Maebashi
Maebashi (前橋市, Maebashi-shi) is the capital city of Gunma Prefecture, in the northern Kantō region of Japan.[2] As of 31 August 2020, the city had an estimated population of 335,352 in 151,171 households,[3] and a population density of 1100 persons per km2. The total area of the city is 311.59 km2 (120.31 sq mi). It was the most populous city within Gunma Prefecture until Takasaki merged with nearby towns between 2006 and 2009.[4] Maebashi is known to be the "City of Water, Greenery and Poets" because of its pure waters, its rich nature and because it gave birth to several Japanese contemporary poets, such as Sakutarō Hagiwara.[5]
Maebashi
前橋市 | |
|---|---|
 A view of Maebashi with Mt. Akagi, from the top of the Prefectural Government building | |
 Flag  Seal | |
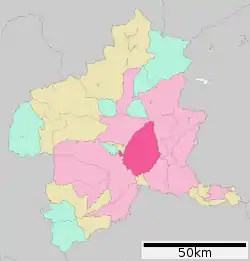 Location of Maebashi in Gunma Prefecture | |
 Maebashi | |
| Coordinates: 36°23′22.2″N 139°3′48.3″E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Kantō |
| Prefecture | Gunma |
| City settled | April 1, 1892 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Ryu Yamamoto (since February 2012) |
| Area | |
| • Core city | 311.59 km2 (120.31 sq mi) |
| Population (August 31, 2020) | |
| • Core city | 335,352 |
| • Density | 1,100/km2 (2,800/sq mi) |
| • Metro [1] (2015) | 1,263,034 (12th) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| - Tree | Ginkgo & Zelkova |
| - Flower | Rose & Azalea |
| Phone number | 027-224-1111 |
| Address | 2-12-1, Ote-Machi, Maebashi-shi, Gunma-ken 371-8601 |
| Website | Official website |

Geography
Maebashi is located at the foot of Mount Akagi in the northeast corner of the Kantō Plain. It is also surrounded by Mount Haruna and Mount Myōgi. Two rivers run through the city: the Tone River, Japan's second-longest, and the Hirose River. Although it is located inland more than 100 kilometers away from the coast, the elevation of the southern part of the city is only around 100 meters.The highest elevation is 1823 meters above sea level on the south side of Mt. Kurohino, a peak of Mount Akagi. Maebashi is the farthest from the sea (about 120 km) of all Japanese prefectural capitals. The surrounding cities comprise an urban zone of over 1 million people, separated by farmland to the south from the built up areas of Greater Tokyo.
Surrounding municipalities
Climate
Maebashi has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa). In the winter, the "karakaze", or "dry wind" blows through Maebashi from the north. This is due to the snow clouds coming from the Sea of Japan being blocked by the Echigo Mountain Range between Gunma and Niigata Prefectures. Because of this, the city has a dry winter and is one of the sunniest places in Japan at over 2,210 hours of sunshine per year.[6] In the summer, it is hot since the location is inland, although less hot than coastal Tokyo on average. On July 24, 2001, Maebashi hit 40 °C (104 °F), the fifth-hottest temperature ever in Japan.
| Climate data for Maebashi, Gunma (1897~2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.0 (71.6) |
24.6 (76.3) |
27.1 (80.8) |
32.4 (90.3) |
36.5 (97.7) |
38.3 (100.9) |
40.0 (104.0) |
39.1 (102.4) |
38.1 (100.6) |
33.0 (91.4) |
26.6 (79.9) |
23.5 (74.3) |
40.0 (104.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.4 (47.1) |
8.9 (48.0) |
12.1 (53.8) |
18.0 (64.4) |
22.4 (72.3) |
25.4 (77.7) |
28.9 (84.0) |
30.1 (86.2) |
25.9 (78.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
15.8 (60.4) |
11.0 (51.8) |
19.0 (66.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.8 (28.8) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
1.5 (34.7) |
7.1 (44.8) |
11.7 (53.1) |
16.6 (61.9) |
20.9 (69.6) |
21.8 (71.2) |
18.0 (64.4) |
11.5 (52.7) |
5.7 (42.3) |
0.8 (33.4) |
9.4 (48.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −11.8 (10.8) |
−9 (16) |
−7.8 (18.0) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
0.3 (32.5) |
6.0 (42.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
13.6 (56.5) |
8.4 (47.1) |
0.6 (33.1) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
−7.4 (18.7) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 24.3 (0.96) |
34.1 (1.34) |
54.1 (2.13) |
79.5 (3.13) |
103.1 (4.06) |
161.5 (6.36) |
189.7 (7.47) |
190.9 (7.52) |
204.1 (8.04) |
121.5 (4.78) |
46.2 (1.82) |
24.1 (0.95) |
1,233.1 (48.56) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 6.5 (2.6) |
7.9 (3.1) |
4.5 (1.8) |
0.5 (0.2) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.9 (0.4) |
20.3 (8.1) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 57.0 | 56.2 | 56.6 | 61.7 | 67.7 | 75.2 | 79.3 | 78.9 | 79.4 | 73.4 | 65.6 | 59.8 | 67.6 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 214.6 | 198.2 | 218.1 | 203.7 | 206.0 | 148.8 | 157.7 | 185.3 | 136.3 | 163.4 | 184.0 | 204.4 | 2,220.5 |
| Source 1: Japan Meteorological Agency[7] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Japan Meteorological Agency (records)[8] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[9] the population of Maebashi has remained relatively steadily over the past 30 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 51,015 | — |
| 1930 | 53,052 | +4.0% |
| 1940 | 52,898 | −0.3% |
| 1950 | 68,710 | +29.9% |
| 1960 | 240,301 | +249.7% |
| 1970 | 273,864 | +14.0% |
| 1980 | 311,121 | +13.6% |
| 1990 | 335,704 | +7.9% |
| 2000 | 341,738 | +1.8% |
| 2010 | 340,390 | −0.4% |
Etymology
The Maebashi area was called Umayabashi (厩橋) during the Nara period. This name finds its origins in the fact that there was a bridge (hashi, 橋) crossing the Tone River and not far from the bridge there was a small refreshment house with a stable (umaya, 駅家), often used by people travelling on the Tōzan-dō (the road connecting the capital to the eastern regions of Japan). The spelling was officially changed into Maebashi (前橋) in 1649 during the Edo period when Maebashi became a castle town and the center of Maebashi Domain, a feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate.[10]
History
The town of Maebashi was established within Higashigunma District, Gunma Prefecture on April 1, 1889 with the creation of the modern municipalities system after the Meiji Restoration. Maebashi was raised to city status on April 1, 1892. In 1901, it annexed a portion of Kamikawabuchi village from Seta District.
On August 5, 1945 approximately 64.2% of the urban core of the city was destroyed during World War II during air raids which followed the dropping of propaganda leaflets warning of the impending attacks.[11][12]
In 1951, a portion of Kaigaya Village from Seta District was merged into Maebashi. The city expanded further on April 1, 1954 by annexing the villages of Kamikawabuchi, Shimokawabuchi, Azuma, Minamitachibana, Kaigaya, Haga, Motosōja, and Sōja from Seta District, followed by a portion of Jōnan village in 1957. On April 1, 1960 a portion of Tamamura Town and another portion of Jōnan village were merged into Maebashi, which finally anned the remainder of Jōnan village in 1967. Maebashi hosted the 1999 IAAF World Indoor Championships.
On April 1, 2001, Maebashi was designated a special city (tokureishi) with increased local autonomy. On December 5, 2004 the town of Ōgo, and the villages of Kasukawa and Miyagi (all from Seta District) were merged into Maebashi. On May 5, 2009, the village of Fujimi (Seta District) was merged into Maebashi. Seta District was dissolved as a result of this merger.[13]
Maebashi became a core city (Chūkakushi) on April 1, 2009.
Government
Maebashi has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 38 members. Maebashi contributes eight members to the Gunma Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is part of Gunma 1st district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy

As of 2010, Greater Maebashi, Maebashi Metropolitan Employment Area, has a GDP of US$59.8 billion.[14][15] The air conditioning system and compressor manufacturing company Sanden Corporation as well as the tofu and tofu products company Sagamiya Foods have manufacturing sites in the city.[16] The Gunma Bank is headquartered in Maebashi.
Education
Universities
Primary and secondary schools
Maebashi has 54 public elementary schools and 21 public middle schools operated by the city government, and two private elementary and two private middle schools. The city has nine public high schools operated by the Gunma Prefectural Board of Education and one by the city government. There are five private high schools and one private combined middle/high school.
International schools:
Transportation
Railway
- Komagata - Maebashi-Ōshima - Maebashi - Shin-Maebashi
- Jōmō Electric Railway Company – Jōmō Line
Highway
.png.webp) Kan-etsu Expressway – Maebashi Interchange
Kan-etsu Expressway – Maebashi Interchange.png.webp) Kita-Kantō Expressway – Maebashi-Minami Interchange
Kita-Kantō Expressway – Maebashi-Minami Interchange National Route 17
National Route 17 National Route 50
National Route 50 National Route 291
National Route 291 National Route 353
National Route 353
Sports
Thespakusatsu Gunma at Shoda Shoyu Stadium Gunma was originally formed in Kusatsu, but plays in Maebashi due to J.League stadium requirements.
Local attractions
- Shikishima Park
- Maebashi Castle
- Maebashi Tōshō-gū
- Gunma Prefectural Government Building
- Kōzuke Kokubun-ji ruins, a National Historic Site
Festivals
- Ogo Gion Festival
Noted people from Maebashi
- Kamiizumi Nobutsuna, founder of Shinkage-ryū martial arts school and master of Yagyū Munetoshi who later introduced Shinkage-ryū to Tokugawa Ieyasu.[18]
- Tōru Furusawa, voice actor
- Sakutarō Hagiwara, poet
- Gran Hamada, professional wrestler (Real Name: Hiroaki Hamada, Nihongo: 浜田 広秋, Hamada Hiroaki)
- Nobuyuki Kojima, professional soccer player
- Kōhei Oguri, film director and screenwriter
- Tetsuya Ota, racecar driver
- Genichiro Sata, politician
- Takashi Shimizu, film director
- Atsuko Tanaka, voice actress
- Yutaka Yoshie, professional wrestler
- Shigesato Itoi, game designer
- Nigo (Real Name: Tomoaki Nagao, Nihongo: 長尾 智明, Nagao Tomoaki), fashion designer, DJ, record producer and entrepreneur
- Great-O-Khan, Japanese professional wrestler (Real Name: Tomoyuki Oka, Nihongo: 岡 倫之, Oka Tomoyuki)
- Sho Sakurai, singer, actor and newscaster
References
- "UEA Code Tables". Center for Spatial Information Science, University of Tokyo. Retrieved January 26, 2019.
- Japan National Tourism Organization (JNTO), "Maebashi area"; retrieved 2015-5-10.
- "Maebashi City official statistics" (in Japanese). Japan.
- Takasaki City Office. September 30, 2014. "Demography Study"
- Maebashi City Office. March 27, 1989. "Declaration from the Municipal Council" Archived 2014-10-12 at the Wayback Machine
- Maebashi Hours of Bright Sunshine
- "Monthly Mean Climate Data". Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved 2010-03-06.
- Maebashi population statistics
- Maebashi no Rekishi (History of Maebashi) Archived 2018-08-17 at the Wayback Machine (July 24, 2012)
- Craven, Wesley; Cate, James, eds. (1953). The Pacific: Matterhorn to Nagasaki. The Army Air Forces in World War II. Volume V. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press. pp. 656, 675. OCLC 256469807.
- Caidin, Martin (1960). A Torch to the Enemy: The Fire Raid on Tokyo. Bantam War Books. ISBN 0-553-29926-3.
- Archived August 21, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- Yoshitsugu Kanemoto. "Metropolitan Employment Area (MEA) Data". Center for Spatial Information Science, The University of Tokyo.
- Conversion rates - Exchange rates - OECD Data
- "Major Corporations in Gunma Prefecture". Department of Industry and Economy, Gunma Prefecture. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- アクセス. Gunma Korean Elementary and Junior High School. December 11, 2007. Archived from the original on December 11, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2015.
群馬朝鮮初中級学校 群馬県前橋市荒牧町 2-2
- Yagyū, Toshinaga (1957, 1989) Shōden Shinkage-ryū. Kōdansha, reprinted by Shimazu Shobō, ISBN 4-88218-012-X.
- "姉妹都市バーミングハム市". city.maebashi.gunma.jp (in Japanese). Maebashi. Retrieved 2020-04-12.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Maebashi, Gunma. |
- Official Website (in Japanese)
- Maebashi Living Guide