Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation
The Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation or Borneo confrontation (also known by its Indonesian/Malay name, Konfrontasi) was a violent conflict from 1963–66 that stemmed from Indonesia's opposition to the creation of Malaysia. The creation of Malaysia was the amalgamation of the Federation of Malaya (now West Malaysia), Singapore and the crown colony/British protectorates of North Borneo and Sarawak (collectively known as British Borneo, now East Malaysia) in September 1963.[22] Vital precursors to the conflict included Indonesia's policy of confrontation against Netherlands New Guinea from March–August 1962 and the Brunei Revolt in December 1962.
| Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Formation of Malaysia and Cold War | |||||||
 A British soldier is winched up by a Westland Wessex helicopter during an operation in Borneo | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
Before Federation:
Supported by: |
Aligned parties:
Supported by: | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Malaysia |
 |
|
|
The confrontation was an undeclared war with most of the action occurring in the border area between Indonesia and East Malaysia on the island of Borneo (known as Kalimantan in Indonesia). The conflict was characterised by restrained and isolated ground combat, set within tactics of low-level brinkmanship. Combat was usually conducted by company- or platoon-sized operations on either side of the border. Indonesia's campaign of infiltrations into Borneo sought to exploit the ethnic and religious diversity in Sabah and Sarawak compared to that of Malaya and Singapore, with the intent of unravelling the proposed state of Malaysia.
The jungle terrain of Borneo and lack of roads straddling the Malaysia–Indonesia border forced both Indonesian and Commonwealth forces to conduct long foot patrols. Both sides relied on light infantry operations and air transport, although Commonwealth forces enjoyed the advantage of better helicopter deployment and resupply to forward operating bases. Rivers were also used as a method of transport and infiltration. Although combat operations were primarily conducted by ground forces, airborne forces played a vital support role and naval forces ensured the security of the sea flanks. The British provided most of the defensive effort, although Malaysian forces steadily increased their contributions, and there were periodic contributions from Australian and New Zealand forces within the combined Far East Strategic Reserve stationed then in West Malaysia and Singapore.[23]
Initial Indonesian attacks into East Malaysia relied heavily on local volunteers trained by the Indonesian Army. Over time, infiltration forces became more organised with the inclusion of a more substantial component of Indonesian forces. To deter and disrupt Indonesia's growing campaign of infiltrations, the British responded in 1964 by launching their own covert operations into Indonesian Kalimantan under the code name Operation Claret. Coinciding with Sukarno announcing a 'year of dangerous living' and the 1964 race riots in Singapore, Indonesia launched an expanded campaign of operations into West Malaysia on 17 August 1964, albeit without military success.[24] A build-up of Indonesian forces on the Kalimantan border in December 1964 saw the UK commit significant forces from the UK-based Army Strategic Command and Australia and New Zealand deployed roulement combat forces from West Malaysia to Borneo in 1965–66. The intensity of the conflict began to subside following the events of the 30 September Movement and Suharto's rise to power. A new round of peace negotiations between Indonesia and Malaysia began on May 1966, and a final peace agreement was signed on 11 August 1966 with Indonesia formally recognising Malaysia.[2]
Background
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Indonesia |
   |
| Timeline |
|
|
Political situation
Before Indonesia's Confrontation of Malaysia, Sukarno had sought to develop an independent Indonesian foreign policy, focused on the acquisition of Netherlands New Guinea as a residual issue from the Indonesian National Revolution, and establishing Indonesia's credentials as a notable international power operating distinct interests from those of the West and East. Indonesia had relentlessly pursued its claim to Netherlands New Guinea during the period 1950–1962, despite facing multiple setbacks in the UN General Assembly to have its claim recognised by the international community. Indonesia was an important country in developing the Non-Aligned Movement, hosting the Bandung Conference in 1955.
Following the Indonesian crisis in 1958, which had included the Permesta rebellion in eastern Indonesia and the declaration of the PRRI, a rebel revolutionary government based in Sumatra; Indonesia had emerged as a notable and rising military power in Southeast Asia.[25] With the influx of Soviet arms aid, Indonesia was able to advance its diplomatic claims to Netherlands New Guinea more forcefully. The diplomatic dispute reached its climax in 1962 when Indonesia launched a substantial campaign of airborne and seaborne infiltrations upon Netherlands New Guinea. While the infiltration forces were soundly defeated by Dutch and indigenous forces, Indonesia was able to lend credence to the threat of an Indonesian invasion of Netherlands New Guinea. The Dutch, facing mounting diplomatic pressure from the Indonesians and the Americans, who were anxious to keep Indonesia from becoming Communist aligned, yielded and agreed to a diplomatic compromise, allowing the Indonesians to gain control of the territory in exchange for pledging to hold a self-determination plebiscite (the Act of Free Choice) in the territory by 1969. Thus by the close of 1962, Indonesia had achieved a considerable diplomatic victory, which possibly emboldened its self-perception as a notable regional power. It was in the context of this recent diplomatic victory that Indonesia cast its attention to the British proposal for a unified Malaysian state.
Before the British government announcing the East of Suez policy in 1968, they had begun to re-evaluate in the late 1950s their force commitment in the Far East. As a part of its withdrawal from its Southeast Asian colonies, the UK moved to combine its colonies in North Borneo with the Federation of Malaya (which had become independent from Britain in 1957), and Singapore (which had become self-governing in 1959). In May 1961, the UK and Malayan governments proposed a larger federation called Malaysia, encompassing the states of Malaya, North Borneo, Sarawak, Brunei, and Singapore. Initially, Indonesia was mildly supportive of the proposed federation, although the PKI (Partai Komunis Indonesia — Indonesian Communist Party) was firmly opposed to it.[6]
In Brunei, it was unclear whether the Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III would support Brunei joining the proposed Malaysian state because of the implied reduction of his political office, and Brunei's oil revenues ensured Brunei's financial viability were it to choose independence. Furthermore, a Brunei politician, Dr. AM Azahari bin Sheikh Mahmud, while supporting a unified North Borneo, also opposed a wider Malaysian federation. In 1961, he had sounded out Indonesia about possible aid in training Borneo recruits; General Abdul Nasution hinted at moral support, and Soebandrio, the Indonesian foreign minister and head of intelligence, hinted at supplying more substantial aid. Azahari was a leftist who had fought in Indonesia in their war for independence.[6] Following these meetings, Indonesia began training in Kalimantan a small volunteer force, the North Kalimantan National Army (TNKU).
On 8 December 1962, the TNKU staged an insurrection—the Brunei Revolt. The insurrection was an abject failure, the poorly trained and equipped forces were unable to seize key objectives such as capturing the Sultan of Brunei, seize the Brunei oil fields, or take European hostages. Within hours of the insurrection being launched, British forces based in Singapore were being mobilised for a prompt response. The failure of the insurrection was evident within 30 hours when Gurkha troops airlifted from Singapore secured Brunei town and ensured the Sultan's safety.
The degree of Indonesian support for the TNKU remains a subject of debate. While Indonesia at the time denied direct involvement, it did sympathise with the TNKU's objectives to destabilise the proposed Malaysian state. Following the TNKU's military setback in Brunei, on 20 January 1963 Indonesian Foreign Minister Subandrio announced that Indonesia would pursue a policy of Konfrontasi with Malaysia, reversing Indonesia's previous policy of compliance with the British proposal. This was followed by the first recorded infiltration of Indonesian forces on 12 April 1963 when a police station in Tebedu, Sarawak, was attacked.[26]
People and terrain
In 1961, the island of Borneo was divided into four separate states. Kalimantan, comprising four Indonesian provinces, was located in the south of the island. In the north, separated from Kalimantan by a border some 1000 miles long, were the Sultanate of Brunei (a British protectorate) and two colonies of the United Kingdom (UK)—British North Borneo (later renamed Sabah) and Sarawak.
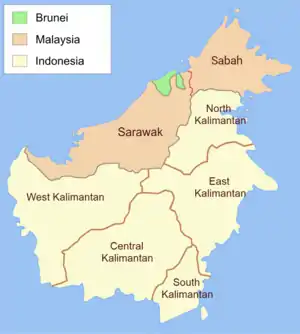
The three UK territories totalled some 1.5 million people, about half of them Dayaks. Sarawak had a population of about 900,000, while Sabah's was 600,000 and Brunei's was around 80,000. Among Sarawak's non-Dayak population, 31% were Chinese, and 19% were Malay. Among non-Dayaks in Sabah, 21% were Chinese, and 7% were Malay; Brunei's non-Dayak population was 28% Chinese and 54% Malay. There was a large Indonesian population in Tawau in southern Sabah and a large and economically active Chinese one in Sarawak. Despite their population size, Dayaks were spread through the country in village longhouses and were not politically organised.
Sarawak was divided into five administrative divisions. Sabah, whose capital city was Jesselton (Kota Kinabalu) on the north coast, was divided into several Residencies; those of the Interior and Tawau were on the border.
Apart from either end, the border generally followed a ridge line throughout its length, rising to almost 2,500 metres in the Fifth Division. In the First Division, there were some roads, including a continuous road from Kuching to Brunei and around to Sandakan on the east coast of Sabah. There were no roads in the Fourth and Fifth Divisions or the Interior Residency, and in Third Division, there was only the coast road, which was some 150 miles from the border. Mapping was generally poor, as British maps of the country only showed tiny topographic detail. Indonesian maps were worse; veterans recall "a single black and white sheet for all of Kalimantan torn from a school textbook" in 1964.[27]
Kalimantan was divided into four provinces, of which East Kalimantan and West Kalimantan face the border. The capital of the West is Pontianak on the west coast, about 100 miles (160 km) from the border, and the capital of the East is Samarinda on the south coast, some 220 miles (350 km) from the border. There were no roads in the border area other than some in the west, and no road existed linking West and East Kalimantan.
The lack of roads and tracks suitable for vehicles on both sides of the border meant that movement was limited to foot tracks mostly unmarked on any map, as well as water and air movement. There were many large rivers on both sides of the border, and these were the primary means of movement, including hovercraft by the UK. There were also quite a few small grass airstrips suitable for light aircraft, as dropping zones for parachuted supplies, and helicopters.
The equator lies about 100 miles south of Kuching, and most of northern Borneo receives over 3000 mm of rain each year. Borneo is naturally covered by tropical rainforest. This covers the mountainous areas cut by many rivers with very steep-sided hills and hilltop ridges often only a few metres wide. The high rainfall means large rivers; these provide a principal means of transport and are formidable tactical obstacles. Dense mangrove forest covering vast tidal flats intersected with numerous creeks is a feature of many coastal areas, including Brunei and either end of the border. There are cultivated areas in valleys and around villages. In the vicinity of abandoned and current settlements are areas of dense secondary regrowth.
Sarawakian opposition
The end of the Second World War had brought an end to the Brooke Dynasty rule in Sarawak. Believing it to be in the best interest of the people of Sarawak, Charles Vyner Brooke ceded the state to the British Crown.[28] Sarawak became a Crown colony, ruled from the Colonial Office in London, which in turn dispatched a governor for Sarawak. The predominantly Malay anti-cession movement, which rejected the British takeover of Sarawak in 1946 and had assassinated Duncan Stewart, the first British High Commissioner of Sarawak, may have been the forerunner of the subsequent anti-Malaysia movement in Sarawak, headed by Ahmad Zaidi Adruce.
According to Vernon L. Porritt and Hong-Kah Fong, Left-wing and communist cell groups had been present among Sarawak's urban Chinese communities since the 1930s and 1940s. Some of the earliest Communist groups in Sabah included the Anti-Fascist League, which later became the Races Liberation Army, and the Borneo Anti-Japanese League, which was made up of the North Borneo Anti-Japanese League and the West Borneo Anti-Japanese League. The latter was led by Wu Chan, who was deported by the Sarawak colonial government to China in 1952. Other Communist groups in Sarawak included the Overseas Chinese Youth Association, which was formed in 1946, and the Liberation League along with its youth wing, the Advanced Youth Association, which emerged during the 1950s. These organisations became the nuclei for two Communist guerrilla movements: the anti-Malaysia North Kalimantan People's Army (PARAKU) and the Sarawak People's Guerrillas (PGRS). These various Communist groups were designated by various British and other Western sources as the Clandestine Communist Organisation (CCO) or the Sarawak Communist Organisation (SCO).[29]

The Sarawak Communist Organisation was predominantly dominated by ethnic Chinese but also included Dayak supporters. However, the Sarawak Communist Organisation had little support from ethnic Malays and other indigenous Sarawak peoples. At its height, the SCO had 24,000 members.[10] During the 1940s and 1950s, Maoism had spread among Chinese vernacular schools in Sarawak. Following the Second World War, Communist influence also penetrated the labour movement and the predominantly-Chinese Sarawak United People's Party, the state's first political party which was founded in June 1959. The Sarawak Insurgency began after the Brunei Revolt in 1962 and SCO would fight alongside the Bruneian rebels and Indonesian forces during the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation (1963–1966).[29][30]
The Sarawak Communist Organisation and the Bruneian rebels supported and propagated the unification of all British Borneo territories to form an independent leftist North Kalimantan state. This idea was originally proposed by A. M. Azahari, leader of the Parti Rakyat Brunei (Brunei People's Party), who had forged links with Sukarno's nationalist movement, together with Ahmad Zaidi, in Java in the 1940s. However, the Brunei People's Party was in favour of joining Malaysia on the condition it was as the unified three territories of northern Borneo with their own sultan, and hence was strong enough to resist domination by Malaya, Singapore, Malay administrators or Chinese merchants.[9]
The North Kalimantan (or Kalimantan Utara) proposal was seen as a post-decolonisation alternative by local opposition against the Malaysia plan. Local opposition throughout the Borneo territories was primarily based on economic, political, historical and cultural differences between the Borneo states and Malaya, as well as the refusal to be subjected under peninsular political domination. Both Azahari and Zaidi went into exile in Indonesia during the confrontation. While the latter returned to Sarawak and had his political status rehabilitated, Azahari remained in Indonesia until his death on 3 September 2002.
In the aftermath of the Brunei Revolt, the remnants of the TNKU reached Indonesia. Possibly fearing British reprisals (which never eventuated), many Chinese communists, possibly several thousand, also fled Sarawak. Their compatriots remaining in Sarawak were known as the CCO by the UK but called the PGRS—Pasukan Gelilya Rakyat Sarawak (Sarawak People's Guerrilla Force) by Indonesia. Soebandrio met with a group of their potential leaders in Bogor, and Nasution sent three trainers from Resimen Para Komando Angkatan Darat (RPKAD) Battalion 2 to Nangabadan near the Sarawak border, where there were about 300 trainees. Some three months later, two lieutenants were sent there.[6]
The PGRS numbered about 800, based in West Kalimantan at Batu Hitam, with a contingent of 120 from the Indonesian intelligence agency and a small cadre trained in China. The PKI (Indonesian Communist Party) was firmly in evidence and led by an ethnic Arab revolutionary, Sofyan. The PGRS ran some raids into Sarawak but spent more time developing their supporters in Sarawak. The Indonesian military did not approve of the leftist nature of the PGRS and generally avoided them.[7]
Conflict
Beginning of hostilities
Sukarno's motives for beginning the Confrontation are contested. Former Indonesian Foreign Minister Ide Anak Agung Gde Agung argued years later that Sukarno intentionally muted Indonesia's opposition to the proposed Malaysian state while Indonesia was preoccupied with advancing its claim to West New Guinea. Following Indonesia's diplomatic victory in the West New Guinea dispute, Sukarno may have been emboldened to extend Indonesia's dominance over its weaker neighbours. Conversely, Sukarno may have felt compelled by the ongoing pressure of the PKI and the general instability of Indonesian politics to divert attention towards a new foreign conflict.
In the late 1950s, Sukarno argued that Malaysia was a British puppet state, a neo-colonial experiment and that any expansion of Malaysia would increase British control over the region, with implications for Indonesia's national security. Sukarno strongly opposed the British decolonisation initiative involving the formation of the Federation of Malaysia that would comprise the Malay Peninsula and North Borneo.
On the other side, Sukarno accused the new nation of Malaysia of being a British puppet state aimed at establishing neo-imperialism and neo-colonialism in Southeast Asia, and also at containing Indonesian ambition to be the regional hegemonic power.[31]
However, it was also suggested that Sukarno's campaign against the formation of Malaysia was actually motivated by a desire to unite the Malay Peninsula and the whole island of Borneo under Indonesian rule and to complete the previously abandoned idea of Greater Indonesia or Greater Malay, a concept that aims to unite the Malay race created by Sukarno and Kesatuan Melayu Muda, Ibrahim Yaacob.[31][32]
Similarly, the Philippines claimed eastern North Borneo, arguing that the Borneo colony had historical links with the Philippines through the Sulu archipelago.
However, while Sukarno made no direct claims to incorporate northern Borneo into Indonesian Kalimantan, he saw the formation of Malaysia as an obstacle to the Maphilindo, a non-political, irredentist union spanning Malaya, Philippines and Indonesia.[33] President of the Philippines Diosdado Macapagal initially did not oppose the concept and even initiated the Manila Accord. However, while the Philippines did not engage in hostilities, Malaysia severed diplomatic ties after the former deferred recognising it as the successor state of Malaya.
In April 1963, the first recorded infiltration and attack occurred in Borneo. An infiltration force training at Nangabadan was split in two and prepared for its first operation. On 12 April 1963, one infiltration force attacked and seized the police station at Tebedu in the 1st Division of Sarawak, about 40 miles from Kuching and 2 miles from the border with Kalimantan.[34] The other group attacked the village of Gumbang, South West of Kuching, later in the month. Only about half returned.[35] The Confrontation could be said to have started from a military perspective with the Tebedu attack.[36]
Before Indonesia's declaration of Confrontation against the proposed Malaysian state on 20 January 1963, the Cobbold Commission in 1962 had reported on the viability of a Malaysian state, finding that there was sufficient support in the Borneo colonies for the creation of a larger Malaysian state. However, due to firming Indonesian and Philippine opposition to the Malaysia proposal, a new round of negotiations was proposed to hear the Indonesian and Philippine points of opposition. To resolve the dispute the would-be member states of Malaysia met representatives of Indonesia and the Philippines in Manila for several days, starting on 30 July 1963. Just days before the summit, on 27 July 1963, President Sukarno had continued his inflammatory rhetoric, declaring that he was going to "crush Malaysia" (Indonesian: Ganyang Malaysia). At the Manila meeting, the Philippines and Indonesia formally agreed to accept the formation of Malaysia if a majority in North Borneo and Sarawak voted for it in a referendum organised by the United Nations. While the fact-finding mission by the UN was expected to begin on 22 August, Indonesian delaying tactics forced the mission to start on 26 August. Nevertheless, the UN expected the report to be published by 14 September 1963.[37]
Before the Manila meeting, the Malayan Government had set 31 August as the date on which Malaysia would come into existence (coinciding with Malaya's independence day celebrations of 31 August). However, at the Manila negotiations, it was persuaded by the Indonesian and Philippine Governments to postpone Malaysia's inauguration until 15 September 1963 by which time a UN mission was expected to report on whether the two Borneo colonies supported the Malaysia proposal.[38] However, following the conclusion of the Manila talks, the Malayan Prime Minister Tunku Abdul Rahman announced that the proposed Malaysian state would come into existence on 16 September 1963, apparently irrespective of the latest UN report.[39]
North Borneo and Sarawak, anticipating a pro-Malaysian UN report, declared their independence as part of Malaysia on the sixth anniversary of Merdeka Day, 31 August 1963, even before the UN report had been published.[37] On 14 September the UN report was published, once again providing general endorsement of the proposed Malaysian state. Malaysia was formally established on 16 September 1963. Indonesia immediately reacted by expelling the Malaysian Ambassador from Jakarta. Two days later, rioters organised by the PKI burned the British embassy in Jakarta. Several hundred rioters ransacked the Singapore embassy in Jakarta and the homes of Singaporean diplomats. In Malaysia, Indonesian agents were captured, and crowds attacked the Indonesian embassy in Kuala Lumpur.[40]
Ongoing campaign of infiltrations
Even as peace talks progressed and stalled, Indonesia maintained its campaign of infiltrations. On 15 August, a headman reported an incursion in the 3rd Division and a follow-up indicated they were about 50 strong. A series of contacts ensued as 2/6 Gurkhas deployed patrols and ambushes, and after a month, 15 had been killed and three captured. The Gurkhas reported that they were well trained and professionally led, but their ammunition expenditure was high, and their fire discipline broke down. The prisoners reported 300 more invaders within a week and 600 in a fortnight.[41] The Battle of Long Jawai was the first major incursion for the centre of the 3rd Division, directed by an RPKAD Major Mulyono Soerjowardojo,[42] who had been sent to Nangabadan earlier in the year.[35] The proclamation of Malaysia in September 1963 meant that Malaysian Army units deployed to Borneo (now East Malaysia).[43]
The deliberate attack by Indonesian forces on Malaysian troops did not enhance Sukarno's "anti-imperialist" credentials, although the Indonesian government tried blaming the KKO as enthusiastic idealists acting independently. They also produced Azahari, who claimed that Indonesian forces were playing no part in active operations. Sukarno next launched a peace offensive and, in late January, declared he was ready for a ceasefire (despite having denied direct Indonesia involvement). Talks started in Bangkok, but border violations continued, and the talks soon failed. They resumed mid-year in Tokyo and failed within days but allowed time for a Thai mission to visit Sarawak and witness smart, well-equipped Indonesian soldiers withdrawing across the border, which they had crossed a short distance away earlier in the day.[44]
Meanwhile, the Indonesian armed forces led by Lt. General Ahmad Yani became increasingly concerned with the worsening domestic situation in Indonesia and began to secretly contact the Malaysian government, while managing to obstruct the confrontation to a minimal level.[45] This was implemented to preserve an already exhausted army recently conducted the Operation Trikora in Western New Guinea, while also maintaining its political position in Indonesian politics, especially against the Communist Party of Indonesia, the ardent supporters of the confrontation.[46]
Expansion of the conflict to the Malaysian Peninsula
.JPG.webp)
Co-ordinated to coincide with Sukarno announcing a 'Year of Dangerous Living' during Indonesian Independence Day celebrations, Indonesian forces began a campaign of airborne and seaborne infiltrations of the Malaysian Peninsula on 17 August 1964. On 17 August 1964, a seaborne force of about 100, composed of air force Komando Pasukan Gerak Tjepat/PGT (Rapid Response Troop Commandos, later known as "Kopasgat"; current spelling: Komando Pasukan Gerak Cepat/PGC, today known as Korps Pasukan Khas "Paskhas") paratroopers, KKO and about a dozen Malaysian communists, crossed the Malacca Straits by boat, landing at Pontian in three parties in the night.[47] Instead of being greeted as liberators, however, they were contained by various Commonwealth forces, and all but four of the infiltrators were captured within a few days.[48] On 2 September, three Lockheed C-130 Hercules aircraft set off from Jakarta for Peninsular Malaysia, flying low to avoid detection by radar. The following night, two of the C-130 managed to reach their objective with their onboard PGT paratroopers, who jumped off and landed around Labis in Johore (about 100 miles north of Singapore). The remaining C-130 crashed into the Malacca Straits while trying to evade interception by an RAF Javelin FAW 9 launched from RAF Tengah.[47] Due to a lightning storm, the drop of 96 paratroopers was widely dispersed. This resulted in them landing close to 1/10 Gurkhas, who were joined by 1st Battalion, Royal New Zealand Infantry Regiment (1 RNZIR) stationed near Malacca with 28 (Commonwealth) Brigade. Operations were commanded by four Malaysian Brigade, but it took a month for the security forces to capture or kill 90 of the 96 parachutists, for the loss of two men killed during the action.[49][50][51]
Indonesia's expansion of the conflict to the Malaysian Peninsula sparked the Sunda Straits Crisis, involving the anticipated transit of the Sunda Strait by the British aircraft carrier HMS Victorious and two destroyer escorts. Commonwealth forces were readied for airstrikes against Indonesian infiltration staging areas in Sumatra if further Indonesian infiltrations of the Malaysian Peninsula were attempted. A tense three-week standoff occurred before the crisis was peacefully resolved.[52]
By the concluding months of 1964, the conflict once again appeared to have reached a stalemate, with Commonwealth forces having placed in check for the moment Indonesia's campaign of infiltrations into Borneo, and more recently, the Malaysian Peninsula. However, the fragile equilibrium looked likely to change once again in December 1964 when Commonwealth intelligence began reporting a build-up of Indonesian infiltration forces in Kalimantan opposite Kuching, which suggested the possibility of an escalation in hostilities. Two additional British battalions were subsequently deployed to Borneo.[53][54] Meanwhile, due to the landings in Malaysia and Indonesia's continued troop build-up, Australia and New Zealand also agreed to begin deploying combat forces to Borneo in early 1965.[55]
Operation Claret

Operation Claret was a long-running series of secretive cross-border raids conducted by British Commonwealth forces in Borneo from June 1964 to early 1966. These raids were undertaken by special forces—including the British Special Air Service, Australian Special Air Service Regiment, and New Zealand Special Air Service—as well as regular infantry. During the early phases of the conflict, British Commonwealth and Malaysian troops had attempted only to control the border and to protect population centres from Indonesian attacks. However, by 1965 they had decided to take more aggressive action, crossing the border to obtain information and in "hot pursuit" of withdrawing Indonesian infiltrators.[36] First approved in May 1965, later they were expanded to include cross-border ambushing in July.[56]
These patrols—which were highly classified at the time—often involved small reconnaissance teams crossing the border from the Malaysian states of Sarawak or Sabah into Indonesian Kalimantan in order to detect Indonesian forces about to enter East Malaysia. Initially, penetration was limited to 3,000 yards (2,700 m) but was later extended to 6,000 yards (5,500 m), and again to 10,000 yards (9,100 m) after the Battle of Plaman Mapu in April 1965.[57][58] Conventional follow-up forces of platoon and company size were then directed into position to ambush the Indonesians, either as they crossed the border or often while they were still in Kalimantan. Such operations were to be "deniable" and were conducted under a policy of "aggressive defence".[56] Given the sensitivity of these operations and the potential consequences if they were exposed, they were controlled at the highest level and conducted within strict parameters known as the "Golden Rules", while the participants were sworn to secrecy.[59]
Claret was largely successful in gaining the initiative for the British Commonwealth forces before being suspended late in the war, inflicting significant casualties on the Indonesians and keeping them on the defensive on their side of the border.[56][60] The operations were only publicly disclosed by Britain in 1974, while the Australian government did not officially acknowledge its involvement until 1996.[61][62]
Easing of tensions

On the night of 30 September 1965, an attempted coup took place in Jakarta. Six senior Indonesian military leaders were killed, while General Nasution narrowly escaped from his would-be captors. In the ensuing confusion, Sukarno agreed to allow Suharto to assume emergency command and control of Jakarta and the armed forces stationed there. Blame for the failed coup was attributed to the Indonesian Communist Party (PKI), and in the following weeks and months a campaign of imprisonment and lynching of PKI members and sympathisers broke out across Jakarta and Indonesia. With Suharto's grip on power in Jakarta and Indonesia delicately poised, the scale and intensity of Indonesia's campaign of infiltrations into Borneo began to ease.[63] The train of events set off by the failed coup led to Suharto's gradual consolidation of power and marginalisation of Sukarno. At the same time, the anti-communist purge spread throughout Indonesia. Suharto's steady consolidation of power after 30 September events allowed him to form a new government and in March 1967 Suharto was able to form a new cabinet that excluded Sukarno.
On 28 May 1966, at a conference in Bangkok, the Malaysian and Indonesian governments declared the conflict was over. However, it was unclear if Suharto was in full control of Indonesia (rather than Sukarno), and vigilance in Borneo could not be relaxed. With Suharto's co-operation a peace treaty was signed on 11 August and ratified two days later.[64]

During Suharto's rise to power Claret operations continued and, in March 1966, a Gurkha battalion was involved in some of the fiercest fighting of the campaign during two raids into Kalimantan.[65] Minor action by Indonesian forces continued in the border area, including an attempt at counter-battery fire against a 105 mm gun position in Central Brigade (reports from locals said the British return fire had turned over the Indonesian gun, thought to be 76 mm).
At the beginning of 1966, with Indonesia's political hiatus beginning to stabilise (it had stopped a major RPKAD operation to capture a British prisoner), the RPKAD linked up with PGRS to establish guerrilla forces in Sabah and Sarawak. The Sabah effort never crossed the border; however, two groups entered Sarawak in February and May and obtained support from local sympathisers. The first group, despite losses in several contacts, lasted until June and exfiltrated on hearing about the end of Konfrontasi. Survivors of the second, after contact with Australian troops, also made it back to Indonesia.[66] However, the final Indonesian incursion was in May and June. Signs of a substantial force were found crossing into Central Brigade. This was some 80 strong, mostly volunteers, led by Lt Sombi (or Sumbi) and a team from 600 Raider Company. They moved fast towards Brunei with 1/7 Gurkhas pursuing and ambushing them; almost all were accounted for. In response to this, a final Claret operation was launched, which was an artillery ambush by 38 Light Battery.
Counter-measures
Command arrangements

In early January 1963, the military forces in northern Borneo, having arrived in December 1962 in response to the Brunei Revolt, were under the command of Commander British Forces Borneo (COMBRITBOR), Major General Walter Walker, who was Director of Borneo Operations (DOBOPS) based on Labuan Island and reported directly to the Commander in Chief Far East Forces, Admiral Sir David Luce.[67] Luce was routinely replaced by Admiral Sir Varyl Begg in early 1963.[68] In the middle of 1963, Brigadier Pat Glennie, normally the Brigadier General Staff in Singapore, arrived as Deputy DOBOPS.
Politico-military authority lay with the Emergency Committees in Sarawak and North Borneo, including their Governors, who were the Commanders in Chief for their colonies. In Brunei, there was a State Advisory Council answerable to the Sultan.[69] After independence, supreme authority changed to the Malaysian National Defence Council in Kuala Lumpur with State Executive Committees in Sabah and Sarawak. Military direction was from the Malaysian National Operations Committee jointly chaired by the Chief of the Malaysian Armed Forces Staff, General Tunku Osman, and the Inspector General of Police, Sir Claude Fenner. The British Commander in Chief Far East Forces was a member. DOBOPS regularly attended its meetings.[70]
Commonwealth order of battle
.JPG.webp)
British forces in Borneo included Headquarters (HQ) 3 Commando Brigade in Kuching with responsibility for the western part of Sarawak, 1st, 2nd and 3rd Divisions, and HQ 99 Gurkha Infantry Brigade in Brunei responsible for the East, 4th and 5th Divisions, Brunei and Sabah.[71] These HQs had deployed from Singapore in late 1962 in response to the Brunei Revolt. The ground forces were initially limited to just five UK and Gurkha infantry battalions usually based in Malaya, Singapore and Hong Kong,[72] and an armoured car squadron.[73] The police also deployed several light infantry of Police Field Force companies.[74] However, as additional resources became available the size of the force available to Walker expanded, and by the end of 1964 British forces had grown to approximately 14,000 troops organised into three brigades (increased to four in 1965).[64] The naval effort, under DOBOPS command, was primarily provided by minesweepers used to patrol coastal waters and larger inland waterways around Wallace Bay. A guardship – a frigate or destroyer – was stationed off Tawau.[75]
Before Confrontation, no British military units had been stationed in Sabah or Sarawak. As Confrontation developed increasing numbers of troops were required. There were three types of British Army deployment: Units stationed in the Far East for two years did a single 4-month tour (this applied to Australian and NZ); Gurkha units (all permanently stationed in the Far East) did 6 month tours, generally once every twelve months; UK based units (from Army Strategic Command) did 12 month tours including 6 weeks jungle warfare training in West Malaysia.
The initial air component based in Borneo consisted of detachments from squadrons stationed in Malaya and Singapore. These included Twin Pioneer and Single Pioneer transport aircraft, probably two or three Blackburn Beverley and Handley Page Hastings transports, and about 12 helicopters of various types. One of Walker's first "challenges" was curtailing the RAF's centralised command and control arrangements and insisting that aircraft tasking for operations in Borneo was by his HQ, not by the RAF Air Command Far East HQ in Singapore.[76] Other aircraft of many types stationed in Malaya and Singapore provided sorties as necessary, including routine transport support into Kuching and Labuan. Rotary wing support included 60 naval and air force troop-lift helicopters and another 40 smaller army variants.[64]
.JPG.webp)
Patrols within Malaysia were supplied while in the field by RN Wessex and RAF Whirlwind helicopters, initially dropping supplies to the patrols from low level, and later after the patrols had cleared a landing area in the dense jungle, by landing. A test Joint Service deployment of a Westland SR.N5 hovercraft at Tawau was also trialled under Major John Simpson.
In addition to the ground and air force units, between 1963 and 1966 there were up to 80 ships from the Royal Navy, Royal Australian Navy, Royal Malay Navy, Royal New Zealand Navy and the Royal Fleet Auxiliary.[77] Most of these were patrol craft, minesweepers, frigates and destroyers patrolling the coast-line to intercept Indonesian insurgents. One of the two Commando Carriers, HMS Albion and HMS Bulwark, was also committed throughout Confrontation usually in their transport role for troops, helicopters and army aircraft between Singapore and Borneo.[78]
In the early stages of the conflict, Indonesian forces were under the command of Lieutenant General Zulkipli in Pontianak, on the coast of West Kalimantan about 200 km (120 mi) from the border. The Indonesian irregulars, led by Indonesian officers, were thought to number about 1500, with an unknown number of regular troops and local defence irregulars. They were deployed the entire length of the border in eight operational units, mostly facing the 1st and 2nd Divisions. The units had names such as "Thunderbolts", "Night Ghosts" and "World Sweepers".[79] However, as the conflict developed, the poorly trained and equipped 'volunteers' had been replaced by regular units.[80] Indonesian forces deployed along the border in Kalimantan increased significantly towards the end of 1964, with estimates of between 15,000 and 30,000 men, up from around 2,500 men in mid-1964.[81]
Intelligence
.JPG.webp)
A useful factor in the containment of the Indonesian forces was the use of intelligence. The Royal Signals were able to intercept the Indonesian military communications. The cyphers were decrypted by the Intelligence Corps based at Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) listening stations in Singapore, one of which was RAF Chia Keng which was linked directly to the RAF Far East Air Force headquarters at RAF Changi. Intelligence from this may have been used in planning some aspects of Claret cross-border operations.
British tactics
Soon after assuming command in Borneo, General Walker issued a directive listing the ingredients for success, based on his experience in the Malayan Emergency:
- Unified operations (army, navy and air force operating fully together)
- Timely and accurate information (the need for continuous reconnaissance and intelligence collection)
- Speed, mobility and flexibility
- Security of bases
- Domination of the jungle
- Winning the hearts and minds of the people (this was added several months later).[82]
Walker recognised the difficulties of limited forces and a long border and, in early 1963, was reinforced with a SAS squadron from the UK, which rotated with another mid-year. When the SAS temporarily adopted 3-man instead of 4-man patrols, they could not closely monitor the border. Increasing the capability of the infantry to create a surveillance network was also considered essential.
Walker raised the Border Scouts, building on Harrison's force of Kelabits, who had mobilised to help intercept the fleeing TNKU forces from the Brunei Revolt. He also utilised the experience of the Royal Marines as well as knowledge of the skill and usefulness of the Sarawak Rangers in the Malayan Emergency. This was approved by the Sarawak government in May as "auxiliary police". Walker selected Lieutenant Colonel John Cross, a Gurkha officer with immense jungle experience, for the task. A training centre was established in a remote area at Mt. Murat in the 5th Division and staffed mainly by SAS. Border Scouts were attached to infantry battalions and evolved into an intelligence-gathering force by using their local knowledge and extended families.[83] In addition, the Police Special Branch, which had proved so effective during the Malayan Emergency in recruiting sources in the communist organisation, was expanded.[84]
British jungle tactics were developed and honed during the Malayan Emergency against a clever and elusive enemy. They emphasised travelling lightly, being undetectable and going for many days without resupplying. Being undetectable meant being silent (hand signals, no rattling equipment) and 'odour free'—perfumed toiletries were forbidden (they could be detected a kilometre away by good jungle fighters), and sometimes eating food cold to prevent cooking smells.

In about 1962, at the end of National Service, British infantry battalions had reorganised into three rifle companies, a support company and an HQ company with logistic responsibilities. Battalion HQ included an intelligence section. Each rifle company was composed of 3 platoons of 32 men each, equipped with light machine guns and self-loading rifles. The support company had a mortar platoon with six medium mortars (3-inch mortar until replaced by 81-mm mortar around the end of 1965) organised into three sections, enabling a section to be attached to a rifle company if required. Similarly organised was an anti-tank platoon; there was also an assault pioneer platoon. The machine gun platoon was abolished, but the impending delivery of the 7.62 mm GPMG, with sustained fire kits held by each company, was to provide a medium machine gun capability. In the meantime, the Vickers machine gun remained available. The innovation in the new organisation was the formation of the battalion reconnaissance platoon,[85] in many battalions a platoon of "chosen men". In Borneo, mortars were usually distributed to rifle companies, and some battalions operated the rest of their support company as another rifle company.
The basic activity was platoon patrolling; this continued throughout the campaign, with patrols being deployed by helicopter, roping in and out as necessary. Movement was usually single file; the leading section rotated but was organised with two lead scouts, followed by its commander and then the remainder in a fire support group. Battle drills for "contact front" (or rear), or "ambush left" (or right) were highly developed. Poor maps meant navigation was important; however, the local knowledge of the Border Scouts in Borneo compensated for the poor maps. So tracks were sometimes used unless ambush was considered possible, or there was the possibility of mines. Crossing obstacles such as rivers was also handled as a battle drill. At night, a platoon harboured in a tight position with all-round defence.
Contact while moving was always possible. However, offensive action usually took two forms: either an attack on a camp or an ambush. The tactic for dealing with a camp was to get a party behind it then charge the front. However, ambushes were probably the most effective tactic and could be sustained for many days. They targeted tracks and, particularly in parts of Borneo, waterways. Track ambushes were close range, 10 to 20 m (11 to 22 yd), with a killing zone typically 20 to 50 m (22 to 55 yd) long, depending on the expected strength of the target. The trick was to remain undetected when the target entered the ambush area and then open fire all together at the right moment.
Fire support was limited for the first half of the campaign. A commando light battery with 105 mm Pack Howitzers had deployed to Brunei at the beginning of 1963 but returned to Singapore after a few months when the mopping-up of the Brunei Revolt ended. Despite the escalation in Indonesian attacks after the formation of Malaysia, little need was seen for fire support: the limited range of the guns (10 km (6.2 mi)), the limited availability of helicopters and the size of the country meant that having artillery in the right place at the right time was a challenge. However, a battery from one of the two regiments stationed in Malaysia returned to Borneo in early to mid-1964. These batteries rotated until the end of the confrontation. In early 1965, a complete UK-based regiment arrived. The short-range and substantial weight of the 3-inch mortars meant they were of minimal use.
Artillery had to adopt new tactics. Almost all guns were deployed in single gun sections within a company or platoon base. The sections were commanded by one of the battery's junior officers, warrant officers or sergeants. Sections had about ten men and did their own technical fire control. They were moved underslung by Wessex or Belvedere helicopters as necessary to deal with incursions or support operations. Forward observers were in short supply, but it seems that they always accompanied normal infantry Claret operations and occasionally special forces ones. However, artillery observers rarely accompanied patrols inside Sabah and Sarawak unless they were in pursuit of a known incursion and guns were in range. Observation parties were almost always led by an officer, but only two or three men strong.
Communications were a problem; radios were not used within platoons, only rearwards. Ranges were invariably beyond the capability of manpack VHF radios (A41 and A42, copies of AN/PRC 9 and 10), although the use of relay or rebroadcast stations helped where they were tactically possible. Patrol bases could use the World War II vintage HF No 62 Set (distinguished by having its control panel labelled in English and Russian). Until the manpack A13 arrived in 1966, the only lightweight HF set was the Australian A510, which did not provide voice, only Morse code.
British psychological operations
The role of the United Kingdom's Foreign Office and Secret Intelligence Service (MI6) during the confrontation was brought to light in a series of exposés by Paul Lashmar and Oliver James in The Independent newspaper beginning in 1997 and has also been covered in journals on military and intelligence history.
The revelations included an anonymous Foreign Office source stating that the decision to unseat President Sukarno was made by Prime Minister Harold Macmillan and then executed under Prime Minister Harold Wilson. According to the exposés, the UK had already become alarmed with the announcement of the "Konfrontasi" policy.[86] It has been claimed that a Central Intelligence Agency memorandum of 1962 indicated that Macmillan and US President John F. Kennedy were increasingly alarmed by the possibility of the Confrontation with Malaysia spreading, and agreed to "liquidate President Sukarno, depending on the situation and available opportunities".[87]

To weaken the regime, the UK Foreign Office's Information Research Department (IRD) coordinated psychological operations (psyops) in concert with the British military, to spread black propaganda casting the Communist Party of Indonesia (PKI), Chinese Indonesians, and Sukarno in a bad light. These efforts were to duplicate the successes of the British psyop campaign in the Malayan Emergency.
These efforts were coordinated from the British High Commission in Singapore, where the BBC, Associated Press, and The New York Times filed their reports on the Crisis in Indonesia. According to Roland Challis, the BBC correspondent who was in Singapore at the time, journalists were open to manipulation by IRD due to Sukarno's stubborn refusal to allow them into the country: "In a curious way, by keeping correspondents out of the country Sukarno made them the victims of official channels, because almost the only information you could get was from the British ambassador in Jakarta."[86]
These manipulations included the BBC reporting that communists were planning to slaughter the citizens of Jakarta. The accusation was based on a forgery planted by Norman Reddaway, a propaganda expert with the IRD. He later bragged in a letter to the British ambassador in Jakarta, Sir Andrew Gilchrist, that it "went all over the world and back again", and was "put almost instantly back into Indonesia via the BBC".[88] Gilchrist himself informed the Foreign Office on 5 October 1965: "I have never concealed from you my belief that a little shooting in Indonesia would be an essential preliminary to effective change."[89]
In April 2000, Denis Healey, Secretary of State for Defence at the time of the war, confirmed that the IRD was active during this time. He officially denied any role by MI6, and denied "personal knowledge" of the British arming of the Army's right-wing faction, though he did comment that if there were such a plan, he "would certainly have supported it".[90]
Although the British MI6 is strongly implicated in this scheme by the use of the Information Research Department (seen as an MI6 office), any role by MI6 itself is officially denied by the UK government, and papers relating to it have yet to be declassified by the Cabinet Office.[90]
British Army
One squadron of the British Army's 22 Special Air Service regiment was deployed to Borneo in early 1963 in the aftermath of the Brunei Revolt to gather information in the border area about Indonesian infiltration.[91] There was a British Army presence until the end of the campaign. Faced with a border of 971 miles, they could not be everywhere, and, at this time, 22 SAS had only three squadrons. Also present were the Special Boat Service (SBS) of the Royal Marine Commandos. They had two sections based in Singapore.[92] Tactical HQ of 22 SAS deployed to Kuching in 1964 to take control of all SAS and SBS operations.[93][94] The shortage of SAS and SBS personnel was exacerbated by the need for them in South Arabia, in many ways, a far more demanding task in challenging conditions against a cunning and aggressive opponent.
The solution was to create new units for Borneo. The first to be employed in Borneo were the Pathfinder Platoon of the Guards Independent Parachute Company, which already existed as the pathfinder force of 16th Parachute Brigade. Next, the Gurkha Independent Parachute Company was raised.[95] Sections of the SBS were also used, but mostly for amphibious tasks.[96] Finally, the Parachute Regiment battalions formed patrol companies (C in the 2nd and D in the 3rd).[97] The situation eased in 1965 when the Australian and New Zealand governments agreed that their forces could be used in Borneo, enabling both Australian and New Zealand SAS squadrons to rotate through Borneo.[98]
SAS activities were mostly covert reconnaissance and surveillance patrols by four-person teams. However, some larger scale raiding missions took place, including amphibious ones by the SBS. Once Claret operations were authorised, most missions were inside Kalimantan, although they conducted operations over the border before Claret from about early 1964.[99]
Aftermath
Casualties
| Origin | Killed | Wounded |
|---|---|---|
| UK Gurkha |
500[100] 43 |
44 83 |
| AUS Army | 23[19] | 8 |
| NZ Army | 12 [20] | 7 |
| Rest | 29 | 38 |
| Total | 607 | 180 |
The conflict lasted nearly four years; however, following General Suharto's replacement of Sukarno, Indonesian interest in pursuing the war with Malaysia declined, and combat eased. Peace negotiations were initiated during May 1966 before a final peace agreement was ratified on 11 August 1966.[101]
Although the Indonesians had conducted a few amphibious raids and an airborne operation against Malaya, the war remained limited throughout its duration and remained largely a land conflict. For either side to have escalated to large scale air or naval attacks "would have incurred disadvantages greatly outweighing the marginal military effect that they might have produced".[64] The UK Secretary of State for Defence at the time, Denis Healey, described the campaign as "one of the most efficient uses of military forces in the history of the world".[102] British Commonwealth forces peaked at 17,000 deployed in Borneo, with another 10,000 more available in Malaya and Singapore.[64]
.JPG.webp)
Total British Commonwealth military casualties were 114 killed and 181 wounded, the greatest number of them Gurkhas.[64] Gurkha losses were 43 killed and 83 wounded, losses among other British armed forces were 19 killed and 44 wounded. Australian casualties were 16 killed, of whom 7 were killed in action, and 9 wounded. New Zealand casualties were 7 killed and another 7 wounded or injured.[103][104] The remaining casualties were that of the Malaysian military, police, and Border Scouts. A significant number of British casualties occurred during helicopter accidents, including a Belvedere crash that killed several SAS commanders and a Foreign Office official, possibly a member of MI6. A Wessex collision also killed several men from 2nd Parachute Battalion, and a Westland Scout crash, on 16 July 1964, near Kluang airfield, killed the two crewmen from 656 Sqn AAC. Finally, in August 1966, there remained two British and two Australian soldiers missing and presumed dead, with the Australians (both from the SASR) probably drowned while crossing a swollen river.[105] The remains of a Royal Marine were recovered some 20 years later. Altogether, 36 civilians were killed, 53 wounded and 4 captured, with most being local inhabitants.[64]
Indonesian casualties were estimated at 590 killed, 222 wounded and 771 captured.[64]
Awards
A number of gallantry awards were made for actions during the campaign. No Distinguished Flying Cross or naval awards were made.
| Regiment | Victoria Cross | Military Cross | Distinguished Conduct Medal | Military Medal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Royal Marines | 2 | 5 | ||
| Royal Artillery | 2 | |||
| Scots Guards | 1 | |||
| Royal Leicestershire Regt | 2 | |||
| Staffordshire Regiment | 1 | |||
| Royal Northumberland Fusiliers | 1 | |||
| Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders | 1 | 1 | ||
| Durham Light Infantry | 2 | |||
| Green Jackets | 4 | |||
| Parachute Regiment | 1 | 2 | ||
| Special Air Service | 1 | |||
| 2 Gurkha Rifles | 10 | 1 | 10 | |
| 6 Gurkha Rifles | 4 | 5 | ||
| 7 Gurkha Rifles | 3 | 6 | ||
| 10 Gurkha Rifles | 1 | 10 | 2 | 6 |
| Gurkha Regiment not identified | 2 | 4 | ||
| Royal New Zealand Artillery | 1 | |||
| Royal Australian Regiment | 4 | 3 |
Legacy
- Memorials
 A soldier statue in Tawau Confrontation Memorial marking the victory during the battle in Kalabakan, Tawau, Sabah, Malaysian Borneo.
A soldier statue in Tawau Confrontation Memorial marking the victory during the battle in Kalabakan, Tawau, Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. A memorial in Ansip Ferry, Keningau, Malaysian Borneo, to the Royal Australian Engineers who served in Sabah by constructing a 123.2-kilometre road between Keningau and Sapulut from 1964 to 1966.
A memorial in Ansip Ferry, Keningau, Malaysian Borneo, to the Royal Australian Engineers who served in Sabah by constructing a 123.2-kilometre road between Keningau and Sapulut from 1964 to 1966. A memorial in Kundasang, Malaysian Borneo to the Commonwealth forces who served in Sabah, especially the Australians together with British, Malaysians and New Zealanders.
A memorial in Kundasang, Malaysian Borneo to the Commonwealth forces who served in Sabah, especially the Australians together with British, Malaysians and New Zealanders. Monument to the victims of the "Konfrontasi" in Singapore
Monument to the victims of the "Konfrontasi" in Singapore
See also
- British military history
- Brunei Revolt
- Communist insurgency in Sarawak
- Operation Claret
- Combat operations in 1963 during the Indonesian-Malaysian Confrontation
- Combat operations in 1964 during the Indonesian-Malaysian Confrontation
- Combat operations in 1965 during the Indonesian-Malaysian Confrontation
- Far East Strategic Reserve
- History of Brunei
- History of Indonesia
- History of Malaysia
- Military history of New Zealand in Malaysia
- Indonesia–New Zealand relations#The Sukarno Era
- MacDonald House bombing
References
Notes
- Andretta Schellinger (12 February 2016). Aircraft Nose Art: American, French and British Imagery and Its Influences from World War I through the Vietnam War. McFarland. pp. 152–. ISBN 978-0-7864-9771-3. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- Dennis & Grey 1996, p. 318.
- "Commonwealth Backing for Malaysia". The Sydney Morning Herald. 24 November 1964. p. 2. Archived from the original on 19 November 2015. Retrieved 19 February 2015.
- Robert Bothwell; Jean Daudelin (17 March 2009). Canada Among Nations, 2008: 100 Years of Canadian Foreign Policy. McGill-Queen's Press – MQUP. pp. 284–. ISBN 978-0-7735-7588-2. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- "Malaysian–American Relations during Indonesia's Confrontation against Malaysia, 1963–66". Cambridge University Press. 24 August 2009.
- Conboy 2003, pp. 93–95.
- Conboy 2003, p. 156.
- Fowler 2006, pp. 11, 41
- Pocock 1973, p. 129.
- Corbett 1986, p. 124.
- Hara, Fujiol (December 2005). "The North Kalimantan Communist Party and the People's Republic of China". The Developing Economies. XLIII (1): 489–513. doi:10.1111/j.1746-1049.2005.tb00956.x. hdl:10.1111/j.1746-1049.2005.tb00956.x.
- Sejarah Indonesia : "The Sukarno Years". Retrieved 30 May 2006.
- A. Dahana (2002). "China Role's in Indonesia's "Crush Malaysia" Campaign". Universitas Indonesia. Archived from the original on 19 July 2016. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- John W. Garver (1 December 2015). China's Quest: The History of the Foreign Relations of the People's Republic of China. Oxford University Press. pp. 219–. ISBN 978-0-19-026106-1.
- Hamilton Fish Armstrong (July 1963). "The Troubled Birth of Malaysia". Foreign Affairs.
- Kurt London (1974). The Soviet Impact on World Politics. Ardent Media. pp. 153–. ISBN 978-0-8015-6978-4.
- Mohd. Noor Mat Yazid (2013). "Malaysia-Indonesia Relations Before and After 1965: Impact on Bilateral and Regional Stability" (PDF). Programme of International Relations, School of Social Sciences, Universiti Malaysia Sabah. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2016. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- "The lost wars: Britain's Malayan campaigns". The Independent. 17 September 2011.
- "Indonesian Confrontation, 1963–66 | Australian War Memorial". www.awm.gov.au.
- "NZ and Confrontation in Borneo - Confrontation in Borneo | NZHistory, New Zealand history online". nzhistory.govt.nz.
- Sulistiyono, Bambang Bahagia. "Konflik Indonesia - Malaysia: Dalam Perspektif Kebangsaan 1963 - 2010". PT Kanisius – via Google Books.
- Mackie 1974, pp. 36–37 & 174.
- Dennis & Grey 1996, p. 25.
- Edwards 1992, p. 306.
- Cain 1997, p. 67.
- Easter 2004, p. 46.
- Conboy 2003, p. 102.
- Reece 1993, p. 72.
- Fong 2005, pp. 183–192.
- Kheng 2009, pp. 132–152.
- Hitoshi Hirakawa; Hiroshi Shimizu (24 June 1999). Japan and Singapore in the World Economy: Japan's Economic Advance Into Singapore 1870-1965. Routledge. p. 180. ISBN 978-1-134-65174-0.
- Greg Poulgrain (1998). The Genesis of Konfrontasi: Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia, 1945-1965. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. p. 142. ISBN 978-1-85065-513-8.
- Pocock 1973, p. 113.
- Pocock 1973, p. 153.
- Conboy 2003, p. 95.
- Dennis et al. 2008, p. 152.
- Tun Hanif Omar. Merdeka and Malaysia Day. The Star. 8 April 2007.
- Edwards 1992, p. 260.
- Mackie 1974, pp. 174–175.
- Pocock 1973, p. 173.
- Pocock 1973, p. 170.
- van der Bijl 2007, pp. 80–85.
- Majid 2007, p. 154.
- Pocock 1973, pp. 179–181, 188.
- Weinstein, Franklin B. (2007). Indonesian Foreign Policy and the Dilemma of Dependence: From Sukarno to Soeharto. Equinox Publishing. ISBN 9789793780566.
- Crouch, Harold (2007). The Army and Politics in Indonesia. Equinox Publishing. ISBN 9789793780504.
- Conboy 2003, p. 161.
- James & Sheil-Small 1971, p. 146.
- van der Bijl 2007, pp. 135–138.
- James & Sheil-Small 1971, pp. 148–150.
- Pugsley 2003, pp. 206–213.
- Edwards 1992, p. 319.
- Gregorian 1991, p. 55.
- Jones 2002, p. 272.
- van der Bijl 2007, p. 165.
- Pugsley 2003, p. 255.
- Smith 1999, p. 41.
- Dennis & Grey 1996, pp. 232–233.
- Horner 2002, pp. 83–84.
- Dennis & Grey 1996, p. 307.
- Forbes, Mark (23 March 2005). "Truth still a casualty of our secret war". The Age. Archived from the original on 2 September 2006. Retrieved 27 April 2009.
- Coates 2006, p. 333.
- Pocock 1973, p. 215.
- Carver 1986, p. 806.
- Pocock 1973, pp. 213–214.
- Conboy 2003, pp. 158–161.
- Dennis & Grey 1996, pp. 239–240.
- James & Sheil-Small 1971, p. 60.
- Mockaitis 1995, p. 29.
- van der Bijl 2007, p. 75.
- van der Bijl 2007, p. 39.
- Gregorian 1991, p. 49.
- van der Bijl 2007, p. 34.
- French 2011, p. 17.
- Grey 1998, pp. 57–58.
- Pocock 1973, pp. 159–160.
- Grey 1998, p. 55.
- Polmar 2008, p. 192.
- Pocock 1973, p. 168.
- Dennis & Grey 1996, p. 204.
- Mackie 1974, p. 215.
- Pimlott 1984, p. 95.
- Pocock 1973, pp. 165–166.
- Pimlott 1984, p. 97.
- Infantry Training Volume IV Tactics, The Infantry Battalion in Battle, 1963
- Lashmar, Paul; Oliver, James (1 December 1998). "How we destroyed Sukarno". The Independent. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- Blum 2003, p. 195.
- Easter 2004, p. 168.
- Pilger 2003, pp. 33–34.
- Lashmar, Paul; Oliver, James (16 April 2000). "How we lied to put a killer in power". The Independent. Archived from the original on 13 November 2010. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- Dickens 2003, pp. 39–55.
- Parker 2005, pp. 154–155.
- Dickens 2003, p. 153.
- Pugsley 2003, p. 263.
- Dickens 2003, p. 72.
- Parker 2005, pp. 153–169.
- van der Bijl 2007, pp. 174 & 224.
- Pugsley 2003, pp. 256 & 263.
- Pocock 1973, pp. 187 & 196.
- https://www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/home-news/lost-wars-britain-s-malayan-campaigns-5329010.html
- Goldsworthy 2001, p. 342.
- Pimlott 1984, p. 99.
- van der Bijl 2007, p. 241. Note incorrect Australian casualty figures cited as 22 killed (including 7 killed in action).
- For Australian casualty figures see: "Australians at war: casualties as a result of service with Australian units". Australian War Memorial. Archived from the original on 2 July 2009. Retrieved 15 December 2009.
- "Unit Information—2nd Squadron, Special Air Service Regiment, Confrontation". Australian War Memorial. Archived from the original on 23 October 2013. Retrieved 8 October 2009.
Bibliography
- Blum, William (2003). Killing Hope: US Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II. Zed Books. ISBN 9781842773697.
- Cain, Frank (1997). Menzies in War and Peace. St Leonards, New South Wales: Allen & Unwin. ISBN 9781864485738.
- Carver, Michael (1986). "Conventional Warfare in the Nuclear Age". In Paret, Peter (ed.). The Makers of Modern Strategy: From Machiavelli to the Nuclear Age. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691027647.
- Conboy, Ken (2003). Kompassus – Inside Indonesia's Special Forces. Jakarta: Equinox Publishing. ISBN 9789799589880.
- Coates, John (2006). An Atlas of Australia's Wars (Second ed.). Melbourne: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-555914-9.
- Corbett, Robin (1986). Guerilla Warfare: from 1939 to the Present Day. London: Orbis Book Publishing Corporation. ISBN 978-0-85613-469-2.
- Dennis, Peter; Grey, Jeffrey (1996). Emergency and Confrontation: Australian Military Operations in Malaya and Borneo 1950–1966. St Leonards: Allen and Unwin. ISBN 978-1-86373-302-1.
- Dennis, Peter; Grey, Jeffrey; Morris, Ewan; Prior, Robin; Bou, Jean (2008). The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History (Second ed.). South Melbourne: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-551784-2.
- Dickens, Peter (2003) [1983]. SAS Secret War in South-East Asia: 22 Special Air Service Regiment in the Borneo Campaign, 1963–1966. London: Greenhill Books. ISBN 9781853675737.
- Easter, David (2004). Britain and the Confrontation with Indonesia, 1960–1966. London: I.B.Tauris. ISBN 978-1-85043-623-2.
- Edwards, Peter (1992). Crises and Commitments: The Politics and Diplomacy of Australia's Involvement in Southeast Asian Conflicts 1948–1965. The Official History of Australia's Involvement in Southeast Asian Conflicts 1948–1975. Volume One. St Leonards: Allen and Unwin. ISBN 978-1-86373-184-3.
- Fong, Hong-Kah (2005). "Book Review: Vernon L. Porritt "The Rise and Fall of Communism in Sarawak 1940–1990"" (PDF). Taiwan Journal of Southeast Asian Studies. 2 (1): 183–192. ISSN 1811-5713. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 December 2013. Retrieved 31 August 2013.
- French, David (2011). The British Way in Counter-Insurgency, 1945–1967. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199587964.
- Gregorian, Raffi (1991). "CLARET Operations and Confrontation, 1964–66". Conflict Quarterly. 11 (1): 46–72. ISSN 0227-1311.
- Grey, Jeffrey (1998). Up Top. the Royal Australian Navy and Southeast Asian Conflicts 1955–1972. The Official History of Australia's Involvement in Southeast Asian Conflicts 1948–1975. St Leonards, New South Wales: Allen & Unwin. ISBN 978-1-86448-290-4.
- Goldsworthy, David (2001). Facing North: A Century of Australian Engagement with Asia. Volume One, 1901 to the 1970s. Carlton South, Victoria: Melbourne University Press. ISBN 9780522850086.
- Horner, David (2002). SAS: Phantoms of War: A History of the Australian Special Air Service (Second ed.). St Leonards, New South Wales: Allen & Unwin. ISBN 978-1-86508-647-7.
- James, Harold; Sheil-Small, Denis (1971). The Undeclared War: The Story of the Indonesian Confrontation 1962–1966. Totowa: Rowman and Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-87471-074-8.
- Jones, M. (2002). Conflict and Confrontation in South East Asia, 1961–1965: Britain: the United States and the Creation of Malaysia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-80111-9.
- Kheng, Cheah Boon (2009). "The Communist Insurgency in Malaysia, 1948–90: Contesting the Nation-State and Social Change" (PDF). New Zealand Journal of Asian Studies. 11 (1): 132–152. ISSN 1174-8915.
- Mackie, J.A.C. (1974). Konfrontasi: The Indonesia-Malaysia Dispute 1963–1966. Kuala Lumpur: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-638247-0.
- Majid, Harun Abdul (2007). Rebellion in Brunei: The 1962 Revolt, Imperialism, Confrontation and Oil. London: I.B.Tauris. ISBN 9780857716231.
- Mockaitis, Thomas R. (1995). British Counterinsurgency in the Post-imperial Era. Manchester: Manchester University Press. ISBN 9780719039195.
- Parker, John (2005) [2003]. S.B.S.: The Inside Story of the Special Boat Service. London: Bounty Books. ISBN 9780753712979.
- Pilger, John (2003). The New Rulers of the World. London: Verso. ISBN 9781859844120.
- Pimlott, John, ed. (1984). British Military Operations 1945–1985. London: Bison. ISBN 978-0-86124-147-7.
- Pocock, Tom (1973). Fighting General – The Public and Private Campaigns of General Sir Walter Walker (First ed.). London: Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-211295-6.
- Poulgrain, G. J. (2014). The genesis of konfrontasi: Malaysia, Brunei, and Indonesia, 1945-1965.
- Polmar, Norman (2008). Aircraft Carriers: A History of Carrier Aviation and Its Influence on World Events. Volume II: 1946–2006. Potomac Books. ISBN 9781574886658.
- Pugsley, Christopher (2003). From Emergency to Confrontation: The New Zealand Armed Forces in Malaya and Borneo 1949–66. South Melbourne, Victoria: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195584530.
- Reece, R.H.W. (1993). The Name of Brooke: The End of White Rajah Rule in Sarawak. Kuala Lumpur: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-580474-4.
- Smith, Neil (1999). Nothing Short of War: With the Australian Army in Borneo 1962–66. Brighton: Mostly Unsung Military History. ISBN 978-1-876179-07-6.
- Tan Ming, Jean (2011). Singapore's Role in Indonesia's Confrontation of Malaysia and the Impact of Confrontation on Singapore-Indonesia Relations (PhD thesis). National University of Singapore.
- van der Bijl, Nick (2007). Confrontation, The War with Indonesia 1962–1966. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Military Press. ISBN 978-1-84415-595-8.
Further reading
- General Assembly 15th Session – The Trusteeship System and Non-Self-Governing Territories (pages:509–510)
- General Assembly 18th Session – the Question of Malaysia (pages:41–44)
- Anonymous. 1964. Gelora Konfrontasi Mengganjang Malaysia. Djakarta: Departemen Penerangan. (Contains Joint Statements of the Manila Agreements, Indonesian presidential decrees and all transcripts of Sukarno's public speeches from July 1963 to May 1964 pertaining the Konfrontasi)
- Doohan, J.T. (2004). Mud Sweat & Tears: An account of 24 Construction Squadron Royal Australian Engineer's Borneo Tour of Duty 1965. Brisbane: John Doohan. ISBN 978-0-646-43718-7.
- Easter, David (February 2005). "'Keep the Indonesian Pot Boiling': Western Covert Intervention in Indonesia, October 1965 – March 1966". Cold War History. 5 (1): 55–73. doi:10.1080/1468274042000283144. ISSN 1468-2745. S2CID 153555254.
- Fowler, Will (2006). Britain's Secret War: The Indonesian Confrontation 1962–66. Men-at-Arms. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 9781846030482.
- Harrison, Ralph; Heron, John (2007). Jungle Conflict: The Durham Light Infantry in Borneo 1965–66. Sunderland: Business Education Publishers. ISBN 978-1-901888-55-3.
- Horner, David (1995). The Gunners: A History of Australian Artillery. St Leonards: Allen and Unwin. ISBN 978-1-86373-917-7.
- Jackson, Robert (2011) [1991]. The Malayan Emergency and Indonesian Confrontation: The Commonwealth's Wars 1948–1966. Barnsley, South Yorkshire: Pen & Sword. ISBN 9781848845558.
- "No. 43959". The London Gazette (Supplement). 21 April 1966. p. 4947.
- Paul, James; Spirit, Martin (2008). "Britains Small Wars – Plaman Mapu". Britains-SmallWars.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2012. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- Porritt, V.L. (2004). The Rise and Fall of Communism in Sarawak 1940–1990. Victoria: Monash Asia Institute. ISBN 978-1-876924-27-0.
- Poulgrain, G. (1998). The Genesis of Konfrontasi: Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia 1945–1965. London: C. Hurst & Co. ISBN 978-1-85065-510-7.
- Rees, Simon. "The Gurkha battle in Borneo". Historical Eye.com. Archived from the original on 15 March 2010. Retrieved 1 June 2009.
- Smith, E. (1985). Counter-Insurgency Operations. 1, Malaya and Borneo. London: Ian Allan. ISBN 9780711014626.
- Jackie Sam; Philip Khoo; Cheong Yip Seng; Abul Fazil; Roderick Pestana; Gabriel Lee (11 March 1965). "Terror Bomb kills 2 Girls at Bank" (reprint). The Straits Times. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- Subritzky, J. (2000). Confronting Sukarno: British, American, Australian and New Zealand Diplomacy in the Malaysian-Indonesian Confrontation, 1961–1965. London: Palgrave. ISBN 978-0-312-22784-5.
- Tuck, C. (2004). "Borneo 1963–66: Counter-insurgency Operations and War Termination". Small Wars and Insurgencies. 15 (3): 89–111. doi:10.1080/0959231042000275588. ISSN 1743-9558. S2CID 143480227.
- Squire, Thomas A. (2018). Always a Commando : the life of Singapore army pioneer Clarence Tan. pp. 163–199. ISBN 978-9814779319.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Indonesia-Malaysia confrontation. |




