Cioteronel
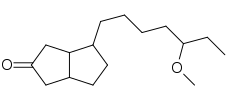
Cioteronel (INN, USAN) (developmental code name CPC-10997; former tentative brand names Cyoctol, X-Andron) is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) that was never marketed.[1][2][3] It was under development between 1989 and 2001 for the topical treatment of androgenetic alopecia (male pattern baldness) and acne and for the oral treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia; it reached phase III clinical trials for acne and phase II studies for androgenetic alopecia, but was ultimately discontinued due to poor efficacy.[3][4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | CPC-10997; Cyoctol; X-Andron |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, topical |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal antiandrogen |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 252.398 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. p. 570. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
- Lednicer D (21 November 1994). The Organic Chemistry of Drug Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 11–. ISBN 978-0-471-58959-4.
- Tiwari A, Krishna NS, Nanda K, Chugh A (November 2005). "Benign prostatic hyperplasia: an insight into current investigational medical therapies". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 14 (11): 1359–72. doi:10.1517/13543784.14.11.1359. PMID 16255676. S2CID 25662071.
- "Cioteronel". Adis Insight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.