Mesoridazine
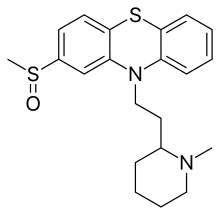
Mesoridazine (Serentil) is a piperidine neuroleptic drug belonging to the class of drugs called phenothiazines, used in the treatment of schizophrenia. It is a metabolite of thioridazine. The drug's name is derived from the methylsulfoxy and piperidine functional groups in its chemical structure.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Serentil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a682306 |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 4% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic/renal |
| Elimination half-life | 24 to 48 hours |
| Excretion | Biliary and renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H26N2OS2 |
| Molar mass | 386.57 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 130 °C (266 °F) |
| Solubility in water | insoluble mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
It has central antiadrenergic, antidopaminergic, antiserotonergic and weak muscarinic anticholinergic effects.
Serious side effects include akathisia, tardive dyskinesia and the potentially fatal neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
Mesoridazine was withdrawn from the United States market in 2004 due to dangerous side effects, namely irregular heart beat and QT-prolongation of the electrocardiogram.[1]
It currently appears to be unavailable worldwide.
References
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (AHFS). "Mesoridazine". Medline Plus. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
| Classes | |
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (TCAs and TeCAs) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Others |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.