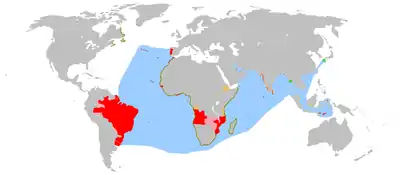
Azores
The Azores (/əˈzɔːrz/ ə-ZORZ, also US: /ˈeɪzɔːrz/ AY-zorz;[3] Portuguese: Açores [ɐˈsoɾɨʃ]), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (Região Autónoma dos Açores), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atlantic Ocean, about 1,400 km (870 mi) west of Lisbon, in continental Portugal, about 1,500 km (930 mi) northwest of Morocco, and about 1,930 km (1,200 mi) southeast of Newfoundland, Canada.
Azores Açores | |
|---|---|
| Autonomous Region of the Azores Região Autónoma dos Açores (Portuguese) | |
| Etymology: açor (Portuguese for Northern goshawk) | |
| Motto: Antes morrer livres que em paz sujeitos (English: "Rather die free than subjected in peace") | |
 Location of the Azores within the European Union | |
| Sovereign state | Portugal |
| Settlement | 1432 |
| Political Autonomy | 30 April 1976 |
| Capitals |
|
| Largest city | Ponta Delgada |
| Official languages | Portuguese |
| Demonym(s) | Açoriano(a) (English: Azorean) |
| Government | Autonomous Region |
• Representative of the Republic | Pedro Manuel dos Reis Alves Catarino |
• President of the Legislative Assembly of the Autonomous Region of the Azores | Luís Garcia |
| José Manuel Bolieiro | |
• Vice-President of the Regional Government of the Azores | Artur Lima |
| Legislature | Legislative Assembly of the Autonomous Region of the Azores |
| National and European Representation | |
| 5 Deputies | |
| 1 MEP | |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,351 km2 (908 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,351 m (7,713 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population | |
• 2019 census | 242,796[1] |
• Density | 110/km2 (284.9/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2017 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Currency | EUR (€) (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC−1 (Atlantic/Azores) |
| UTC (Atlantic/Azores) | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (CE) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +351 (292) |
| ISO 3166 code | PT-20 |
| Internet TLD | |
| Usual abbreviation | RAA |
| Website | azores |
Its main industries are agriculture, dairy farming, livestock, fishing, and tourism, which is becoming the major service activity in the region. In addition, the government of the Azores employs a large percentage of the population directly or indirectly in the service and tertiary sectors. The capital is Angra do Heroísmo but the main city of the Azores is Ponta Delgada.
There are nine major Azorean islands and an islet cluster, in three main groups. These are Flores and Corvo, to the west; Graciosa, Terceira, São Jorge, Pico, and Faial in the centre; and São Miguel, Santa Maria, and the Formigas Reef to the east. They extend for more than 600 km (370 mi) and lie in a northwest–southeast direction.
All the islands have volcanic origins, although some, such as Santa Maria, have had no recorded activity since the islands were settled several centuries ago. Mount Pico, on the island of Pico, is the highest point in Portugal, at 2,351 m (7,713 ft). If measured from their base at the bottom of the ocean to their peaks, which thrust high above the surface of the Atlantic, the Azores are among the tallest mountains on the planet.
The climate of the Azores is very mild for such a northerly location, being influenced by its distance from the continents and by the passing Gulf Stream. Due to the marine influence, temperatures remain mild year-round. Daytime temperatures normally fluctuate between 16 °C (61 °F) and 25 °C (77 °F) depending on season.[4][5] Temperatures above 30 °C (86 °F) or below 3 °C (37 °F) are unknown in the major population centres. It is also generally wet and cloudy.
The culture, dialect, cuisine, and traditions of the Azorean islands vary considerably, because these remote islands were settled sporadically over a span of two centuries.
History
A small number of alleged hypogea, earthen structures carved into rocks that were used for burials, have been identified on the islands of Corvo, Santa Maria, and Terceira by Portuguese archaeologist Nuno Ribeiro, who speculated that they might date back 2000 years, implying a human presence on the island before the Portuguese.[6] These kinds of structures have been used in the Azores to store cereals, however. Any suggestions by Ribeiro that they might be burial sites are unconfirmed. Detailed examination and dating to authenticate the validity of these speculations is lacking; thus it is unclear whether these structures are natural or human-made and whether they predate the 15th-century Portuguese colonization of the Azores.[7]
Discovery

The islands were known to Europeans in the fourteenth century, and parts of them appear in the Catalan Atlas. In 1427, a captain sailing for Prince Henry the Navigator, possibly Gonçalo Velho, may have rediscovered the Azores, but this is not certain. In Thomas Ashe's 1813 work, A History of the Azores,[8] the author identified a Fleming, Joshua Vander Berg of Bruges, who made landfall in the archipelago during a storm on his way to Lisbon.[8] He stated that the Portuguese explored the area and claimed it for Portugal.[8] Other stories note the discovery of the first islands (São Miguel Island, Santa Maria Island and Terceira Island) by sailors in the service of Henry the Navigator, although there are few documents to support the claims.
Although it is commonly said that the archipelago received its name from açor (goshawk in Portuguese), a common bird at the time of discovery, it is unlikely that the bird nested or hunted on the islands.
Settlement
There were no large animals on Santa Maria, so after its discovery and before settlement began, sheep were let loose on the island to supply future settlers with food. Settlement did not take place right away, however. Gonçalo Velho Cabral gathered resources and settlers for the next three years (1433–1436), however, and sailed to establish colonies, first on Santa Maria and then on São Miguel. Settlers cleared bush and rocks to plant crops: grain, grapevines, sugar cane, and other plants suitable for local use and of commercial value. They brought domesticated animals, such as chickens, rabbits, cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs, and built houses and established villages.
The archipelago was largely settled from mainland Portugal. Portuguese settlers came from the provinces of Algarve, Minho, Alentejo and Ribatejo as well as Madeira. São Miguel was first settled in 1449, the settlers – mainly from the Estremadura, Alto Alentejo and Algarve areas of mainland Portugal, under the command of Gonçalo Velho Cabral – landed at the site of modern-day Povoação. Many of the early settlers were Portuguese Sephardic Jews who were banished/exiled there by the inquisition on mainland Portugal - many had well known Sephardic surnames such as: Pereira, Oliveira, Cardoso, Pimentel, Pinto, Rodrigues, Mendes, or Nunes.
In 1522, Vila Franca do Campo, then the capital of the island, was devastated by an earthquake and landslide that killed about 5,000 people, and the capital was moved to Ponta Delgada. The town of Vila Franca do Campo was rebuilt on the original site and today is a thriving fishing and yachting port. Ponta Delgada received its city status in 1546. From the first settlement, the pioneers applied themselves to agriculture and by the 15th century Graciosa exported wheat, barley, wine and brandy. The goods were sent to Terceira largely because of the proximity of the island.
_(cropped).jpg.webp)
The first reference to the island of São Jorge was made in 1439, but the actual date of discovery is unknown. In 1443 the island was already inhabited, but active settlement only began with the arrival of the noble Flemish native Willem van der Haegen. Arriving at Topo, where he lived and died, he became known as Guilherme da Silveira to the islanders. João Vaz Corte-Real received the captaincy of the island in 1483. Velas became a town before the end of the 15th century. By 1490, there were 2,000 Flemings living in the islands of Terceira, Pico, Faial, São Jorge and Flores. Because there was such a large Flemish settlement, the Azores became known as the Flemish Islands or the Isles of Flanders. Prince Henry the Navigator was responsible for this settlement. His sister, Isabel, was married to Duke Philip of Burgundy of which Flanders was a part. There was a revolt against Philip's rule and disease and hunger became rampant. Isabel appealed to Henry to allow some of the unruly Flemings to settle in the Azores. He granted this and supplied them with the necessary transportation and goods.
The settlement of the then-unoccupied islands started in 1439 with people mainly from the continental provinces of Algarve and Alentejo. In 1583, Philip II of Spain, as king of Portugal, sent his fleet to clear the Azores of a combined multinational force of adventurers, mercenaries, volunteers and soldiers who were attempting to establish the Azores as a staging post for a rival pretender to the Portuguese throne. Following the success of his fleet at the Battle of Ponta Delgada captured enemies were hanged from yardarms, as they were considered pirates by Philip II. Opponents receiving the news variously portrayed Philip II as a despot or "Black Legend"; the sort of insult widely made against contemporary monarchs engaged in aggressive empire building and the European Wars of Religion. An English raid of the Azores in 1589 successfully plundered some harbouring ships and islands; a repeat eight years later, the Islands Voyage, failed. Spain held the Azores under the "Babylonian captivity" of 1580–1642. In the late 16th century, the Azores and Madeira began to face problems of overpopulation. Spawning from that particular economic problem, some of the people began to emigrate to Brazil.[9]
Iberian Union

Following the death (1580) of Henry, the Cardinal-King of Portugal the nation fell into a dynastic crisis with various pretenders to the Crown of Portugal.[10] Following his proclamation in Santarém, António, Prior of Crato was acclaimed in the Azores in 1580 (through his envoy António da Costa), but was expelled from the continent following the Battle of Alcântara.[10] Yet, through the administration of Cipriano de Figueiredo, governor of Terceira (who continued to govern Terceira in the name of ill-fated, former-king Sebastian of Portugal), the Azoreans resisted attempts to conquer the islands (including specifically at the Battle of Salga).[11] It was Figueiredo and Violante do Canto who helped organize a resistance on Terceira that influenced some of the response of the other islands, even as internal politics and support for Philip's faction increased on the other islands (including specifically on São Miguel, where the Gonçalvez da Câmara family supported the Spanish pretender).[11]
The Azores were the last part of the Portuguese Empire to resist Philip's reign over Portugal (Macau resisted any official recognition), until the defeat of forces loyal to the Prior of Crato with the Conquest of the Azores in 1583. Portuguese control resumed with the end of the Iberian Union in 1640, and the beginning of the Portuguese Restoration War, not by the professional military, who were occupied with warfare on the Portuguese mainland, but by local people attacking a fortified Castilian garrison.
Liberal Wars

The Portuguese Civil War (1828–1834) had strong repercussions in the Azores. In 1829, in Praia da Vitória, the Liberals won over the absolutists, making Terceira Island the main headquarters of the new Portuguese regime and also where the Council of Regency (Conselho de Regência) of Maria II of Portugal was established.
Beginning in 1868, Portugal issued its stamps overprinted with "AÇORES" for use in the islands. Between 1892 and 1906, it also issued separate stamps for the three administrative districts of the time.
During the 18th and 19th centuries, Graciosa was host to many prominent figures, including Chateaubriand, the French writer who passed through upon his escape to America during the French revolution; Almeida Garrett, the Portuguese poet who visited an uncle and wrote some poetry while there; and Prince Albert of Monaco, the 19th century oceanographer who led several expeditions in the waters of the Azores. He arrived on his yacht Hirondelle, and visited the furna da caldeira, the noted hot springs grotto. In 1869, the author Mark Twain published The Innocents Abroad, a travel book, where he described his time in the Azores.
From 1836 to 1976, the archipelago was divided into three districts, equivalent (except in area) to those in the Portuguese mainland. The division was arbitrary, and did not follow the natural island groups, rather reflecting the location of each district capital on the three main cities (none of which were on the western group).
- Angra do Heroísmo consisted of Terceira, São Jorge, and Graciosa, with the capital at Angra do Heroísmo on Terceira.
- Horta consisted of Pico, Faial, Flores, and Corvo, with the capital at Horta on Faial.
- Ponta Delgada consisted of São Miguel and Santa Maria, with the capital at Ponta Delgada on São Miguel.
Modern period

In 1931 the Azores (together with Madeira and Portuguese Guinea) revolted against the Ditadura Nacional and were held briefly by military rebels.[12]
In 1943, during World War II, the Portuguese ruler António de Oliveira Salazar leased air and naval bases in the Azores to Great Britain.[13] The occupation of these facilities in October 1943 was codenamed Operation Alacrity by the British.[14]
This was a key turning point in the Battle of the Atlantic, enabling the Royal Air Force, the U.S. Army Air Forces, and the U.S. Navy to provide aerial coverage in the Mid-Atlantic gap. This helped them to protect convoys and to hunt hostile German U-boats.
In 1944, the U.S. constructed a small and short-lived air base on the island of Santa Maria. In 1945, a new base was constructed on the island of Terceira, and it is named Lajes Field. This air base is in an area called Lajes, a broad, flat sea terrace that had been a large farm. Lajes Field is a plateau rising out of the sea on the northeast corner of the island. This air base is a joint American and Portuguese venture. Lajes Field continues to support the American and Portuguese Armed Forces.

During the Cold War, U.S. Navy P-3 Orion antisubmarine warfare squadrons patrolled the North Atlantic Ocean for Soviet Navy submarines and surface warships. Since its opening, Lajes Field has been used for refuelling American cargo planes bound for Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. The U.S. Navy keeps a small squadron of its ships at the harbor of Praia da Vitória, three kilometres (1.9 miles) southeast of Lajes Field.
The airfield also has a small commercial terminal handling scheduled and chartered passenger flights from the other islands in the Azores, Europe, Africa, and North America.
Following the Carnation Revolution of 1974, which deposed the Estado Novo dictatorship in Lisbon, Portugal and its territories across the world entered into a period of great political uncertainty. The Azorean Liberation Front attempted to take advantage of this instability immediately after the revolution, hoping to establish an independent Azores, until operations ceased in 1975.
In 1976, the Azores became the Autonomous Region of the Azores (Região Autónoma dos Açores), one of the autonomous regions of Portugal, and the subdistricts of the Azores were eliminated.
In 2003, the Azores saw international attention when United States president George W. Bush, British prime minister Tony Blair, Spanish prime minister José María Aznar and Portuguese prime minister José Manuel Durão Barroso held a summit there days before the commencement of the Iraq War.[15]
Geography
Physical geography
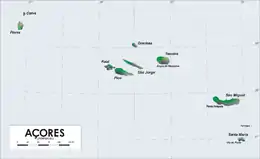
| Island | Area | |
|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi | |
| São Miguel | 759 | 293 |
| Pico | 446 | 172 |
| Terceira | 403 | 156 |
| São Jorge | 246 | 95 |
| Faial | 173 | 67 |
| Flores | 143 | 55 |
| Santa Maria | 97 | 37 |
| Graciosa | 62 | 24 |
| Corvo | 17 | 7 |
The archipelago of the Azores is located in the middle of the northern hemisphere of the Atlantic Ocean and extends along a west-northwest to east-southeast orientation (between 36.5°–40° North latitudes and 24.5°–31.5° West longitudes) in an area approximately 600 kilometres (373 miles) wide. The islands of the Azores emerged from what is called the Azores Plateau, a 5.8 million km2 region that is morphologically accented by a depth of 2,000 metres (6,600 feet).[16][17]
From a geostructural perspective the Azores is located above an active triple junction between three of the world's major tectonic plates (the North American Plate, the Eurasian Plate and the African Plate),[17] a condition that has translated into the existence of many faults and fractures in this region of the Atlantic.[18] The westernmost islands of the archipelago (Corvo and Flores) are located in the North American Plate, while the remaining islands are located within the boundary that divides the Eurasian and African Plates.
The principal tectonic structures that exist in the region of the Azores are the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the Terceira Rift, the Azores Fracture Zone and the Glória Fault.[17] The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is the main frontier between the American Plate and the African-Eurasian Plates that crosses the Azores Plateau between the islands of Flores and Faial from north to south then to the southwest; it is an extensive form crossed by many transform faults running perpendicular to its north–south orientation, that is seismically active and susceptible to volcanism.
The Terceira Rift is a system of fractures that extends from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge to the Glória Fault that represents the main frontier between the Eurasian and African Plates. It is defined by a line of submarine volcanoes and island mounts that extend northwest to southeast for about 550 kilometres (342 miles), from the area west of Graciosa until the islets of the Formigas, that includes the islands of Graciosa, Terceira and São Miguel. Its northwest limit connects to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, while the southeast section intersects the Gloria Fault southeast of the island of Santa Maria.
The Azores Fracture Zone extends from the Glória Fault and encompasses a relatively inactive area to the south of the islands of the Central and Eastern groups north to the Terceira Rift, along a 45° angle. The Glória Fault, for its part, extends 800 kilometres (497 miles) along a linear line from the Azores to the Azores–Gibraltar Transform Fault.[19]
The island's volcanism is associated with the rifting along the Azores Triple Junction; the spread of the crust along the existing faults and fractures has produced many of the active volcanic and seismic events,[20] while supported by buoyant upwelling in the deeper mantle, some associate with an Azores hotspot.[21] Most of the volcanic activity has centered, primarily, along the Terceira Rift. From the beginning of the island's settlement, around the 15th century, there have been 28 registered volcanic eruptions (15 terrestrial and 13 submarine). The last significant volcanic eruption, the Capelinhos volcano (Vulcão dos Capelinhos), occurred off the coast of the island of Faial in 1957; the most recent volcanic activity occurred in the seamounts and submarine volcanoes off the coast of Serreta and in the Pico-São Jorge Channel.[22]
.jpg.webp)
The islands have many examples of volcano-built geomorphology including caves and lava tubes (such as the Gruta das Torres, Algar do Carvão, Gruta do Natal, Gruta das Cinco Ribeiras), the coastal lava fields (like the coast of Feteiras, Faial, the Mistério of Prainha or São João on Pico Island) in addition to the inactive cones in central São Miguel Island, the aforementioned Capelinhos on Faial, the volcanic complexes of Terceira or Plinian caldeira of Corvo Island. The islands of the archipelago were formed through volcanic and seismic activity during the Neogene Period; the first embryonic surfaces started to appear in the waters of Santa Maria during the Miocene epoch (from circa 8 million years ago).
The sequence of the island formation has been generally characterized as: Santa Maria (8.12 Ma), São Miguel (4.1 Ma), Terceira (3.52 Ma), Graciosa (2.5 Ma), Flores (2.16 Ma), Faial (0.7 Ma), São Jorge (0.55 Ma), Corvo (0.7 Ma) and the youngest, Pico (0.27 Ma).[23] Although all islands have experienced volcanism during their geological history, within recorded "human settlement" history the islands of Santa Maria, Graciosa, Flores, and Corvo have not experienced any volcanic eruptions; in addition to active fumaroles and hot-springs, the remaining islands have had sporadic eruptions since the 14th century. Apart from the Capelinhos volcano in 1957–58, the last recorded instance of "island formation" occurred off the coast of São Miguel, when the island of Sabrina was briefly formed.
.jpg.webp)
Owing to its geodynamic environment, the region has been a center of intense seismic activity, particularly along its tectonic boundaries on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Terceira Rift. Seismic events although frequent, are usually tectonic or vulco-tectonic in nature, but in general are of low to medium intensities, occasionally punctuated by events of level 5 or greater on the Richter magnitude scale.[24][25] The most severe earthquake was registered in 1757, near Calheta on the island of São Jorge, which exceeded 7 on the Richter magnitude scale. In comparison, the 1522 earthquake that was mentioned by historian Gaspar Frutuoso measured 6.8, but its effects were judged to be X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale,[26] and was responsible for the destruction of Vila Franca do Campo and landslides that may have killed more than 5,000 of the inhabitants.
The nine islands that compose the archipelago occupy a surface area of 2,346 km2 (906 sq mi), that includes both the main islands and many islets located in their vicinities. They range in surface area from the largest, São Miguel, at 759 km2 (293 sq mi) to the smallest, Corvo, at approximately 17 km2 (7 sq mi).
Each of the islands has its own distinct geomorphological characteristics that make them unique: Corvo (the smallest island) is a crater of a major Plinian eruption; Flores (its neighbor on the North American Plate) is a rugged island carved by many valleys and escarpments; Faial characterized for its shield volcano and caldera (Cabeço Gordo); Pico, is the highest point, at 2,351 meters (7,713 ft), in the Azores and continental Portugal; Graciosa is known for its active Furnas do Enxofre and mixture of volcanic cones and plains; São Jorge is a long slender island, formed from fissural eruptions over thousands of years; Terceira, almost circular, is the location of one of the largest craters in the region; São Miguel is the largest island, and is pitted with many large craters and fields of spatter cones; and Santa Maria, the oldest island, is heavily eroded, being one of the few places to encounter brown sandy beaches in the archipelago.

These islands can be divided into three recognizable groups located on the Azores Plateau:
- The Eastern Group (Grupo Oriental) of São Miguel, Santa Maria and Formigas Islets
- The Central Group (Grupo Central) of Terceira, Graciosa, São Jorge, Pico and Faial
- The Western Group (Grupo Ocidental) of Flores and Corvo.
In addition, several sub-surface reefs (particularly the Dollabarat on the fringe of the Formigas), banks (specifically the Princess Alice Bank and D. João de Castro Bank), as well as many hydrothermal vents and sea-mounts are monitored by the regional authorities, owing to the complex geotectonic and socioeconomic significance within the economic exclusion zone of the archipelago.
Biome
.jpg.webp)

The archipelago lies in the Palearctic realm, and has a unique biotic community that includes the Macaronesian subtropical laurissilva, with many endemic species of plants and animals.[27][28] In total, there are at least 6112 terrestrial species, of which about 411 are endemic. The majority (75%) of these endemics are animals, mostly arthropods and mollusks. New species are found regularly in the Azores (e.g., 30 different new species of land snails were discovered circa 2013[29]).

Even though the Azores look very green and sometimes wild, the vegetation has been extremely altered. A great part of it has been wiped out in the past 600 years for its valuable wood (for tools, buildings, boats, fire wood, and so on) and to clear land for agriculture. As a result, it is estimated that more than half of insects on the Graciosa island have disappeared or will become extinct.[27] Many cultivated places (which are traditionally dedicated to pasture or to growing colocasia, potatoes, maize and other crops) have now been abandoned, especially as a result of emigration. Consequently, some invasive plants have filled these deserted and disturbed lands. Hydrangeas are another potential pest, but their threat is less serious. Notwithstanding the fact that hydrangeas were introduced from America or Asia, some locals consider them a symbol of the archipelago and propagate them along roadsides, helping the plants to escape into the wild. Cryptomeria, the Japanese cedar, is a conifer extensively grown for its timber. The two most common of these alien species are Pittosporum undulatum and Hedychium gardnerianum.[30] They are usually restricted to ancient agricultural land and only rarely penetrate into undisturbed native vegetation.
_(cropped).jpg.webp)
Reforestation efforts with native laurissilva vegetation have been done successfully in many parts of the Azores.[31][32][33]
The Azores has at least two endemic living bird species. The Azores bullfinch, or Priolo, is restricted to remnant laurisilva forest in the mountains at the eastern end of São Miguel[34] and is classified by BirdLife International as endangered. Monteiro's storm-petrel, described to science as recently as 2008, is known to breed in just two locations in the islands, but may occur more widely. An extinct species of owl, the São Miguel scops owl, has also recently been described, which probably became extinct after human settlement due to habitat destruction and the introduction of alien species. Five species of flightless rail also once existed on the islands, as did another species of bullfinch, but these also went extinct after human colonization. 11 subspecies of bird are also endemic to the islands.[35] A flightless extinct quail is also known.[36] The Azores also has an endemic bat, the Azores noctule, which has an unusually high frequency of diurnal flight.
The islets of the Formigas (the Portuguese word for "ants"), including the area known as the Dollabarat Reef, have a rich environment of maritime species, such as black coral and manta rays, different species of sharks, whales, and sea turtles. On São Miguel there are notable micro-habitats formed by hot springs that host extremophile microorganisms.[37]
17 new marine reserves (with special conservation status) were added to the Azorean Marine Park (which covers around 900.000 km2 (347.492 sq mi)).[38]
Climate

The archipelago is spread out at roughly the same latitude as the southern half of mainland Portugal, giving it a generally tepid, oceanic, warm subtropical climate, with mild annual oscillations. Daily maximum temperatures at low altitudes usually range between 16 and 25 °C (61 and 77 °F). The average annual rainfall increases from east to west, ranging from 700 mm (28 in) in Santa Maria to 1,600 mm (63 in) in Flores and reaching 6,300 millimetres (250 in) on Mount Pico.[39]
The Azores High, an area of high atmospheric pressure, is named after the islands. Under the Köppen climate classification, the eastern group is usually classified as Mediterranean while the central and western group is increasingly more humid subtropical due to the effects of the Gulf Stream.

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
Salvador Rivas-Martínez data presents several different bioclimatic zones for the Azores.[40] Seasonal lag is extreme in the low-sun half of the year, with December being milder than April regarding mean temperatures. Although temperatures as warm as 32.1 °C (89.8 °F) have been recorded on Pico, neither Ponta Delgada nor Angra do Heroísmo, the two largest cities, have ever gone above 30 °C (86 °F).
The Azores have the warmest winters in Europe (still within the European continental plate). During summer the lag is somewhat lower, with August being the warmest month, though September is usually as warm or warmer than July. There has never been a frost, snowfall, freeze or even temperatures below 5 °C (41 °F) recorded at sea level on any of the islands. The coldest weather in winter usually comes from northwesterly air masses originating from Labrador in Canada. However, since those air masses are warmed up as they pass across the warmer Atlantic Ocean, temperatures by day even then exceed 10 °C (50 °F). The westernmost islands of the archipelago, namely Flores and Corvo, get the strongest maritime moderation and the most rainfall since both are right on the Gulf Stream waters.
Humidity is also a big factor to consider in these islands. The average relative humidity can range from 80% at the coast and 90% at higher elevations. Summers are especially humid in August and may increase the perceived temperature by a few degrees. Winters are not only very mild but also very humid and as so are relatively comfortable, though rainy and dull.[41]
In addition, the Instituto de Meteorologia has identified the following weather extremes[42]
- Highest minimum air temperature: 24.3 °C (75.7 °F), in Angra do Heroísmo, Terceira (30 June 1996)
- Lowest minimum air temperature: −3.5 °C (25.7 °F), in Chã das Lagoinhas, São Jorge (2 January 1973)
- Highest maximum air temperature: 32.1 °C (89.8 °F), in Madalena, Pico (7 September 1985)
- Lowest maximum air temperature: 4.0 °C (39.2 °F), Chã das Lagoinhas, São Jorge (20 February 1972)
- Maximum precipitation in 24 hours: 276 mm (10.87 in), Furnas, São Miguel (3 October 1974)
- Maximum wind speed: >176 km/hour, Santa Maria, (15 December 1989)
| Vila do Porto, Santa Maria | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Angra do Heroísmo, Terceira | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Santa Cruz das Flores, Flores | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hurricanes
The Azores are known for small hurricanes. A total of 14 tropical or subtropical cyclones have affected the region in history. Most of them were either extratropical or tropical storms when they affected the region, although several Category 1 hurricanes have reached the Azores. Only one major hurricane has ever impacted the Azores; Hurricane Ophelia in 2017, at Category 3 intensity. The following storms have impacted the region while at Category 1 strength: Hurricane Fran in 1973, Hurricane Emmy in 1976, Hurricane Gordon in 2006, Hurricane Gordon in 2012 and Hurricane Alex in 2016. Several tropical storms have hit the region, including Tropical Storm Irma in 1978, Hurricane Bonnie in 1992, Hurricane Charley in 1992, Hurricane Erika in 1997, and Hurricane Gaston in 2016. Storms that were extratropical when they impacted the region include Hurricane Tanya in 1995, Tropical Storm Ana in 2003 and Tropical Storm Grace in 2009. In addition, the 2005 Azores subtropical storm affected the region in October 2005.
Economy
In order of importance, the main sectors of employment of the Azores are services, agriculture, fishery, industry and tourism.[43][44]
Demographics
The Azores are divided into 19 municipalities (concelhos); each municipality is further divided into freguesias (civil administrative parishes), of which there is a total of 156 in all of the Azores.
There are six cities (Portuguese: cidades) in the Azores: Ponta Delgada, Lagoa and Ribeira Grande on the island of São Miguel; Angra do Heroísmo and Praia da Vitória on the island of Terceira, and Horta on Faial. Three of these, Ponta Delgada, Angra and Horta are considered capital/administrative cities to the regional government: homes to the President (Ponta Delgada), the Judiciary (Angra) and the Regional Assembly (Horta). Angra also serves as the ecclesiastical centre of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Angra, the episcopal see of the Azores.
| Island | Group | Population[45] | Municipalities of the Azores | Main Settlement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | % Total | No | Municipalities (Concelho) | |||
| São Miguel | Eastern | 137,830 | 55.86 | 6 | Lagoa, Nordeste, Ponta Delgada, Povoação, Ribeira Grande, Vila Franca do Campo | Ponta Delgada |
| Terceira | Central | 56,437 | 22.87 | 2 | Angra do Heroísmo, Praia da Vitória | Angra do Heroísmo |
| Faial | Central | 14,994 | 6.08 | 1 | Horta | Horta |
| Pico | Central | 14,148 | 5.73 | 3 | Lajes do Pico, Madalena, São Roque do Pico | Madalena |
| São Jorge | Central | 9,171 | 3.72 | 2 | Calheta, Velas | Velas |
| Santa Maria | Eastern | 5,552 | 2.25 | 1 | Vila do Porto | Vila do Porto |
| Graciosa | Central | 4,391 | 1.78 | 1 | Santa Cruz da Graciosa | Santa Cruz da Graciosa |
| Flores | Western | 3,793 | 1.54 | 2 | Lajes das Flores, Santa Cruz das Flores | Santa Cruz das Flores |
| Corvo | Western | 430 | 0.17 | 1 | Vila do Corvo | Vila do Corvo |
| Total | 246,746 | 19 | ||||
Population
_(cropped)_(cropped).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
According to the 2019 Census, population in the Azores was 242,796[1]
The Azores were uninhabited when Portuguese navigators arrived in the early 15th century; settlement began in 1439 with migrants from several regions of mainland Portugal and from Madeira. The islands were populated mainly by Portuguese immigrants from the Algarve, Alentejo, and Minho in an effort to escape the dangers of the Portuguese inquisition on mainland Portugal. However, many Portuguese Sephardic Jews settled on the islands in large numbers. Azorean Jews had surnames such as Rodrigues, Pacheco, Oliveira, Pereira, Pimentel, Nunes, Mendes, Pinto, Álvares, Henriques, Cardozo, Teixeira, and Vasconcelos. The islands were also settled by Moorish prisoners and African slaves from Guinea, Cape Verde and São Tomé. Flemish, French, and Galicians also contributed to the initial settlement. Thus the Azorean population received a significant contribution from people with genetic backgrounds other than Portuguese.
The nature of the economy dictated that African slavery never became common in the Azores because the slaves were sent to Brazil and the Caribbean. Only a few remained in the Azores for forced labor such as domestic chores, although the islands sometimes served as a waypoint for ships carrying African slaves.[46]
Africans, Moors, Jews, Scots, Germans, Italians, French, Spanish, Flemish, and Portuguese all migrated to the Azores.[47]
Genetics
.JPG.webp)
As in continental Portugal, the most frequent mtDNA haplogroup in the Azores is H (45.2%), followed by U (16.7%), T (10.1%), K (6.5%), pre-HV clades (5.6%) and a smaller African L haplogroups frequency (3.4%) than in Madeira.
Inhabitants of the various islands have DNA of various origins.[48][49] A minority on the islands has non-European ancestry.[50]
.JPG.webp)
Emigration
Since the 17th century, many Azoreans have emigrated, mainly to Brazil, Uruguay, the United States and Canada.[51] Rhode Island and Southeastern Massachusetts, especially the cities of Lowell, New Bedford, Bristol, Barrington, Pawtucket, Central Falls, West Warwick, Hudson, Marlborough, East Providence, River Point, Somerset, Taunton and Fall River have been, and remain, the primary destination for Azorean emigrants.[52] Emigrants from the East coast returned to their homeland and taught the American dory fishing technique to the Portuguese who began catching cod again on the Grand Bank in the 19th century.[53]
Northern California was the final destination for many of the Massachusetts immigrants who then moved on to the San Joaquin Valley, especially the city of Turlock, just south of Modesto. In the late 1800s many Azoreans emigrated to the Hawaiian islands. The tuna fishing industry drew a significant number of Azoreans to the Point Loma neighborhood of San Diego, in Southern California.[54] From 1921 to 1977, about 250,000 Azoreans immigrated to Rhode Island and Massachusetts.[55]
Some Azoreans also moved to Hawai'i.[56] Florianópolis and Porto Alegre in the Southern Region of Brazil were founded by Azoreans, who accounted for over half of Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina's population in the late 18th century.[57] As late as 1960 mass immigration currents were registered to Brazil, and many were from the Azores.[56]
During the Great Recession of the early 21st century, Portugal was in a recession from 2011 until 2013, which resulted in high levels of unemployment across the mainland as well as the Azores.[58] The Great Recession led to an increase of out-migration from the Azores.[59]
Politics
_(cropped).jpg.webp)

Since 1976, the Azores has been an autonomous region integrated within the framework of the Portuguese Republic. It has its own government and autonomous legislature within its own political-administrative statute and organic law. Its governmental organs include: the Legislative Assembly, a unicameral parliament composed of 52 elected deputies, elected by universal suffrage for a four-year term; the regional government and presidency, with parliamentary legitimacy, composed of a president, a vice-president and seven regional secretaries responsible for day-to-day operations. It is represented in the Council of Ministers by a representative appointed by the president of the Republic, which was created during the revision of the constitution of 2004 (which, among other things, removed the older Portuguese representative that was appointed by the president of the Republic, beholden to the Council of State and coincident with the president).
Since becoming a Portuguese autonomous region, the executive branch of the regional authority has been located in Ponta Delgada, the legislative branch in Horta, and the judicial branch in Angra do Heroísmo.

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
The islands of the archipelago do not have independent status in law, except in electoral law and are governed by 19 municipalities that subdivide the islands. In addition, until the administrative reform of the 19th century, the following civil parishes had municipal standing: Topo (today integrated into the municipality of Calheta, São Jorge); Praia (today integrated into municipality of Santa Cruz da Graciosa); São Sebastião (today an integral part of the municipality of Angra do Heroísmo); Capelas (now part of the municipality of Ponta Delgada); and Água de Pau (now a civil parish in the municipality of Lagoa). These civil parishes still retain their titles of "vila" in name only; the populations of Capelas and neighbouring parish still protest the change and promote the restoration of their status.
The municipalities are further subdivided into several civil parishes, with the exception of Corvo (the only municipality by law without a civil parish, owing to its size).
Azorean politics is dominated by the two largest Portuguese political parties, the Socialist Party (PS) and Social Democratic Party (PSD), the former holding a majority in the Legislative Assembly. The Democratic and Social Center / People's Party (CDS/PP), the Left Bloc (BE), the Unitarian Democratic Coalition (CDU) and the People's Monarchist Party (PPM) are also represented. As of the 2020 regional election, the President of the Azores is Social Democratic Party (PSD) leader José Manuel Bolieiro. Although the PS dominates the regional politics, the PSD is traditionally popular in city and town council elections.
European Union
As part of Portugal, the Azores are in the European Union and Schengen Area. They are also in the European Union Customs Union and VAT area,[60] but levy a lower rate of VAT than applies on the mainland. The Azores, like Madeira and the Canary Islands, are among member state territories with special status, as one of the designated "Outermost Regions".
Transport
.jpg.webp)
Aviation
.jpg.webp)
Each of the nine islands has an airport,[61] although the majority are airfields rather than airports. The commercial terminals in Ponta Delgada, Horta, Vila do Porto and Santa Cruz das Flores are operated by ANA – Aeroportos de Portugal, a public entity that oversees the operations of airports across Portugal. The remaining, except for Lajes Field, are operated by the Regional Government. Lajes is a military airbase, as well as a commercial airport, and is operated by the Portuguese Armed Forces in conjunction with the United States.
The airports are:
- Santa Maria: Santa Maria Airport (LPAZ)
- São Miguel: João Paulo II Airport (LPPD)
- Terceira: Lajes Airport (LPLA)
- São Jorge: São Jorge Airport (LPSJ)
- Pico: Pico Airport (LPPI)
- Faial: Horta Airport (LPHR)
- Graciosa: Graciosa Airport (LPGR)
- Flores: Flores Airport (LPFL)
- Corvo: Corvo Airport (LPCR)
Marine transportation
.jpg.webp)
The Azores has had a long history of marine transport to overcome distances and establish inter-community contacts and trade. Consequently, the shipbuilding industry developed in many islands, from small fishing boats, to whaling sloops to larger passenger services.[62] Passenger traffic to the main islands (São Miguel, Santa Maria, Terceira and Faial) began in the 17th century, and between the 18th–19th century, the Pico Yacht controlled the lucrative summer traffic season.[62]
After 1871, the Insulana Shipping Company was the only entity responsible for regular traffic between the islands (except Corvo), Madeira and the United States.[62] Finally, cargo and passenger transportation ceased in the 1970s, and the ships were sold or converted into tuna fishing boats. For the next 20 years, commercial maritime service between the islands ceased (except between Faial-Pico and Lajes das Flores-Vila do Corvo).[62]
_julesvernex2.jpg.webp)
Transmaçor (Transportes Marítimos Açorianos, Lda.) was founded on 22 December 1987, resulting from the fusion of Empresa das Lanchas do Pico, Lda, owners of the ships Espalamaca and Calheta (ships that had travelled the canal between Faial and Pico for several years); Empresa Açoreana de Transportes Marítimos, Lda, which operated the ship Terra Alta; and Transcanal (Transportes Marítimos do Canal, Lda.) operator the traditional boats Picaroto and Manuel José.[64][65] In the Central Group, the shipping company operates four to six time daily connections between Horta and Madalena throughout the year, using its small fleet of ships (Cruzeiro das Ilhas, Cruzeiro do Canal, Expresso das Ilhas and Expresso do Triângulo), in addition to inter-island connections between Faial, Pico, São Jorge and Terceira during the summer months.[64]
.jpg.webp)
Meanwhile, new initiatives began in the late 1990s: the catamaran Iapetos began services, followed by Lady of Mann and Golfinho Azul (chartered by Açorline).[62]
In 2005, Atlânticoline was established, providing services with the ships Ilha Azul and Express Santorini, later adding the Viking in 2009.[62] In 2009, Atlanticoline was involved in a controversial rejection of a 750-passenger, 150-vehicle ship ordered from the Estaleiros de Viana do Castelo (Viana do Castelo Shipyards).[66] The Atlantida, a 50 million Euro cruiser (as part of a two-ship deal with the other named Anticiclone) was rejected in 2009 by Atlanticoline for the under-performance of the power-plant.[66] Although it would only result in a five-minute delay between islands, the public company rejected the ship, and the contract was broken over the builder's inability to deliver the required ship on time.[66] While, the ship was being shopped to other interested parties (Hugo Chávez once considered purchasing the ferryboat in 2010), no interested buyers appeared, and ENVC decided to cede the Atlantida to Atlânticoline as part of the latter's open international competition to charter two ships in 2012.[66]
On 20 June 2011, the Regional Government announced that it would purchase 60% of Transmaçor, equivalent to 500,000 Euro of the company's capital.[67] With this transaction the Autonomous government of the Azores ceded control, of which it once had 88% of the capital.[67] The signed memorandum of understanding concluded negotiations between the various parties involved, under which the liability of Transmaçor (worth a total of 8 million Euro) was divided equally between the Region and businessman José E. Almeida, who is now the holder of a majority stake in the company.[67]
Similarly, the Regional Government approved the consolidation of the three individual port authorities (Administração dos Portos do Triângulo e Grupo Ocidental, Administração dos Portos da Terceira e Graciosa and the Administração dos Portos das Ilhas de São Miguel e Santa Maria) and regional Portos dos Açores into one entity that resulted in a 2.2 million Euro cost savings, in addition to a reduction from 11 to three administrators.[68]
Marine ports sorted by reported size:[69]
Ferry ports -
- Porto Velas, Azores, Latitude: 38° 40' 42" N Longitude: 28° 12' 11" W, Port Type: Ferry, Port Size: Small
Small harbours -
- Porto da Ponta Delgada, Azores, Latitude: 37° 44' 13" N Longitude: 25° 39' 50" W, UN/LOCODE: PTPDL, Port Size: Small
- Porto da Praia Da Vitoria, Azores, Latitude: 38° 43' 25" N Longitude: 27° 3' 16" W, UN/LOCODE: PTPRV, Port Size: Small
Very small harbours -
- Marina Vila Franca do Campo, Azores, Latitude: 37° 42' 51" N Longitude: 25° 25' 47" W, Port Type: Marina, Port Size: Very Small
- Porto da Angra do Heroismo, Azores, Latitude: 38° 39' 9" N Longitude: 27° 12' 57" W, UN/LOCODE: PTADH, Port Size: Very Small
- Porto da Corvo, Azores, Latitude: 39° 40' 18" N Longitude: 31° 6' 36" W, Port Type: Pier, Jetty or Wharf, Port Size: Very Small
- Porto da Horta, Azores Latitude: 38° 31' 48" N Longitude: 28° 37' 30" W, UN/LOCODE: PTHOR, Port Size: Very
- Porto da Madalena, Azores, Latitude: 38° 32' 7" N Longitude: 28° 31' 48" W, Port Size: Very Small
- Porto do Lagoa, Azores, Latitude: 39° 3' 10" N Longitude: 27° 58' 7" W, Port Size: Very Small
- Porto Lajes Do Pico, Azores, Latitude: 38° 23' 47" N Longitude: 28° 15' 15" W, Port Size: Very Small
- Porto Martins, Azores, Latitude: 38° 40' 34" N Longitude: 27° 3' 50" W, Port Size: Very Small
- Porto Povoacao, Azores, Latitude: 37° 44' 43" N Longitude: 25° 14' 47" W, Port Size: Very Small
- Rabo de Piexe, Azores, Latitude: 37° 48' 54" N Longitude: 25° 35' 2" W Port Size: Very Small
- Vila Do Porto, Azores, Latitude: 36° 56' 38" N Longitude: 25° 8' 48" W, Port Size: Very Small
Piers, jetties or wharves -
- Porto de Recreio de Calheta, Azores, Latitude: 38° 36' 1" N Longitude: 28° 0' 37" W, Port Type: Pier, Jetty or Wharf, Port Size: Very Small
- Porto Santo Amaro, Azores, Latitude: 38° 27' 23" N Longitude: 28° 10' 0" W, Port Type: Pier, Jetty or Wharf, Port Size: Very Small
- Santa Cruz Da Graciosa, Azores, Latitude: 39° 5' 1" N Longitude: 27° 59' 49" W, Port Type: Pier, Jetty or Wharf, Port Size: Very Small
- Santa Cruz Das Flores, Azores, Latitude: 39° 27' 6" N Longitude: 31° 7' 31" W, Port Type: Pier, Jetty or Wharf, Port Size: Very Small
Culture
.jpg.webp)
Azoreans have developed their own distinct regional identity and cultural traits, from a combination of continental Portuguese customs brought by various waves of immigration and local political and environmental factors.
Religious festivals, patron saints and traditional holidays mark the Azorean calendar. The most important religious events are tied with the festivals associated with the cult of the Holy Spirit, commonly referred to as the festivals of the Holy Spirit (or Espírito Santo), rooted in millenarian dogma and held on all islands from May to September. These festivals are very important to the Azorean people, who are primarily Roman Catholic, and combine religious rituals with processions celebrating the benevolence and egalitarianism of neighbours.
These events are centred around treatros or impérios, small buildings that host the meals, adoration and charity of the participants, and used to store the artefacts associated with the events. On Terceira, for example, these impérios have grown into ornate buildings painted and cared for by the local brotherhoods in their respective parishes. The events focus on the members of local parishes, not tourists, but all are welcome, as sharing is one of the main principles of the festivals. Some limited events focus on tourists, including a public event that the city government of Ponta Delgada on the island of São Miguel holds, which attracts visitors and locals.

Another event, the Festival of the Lord Holy Christ of the Miracles (or Senhor Santo Cristo dos Milagres) in Ponta Delgada on the island of São Miguel, is the largest individual religious event in the Azores, and takes place on Rogation Sunday. Pilgrims from within the Portuguese diaspora normally travel to Ponta Delgada to participate in an afternoon procession behind the image of Christ along the flower-decorated streets of the city. Although the solemn procession is only held on one day, the events of the Festival of Senhor Santo Cristo occur over a period of a week and involve a ritual of moving the image between the main church and convent nightly, ultimately culminating in the procession, which is televised within the Azores and to the Portuguese diaspora. The Sanjoaninas Festivities in Angra do Heroísmo on Terceira are held in June honoring Saint Anthony, Saint Peter and Saint John the Baptist, in a large religious celebration.
The festival of Our Lady of Lourdes (or Nossa Senhora de Lourdes), patron saint of whalers, begins in Lajes on Pico Island on the last Sunday of August and runs through the week—Whalers Week. It is marked by social and cultural events connected to the tradition of whale hunting. The Wine Harvest Festival (or Festa das Vindimas), takes place during the first week of September and is a century-old custom of the people of Pico.
On Corvo the people celebrate their patron saint Nossa Senhora dos Milagres (Our Lady of Miracles) on 15 August every year in addition to the festivals of the Divine Holy Spirit. The Festival da Maré de Agosto (August Sea Festival), takes place every year beginning on 15 August in Praia Formosa on Santa Maria. Also, the Semana do Mar (Sea Week), dedicated almost exclusively to water sports, takes place in August in the city of Horta, on Faial.
Carnaval is also celebrated in the Azores. Parades and pageants are the heart of the Carnaval festivities. There is lively music, colorful costumes, hand-made masks, and floats. The traditional bullfights in the bullring are ongoing as is the running of bulls in the streets.
References
Notes
- "População residente". Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- "Contas Económicas e Regionais". Serviço Regional de Estatística dos Açores. 2017. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
- "Azores". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Retrieved 31 May 2019.; "Azores". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved 31 May 2019.; "Azores" (US) and {{Cite Oxford Dictionaries|Azores|accessdate=31 May 2019}}; "Azores". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- "Ponta Delgada Climate Normals 1981–2010". IPMA. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- "Angra do Heroísmo Climate Normals 1981–2010". IPMA. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- J.M.A., ed. (5 March 2011), "Estruturas podem ter mais de dois mil anos: Monumentos funerários descobertos nos Açores", Correio da Manhã (in Portuguese), Lisbon, Portugal: Cofina Media, archived from the original on 14 May 2011, retrieved 18 June 2011
- AO Online, ed. (27 June 2011), Estudos arqueológicos podem indicar presença prévia ao povoamento das ilhas (in Portuguese), Ponta Delgada (Azores), Portugal: Açoreana Oriental, retrieved 27 June 2011
- Ashe, Thomas (1813). History of the Azores, or Western Islands. Oxford University.
- Scammell, G.V. (1989). The First Imperial Age. Unwin Hyman.
- Melo Bento (2008), p. 34.
- Melo Bento (2008), p. 36.
- Payne, Stanley (1972). "A History of Spain and Portugal – Ch27". Madison WI: University of Wisconsin. Archived from the original on 25 May 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- "The Role of Portugal -co-opting Nazi Gold, Jonathan Petropoulos, "Dimensions", Vol 11, No 1, 1997". Adl.org. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- M B Barrass (2001–2008). "Air of Authority – A History of RAF Organisation: Air Vice-Marshal Sir Geoffrey Bromet". Royal Air Force Organization (RAFWeb.org). Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- "CNN.com - Bush: Monday is 'a moment of truth' on Iraq - Mar. 17, 2003". www.cnn.com.
- Miranda, et al., 1998
- Machado, et al., 2008, p. 14.
- Lúis, 1994, pp. 439–440.
- Madeira, 1998
- Ferreira, 2005, p. 4
- Ting Yang, et al., 2006, p. 20
- "Erupções vulcânicas históricas" [Historical Volcanic Eruptions]. Centro de Vulcanologia e Avaliação de Riscos Geológicos (CVARG). 2010. Archived from the original on 5 March 2012. Retrieved 15 April 2010.; Evidence for the submarine eruptions off the coasts of [[Velas, Azores|]], São Jorge Island and Cachorro, Santa Luzia, Pico Island included primarily from inferences and eyewitness testimonies about sulfuric gases and vapors released from the waters along the coast (15–24 February 1964 and 15 December 1963, respectively)
- Carine, 2010, p. 78
- Ferreira, 2005, p. 110
- "Actividade Sísmica" [Seismic Activity] (in Portuguese). CVARG. 2010. Archived from the original on 5 March 2012. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- Ferreira, 2005, p. 111
- Triantis, K. A.; Borges, P. A. V.; Ladle, R. J.; Hortal, J.; Cardoso, P.; Gaspar, C.; Dinis, F.; Mendonça, E.; Silveira, L. M. A.; Gabriel, R.; Melo, C.; Santos, A. M. C.; Amorim, I. R.; Ribeiro, S. R. P.; Serrano, A. R. M.; Quartau, J. A.; Whittaker, R. J. (2010). "Extinction debt on oceanic islands" (PDF). Ecography. 33: 285–294. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.730.8154. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0587.2010.06203.x. hdl:10400.3/1712.
- Borges, P.A.V.; Costa, A.; Cunha, R.; et al., eds. (2010). A list of the terrestrial and marine biota from the Azores (PDF). Princípia, Cascais. 432 pp. ISBN 978-989-8131-75-1.
- "Investigador dos Açores descobriu 30 novas espécies de moluscos nas ilhas". Açoriano Oriental.
- "Invasive Alien Plants in the Azorean Protected Areas: Invasion Status and Mitigation Actions". L.C. Foxcroft, D.M. Richardson, P. Pyšek, P. Genovesi. Retrieved 2 November 2020.
- "APGHE da Tronqueira e Planalto dos Graminhais". www.azores.gov.pt.
- Laurel, Project Life Sustainable (2011). "Laurissilva Sustentável: Plantação de endémicas dos Açores".
- "LIFE Laurissilva Sustentável". life-laurissilva.spea.pt.
- "Azores temperate mixed forests". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 7 March 2017.
- Rando, Juan Carlos; Alcover, Josep Antoni; Olson, Storrs L. & Pieper, Harald. (2013). "A new species of extinct scops owl (Aves: Strigiformes: Strigidae: Otus) from São Miguel Island (Azores Archipelago), North Atlantic Ocean" (PDF). Zootaxa. 3647 (2): 343–357. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3647.2.6. hdl:10261/85708. PMID 26295111.
- Rando, Juan C.; Alcover, Josep A.; Pieper, Harald; Olson, Storrs L.; Hernández, C Nayra; López-Jurado, L Felipe (2020). "Unforeseen diversity of quails (Galliformes: Phasianidae: Coturnix) in oceanic islands provided by the fossil record of Macaronesia". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 188 (4): 1296–1317. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlz107.
- Hogan, C. Michael (10 December 2010). "Extremophile". In Monosson, Emily; Cleveland, Cutler J. (eds.). Encyclopedia of Earth. Washington D.C.: National Council for Science and the Environment. Retrieved 10 January 2010.
- "Aumento do Parque Marinho dos Açores". Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Climate of the Azores islands". Azores Weather. Archived from the original on 14 May 2009. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- "Mapas bioclimáticos y biogeográficos". www.globalbioclimatics.org.
- "Average Weather in Horta Portugal". weatherspark.com. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- "Climate records - Azores Islands". IPMA. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- "Research for REGI Committee: The economic, social and territorial situation of the Azores (Portugal)" (PDF). Briefing for the European Parliament.
- "Economy Azores". azoresweb.com. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- INE, ed. (2010), Censos 2011 – Resultadas Preliminares [2011 Census – Preliminary Results] (in Portuguese), Lisbon, Portugal: Instituto Nacional de Estatística, retrieved 1 January 2012
- Page, Melvin Eugene & Penny M. Sonnenburg (2003). Colonialism: An International, Social, Cultural, and Political Encyclopedia. ISBN 978-1-57607-335-3.
- Pacheco, Paula R.; Branco, Claudia C.; Gomes, Cidália T.; Cabral, Rita; Mota-Vieira, Luisa (12 May 2010). "HLA Class I and II profiles in São Miguel Island (Azores): genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium". BMC Research Notes. 3 (134): 134. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-3-134. PMC 2883542. PMID 20462405.
- Silva, Francisca; Pereira, Rui; Gusmão, Leonor; Santos, Cristina; Amorim, António; Prata, Maria João; Bettencourt, Conceição; Lourenço, Paula; Lima, Manuela (10 July 2009). "Genetic profiling of the Azores Islands (Portugal): Data from 10 X-chromosome STRs". American Journal of Human Biology. 22 (2): 221–223. doi:10.1002/ajhb.20971. PMID 19593741.
- John M. Butler (2014). Advanced Topics in Forensic DNA Typing: Interpretation. Academic Press. p. 441. ISBN 978-0124058545.
- Brehm, António; Pereira, Luísa; Kivisild, Toomas; Amorim, António (1 December 2003). "Mitochondrial portraits of the Madeira and Açores archipelagos witness different genetic pools of its settlers". Human Genetics. 114 (1): 77–86. doi:10.1007/s00439-003-1024-3. hdl:10400.13/3046. PMID 14513360.
- "Azores Islands". Library.csustan.edu. 17 January 1997. Archived from the original on 12 May 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- da Silva, Lurdes C. 22 August 2008 (22 August 2008). "Mass.- Azores links inked". O Jornal. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- SILVA, A. J. M. (2015). "The fable of the cod and the promised sea. About portuguese traditions of bacalhau", in BARATA, F. T. and ROCHA, J. M. (eds.). Heritages and Memories from the Sea, Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of the UNESCO Chair in Intangible Heritage and Traditional Know-How: Linking Heritage, 14–16 January 2015. University of Evora, Évora, pp. 130–143. PDF version
- Orbach, Michael K. (1977). Hunters, Seamen, and Entrepreneurs: The Tuna Seinermen of San Diego. University of California Press. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-520-03348-1.
- "Azorean Immigration into the United States" Archived 3 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Library.csustan.edu.
- Russell King, John Connell (1999). Small worlds, global lives: islands and migration. Continuum International Publishing Group. pp. 61–65. ISBN 1-85567-548-X
- "Imigrantes: Açorianos". Archived from the original on 31 December 2007.
- "Europe :: Portugal—The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
- Minder, Raphael (4 June 2015). "Azorean Diaspora Can't Resist the Powerful Pull of Home". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
- Territorial status of EU countries and certain territories – European Commission, retrieved 18 December 2018
- "Flughäfen in Portugal (PT)". Flugplaetze.org. Archived from the original on 7 January 2009. Retrieved 7 July 2009.
- "atlanticoline.pt: History" (in Portuguese). Ponta Delgada (Azores), Portugal: Atlânticoline. 2009. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- Cardoso, Fernando Teixeira & Izabela. "A post office in the middle of the Atlantic". www.bbc.com.
- Transmaçor, ed. (2010). "Transmaçor – Transportes Marítimos Açorianos, Ldª" (in Portuguese). Horta (Azores), Portugal: Transportes Marítimos Açorianos, Lda. Archived from the original on 10 March 2016.
- The societies and companies comprise 80% of the capital, with the remaining shares owned by the Azores Regional Government.
- Agência Lusa/AO online/Hoje (28 August 2012). ""Atlântida" está há um ano ancorado em Lisboa e ainda sem destino" (in Portuguese). Ponta Delgada (Azores), Portugal. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
- Lusa (20 June 2011). AO Online (ed.). "Concluídas negociações para compra da Transmaçor" (in Portuguese). Retrieved 21 June 2011.
- Pinheiro, Maria (8 June 2011). "Portos dos Açores – Fusão administrativa aprovada na Assembleia Regional" (in Portuguese). Horta, Portugal: Tribuna das Ilhas. Archived from the original on 11 July 2011. Retrieved 5 September 2011.
- http://www.worldportsource.com/ accessed 19 Nov 2020
Sources
- Costa, Antonieta (2007). Pelo sinal do Espírito Santo By the sign of the Holy Spirit. Angra do Heroísmo: Presidência do Governo Reginal dos Açores. Direcção Regional da Cultural. pp. 120p.
- Twain, Mark (1869). The Innocents Abroad, or the New Pilgrims Progress. Hartford, CT: American Publishing Co. OCLC 1047562.
- Dervenn, Claude (1956). The Azores : with 104 photographs in photogravure and a map. Translated by Bryans, Robin. London: George G. Harrap and Co.
- Dervenn, Claude (1957). Madeira. Translated by Hogarth-Gaute, Frances. London: George G. Harrap and Co.
- Lourenço, N.; Miranda, J.M.; Luis, J.F.; Ribeiros, A.; Mendes Victor, L.A.; Madeira, J.; H. Needham (1998). Morpho-tectonic analysis of the Azores Volcanic Plateau from a new bathymetric compilation of the area. 20. Marine Geophysical Researches. pp. 141–156.
- Luís, J.F.; Miranda, J.M; Galdeano, A.; Patriat, P.; Rossignol, J.C. and L.A. Mendes Victor (1994). The Azores triple junction evolution since 10 Ma from an aeromagnetic survey of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. 125. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. pp. 439–459.
- Madeira, J. (1998). Estudos de neotectónica nas ilhas do Faial, Pico e S. Jorge: uma contribuição para o conhecimento geodinâmico da junção tripla dos Açores [Neotectonic studies on the islands of Faial, Pico and S. Jorge: a contribution to the geodynamic knowledge in the triple junction of the Açores] (in Portuguese). Lisbon: Faculdade de Ciências, Universidade de Lisboa.
- Ridley, W.; Watkins, N. and D.Macfarlane (1974). "The oceanic islands: Azores". In E. Nairn; F. Stehli (eds.). The ocean basins and margins. New York: Plenum Press. pp. 445–478.
- Upper mantle structure beneath the Azores hotspot from finite-frequency seismic tomography. 260. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 2006. pp. 11–26.
- Needham, H; J. Francheteau (1974). Some characteristics of the rift valley in the Atlantic Ocean near 36o48' north. 22. Earth Planetary Science Letters. pp. 29–43.
- Ferreira, António de Brum (2005). "Geodinâmica e perigosidade natural nas ilhas dos Açores" [Geodynamics and Natural Risks on the Islands of the Azores]. Finisterra (in Portuguese). XL (79): 013–120.
- Carine, Mark; Schaefer, Hanno (2010). "The Azores diversity enigma: why are there so few Azorean endemic flowering plants and why are they so widespread?". Journal of Biogeography. 37 (1): 77–89. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2009.02181.x.
- "Centro de Vulcanologia e Avaliação de Riscos Geológicos: Observatório Vulcanológica e Sismológico da Universidade dos Açores". Centro de Vulcanologia e Avaliação de Riscos Geológicos (CVARG). 2010. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- Machado, Adriane; Azevedo, José M. M.; Alemeida, Delia P.M.; Farid Chemale Jr. (2008). "Geochemistry of Volcanic Rocks from Faial Island (Azores)" (PDF). Lisbon: e-Terra, GEOTIC – Sociedade Geológica de Portugal. pp. 1–14. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- R.C. Mitchell-Thomé (1980). "Some geomorphological aspects of the Azores Archipelago" (PDF). Finistrerra: Revista Portuguesa de Geografia. XV (30): 201–219.
- Scammell, G. V. (1989). The First Imperial Age. London: Unwin Hyman. pp. 51–70.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Azores. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Azores. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Azores. |



_4_julesvernex2.jpg.webp)

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)