Bunuban languages
The Bunuban languages (or Bunaban) are a small family of Australian Aboriginal languages spoken in northern Australia. The family consists of two languages, Bunuba and Gooniyandi, which are related to each other to about the same degree that English is related to Dutch. Bunuba has about 100 speakers and Gooniyandi about 400. Both are endangered.
| Bunuban | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | around Fitzroy Crossing, Kimberley region |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Subdivisions | |
| Glottolog | buna1274 |
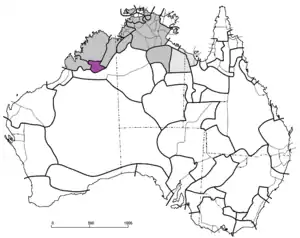 Bunuban languages (purple), among other non-Pama-Nyungan languages (grey) | |
Vocabulary
Capell (1940) lists the following basic vocabulary items:[1]
gloss Bunaba Gunian man gujɽäma juwulu woman wiːji maŋo head guŋgulu walu eye mulu mɔːlu nose wuɽa manili mouth djäläṉ daŋandi tongue djälän djäläṉ stomach giniŋa djulu bone gudju gudji blood gili wari kangaroo wandjiri wandjiri opossum läŋgur djämbidjin emu ganaŋandja crow waŋgaɳa waŋgide fly ŋirinji ŋurinj sun gawara miri moon gilimana djaːlin fire windäli weandi smoke bindja wangi water gaɽwa gaːmba
References
- Capell, Arthur. 1940. The Classification of Languages in North and North-West Australia. Oceania 10(3): 241-272, 404-433. doi:10.1002/j.1834-4461.1940.tb00292.x
- McGregor, William (2004). The Languages of the Kimberley, Western Australia. London, New York: Taylor & Francis. pp. 39–40.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.