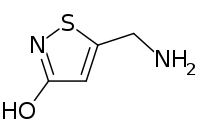
Thiomuscimol
Thiomuscimol is a GABAA receptor agonist which is structurally related to muscimol.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-(aminomethyl)-1,2-thiazol-3-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6N2OS | |
| Molar mass | 130.17 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 140 °C (decomp.)[1] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 6.06 ± 0.03, 8.85 ± 0.04 (H2O, 21 °C) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Lykkeberg, Jytte; Krogsgaard-Larsen, Povl; Garegg, Per J.; Norberg, Thomas; Pilotti, Anne-Marie; Anthonsen, T. (1976). "Structural Analogues of GABA. Synthesis of 5-Aminomethyl-3-isothiazolol (Thiomuscimol)". Acta Chemica Scandinavica. 30b: 781–785. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.30b-0781.
- Krogsgaard-Larsen, P; Hjeds, H; Curtis, DR; Lodge, D; Johnston, GA (1979). "Dihydromuscimol, thiomuscimol and related heterocyclic compounds as GABA analogues". Journal of Neurochemistry. 32 (6): 1717–24. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb02284.x. PMID 448364.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.