 3/Route 20 intersection in eastern Orange County. The Orange County Board of Supervisors formally approved the application on 25 August 2009. On 23 September 2009, the National Trust for Historical Preservation, Friends of the Wilderness Battlefield and six nearby citizens filed suit against the Board of Supervisors claiming the store was likely to produce a significant increase in traffic and subsequent development, among other counts. The National Trust was dropped from the suit for lack of legal standing, and Wal-Mart, its chosen developer and the property owner were later named as additional defendants.[51]
The lawsuit attracted national media attention, with the actor Robert Duvall and the filmmaker Ken Burns taking a formal stand against the project.[52] On 26 January 2011, the morning before the trial was set to begin, Wal-Mart submitted a statement to the court abandoning its plans for the store. In that statement, the company also agreed to purchase the subject property without developing it, to reimburse Orange County for its legal and administrative expenses related to the lawsuit and to find another site elsewhere in the county. The lawsuit was formally dismissed on 12 May 12011.[53]
Wal-Mart announced its selection on 23 May 2011 of a new site in the county, approximately 4 miles west of the original site, in the Germanna area of Locust Grove. Following approval of a new special use permit from the Board of Supervisors, the new store officially opened on 10 July 2013. The original plaintiffs in the lawsuit, along with other preservationist groups, expressed approval of Wal-Mart's new site and its decision to abandon the original plans.[54] In August 2013, Wal-Mart dedicated 25 feet of right-of-way from the original site to the Commonwealth of Virginia[55] and 70 feet of right-of-way to the county[56] for future transportation improvements. In September 2013, Walmart deeded the remainder of the site (approximately 48 acres) to the Virginia Department of Historic Resources.[57]
Subsequent to the selection of the new location, the county board of supervisors reduced the amount of tax revenue collected annually through the merchant's capital tax by 15% (11% in 2010, 2% in 2011 and 2% in 2012). This tax is determined by the value of inventory carried by a local business. In 2011, the county lost $599,690 in revenue provided by the federal government and, rather than adjust the annual budget or restore the merchants capital tax, the board approved a 16% personal property tax increase to raise an additional $666,141 of revenue for the county.[58]
An October 2013 revision to the county's 2009 comprehensive plan was met with overwhelming opposition by local residents concerned that the plan's vision to "sustain the rural character of Orange County while enhancing and improving the quality of life for all its citizens" was not accurately reflected in the document's development-friendly wording.[59] The plan was passed by the Board of Supervisors on 17 December 2013 by a vote of 3–1.[60]
On 21 February 2013,[61] members of the Orange County planning commission, voted to approve a re-zoning application in the Germanna area, and redesignate what had been an agricultural zone to a commercial and high-density residential area. Despite 90% of the local residents in attendance making a request for denial, the application was passed by J.P. Tucker III (owner of a construction company),[62] Andy Hutchinson (owner of a sod company),[63] and Donald Brooks (political candidate for sheriff).[64]
In May 2013, the county board of supervisors passed a resolution to create the Route 3 Strategic Initiative;[65] this resolution was based on a nine-year-old survey taken at the beginning of the 60% increase in population during the 2000s.[66] Public comment was solicited in three half-hour sessions only after the board dinner break during three monthly board meetings. The initiative which affects Districts 4 and 5 was spearheaded by District 2 supervisor Jim White, and may further the conflict between developers and local residents wishing to keep the area rural in character.
On 9 December 2014, Orange County supervisors Lee Frame and James White, planning commission member P. Nigel Goodwin, and Economic Authority members William Hager and Winston Sides proposed a land use plan entitled the Germanna-Wilderness Area Plan (GWAP) after consulting with private sector developers, financial analysts, and engineers.[67] This plan is a 50-year vision to develop a "place to live, work, and play with a higher standard of design and development which is a self-contained, complete community that is appealing to current and prospective residents." [68] The document was adopted in 2015.
On 9 July 2018, the Orange County Board of Supervisors considered adding three new zoning districts to the Germanna-Wilderness Area Plan (GWAP). The vote was unanimous in approving these changes.
Places of historical significance
In November 2013, Orange County had 34 sites listed on the National Register of Historic Places, including Barboursville, the Germanna Site, the Madison-Barbour Rural Historic District (the largest such district in Virginia) and the historic downtowns of both Orange and Gordonsville.
The James Madison Museum
Part of the registered historic commercial district, the first museum in the United States to honor James Madison is housed in a late 1929 building formerly known as Powell Motor Company and Hilltop restaurant. The museum is dedicated to serving the community by collecting and preserving the artifacts and cultural heritage of 18th, 19th and 20th century rural Virginia, and promoting an awareness and appreciation of the lives and achievements of James Madison and others who made a unique contribution to the region. Exhibits include "Presidential Cousins" James Madison and Zachary Taylor, presidential artifacts, a Black History Room, pictorial gallery and a large Hall of Agriculture and Transportation.

The Wilderness Battlefield
The Battle of the Wilderness was fought in Orange County on 5–7 May 1864. The battle was the first occasion that Generals Ulysses S. Grant and Robert E. Lee faced each other in the Civil War. The fighting at the Wilderness, while tactically inconclusive, was the first battle in Grant's Overland Campaign that ultimately led to the fall of Richmond and Lee's surrender at Appomattox.
Over 160,000 troops were engaged at the Wilderness in trench warfare and back-and-forth flanking attacks through the surrounding woodlands. When the guns fell silent on 7 May, over 23,000 soldiers lay dead or wounded, with thousands more either captured or missing. Grant's Union army disengaged and continued southward to fight the Battle of Spotsylvania Court House and ultimately press on toward Richmond.
Today, the Battle of the Wilderness is a part of the Fredericksburg and Spotsylvania National Military Park, which has preserved 2,773 acres (11.22 km2) of the original battlefield.
Ellwood Manor
.jpg.webp)
Ellwood Manor is the only surviving house that witnessed the Battle of the Wilderness in May 1864. During the battle, Ellwood became a base of operations for the Union Army as Union General Grant made his headquarters nearby. Ellwood also played a role in the Battle of Chancellorsville in 1863 when Confederate General Stonewall Jackson, who was wounded during the battle, had his arm amputated and buried in the family cemetery at Ellwood. Following the battle at Chancellorsville, Ellwood was a Confederate hospital.
In 2008, Ellwood was named "Favorite Virginia Civil War Site" by the Rappahannock Electric Cooperative's Cooperative Living magazine.[69]
Montpelier

Montpelier is the 2,700-acre plantation estate of James Madison, the 4th President of the United States and oft-hailed "Father of the Constitution." The original portion of the home was constructed around 1764 by Madison's father, James Madison Sr., with 2 major additions coming later in 1800 and 1812. The National Trust for Historic Preservation has owned the Montpelier estate since 1984. From 2003 to 2008 a $25 million renovation was performed on the property, returning both the home and grounds to their 1820 state as they were when occupied by James and his wife Dolley. Montpelier was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1960 and has been on the National Register of Historic Places since 1966. Both Madison and Dolley are buried in the family cemetery on the property.
The Exchange Hotel

A well-preserved example of 19th century Georgian architecture, the Exchange Hotel stands in the Town of Gordonsville as a living piece of Civil War history. Built in 1860 as a hotel on the Virginia Central Railroad, the building was soon transformed into the Gordonsville Receiving Hospital following the onset of the American Civil War. Because of its strategic location along a major railroad and proximity to nearby battlefields, the hospital treated over 70,000 wounded men by the end of the war. During Reconstruction, the hotel was known as the Freedman's Bureau Hospital which served newly freed slaves. The building eventually returned to its former use as a hotel, before being restored in 1971 and transformed into a museum. It is the only remaining Civil War era receiving hospital in Virginia.[70]
Receiving hospitals during the Civil War functioned as triage centers, providing short-term medical care until doctors forwarded patients to other towns or medical facilities. These hospitals were normally located in large cities or on routes where patients were to change their mode of transportation and continue on to other destinations. Receiving hospitals, otherwise known as depot hospitals or clearing hospitals, were marked by short patient stays and a high turnover rate.[71]
Media
The county is served locally by the Orange County Review, a BH Media Group-owned weekly newspaper, and regionally by the Fredericksburg-based The Free Lance Star, Culpeper Star-Exponent and the Charlottesville Daily Progress. WVCV is licensed to Orange and the county is also served by radio stations in the Fredericksburg and Charlottesville radio markets.
Communities
Towns
Census-designated place
Unincorporated communities
Notable people
- Edna Lewis, African-American cookbook author and chef, "whose cookbooks revived the nearly forgotten genre of refined Southern cooking"[72]
- Nannie Helen Burroughs, African-American educator, orator, religious leader and businesswoman
- Elijah Craig, Baptist minister who was arrested in Fredericksburg in the cause of religious freedom before the Revolution; later followed after brother Rev. Lewis Craig, leader of "The Travelling Church" to Kentucky in 1781
- Chris Haney, Major League Baseball pitcher
- Patrick Kilpatrick, actor
- Dwayne "The Rock" Johnson, actor and professional wrestler; maintains an estate in the county[73]
- Randolph Scott, western film actor
- James Taliaferro, former U.S. senator for Florida
- Zachary Taylor, 12th President of the United States
- James Barbour, the 18th Governor of Virginia, US Senator, and United States Secretary of War
- James Madison, the 4th President of the United States and "Father of the Constitution"
- Lewis R. Bradley, second Governor of Nevada in the United States from 1871 to 1879; born in Orange County.[74]
See also
References
- "Orange County Virginia". Orange County Virginia. Archived from the original on 14 September 2012. Retrieved 26 September 2012.
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved January 4, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 3, 2015. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- Knepper, Robin. 5 October 2009. "Orange County Marks 275 Years of History"
- Swanton, John R. (1952). The Indian Tribes of North America. Smithsonian Institution. pp. 61–62. ISBN 0-8063-1730-2. OCLC 52230544.
- Gwathmey, John. 1937. Twelve Virginia Counties, p. 277.
- "Orange Commercial Historic District", National Register of Historic Places Registration Form. June 1998. Form prepared by Debra McClane of Gray & Pape, Inc. Retrieved 15 November 2013. "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 September 2013. Retrieved 8 September 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Scribner, Robert L.; Brent Tarter (1977). Revolutionary Virginia: The Road to Independence, Vol. 3. Charlottesville: Virginia Independence Bicentennial Commission and University of Virginia Press. p. 466.
- Scott pp. 70-76
- W. W. Scott, History of Orange County, Virginia (Baltimore, Regional Publishing Company, 1974 reprint of 1907 Richmond publication) pp. 154-156
- Scott p. 164
- Scott p. 166
- "Madison-Barbour Rural Historic District." National Register of Historic Places registration form. December 1989. Form prepared by Jeff O'Dell and John S. Salmon, Virginia Dept. of Historic Resources. Retrieved 15 November 2013. "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2012. Retrieved 19 March 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 12 February 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- Orange County 2009 Comprehensive Plan. Retrieved 26 July 2013. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 20 August 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Virginia Watersheds. Retrieved 26 July 2013. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 13 August 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved 4 Feb 2021.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Archived from the original on 11 August 2012. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 15 December 2013. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 December 2014. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- Virginia, State of (1998–2009). "Virginia.gov - Education - Home Page". Archived from the original on 7 June 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
- "Orange County Schools Office of the Superintendent". Orange County Public Schools. Archived from the original on 21 July 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2009.
- "Locations- Locust Grove Campus". Germanna Community College. Archived from the original on 7 August 2013. Retrieved 18 July 2013.
- http://www.dailyprogress.com/orangenews/news/six-of-nine-county-schools-earn-full-state-accreditation/article_1aad9952-4fe4-11e4-b90c-001a4bcf6878.html School Accreditation
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 11 December 2014. Retrieved 11 December 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) OC County Budget
- Closed School Key Topic
- "OC Student Totals". Archived from the original on 15 January 2014. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- "Spanberger wins Democratic primary in Virginia's 7th Congressional District". The Washington Post website. Retrieved July 17, 2018.
- Almukhtar, Sarah (November 7, 2018). "Virginia's 7th House District Election Results: Dave Brat vs. Abigail Spanberger". The New York Times. Retrieved November 7, 2018.
- Sullivan, Robert David; "How the Red and Blue Map Evolved Over the Past Century" Archived 16 November 2016 at the Wayback Machine; America Magazine in The National Catholic Review, 29 June 2016
- "Orange County Election Results 1995-Present". Archived from the original on 5 July 2014. Retrieved 11 June 2014.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". US Election Atlas. Archived from the original on 9 December 2020.
- O"C Adopted Budgets". Archived from the original on 11 December 2014. Retrieved 11 December 2014.
- "Orange County Tax Rates". Orange County. Archived from the original on 10 January 2014. Retrieved 10 January 2014.
- "Legislative Information System". leg1.state.va.us. Archived from the original on 10 January 2014. - "VA State Police Sex Offender Registry". Archived from the original on 30 December 2013. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- "Sheriff Investigates Fatal Shooting of 10-Year-Old, 2 Charged". NBC News. Archived from the original on 7 December 2014. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- "2 Charged in Connection with Orange Boy's Death to Appear in Court". NBC News. Archived from the original on 7 December 2014. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- Carie, Julie (8 April 2014). "Prosecutors Believe Virginia Man Shot Fiancee's 10-Year-Old Son Intentionally". NBC Washington. Retrieved 8 October 2020.
- "Gordonsville Shooting", Daily Progress
- "AGuilty Plea Entered in Orange County Murder". NBC News. Archived from the original on 7 December 2014. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- Hillier, Bianca (31 August 2018). "Samantha Clarke still missing eight years after vanishing from family home in Virginia". NBC News. Retrieved 8 October 2020.
- "2012 VSP-UCR". Archived from the original on 25 November 2011. Retrieved 18 November 2011.
- ]http://www.dailyprogress.com/eedition/mapping/jobless-rate-rises-in-region/article_0817d1bf-2e27-5a87-a95d-647710a40d61.html?mode=image&photo=0 "July/August 2014 Unemployment Rate"], Daily Progress
- "AOrange County Draft 2013 Comprehensive Plan". Archived from the original on 29 July 2013. Retrieved 28 July 2013.
- "Orange County Community Profile" (PDF). Virginia Employment Commission. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 12 August 2013. - Virginia Wine Association
- "Virginia 2012 Commercial Grape Report" (PDF). Virginia Wine Marketing Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 July 2014. Retrieved 28 July 2013.
- Schemmer, Clint, "Group wants to sidetrack Orange project", 22 August 2008
- Boyd, Scott C. (9 November 2009). "County Claims Wal-mart Opponents Lack Standing in Court". Civil War News. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 23 July 2013. - "Va. battle of Wal-Mart continues", Washington Post, 30 April 2010
- Boyd, Scott C. (June 2011). "Wal-mart Wilderness Case Finally Over". Civil War News. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 23 July 2013.
- Boyd, Scott C. (July 2011). "Wal-mart Finds Orange County Site". Civil War News. Archived from the original on 14 January 2014. Retrieved 23 July 2013.
- Instrument #130008956. Retrieved from the Orange County Circuit Court on 15 November 2013.
- Instrument #130008955. Retrieved from the Orange County Circuit Court on 15 November 2013.
- Instrument #130008957. Retrieved from the Orange County Circuit Court on 15 November 2013.
- 2009, 2010, 2011 tax rates
- "OC Comp Plan Debate", Daily Progress
- "Comp Plan Passed", Daily Progress
- Signature Station REZ 11-01Archived 16 December 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 April 2017. Retrieved 16 April 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 December 2014. Retrieved 15 December 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Service, Drew Jackson, Media General News. "Familiar foes face off in Orange sheriff race". Daily Progress.
- "Route 3 Strategic Visioning Initiative". Orange County. Archived from the original on 16 April 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2014.
- "564". Orange County. Archived from the original on 30 September 2013. Retrieved 15 December 2014.
- "AGermanna-Wilderness Area Plan". Orange County. Archived from the original on 16 December 2014. Retrieved 15 December 2014.
- Galaviz, Amber. "GWAP zoning up for review". The Daily Progress. Retrieved 29 August 2018.
- "Ellwood named favorite Virginia Civil War site - Culpeper Star-Exponent". starexponent.com. Archived from the original on 22 August 2008.
- "HGI Exchange Hotel". Archived from the original on 15 September 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Schroeder-Lein, Glenna R. The Encyclopedia of Civil War Medicine, M E Sharpe, Inc. ISBN 978-0765621306
- https://www.nytimes.com/2006/02/14/us/edna-lewis-89-dies-wrote-cookbooks-that-revived-refined-southern-cuisine.html
- "Orange County property tax records". Archived from the original on 17 August 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- "Nevada Governor Lewis Rice Bradley". National Governors Association. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 26 September 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Orange County, Virginia. |
- Orange County official government web site
- Orange County Historical Society
- The Journey Through Hallowed Ground official web site
- Memorial Foundation of the Germanna Colonies in Virginia
- City-Data.com Comprehensive statistical data and more about Orange County
- Friends of Wilderness Battlefield