Tutin (toxin)
Tutin is a poisonous plant derivative found in New Zealand tutu plants (several species in the genus Coriaria). It acts as a potent antagonist of the glycine receptor,[1] and has powerful convulsant effects.[2] It is used in scientific research into the glycine receptor. It is sometimes associated with outbreaks of toxic honey poisoning when bees feed on honeydew exudate from the sap-sucking passionvine hopper (Scolypopa australis) insect, when the vine hoppers have been feeding on the sap of tutu bushes. Toxic honey is a rare event and is more likely to occur when comb honey is eaten directly from a hive that has been harvesting honeydew from passionvine hoppers feeding on tutu plants.[3]
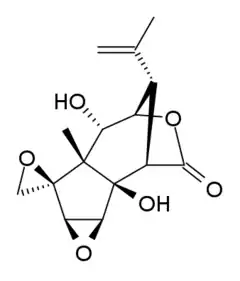 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.236.780 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H18O6 |
| Molar mass | 294.303 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Fuentealba J, Guzmán L, Manríquez-Navarro P, Pérez C, Silva M, Becerra J, Aguayo LG (March 2007). "Inhibitory effects of tutin on glycine receptors in spinal neurons". European Journal of Pharmacology. 559 (1): 61–4. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.12.018. PMID 17303114.
- Zhou H, Tang YH, Zheng Y (May 2006). "A new rat model of acute seizures induced by tutin". Brain Research. 1092 (1): 207–13. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.03.081. PMID 16674929.
- Background on toxic honey. New Zealand Food Safety Authority.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.