Murray County, Oklahoma
Murray County is a county located in the southern part of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. As of the 2010 census, the population was 13,488.[1] This is a 6.9 percent increase from 12,623 at the 2000 census.[2] The county seat is Sulphur.[3] The county was named for William H. Murray, a member and president of the Oklahoma Constitutional Convention and later a Governor of Oklahoma.[4]
Murray County | |
|---|---|
 Murray County Courthouse in September 2014 | |
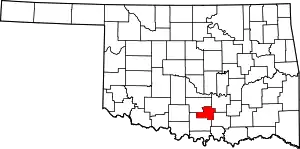 Location within the U.S. state of Oklahoma | |
 Oklahoma's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 34°29′N 97°04′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1907 |
| Seat | Sulphur |
| Largest city | Sulphur |
| Area | |
| • Total | 425 sq mi (1,100 km2) |
| • Land | 416 sq mi (1,080 km2) |
| • Water | 8.6 sq mi (22 km2) 2.0%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2018) | 13,953 |
| • Density | 32/sq mi (12/km2) |
| Congressional district | 4th |
| Website | www |
History
The area now occupied by Murray County was part of the land granted to the Choctaw Nation by the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek in 1820. The Chickasaw received part of the land under the Treaty of Doaksville in 1838. The area became part of the Chickasaw Nation in 1855. There was an extended conflict before the U.S. Civil War between the Plains Indians and the newly arrived Choctaws and Chickasaws. The U.S. Army built Fort Towson (1824); Fort Washita (1842) and Fort Arbuckle (1851) to protect the Chickasaws. After the conflict between the tribes was settled, various bands of outlaws moved in and continued to create law enforcement problems.[4]
Sulphur began developing in the 1880s around the springs for which it was named. The springs encouraged the building of bathhouses and spas. Several were established by the time that a post office was established in 1898. The Sulphur Springs Railway (acquired by the St. Louis and San Francisco Railway in 1907) arrived there in 1902, and the 1904 establishment of Platt National Park, with headquarters at Sulphur, spurred the expansion of services for health-seekers. Other visitors were drawn to the park and to nearby Turner Falls, making Sulphur one of the state's earliest recreational centers.[4]
Until statehood, the area of the present-day county was a part of Pickens County, Chickasaw Nation.[5] Murray County was created when the Chickasaw Nation was disestablished immediately before Oklahoma statehood. Sulphur was declared as the county seat.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 425 square miles (1,100 km2), of which 416 square miles (1,080 km2) is land and 8.6 square miles (22 km2) (2.0%) is water.[6] It is the third-smallest county in Oklahoma by land area and second-smallest by total area.[4] The county's northern section lies in the Sandstone Hills physiographic region and is suitable for farming, while the southern portion is in the Arbuckle Mountains region, which is dominated by rolling hills and rock outcrops. The Washita River drains the county. Chickasaw National Recreation Area (CNRA) lies in the county. Lake of the Arbuckles, part of CNRA, was completed on Rock Creek in 1966.[4]
Major highways
.svg.png.webp) Interstate 35
Interstate 35 U.S. Highway 77
U.S. Highway 77 U.S. Highway 177
U.S. Highway 177 Chickasaw Turnpike
Chickasaw Turnpike State Highway 1
State Highway 1 State Highway 7
State Highway 7 State Highway 110
State Highway 110


Protected areas
Adjacent counties
- Pontotoc County (northeast)
- Johnston County (southeast)
- Carter County (southwest)
- Garvin County (northwest)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1910 | 12,744 | — | |
| 1920 | 13,115 | 2.9% | |
| 1930 | 12,410 | −5.4% | |
| 1940 | 13,841 | 11.5% | |
| 1950 | 10,775 | −22.2% | |
| 1960 | 10,622 | −1.4% | |
| 1970 | 10,669 | 0.4% | |
| 1980 | 12,147 | 13.9% | |
| 1990 | 12,042 | −0.9% | |
| 2000 | 12,623 | 4.8% | |
| 2010 | 13,488 | 6.9% | |
| 2018 (est.) | 13,953 | [7] | 3.4% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[8] 1790-1960[9] 1900-1990[10] 1990-2000[11] 2010-2013[1] | |||

As of the census[12] of 2000, there were 12,623 people, 5,003 households, and 3,587 families residing in the county. The population density was 12/km2 (30/mi2). There were 6,479 housing units at an average density of 6/km2 (16/mi2). The racial makeup of the county was 80.76% White, 1.90% Black or African American, 11.57% Native American, 0.32% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander, 1.16% from other races, and 4.26% from two or more races. 3.15% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 5,003 households, out of which 30.90% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 57.70% were married couples living together, 10.20% had a female householder with no husband present, and 28.30% were non-families. 25.20% of all households were made up of individuals, and 12.70% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.45 and the average family size was 2.92.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 24.20% under the age of 18, 8.00% from 18 to 24, 25.10% from 25 to 44, 24.30% from 45 to 64, and 18.50% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 40 years. For every 100 females there were 97.40 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 92.80 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $30,294, and the median income for a family was $37,303. Males had a median income of $28,381 versus $19,727 for females. The per capita income for the county was $16,084. About 11.10% of families and 14.10% of the population were below the poverty line, including 16.90% of those under age 18 and 15.10% of those age 65 or over.
Politics
| Voter Registration and Party Enrollment as of January 15, 2019[13] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Number of Voters | Percentage | |||
| Democratic | 4,183 | 54.25% | |||
| Republican | 2,610 | 33.85% | |||
| Others | 918 | 11.91% | |||
| Total | 7,711 | 100% | |||
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 75.5% 4,175 | 19.7% 1,087 | 4.8% 266 |
| 2012 | 70.1% 3,606 | 29.9% 1,540 | |
| 2008 | 70.2% 3,746 | 29.8% 1,592 | |
| 2004 | 63.2% 3,665 | 36.8% 2,130 | |
| 2000 | 53.0% 2,609 | 46.0% 2,263 | 1.0% 50 |
| 1996 | 33.8% 1,712 | 51.7% 2,620 | 14.5% 736 |
| 1992 | 27.5% 1,536 | 46.4% 2,594 | 26.1% 1,458 |
| 1988 | 42.9% 2,056 | 56.3% 2,697 | 0.9% 41 |
| 1984 | 57.5% 3,073 | 41.7% 2,229 | 0.8% 45 |
| 1980 | 49.2% 2,494 | 47.1% 2,384 | 3.7% 189 |
| 1976 | 34.5% 1,563 | 64.6% 2,932 | 0.9% 41 |
| 1972 | 68.2% 2,983 | 29.6% 1,294 | 2.2% 95 |
| 1968 | 34.2% 1,454 | 41.7% 1,773 | 24.1% 1,027 |
| 1964 | 28.6% 1,236 | 71.4% 3,083 | |
| 1960 | 48.4% 1,993 | 51.7% 2,129 | |
| 1956 | 42.2% 1,809 | 57.8% 2,482 | |
| 1952 | 39.7% 1,885 | 60.3% 2,868 | |
| 1948 | 20.7% 798 | 79.3% 3,054 | |
| 1944 | 27.8% 1,005 | 72.0% 2,602 | 0.3% 9 |
| 1940 | 28.3% 1,238 | 71.4% 3,126 | 0.4% 17 |
| 1936 | 20.4% 823 | 79.0% 3,181 | 0.6% 23 |
| 1932 | 14.7% 532 | 85.3% 3,086 | |
| 1928 | 51.5% 1,631 | 47.3% 1,498 | 1.1% 36 |
| 1924 | 26.0% 784 | 69.1% 2,083 | 4.9% 148 |
| 1920 | 42.2% 1,362 | 54.0% 1,744 | 3.8% 121 |
| 1916 | 21.6% 458 | 61.6% 1,305 | 16.8% 356 |
| 1912 | 17.2% 321 | 53.0% 987 | 29.8% 555 |
Economy
Farming and ranching were the basis of the economy during the time when the area was part of the Chickasaw Nation. The area was called "the Prairie of Eden" because its plentiful grasslands attracted abundant game, Chickasaw ranchers Noah Lael and Perry Froman operated and headquartered near Sulphur by 1881. Settlements of farmers and businesses expanded through the decade, spurred by the construction of rail lines by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway lines through to Dougherty and Davis in 1886–87. Post offices were established at Dougherty in 1887 and Davis in 1890.[4]
Cattle ranching, the other primary industry, continued into the twenty-first century, and Murray County has long been recognized as the center of "Hereford Heaven." Notable ranching operations included those of Oklahoma Gov. Roy J. Turner. On New Year's Eve, 1947, the Flying L Ranch near Davis was the site for the marriage of Roy Rogers, "King of the Cowboys," and Dale Evans.[4]
The location of the Oklahoma School for the Deaf at Sulphur in 1907, and a veterans center added to the region's economy. Limestone quarries were also significant. The most important example of this activity began in the 1890s at Big Canyon, home to operations of the Dolese Brothers, whose company became a major state employer.[4]
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved November 9, 2013.
- CensusViewer:Population of Murray County, Oklahoma
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- Turner, Alvin O. "Murray County," Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture, Oklahoma Historical Society, 2009. Accessed April 4, 2015.
- Charles Goins, Historical Atlas of Oklahoma (Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 2006), plate 105.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- "County Population Totals and Components of Change: 2010-2018". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 2, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- "Oklahoma Registration Statistics by County" (PDF). OK.gov. January 15, 2019. Retrieved 2019-02-27.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2018-03-29.
