Nicardipine
Nicardipine (Cardene) is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and angina. It belongs to the dihydropyridine class of calcium channel blockers. It is also used for Raynaud's phenomenon. It is available in by mouth and intravenous formulations. It has been used in percutaneous coronary intervention.[1]
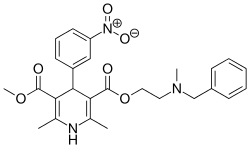 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cardene |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a695032 |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >95% |
| Elimination half-life | 8.6 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.466 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H29N3O6 |
| Molar mass | 479.533 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 136–138 °C (277–280 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Its mechanism of action and clinical effects closely resemble those of nifedipine and the other dihydropyridines (amlodipine, felodipine), except that nicardipine is more selective for cerebral and coronary blood vessels. Nicardipine also has a longer half-life than nifedipine. Nicardipine was approved by the FDA in December 1988. The patent for both Cardene and Cardene SR expired in October 1995.[2]
It was patented in 1973 and approved for medical use in 1981.[3]
References
- Huang RI, Patel P, Walinsky P, et al. (November 2006). "Efficacy of intracoronary nicardipine in the treatment of no-reflow during percutaneous coronary intervention". Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions. 68 (5): 671–6. doi:10.1002/ccd.20885. PMID 17034064. S2CID 37071966.
- Nicardipine at Medline PLus
- Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 464. ISBN 9783527607495.