Congress of Deputies
The Congress of Deputies (Spanish: Congreso de los Diputados; Basque: Diputatuen Kongresua; Catalan: Congrés dels Diputats; Galician: Congreso dos Deputados) is the lower house of the Cortes Generales, Spain's legislative branch. The Congress meets in the Palace of the Parliament (Palacio de las Cortes) in Madrid.
Congress of Deputies Congreso de los Diputados | |
|---|---|
| 14th Congress of Deputies | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 1834 |
| Leadership | |
President (speaker) | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 350 |
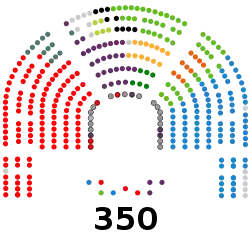 | |
Political groups | Government (155)
Supported by (34) Opposition (161) |
| Elections | |
| Party-list proportional representation, D'Hondt method | |
Last election | 10 November 2019 |
Next election | 2023 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Palacio de las Cortes Madrid, Community of Madrid Kingdom of Spain | |
| Website | |
| congreso | |
| Rules | |
| Standing Orders of the Congress of Deputies (English) | |
_heute_Palacio_de_las_Cortes_span_Parlament_Madrid_Espa%C3%B1a_-_Foto_Wolfgang_Pehlemann_P1250289.jpg.webp)
It has 350 members elected by constituencies (matching fifty Spanish provinces and two autonomous cities) by closed list proportional representation using the D'Hondt method. Deputies serve four-year terms. The presiding officer is the President of the Congress of Deputies, who is elected by the members thereof. It is the analogue to a speaker.
In the Congress, MPs from the political parties, or groups of parties, form parliamentary groups. Groups must be formed by at least 15 deputies, but a group can also be formed with only five deputies if the parties got at least 5% of the nationwide vote, or 15% of the votes in the constituencies in which they ran. The deputies belonging to parties who cannot create their own parliamentary group form the Mixed Group.[2]
After the 2019 general election in April, the number of female deputies was up to 168 representing 48% of all members, making Spain the European country with the highest percentage of women in parliament; surpassing Sweden and Finland.[3]
Constitutional position
Composition

Section 68.1 of the Spanish Constitution establishes that the Congress of Deputies must be composed of among 300 deputies at least and 400 deputies at most. At present, the house has 350 deputies which is determined by the General Electoral Regime Organic Act, which was approved in 1985.
Electoral system
.svg.png.webp)
The Spanish Constitution establishes that the deputies are chosen by universal, free, equal, direct and secret suffrage. The election is held every four years or before in case of snap election. The members of the Congress are elected by proportional representation with closed lists in each constituency.
There are 50 multi-member constituencies for the Congress of Deputies which belong to the 50 provinces of Spain and the two single-member constituencies which belong to two autonomous cities (Ceuta and Melilla). According to the Spanish Electoral Act, each province shall be represented by at least two deputies, thus 102 deputies already apportioned. The remaining 248 deputies are allocated proportionally by constituency. This distribution can change in each election and it is specified when writs of election are issued. After the General Election, seats are assigned to the electoral lists in each constituency using the D'Hondt method in each constituency separately; parties receive seats in approximate proportion to the number of votes each received in the constituency. A strictly proportional system would result in fractional seats. The D'Hondt method resolves this by favoring parties receiving larger votes.
The 1985 General Electoral Regime Act establishes a 3% minimum valid votes by constituency requirement (blank votes count towards the total votes, but invalid ballots do not count) for a party to participate in the seat distribution for a constituency. This applies to the provinces that elect at least 24 deputies. At present, this condition applies only to Madrid and Barcelona.
In March 2011, the General Electoral Regime Organic Act was remodeled, requiring parties that are not represented either in Congress or in the Senate to collect signatures to support their candidacy to be able to run in the election. One-tenth of a percent of those registered to vote in a constituency are required to be on the ballot and each citizen can sign only once for a party candidacy. The Electoral Board establishes the regulations for collection of signatures.
Criticisms
With this system, the least populated provinces are overrepresented as the population is lower than other provinces which are still awarded one seat, than if the seats would be strictly distributed in proportion to the population of each province. Likewise, the most populated provinces are underrepresented.
This system tends to favour the biggest political parties. Despite using a proportional representation system, the electoral system of the Congress of Deputies favours the creation of a two-party system. It is due to different reasons such as:
- The large disparity of population between the provinces. Despite the smaller provinces being overrepresented, the number of deputies assigned to each one is small and tends to go to the two main parties.
- The election threshold of 3% only acts in the provinces which elect more than 30 deputies, that is Madrid and Barcelona. In the rest of constituencies where fewer seats are distributed, the real barrier to enter to the Congress is meaningfully larger. For example, the barrier of the provinces which have 3 seats is 25%.[4]
- The average number of seats per constituency is one of the lowest in Europe. That is because of the use of provinces as constituencies. Consequently, the number of useless votes is huge, that is there is a significant number of votes which cannot affect the result because they have been cast for a political party which does not get representation in the constituency where votes have been cast.
- The D'Hondt method favours the biggest parties compared to other electoral formulas such as the Webster/Sainte-Laguë method or the largest remainder method. This effect is larger than in many countries because of the small number of seats per constituency. However, the influence of the D'Hondt method in the bipolarization of the electoral system is limited compared to the factors mentioned above.
- The size of the Congress of Deputies is small (350 seats, compared to over 600 for e.g. the German Bundestag), which, together with the aforementioned factors, favours the biggest parties and disproportional distribution of seats, compared to national or multi-province regional election results.
Mandate
The deputies' term of office finishes four years after their election or when the Cortes are dissolved, which can take place jointly or separately with the dissolution of the Senate. The dissolution's right belongs to the Monarch who exercises it by request of the President of the Government after the deliberation of the Council of Ministers and under its sole responsibility. The dissolution of the Cortes also takes place if there is a failed legislature or two months after a failed investiture session, in this case the Sovereign dissolves the house with the countersign of the President of the Congress of Deputies. During their mandate, the deputies have some guarantees and privileges to carry their responsibilities out according to Section 97 of the Spanish Constitution.
Bodies of the Congress
Exercising the autonomy recognised by the Constitution to the Congress of Deputies, the house is regulated by some internal rules established by itself in 1982 and it configures different government bodies to carry the pertinent competencies out.
Governing bodies
The governing bodies of the Congress of Deputies are the bodies which under their authority the House is manage. Those bodies are the President, the Bureau and the Board of Spokespersons.[5]
The President of the Congress of Deputies is the highest authority and it represents the House and it is, de facto, the whole parliament leader. As head of the Congress, it also chairs the Bureau, the Board of Spokespersons and the Permanent Deputation, and is the maximum responsible authority of the Congress' Police.[6][7]
The Bureau of the Congress of Deputies is the collective body that represents the House and manages the day-to-day of the Chamber, preparing the budget and making all the necessary decisions to allow the proper functioning of the functions of the Congress.[8]
The Board of Spokespersons of the Congress of Deputies is the collective body formed by representatives of the parliamentary groups and normally, government representatives, that establishes the agenda of the House.
Working bodies
The working bodies of the Congress of Deputies are the Plenary, the Committees, the Permanent Deputation and the Parliamentary Groups.[9]
The Plenary is the central body of the Congress of Deputies which allows the house for exercising their choices. It is the reunion of all the members of the Parliament when half plus one of its members are attending the house. This body represents the unity of the house and it works through the plenary sessions which can be ordinary or extraordinary.
The ordinary sessions take place during the two meeting terms: September to December and February to June. They are convened by a calendar which has already been set. The extraordinary sessions are convened at the request of the President of the Government, the Permanent Council or the absolute majority of the house. In this kind of sessions a particular agenda is presented and the sessions end when all items have been treated.
The Committees are the basic working bodies of the Congress. They are composed of a proportional number of deputies depending on the numerical importance of the parliamentary groups of the house. The committees are classified as follows: permanent or non-permanent and legislative or non-legislative.
The permanent legislative committees examine and rule the projects and bills. The Plenary of the Congress can confer them full legislative power in relation to a matter, so they can permanently approve or reject any project or bill. The regulations of the Congress establish 17 permanent legislative committees. The permanent non-legislative committees have responsibilities not related to the legislative production. The regulations of the Congress establish 3 permanent non-legislative committees, and they allow the Plenary to create another ones at the beginning of each legislature. The non-permanent committeesare created with a specific purpose and their themes and duration are beforehand determined by the Plenary of the Congress.
The Permanent Deputation is a body created in order to have a permanent constituted legislative power. It is responsible for safeguarding the powers of the house between the legislative sessions (January, July and August) or when their term has finished because of termination or dissolution. In these three cases, the Permanent Deputation is a temporary extension of the house. The Permanent Deputation is presided by the President of the Congress. It is composed of a proportional number of deputies depending on the numerical importance of the different Parliamentary Groups.
The Parliamentary Groups are groups of members of the house which join together depending on their ideology.[9] The Rules of the Congress establish that 15 deputies at least are needed to make a parliamentary group. However, they can make a group if they are at least 5 deputies and they have got at least 15% of the total votes of the constituency where they have run at or 5% of the total votes of the country.[10] The formation of the parliamentary groups takes place at the beginning of each legislature. The deputies who do not enrol in any parliamentary group constitute the Mixed Group.
Composition of the XIV legislature
The XIV legislature of Spain started on 3 December 2019 when the Cortes Generales were constituted, once the 2019 general election was held.
Bureau of the Congress of Deputies
| Position | Holder | Party |
|---|---|---|
| President | Meritxell Batet Lamaña | |
| First Vice President | Alfonso Rodríguez Gómez de Celis | |
| Second Vice President | Ana Pastor Julián | |
| Third Vice President | Gloria Elizo Serrano | |
| Fourth Vice President | Ignacio Gil Lázaro | |
| First Secretary | Gerardo Pisarello Prados | |
| Second Secretary | Sofía Hernanz Costa | |
| Third Secretary | Javier Sánchez Serna | |
| Fourth Secretary | Adolfo Suárez Illana |
Committees
The Congress of Deputies creates at the beginning of each meeting a series of committees and subcommittees. These bodies purpose is to facilitate the work of the house. The committees have the same powers as the House' Plenary: to control the government by requesting information to the Administration or by requesting the appearance of any member of the Government or Administration; and to legislate by delegation of the plenary and at the request of the Congress' Bureau. The committees also debate the bills originated at the Plenary and the possible amends.
According to the Spanish parliamentary system, in the Congress there are two type or subcommittees, the ordinary subcommittees which purpose is to discuss and make a report about a specific issue and the reporting subcommittees which purpose is to write a first bill proposal to be discussed in the committee.
The committees can be standing committees, which creation is mandatory by the Congress' standing rules or other laws or non-standing committees, which are created by the Plenary. The subcommittees are also created by the Plenary at the request of the committees.
The members of the committees are designated by the parliamentary groups, and once the committees are created they must elect in their first meeting the Bureau of the committee, composed by a chair, two deputy charis and two secretaries. The members of the subcommittees are designated by the committee.
Current committees
| Committee | Chair(s) | Term | Refs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-committee | ||||
| Constitutional | Patxi López (PSOE) | [11] | ||
| Foreign Affairs | Sergio Gutiérrez Prieto (PSOE) | [12] | ||
| Defence | Juan Carlos Girauta (Cs) | [13] | ||
| Justice | Beatriz Corredor (PSOE) | [14] | ||
| Finance | Eloy Suárez Lamata (PP) | [15] | ||
| Budget | Txema Guijarro García (UP) | [16] | ||
| Home Affairs | José Antonio Bermúdez de Castro (PP) | [17] | ||
| Public Works | José Javier Izquierdo Roncero (PSOE) | [18] | ||
| Education and Vocational Training | José Manuel Franco (PSOE) | [19] | ||
| Labour, Migrations and Social Security | Héctor Illueca Ballester (UP) | [20] | ||
| Industry, Trade and Tourism | Joan Capdevila i Esteve (ERC) | [21] | ||
| Agriculture, Fisheries and Food | Joseba Andoni Agirretxea Urresti (EAJ-PNV) | [22] | ||
| Territorial Policy and Civil Service | Isaura Leal Fernández (PSOE) | [23] | ||
| Ecological Transition | Eva García Sempere (UP) | [24] | ||
| Culture and Sport | Pablo Arangüena Fernández (PSOE) | [25] | ||
| Economy and Business | María Muñoz Vidal (Cs) | [26] | ||
| Health, Consumer Affairs and Social Welfare | Rosa Romero Sánchez (PP) | [27] | ||
| Science, Innovation and Universities | Joan Mena Arca (UP) | [28] | ||
| International Cooperation for Development | José María Espejo-Saavedra (Cs) | [29] | ||
| Equality | Pilar Cancela Rodríguez (PSOE) | [30] | ||
| Comprehensive Disability Policies | Joan Ruiz Carbonell (PSOE) | [31] | ||
| Rules | Meritxell Batet (PSOE) | [32] | ||
| Members' Status | Begoña Nasarre Oliva (PSOE) | [33] | ||
| Petitions | Agustín Javier Zamarrón (PSOE) | [34] | ||
| Monitoring and Evaluation of the Agreements of the Toledo Pact | Josefa Andrés Barea (PSOE) | 2019–present | [35] | |
| Road Safety and Sustainable Mobility | Juan José Matarí (PP) | 2019–present | [36] | |
| Children and Adolescents' Rights | Francesc Xavier Eritja Ciuró (ERC) | 2019–present | [37] | |
| Democratic Quality, Against Corruption and for Institutional and Legal Reforms | Carina Mejías (Cs) | 2019–present | [38] | |
| Monitoring and Evaluation of the Agreements of the State Pact against Gender Violence | Beatriz Carrillo (PSOE) | 2019–present | [39] | |
Presidency of the Congress of Deputies
Legislature President Party Start End Constituent Fernando Álvarez de Miranda  UCD
UCD13 July 1977 22 March 1979 I legislature Landelino Lavilla  UCD
UCD23 March 1979 17 November de 1982 II legislature Gregorio Peces-Barba  PSOE
PSOE18 November 1982 14 July 1986 III legislature Félix Pons Irazazábal  PSOE
PSOE15 July 1986 26 March 1996 IV legislature V legislature VI legislature Federico Trillo-Figueroa _Logo_(1993-2000).svg.png.webp) PP
PP27 March 1996 4 April 2000 VII legislature Luisa Fernanda Rudi Úbeda _Logo_(2000-2007).svg.png.webp) PP
PP5 April 2000 1 April 2004 VIII legislature Manuel Marín González  PSOE
PSOE2 April 2004 31 March de 2008 IX legislature José Bono Martínez  PSOE
PSOE1 April 2008 12 December 2011 X legislature Jesús Posada Moreno _Logo_(2008-2015).svg.png.webp) PP
PP13 December 2011 12 January 2016 XI legislature Patxi López Álvarez  PSOE
PSOE13 January 2016 18 July 2016 XII legislature Ana Pastor Julián _Logo.svg.png.webp) PP
PP19 July 2016 20 May 2019 XIII legislature Meritxell Batet Lamaña  PSC
PSC21 May 2019 Incumbent XIV legislature
Congress of Deputies building
_02.jpg.webp)
.svg.png.webp) |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Spain |
The building, Palacio de las Cortes, has a neoclassical style. It was designed by Narciso Pascual Colomer, and built between 1843 and 1850. It sits by the Carrera de San Jerónimo, in Madrid. The relief on the facade by sculptor Ponciano Ponzano centers on a sculpture of Spain embracing the constitutional state, represented by a woman with her arm around a young girl. Surrounding the pair are figures that represent in allegorical form Justice and Peace, Science, Agriculture, Fine Arts, Navigation, Industry, Commerce and so on. Ponzano also executed two bronze lions for the building's access stairway in a more realistic manner.[40]
Notes
See also
References
- "El PRC y el PSOE cierran su crisis a cambio del apoyo de Revilla a los Presupuestos de Sánchez". El Español (in Spanish). 13 January 2020. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- Information about Parliamentary Groups – Congress of Deputies of Spain
- "Which European country has the most female politicians?". The Economist. 3 May 2019. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 13 June 2019.
- H/Creada:09-11-2019, Irene Barbero | La RazónÚltima actualización:09-11-2019 | 15:41 (9 November 2019). "Ley D´Hont: ¿Cómo se decide cuántos diputados habrá en el Congreso por cada partido?". La Razón (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- "Qué es el Congreso de los Diputados". Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- "El Presidente del Congreso de los Diputados" [The President of the Congress of Deputies] (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- "De las Funciones de la Mesa y sus miembros. (Arts. 30–35)". Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- "Funciones de la Secretaría General" (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- "Funciones de los Grupos Parlamentarios" (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- "TITULO II. De los Grupos Parlamentarios" (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- "Composición actual de la Comisión Constitucional".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Asuntos Exteriores".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Defensa".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Justicia".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Hacienda".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Presupuestos".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Interior".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Fomento".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Educación y Formación Profesional".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Trabajo, Migraciones y Seguridad Social".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Industria, Comercio y Turismo".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Política Territorial y Función Pública".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Transición Ecológica".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Cultura y Deporte".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Economía y Empresa".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Sanidad, Consumo y Bienestar Social".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Cooperación Internacional para el Desarrollo".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Igualdad".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión para las Políticas Integrales de la Discapacidad".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Reglamento".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión del Estatuto de los Diputados".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Peticiones".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Seguimiento y Evaluación de los Acuerdos Pacto de Toledo".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión sobre Seguridad Vial y Movilidad Sostenible".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de Derechos de la Infancia y Adolescencia".
- "Composición actual de la Comisión calidad democrática, contra corrupción y reform. inst. y leg."
- "Composición actual de la Comisión de segto. y eval. Acuerdos Pacto de Estado Violencia Género".
- "Ponzano y Gascón, Ponciano". Gran Enciclopedia Aragonesa (in Spanish). Retrieved 28 May 2012.
External links
 Media related to Congress of Deputies of Spain at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Congress of Deputies of Spain at Wikimedia Commons- Official website (Spanish)
