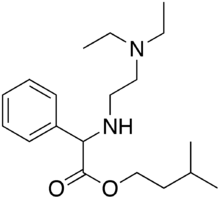
Camylofin
Camylofin is a smooth muscle relaxant with both anticholinergic action as well as direct smooth muscle action. Anticholinergic action is produced by inhibiting the binding of acetylcholine to muscarinic receptors, but the action is less pronounced.[2] Direct smooth muscle relaxation is achieved by inhibiting phosphodiesterase type IV, which leads to increased cyclic AMP and eventually reduced cytosolic calcium. Thus camylofin has a comprehensive action to relieve smooth muscle spasm. It is used to treat stomach ache in infants and children. Usually it is given in combination with paracetamol to treat stomach ache, as well as pyrexia.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Acamylophenine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.184 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H32N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 320.477 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Camylofin is an antimuscarinic drug.[1]
References
- "Camylofin". PubChem. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
- Mayadeo N (January 2019). "Camylofin dihydrochloride injection: a drug monograph review". International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology. 8 (1): 359–367. doi:10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20185453.
- Sarbhjit K, Bajwa SK, Parmjit K, Surinder B (September 2013). "To compare the effect of camylofin dihydrochloride (anafortin) with combination of valethamate bromide (epidosin) and hyoscine butyl-N-bormide (buscopan) on cervical dilation". Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 7 (9): 1897–9. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2013/6231.3345. PMC 3809631. PMID 24179892.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
