Anisodine
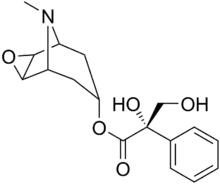
Anisodine, also known as daturamine and α-hydroxyscopolamine, is an antispasmodic and anticholinergic drug used in the treatment of acute circulatory shock in China.[1][2] It is a tropane alkaloid and is found naturally in plants of the family Solanaceae.[2] Anisodine acts as a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NO5 |
| Molar mass | 319.357 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
See also
References
- Varma DR, Yue TL (March 1986). "Adrenoceptor blocking properties of atropine-like agents anisodamine and anisodine on brain and cardiovascular tissues of rats". British Journal of Pharmacology. 87 (3): 587–94. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10201.x. PMC 1916562. PMID 2879586.
- Ganellin, C. R.; Triggle, David J. (21 November 1996). Dictionary of pharmacological agents - Google Books. ISBN 9780412466304.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
