Mérida, Spain
Mérida (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈmeɾiða]) is a city and municipality of Spain, part of the Province of Badajoz, and capital of the autonomous community of Extremadura. Located in the western-central part of the Iberian Peninsula at 217 metres above sea level, the city is crossed by the Guadiana and Albarregas rivers. The population is 60,119 in 2017.
Mérida | |
|---|---|
 Collage of Mérida, Top:Merida Ancient Roman Theater, Second left:Asanblea de Extremadura (Extremadura Assembly), Second right:Acueducto de Los Milagros (Los Milagros Aqueduct), Third left:A interior of Merida National Roman Art Museum, Third upper right:Merida Roman Bridge, Third lower right:Templo de Diana (Diana Temple), Bottom:A night view of Lusitania Bridge and Guadiana River | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 Mérida  Mérida | |
| Coordinates: 38°54′N 6°20′W | |
| Country | |
| Autonomous community | |
| Province | |
| Founded | 25 BC |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Antonio Rodríguez Osuna (2015) (PSOE) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 865.6 km2 (334.2 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 217 m (712 ft) |
| Population (2018)[1] | |
| • Total | 59,352 |
| • Density | 69/km2 (180/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Emeritenses |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 06800 |
| Website | Official website |
Emerita Augusta was founded as a Roman colony in 25 BC under the order of the emperor Augustus to serve as a retreat for the veteran soldiers (emeritus) of the legions V Alaudae and X Gemina. The city, one of the most important in Roman Hispania, was endowed with all the comforts of a large Roman city and served as capital of the Roman province of Lusitania since its founding and as the capital of the entire Diocese of Hispania during the fourth century. Following invasions from the Visigoths, Merida remained an important city of the Visigothic Kingdom of Hispania in the 6th century. In the 713, the city was conquered by the Umayyad Caliphate, and remained under Muslim rule. The Mozarabic people of the island rebelled repeatedly against the Caliphate authorities in the 9th century and the city began a slow decline. After the Almohad rule, Mérida, that had acknowledged Ibn Hud against the former, was seized by Alfonso IX of León in 1230. It is, together with Badajoz, ecclesiastically the metropolitan seat of the Archdiocese of Mérida-Badajoz. It became the capital of the autonomous community of Extremadura in 1983. The archeological site in the city has been a UNESCO World Heritage site since 1993.
The current Mayor (since 2015) is Antonio Rodríguez Osuna, from the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party.
Etymology
The place name of Mérida derives from the Latin Emerita, with a meaning of retired or veteran. It is part of the name that the city received after its foundation by the emperor Augustus in 25 BC, Augusta Emerita, colony in which veteran soldiers or emeritus settled.
History
Mérida has been populated since prehistoric times as demonstrated by a prestigious hoard of gold jewellery that was excavated from a girl's grave in 1870. Consisting of two penannular bracelets, an armlet and a chain of six spiral wire rings, it is now preserved at the British Museum.[2] The town was founded in 25 BC, with the name of Emerita Augusta (meaning the veterans – discharged soldiers – of the army of Augustus, who founded the city; the name Mérida is an evolution of this) by order of Emperor Augustus, to protect a pass and a bridge over the Guadiana river. Emerita Augusta was one of the ends of the Vía de la Plata (Silver Way), a strategic Roman Route between the gold mines around Asturica Augusta and the most important Roman city in the Iberian Peninsula. The city became the capital of Lusitania province, and one of the most important cities in the Roman Empire. Mérida preserves more important ancient Roman monuments than any other city in Spain, including a triumphal arch and a theatre.
After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, during the Visigothic period, the city maintained much of its splendor, especially under the 6th-century domination of the bishops, when it was the capital of Hispania. In 713 it was conquered by the Muslim army under Musa bin Nusair, and became the capital of the cora of Mérida; the Arabs re-used most of the old Roman buildings and expanded some, such as the Alcazaba. During the fitna of al-Andalus, Merida fell in the newly established Taifa of Badajoz.
The city was brought under Christian rule in 1230, when it was conquered by Alfonso IX of León, and subsequently became the seat of the priory of San Marcos de León of the Order of Santiago. A period of recovery started for Mérida after the unification of the crowns of Aragon and Castile (15th century), thanks to the support of Alonso de Cárdenas, Grand Master of the Order. In 1720 the city became the capital of the Intendencia of Mérida. It is on the Via de la Plata path of the Camino de Santiago as an alternative to the French Way.
In the 19th century, in the course of the Napoleonic invasion, numerous monuments of Mérida and of Extremadura were destroyed or damaged. Later the city became a railway hub and underwent massive industrialization.
On 10 August, 1936, during the Spanish Civil War, in the Battle of Mérida[3] the Nationalists gained control of the city.
Climate
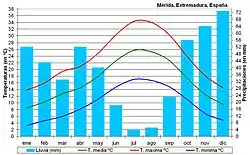
Mérida has a Mediterranean climate with Atlantic influences, due to the proximity of the Portuguese coast. The winters are mild, with minimum temperature rarely below 0 °C (32 °F), and summers are hot with maximum temperatures occasionally exceeding 40 °C (104 °F).
Precipitation is normally between 450 to 500 mm (17.7 to 19.7 in) annually. The months with most rainfall are November and December. Summers are dry, and in Mérida, as in the rest of southern Spain, cycles of drought are common, ranging in duration from 2 to 5 years.
In autumn the climate is more changeable than in the rest of the year. Storms occur with some frequency, but the weather is often dry.
Both humidity and winds are low. However, there is frequent fog, especially in the central months of autumn and winter.
| Climate data for Mérida, 1981-2010 normals | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 14.0 (57.2) |
16.1 (61.0) |
20.1 (68.2) |
21.6 (70.9) |
25.9 (78.6) |
31.6 (88.9) |
34.8 (94.6) |
34.7 (94.5) |
30.6 (87.1) |
24.4 (75.9) |
18.3 (64.9) |
14.5 (58.1) |
23.9 (75.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 8.9 (48.0) |
10.5 (50.9) |
13.4 (56.1) |
15.2 (59.4) |
18.9 (66.0) |
23.6 (74.5) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.3 (79.3) |
23.2 (73.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
13.0 (55.4) |
9.9 (49.8) |
17.3 (63.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 3.8 (38.8) |
4.8 (40.6) |
6.8 (44.2) |
8.7 (47.7) |
11.9 (53.4) |
15.7 (60.3) |
17.8 (64.0) |
17.8 (64.0) |
15.9 (60.6) |
12.2 (54.0) |
7.6 (45.7) |
5.3 (41.5) |
10.7 (51.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 51.4 (2.02) |
40.7 (1.60) |
33.2 (1.31) |
49.2 (1.94) |
43.0 (1.69) |
15.3 (0.60) |
3.6 (0.14) |
5.7 (0.22) |
25.4 (1.00) |
61.4 (2.42) |
69.3 (2.73) |
69.3 (2.73) |
467.5 (18.4) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 10.3 | 9.4 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 7.7 | 2.4 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 4.6 | 9.8 | 9.9 | 12.5 | 86.3 |
| Source: World Meteorological Organization[4] | |||||||||||||
Culture
Main sights
Among the remaining Roman monuments are:
The Puente Romano, a bridge over the Guadiana River that is still used by pedestrians, and the longest of all existing Roman bridges.[5] Annexed is a fortification (the Alcazaba), built by the Muslim emir Abd ar-Rahman II in 835 on the Roman walls and Roman-Visigothic edifices in the area. The court houses Roman mosaics, while underground is a Visigothic cistern.
- remains of the Forum, including the Temple of Diana, and of the Roman Provincial Forum, including the so-called Arch of Trajan
- remains of the Circus Maximus (1st century BC), one of the best preserved Roman circus buildings
- Acueducto de los Milagros (aqueduct of Miracles)
- patrician villa called the Villa Mitreo, with precious mosaic pavements
- Proserpina Dam and Cornalvo Dam, two Roman reservoirs still in use
- the Amphitheatre, and the Roman theatre, where a summer festival of Classical theatre is presented, usually with versions of Greco-Roman classics or modern plays set in ancient times.
- Morerías archaeological site
- Museo Nacional de Arte Romano (National Museum of Roman Art) designed by Rafael Moneo
- Church of Santa Eulalia, dating to the 4th century but rebuilt in the 13th century. Its portico reuses parts of an ancient temple of Mars.

Other sights include:
- Cathedral of Saint Mary Major (13th-14th centuries)
- Renaissance Ayuntamiento (Town Hall)
- Church of Santa Clara (17th century)
- Gothic church of Nuestra Señora de la Antigua (15th-16th centuries)
- Baroque church of Nuestra Señora del Carmen (18th century)
Several notable buildings were built more recently, including the Escuela de la Administración Pública (Public Administration College), the Consejerías y Asamblea de Junta de Extremadura (councils and parliament of Extremadura), the Agencía de la Vivienda de Extremadura (Housing Agency of Extremadura), the Biblioteca del Estado (State Library), the Palacio de Congresos y Exposiciones (auditorium), the Factoría de Ocio y Creación Joven (cultural and leisure center for youth), the Complejo Cultural Hernán Cortés (cultural centre), the Ciudad Deportiva (sports city), the Universidad de Mérida (Mérida University), the Confederación Hidrografica del Guadiana (Guadiana Hydrographic Confederation designed by Rafael Moneo), the Lusitania Bridge over the Guadiana River designed by Santiago Calatrava), the Palacio de Justicia (Justice Hall), etc.
Sport
Mérida AD is the principal football team of the city, founded in 2013 as a successor to Mérida UD, which itself was a successor to CP Mérida. The last of these teams played two seasons in Spain's top division, La Liga, in the late 1990s.
All three clubs played at the city's 14,600-capacity Estadio Romano. On 9 September 2009, it hosted the Spanish national team as they defeated Estonia 3–0 to qualify for the 2010 FIFA World Cup, which they went on to win. Mayor of Mérida Ángel Calle said, “We want to use the Estonia match to promote Mérida and Extremadura, we will welcome the players as if they were 21st-century gladiators.”[6]
Notes
- Municipal Register of Spain 2018. National Statistics Institute.
- British Museum Collection
- Beevor, Antony. (2006). The Battle for Spain. The Spanish Civil War, 1936-1939. Penguin Books. London. p. 120
- O’Connor 1993, pp. 106–107
- Rogers, Iain (10 September 2009). "Spain's '21st century gladiators' do Merida proud". Reuters. Retrieved 24 January 2014.
Sources
- O’Connor, Colin (1993), Roman Bridges, Cambridge University Press, pp. 106–107, ISBN 0-521-39326-4
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mérida (Spain). |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Mérida (Spain). |
- Official website
- Roman Art National Museum
- Pictures of Roman Mérida
- Photos of Mérida: Roman monuments and other views of the city

.jpg.webp)