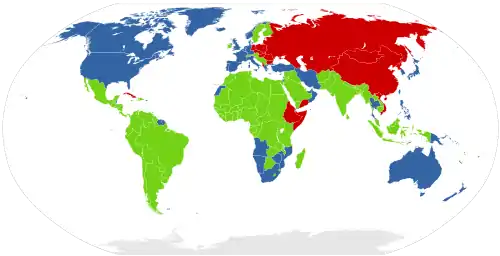
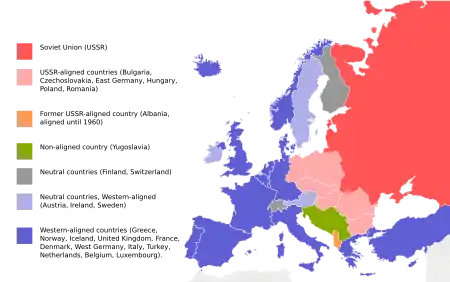
Western Bloc
The Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, was a coalition of the countries that were allied with the United States and its ideology, a member of NATO, and/or opposed the Soviet Union, Warsaw Pact, and communism during the Cold War 1947-1991. The latter were referred to as the Eastern Bloc. The governments and the press of the Western Bloc were more inclined to refer to themselves as the "Free World" or the "Western world", whereas the Eastern Bloc was often called the "Communist world or Second world".
Western Bloc associations
NATO
.svg.png.webp) Belgium
Belgium.svg.png.webp) Canada
Canada Denmark
Denmark France
France Germany (from 1990)
Germany (from 1990)
 West Germany (1955–1990)
West Germany (1955–1990)
 Greece (from 1952)
Greece (from 1952) Iceland
Iceland Italy
Italy Luxembourg
Luxembourg Netherlands
Netherlands Norway
Norway Portugal
Portugal Spain (from 1982)
Spain (from 1982) Turkey (from 1952)
Turkey (from 1952) United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States
Countries which have become NATO members after the end of the Cold War
 Czech Republic (from 1999)
Czech Republic (from 1999) Hungary (from 1999)
Hungary (from 1999) Poland (from 1999)
Poland (from 1999) Bulgaria (from 2004)
Bulgaria (from 2004) Estonia (from 2004)
Estonia (from 2004) Latvia (from 2004)
Latvia (from 2004) Lithuania (from 2004)
Lithuania (from 2004) Romania (from 2004)
Romania (from 2004) Slovakia (from 2004)
Slovakia (from 2004) Slovenia (from 2004)
Slovenia (from 2004) Albania (from 2009)
Albania (from 2009) Croatia (from 2009)
Croatia (from 2009) Montenegro (from 2017)
Montenegro (from 2017) North Macedonia (from 2020)
North Macedonia (from 2020)
Other NATO-affiliated states and partners
Rio Treaty
 Argentina
Argentina Bahamas (from 1982)
Bahamas (from 1982) Bolivia (until 2012)
Bolivia (until 2012) Brazil
Brazil Chile
Chile Colombia
Colombia Costa Rica
Costa Rica Cuba (until 1959)
Cuba (until 1959) Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Ecuador (until 2012)
Ecuador (until 2012) El Salvador
El Salvador Guatemala
Guatemala Haiti
Haiti Honduras
Honduras Mexico (until 2004)
Mexico (until 2004) Nicaragua (until 1979)
Nicaragua (until 1979) Panama
Panama Paraguay
Paraguay.svg.png.webp) Peru
Peru Trinidad and Tobago (from 1967)
Trinidad and Tobago (from 1967) United States
United States Uruguay
Uruguay Venezuela
Venezuela
SEATO
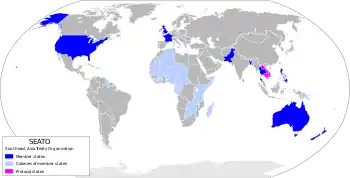
Map of SEATO members in 1959, shown in blue
.svg.png.webp) Australia
Australia France (until 1965)
France (until 1965).svg.png.webp) Laos (until 1975)
Laos (until 1975) New Zealand
New Zealand Pakistan (until 1972)
Pakistan (until 1972) Philippines
Philippines South Vietnam (until 1975)
South Vietnam (until 1975) Thailand
Thailand United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States
Middle East/North Africa Region
 Bahrain
Bahrain Egypt (from 1979)
Egypt (from 1979).svg.png.webp) Iran (until 1979)
Iran (until 1979).svg.png.webp) Iraq (until 1959)
Iraq (until 1959) Israel
Israel Jordan
Jordan Kuwait
Kuwait Lebanon
Lebanon Libya (from 2011)
Libya (from 2011) Morocco
Morocco Oman
Oman Palestine (West Bank government, until 2019)
Palestine (West Bank government, until 2019) Qatar
Qatar Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Somalia
Somalia Sudan
Sudan Syrian opposition
Syrian opposition Tunisia
Tunisia Turkey
Turkey United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates Yemen (Hadi government)
Yemen (Hadi government)
 North Yemen (1962–1990)
North Yemen (1962–1990)
East Asia
 Republic of China (Taiwan)
Republic of China (Taiwan).svg.png.webp) British Hong Kong (until 1997)
British Hong Kong (until 1997) Portuguese Macau (until 1967)
Portuguese Macau (until 1967) Japan
Japan South Korea
South Korea
See also
References
Sources
- Matloff, Maurice. Makers of Modern Strategy. Ed. Peter Paret. Princeton: Princeton UP, 1971. 702.
- Kissinger, Henry. Diplomacy. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1994. 447,454.
- Lewkowicz, Nicolas. The United States, the Soviet Union and the Geopolitical Implications of the Origins of the Cold War New York and London: Anthem Press, 2018.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.