U-77891
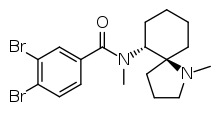
U-77891 is an opioid analgesic drug that was first synthesized in 1983 by the Upjohn company.[1] It was originally synthesized to prove that the removal of a single methylene spacer of the benzamide would alter a κ-opioid receptor agonist such as U-50488 into an μ-opioid receptor agonist, as well as producing a semi-rigid derivative of U-47700. This would help elucidate the relative positions of the hydrogen-bond acceptors and substituted aromatic system to find the compound with the lowest Ki value in a series of benzamide opioids dating back to the 1970s.[2] The original work found a mixture of agonists and antagonists.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | oral, parenteral |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H24Br2N2O |
| Molar mass | 444.211 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
U-77891 acts as an agonist of the μ-opioid, δ-opioid and κ-opioid receptors with Ki values of 2, 105 and 2300 nM, respectively.[2] The compound has ED50 values of 0.02 mg/kg and 0.21 mg/kg in mouse phenylquinone writhing and tail-flick assays.[2] One reason for the high potency is the LogP of 4.57,[4] allowing it to accumulate in fatty tissue such as the brain.
References
- Jacob Szmuszkovicz, John M. McCall, Lester J. Kaplan, Moses W. McMillan (18 May 1983). "US Patent 4598088 - 2-pyrrolyl-cycloalkyl-amide analgesics". The Upjohn Company.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Fujimoto RA, Boxer J, Jackson RH, Simke JP, Neale RF, Snowhill EW, et al. (June 1989). "Synthesis, opioid receptor binding profile, and antinociceptive activity of 1-azaspiro[4.5]decan-10-yl amides". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 32 (6): 1259–65. doi:10.1021/jm00126a019. PMID 2542556.
- Moses W. McMillan, Jacob Szmuszkovicz (9 April 1981). "US Patent 4466977 - N-[2-Amino(oxy- or thia- group-substituted-cycloaliphatic)]benzeneacetamides and -benzamide analgesics". The Upjohn Company.
- "Properties Viewer". chemicalize.org.