Beijing–Guangzhou high-speed railway
The Beijing–Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong high-speed railway or Jingguangshengang high-speed railway from its Chinese name is a high-speed railway corridor of the CRH passenger service, connecting Beijingxi Station in Beijing and Futian Station in Shenzhen. It crosses the border and follows Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Express Rail Link Hong Kong section to West Kowloon Station in Hong Kong. It is 2,230 kilometres (1,390 mi) long, and is the only Chinese high-speed railway to cross a border that requires immigration and customs clearance.[1][2][3] The existing, conventional Jingguang railway runs largely parallel to the line.
| Beijing–Guangzhou high-speed railway | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 京广深港高速铁路 | ||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 京廣深港高速鐵路 | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
The line forms part of the Beijing–Harbin, Beijing–Hong Kong (Macau) passageway, based on the "Eight Verticals and Eight Horizontals" railway master plan announced in 2016.
History
Construction started in 2005. The Wuhan–Guangzhou section opened in December 2009, the Guangzhou–Shenzhen section opened in December 2011, the Zhengzhou–Wuhan section opened in September 2012, and the Beijing–Zhengzhou section was opened in December 2012. The 36-kilometre (22 mi) cross-border Shenzhen–Hong Kong section opened on the 23rd of September 2018.[4] The line is the world's longest high-speed rail route.[5] The high speed rail line cuts travel time by more than half.[5] The line fully opened on September 23, 2018.[6]
Through-services with other high-speed lines
Besides trains running between Beijing, Shijiazhuang, Zhengzhou, Wuhan, Changsha, Guangzhou and Shenzhen, the railway also has direct service with other connecting high-speed lines. The direct Xi'an–Zhengzhou–Wuhan–Guangzhou–Shenzhen service started simultaneously with the opening of the Zhengzhou–Wuhan section in September 2012, as well as the direct interline service Xi'an-Zhengzhou–Beijing, Taiyuan–Shijiazhuang–Guangzhou, Taiyuan–Shijiazhuang–Wuhan–Guangzhou.[7][8] The Hangzhou–Fuzhou–Shenzhen high-speed railway have through operation to Guangzhou South albeit limited due to track situation in Shenzhen North Station.
Connections to local transport
To minimize disruptions to existing urban areas and provide large curve radii, the Beijing–Guangzhou high-speed railway, similar to other such railways in China, was constructed in an alignment somewhat different from the existing Beijing–Guangzhou Railway. In most cities served by the high-speed railway, its trains stop at stations built specifically for the new line, which are away from the urban core and the city's conventional railway station. In some of the larger cities, it may take more than an hour to ride a bus or taxi from the city centre to the high-speed rail station.[9] One notable exception is Shijiazhuang Station, which is shared with conventional trains and located in city centre (but moved south from the original). It is also possible for high-speed trains to stop at Zhengzhou Station and Hankou Station, which shared the characteristics of Shijiazhuang Station, but unlike Shijiazhuang they are not on main track of the Beijing-Guangzhou High Speed line.
To alleviate this most of the cities involved have improved the public transit access to the new high-speed rail stations, or plan to do so. Guangzhounan Station is already served by Guangzhou Metro (Line 2) and Beijingxi Station served by Beijing Metro (Line 7,9). Wuhan Station is served by Wuhan Metro's Line 4 and Zhengzhoudong Station by Zhengzhou Metro's Line 1, both of which opened in December 2013, and Shijiazhuang Station by Shijiazhuang Metro's Line 3, opened in June 2017.
Transfers to other rail lines
Guangzhounan Station and Wuhan Station are designed as hubs for several high-speed railway (HSR) lines. Frequent service to Zhuhai is available at Guangzhou South, while a connection to Yichang can be made at Wuhan.
Although the Beijing–Guangzhou HSR largely parallels the older conventional Beijing–Guangzhou line, most of the HSR stations are located away from the local conventional train stations. Therefore, direct transfer to conventional (not high-speed) trains is possible only at a few stations along the route. Among them are Beijing West (which is one of the nation's main passenger railway hubs), Shijiazhuang, and Guangzhoubei.
Immigration clearance
As Hong Kong is a Special Administrative Region, the Shenzhen-Hong Kong portion of the high speed rail passes through an immigration control point. The West Kowloon Terminus was designed to allow both Mainland and Hong Kong officials to conduct immigration control in Hong Kong,[10] but for several years there was an unclear constitutional issue as Mainland officials were thought not to have the constitutional authority to enforce Mainland law in Hong Kong.[11][12] In November 2017, the Government of Hong Kong resolved this question by signing the Co-operation Arrangement for Implementing Co-location Arrangement, designating a portion of West Kowloon railway station as the "Mainland Port Area" that would be subject to Mainland law.[13] Travelers coming from Hong Kong therefore pass through Mainland immigration and customs clearance before boarding their trains, allowing direct service to the entire Mainland high-speed rail network without having to stop at the Mainland-Hong Kong border.[14]
Sections
Operational lines in the table below are marked with green background.
| Section | Description | Designed speed (km/h) |
Length (km) |
Construction start date |
Open date |
Top trip speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Beijing–Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong high-speed railway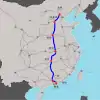 |
HSR Corridor connecting North with Central China, consisting of four segments between Beijing, Shijiazhuang, Wuhan, Guangzhou and Hong Kong. | 350 | 2230 | 2005-09-01 | 2018 | See below |
| Beijing–Shijiazhuang section (Beijing–Shijiazhuang high-speed railway) |
HSR from Beijingxi (further: Fengtai) to Shijiazhuang | 350 | 281 | 2008-10-08 | 2012-12-26[15] | - |
| Shijiazhuang–Wuhan section (Shijiazhuang–Wuhan high-speed railway) 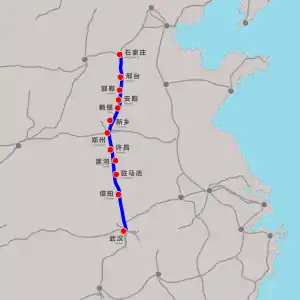 |
HSR from Shijiazhuang to Wuhan via Zhengzhoudong | 350 | 838 | 2008-10-15 | 2012-09-28 (ZZD–WH) 2012-12-26 (SJZ–ZZD) |
- |
| Wuhan–Guangzhou Section (Wuhan–Guangzhou high-speed railway) 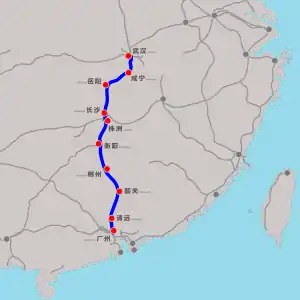 |
HSR from Wuhan to Guangzhounan via Changshanan | 350 | 968 | 2005-09-01 | 2009-12-26 | 313[16] |
| Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Section Mainland Portion (Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Express Rail Link) 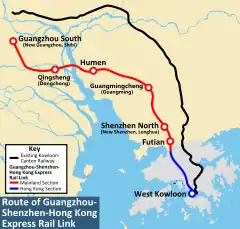 |
HSR from Guangzhounan to Futian via Shenzhenbei | 350 (GZN–SZB) 200 (SZB–FT) |
106 | 2005-12-18 | 2011-12-26 (GZN–SZB) 2014-07[17] (SZB–FT) |
308 |
| Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Section Hong Kong Portion (Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Express Rail Link)  |
HSR from Futian to West Kowloon | 200 | 36 (26 km in Hong Kong) | 2010-01-27 | 2018-09-23[18] |
Station list
Major railway terminals are in bold. Medium-size stations that trains can regularly terminate are in Italics
| Station name |
Chinese | Total distance (km) |
Travel time | Rail transfers* |
Metro and Commuter rail transfers* |
Platforms | Tracks served by platform |
Location | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 km/h | 350 km/h | Prefecture/ City |
Province/ Territory | |||||||
| Beijing West | 北京西 | 0 | 0:00 (D2031) | 0:00 (G71) | Beijing–Guangzhou railway Beijing–Kowloon railway Beijing underground cross-city railway | Beijing | Beijing | |||
| Zhuozhou East | 涿州东 涿州東 | 59 | 0:25 (D2021)[19] | 0:25 (G527)[20] | Baoding | Hebei | ||||
| Gaobeidian East | 高碑店东 高碑店東 | 84 | 0:30 (D2031)[21] | 0:30 (G567)[22] | ||||||
| Baoding East | 保定东 保定東 | 139 | 0:54 (D2031) | 0:41 (G71)[23] | ||||||
| Dingzhou East | 定州东 定州東 | 200 | 2:13 (D2021) | 1:01 (G567) | ||||||
| Zhengding Airport | 正定机场 正定機場 | 244 | 1:38 (D2031) | 1:17 (G6701)[24] | Shijiazhuang | |||||
| Shijiazhuang | 石家庄 石家莊 | 280 | 1:54 (D2031) | 1:19 (G71) | Beijing–Guangzhou railway Shijiazhuang–Dezhou railway Shijiazhuang–Taiyuan railway Shijiazhuang–Taiyuan passenger railway | |||||
| Gaoyi West | 高邑西 | 323 | 2:12 (D2031) | 1:38 (G563)[25] | ||||||
| Xingtai East | 邢台东 邢台東 | 384 | 2:39 (D2031) | 1:58 (G563) | Xingtai | |||||
| Handan East | 邯郸东 邯鄲東 | 437 | 2:58 (D2031) | 2:01 (G71) | Handan | |||||
| Anyang East | 安阳东 安陽東 | 496 | 3:17 (D2031) | 2:28 (G567) | Anyang | Henan | ||||
| Hebi East | 鹤壁东 鶴壁東 | 542 | 3:54 (D2031) | 2:31 (G527) | Hebi | |||||
| Xinxiang East | 新乡东 新鄉東 | 595 | 4:12 (D2031) | 2:41 (G71) | Xinxiang | |||||
| Zhengzhou East | 郑州东 鄭州東 | 663 | 4:44 (D2031) | 3:04 (G71) | Xuzhou–Lanzhou high-speed railway Zhengzhou–Kaifeng intercity railway Zhengzhou–Xinzheng Airport intercity railway | Zhengzhou | ||||
| Xuchang East | 许昌东 許昌東 | 744 | 5:09 (D2031) | 3:31 (G527) | Xuchang | |||||
| Luohe West | 漯河西 | 799 | 5:38 (D2031) | 3:50 (G503)[26] | Luohe | |||||
| Zhumadian West | 驻马店西 駐馬店西 | 864 | 5:58 (D2031) | 3:53 (G71) | Zhumadian | |||||
| Minggang East | 明港东 明港東 | 917 | 6:17 (D2031) | Xinyang | ||||||
| Xinyang East | 信阳东 信陽東 | 960 | 6:32 (D2031) | 4:22 (G527) | ||||||
| Xiaogan North | 孝感北 | 1024 | 6:52 (D2031) | 4:33 (G71) | Xiaogan | Hubei | ||||
| Hengdian East | 横店东 橫店東 | Wuhan | ||||||||
| Wuhan | 武汉 武漢 | 1136 | 7:25 (D2031) | 4:17 (G79) | Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu high-speed railway Wuhan–Jiujiang passenger railway Wuhan–Huangshi intercity railway Wuhan–Huanggang intercity railway |
|||||
| Wulongquan East | 乌龙泉东 烏龍泉東 | |||||||||
| Xianning North | 咸宁北 咸寧北 | 1221 | 7:49 (D2103)[27] | 5:32 (G501)[28] | Xianning | |||||
| Chibi North | 赤壁北 | 1264 | 8:10 (D2103) | 5:46 (C503) | ||||||
| Yueyang East | 岳阳东 岳壁東 | 1346 | 8:33 (D2103) | 5:58 (G71) | Yueyang | Hunan | ||||
| Miluo East | 汨罗东 汨羅東 | 1416 | 8:59 (D2103) | 6:19 (G501) | ||||||
| Changsha South | 长沙南 長沙南 | 1484 | 9:25 (D2103) | 6:34 (G71) | Shanghai–Kunming high-speed railway | Changsha | ||||
| Zhuzhou West | 株洲西 | 1524 | 9:46 (D2103) | Zhuzhou | ||||||
| Hengshan West | 衡山西 | 1591 | 10:10 (D2103) | 7:07 (G71) | Hengyang | |||||
| Hengyang East | 衡阳东 衡陽東 | 1632 | 10:28 (D2103) | 7:22 (G71) | ||||||
| Leiyang West | 耒阳西 耒陽西 | 1687 | 10:53 (D2103) | 7:41 (G71) | ||||||
| Chenzhou West | 郴州西 | 1766 | 11:22 (D2103) | 8:09 (G71) | Chenzhou | |||||
| Lechang East | 乐昌东 樂昌東 | Shaoguan | Guangdong | |||||||
| Shaoguan | 韶关 韶關 | 1896 | 11:55 (D2103) | 8:29 (G81)[29] | ||||||
| Yingde West | 英德西 | 1966 | 12:21 (D2103) | Qingyuan | ||||||
| Qingyuan | 清远 清遠 | 2023 | 12:59 (D2103) | |||||||
| Guangzhou North | 广州北 廣州北 | 2060 | 13:13 (D2103) | Guangzhou | ||||||
| Guangzhou South | 广州南 廣州南 | 2105 | 13:55 (D2103) | 9:38 (G71) | Guangzhou–Zhuhai intercity railway Guiyang–Guangzhou high-speed railway Nanning–Guangzhou high-speed railway | |||||
| Qingsheng | 庆盛 慶盛 | 2136 | ||||||||
| Humen | 虎门 虎門 | 2155 | Dongguan | |||||||
| Guangmingcheng | 光明城 | 2191 | Shenzhen | |||||||
| Shenzhen North | 深圳北 | 2208 | 10:16 (G71) | Hangzhou–Fuzhou–Shenzhen high-speed railway Shenzhen–Zhanjiang high-speed railway | ||||||
| Futian | 福田 | 2216 | ||||||||
| Hong Kong West Kowloon | 香港西九龍 香港西九龙 | 2247 | 8:58 (G79) | Hong Kong | Hong Kong | |||||
References
- http://www.legco.gov.hk/yr09-10/english/panels/itb/papers/itb0111cb1-847-1-e.pdf#page=5
- "Hong Kong Update - Invest Hong Kong celebrates new milestone". www.hketotoronto.gov.hk. Archived from the original on 17 November 2016. Retrieved 2 January 2013.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 7 January 2013. Retrieved 2 January 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- https://edition.cnn.com/2018/09/23/asia/hong-kong-high-speed-rail-china-intl/index.html
- "China opens world's longest high-speed rail route". BBC. 25 December 2012. Retrieved 27 December 2012.
- "Travel from Hong Kong to China with its 1st high-speed railway". Rappler. 27 September 2018. Retrieved 27 September 2018.
- 京广高铁拟12月下旬开通届时广州直达北京最快约8小时,二等座票价估计近千元 Archived 6 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Xinxi Shibao (信息时报), 2012-11-21.
- "铁路客户服务中心". www.12306.cn.
- Hung, Wing-tat; Brunello, Lara; Bunker, Jonathan, Critical Issues of High Speed Rail Development in China (PDF), p. 4
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 February 2013. Retrieved 3 January 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- WebsiteBuilder, 1&1. "WHAT'S PLANNED - HONG KONG EXTRAS3". www.hongkongextras.com.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 15 February 2013. Retrieved 3 January 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "HKSAR and the Mainland signed the Co-operation Arrangement for the XRL co-location arrangement (with photos/video)". www.info.gov.hk. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- "CE welcomes passage of Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Express Rail Link (Co-location) Bill". www.info.gov.hk. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- 京石高铁 26日有望通车 Archived 26 January 2013 at Archive.today
- (Achieved by G1001,G1003) G1003列车时刻表 Archived 22 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine (Chinese) Wuhan-Guangzhou North/2hr57min)
- "福田至九龙乘高铁仅14分钟 广深港福田站2014年建成". Archived from the original on 5 November 2016. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- "Hong Kong Launches First High Speed Rail Service". finance.yahoo.com. Retrieved 26 September 2018.
- D2021车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- G527车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 3 January 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- D2031车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 28 March 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- G567车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- G71车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 2 January 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- G6701车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- G563车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 15 May 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- G503车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 25 February 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- D2103车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 3 December 2012. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- G501车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 25 February 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- G81车次查询. 火车票网. Archived from the original on 2 January 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
.JPG.webp)