Outline of underwater diving
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to underwater diving:

Underwater diving – as a human activity, is the practice of descending below the water's surface to interact with the environment.
What type of thing is underwater diving?
Underwater diving can be described as all of the following:
- A human activity – intentional, purposive, conscious and subjectively meaningful sequence of actions. Underwater diving is practiced as part of an occupation, or for recreation, where the practitioner submerges below the surface of the water or other liquid for a period which may range between seconds to the order of a day at a time, either exposed to the ambient pressure or isolated by a pressure resistant suit, to interact with the underwater environment for pleasure, competitive sport, or as a means to reach a work site for profit or in the pursuit of knowledge, and may use no equipment at all, or a wide range of equipment which may include breathing apparatus, environmental protective clothing, aids to vision, communication, propulsion, maneuverability, buoyancy and safety equipment, and tools for the task at hand.
Diving activity, by type
Modes of underwater diving

There are several modes of diving distinguished by the equipment and procedures used:
- Freediving – Underwater diving without breathing apparatus
- Scuba diving – Swimming underwater breathing gas carried by the diver
- Surface-supplied diving – Underwater diving breathing gas supplied from the surface
- Saturation diving – Diving for periods long enough to bring all tissues into equilibrium with the partial pressures of the inert components of the breathing gas
- Atmospheric pressure diving – Diving where the diver is isolated from the ambient pressure by an articulated pressure resistant diving suit.
- Unmanned diving – Diving by mechanisms under the direct or indirect control of remote human operators for observation, data collection or manipulation of the environment using on-board actuator devices
Diving procedures




Diving procedures – Standardised methods of doing things that are known to work effectively and acceptably safely
- Ascending and descending (diving) – Procedures for safe ascent and descent in underwater diving
- Ear clearing – Equalising of pressure in the middle ears
- Emergency ascent – An ascent to the surface by a diver in an emergency
- Controlled emergency swimming ascent – A technique used by scuba divers to return to the surface in an out-of-gas emergency in shallow water
- Controlled buoyant lift – A technique used by scuba divers to raise an incapacitated diver to the surface
- Boat diving – Procedures specific to diving from boats
- Canoe and kayak diving – Recreational diving from a canoe or kayak
- Decompression (diving) – The reduction of ambient pressure on underwater divers after hyperbaric exposure and the elimination of dissolved gases from the diver's tissues
- Decompression practice – Techniques and procedures for safe decompression of divers
- Pyle stop – A series of short deep decompression stops in addition to the standard profile
- Ratio decompression – Rule of thumb for estimating a decompression schedule for a given set of breathing gases
- Decompression practice – Techniques and procedures for safe decompression of divers
- Dive log – Record of diving history of an underwater diver
- Dive planning – The process of planning an underwater diving operation
- Diver communications – Methods used by underwater divers to communicate
- Diver navigation – Underwater navigation by scuba divers
- Diver rescue – Rescue of a distressed or incapacitated diver
- Diver trim – Balance and orientation skills of an underwater diver
- Drift diving – Scuba diving where the diver is intentionally transported by the water flow
- Finning techniques – Techniques used by divers and surface swimmers using swimfins
- Combat sidestroke – Variation of side-stroke swimming used by United States Navy SEALs
- Scuba skills – The skills required to dive safely using self-contained underwater breathing apparatus
- Buddy breathing – Technique for sharing breathing gas from a single mouthpiece
- Buddy diving – Practice of mutual monitoring and assistance between two divers
- Buddy check – Pre-dive safety checks carried out by two-diver dive teams
- Gas blending for scuba diving – Mixing and filling cylinders with breathing gases for use when scuba diving
- Low impact diving – Scuba diving that has minimal environmental effect
- Penetration diving – Diving under a physical barrier to a direct vertical ascent to the surface
- Rebreather diving – Underwater diving using self contained breathing gas recycling apparatus
- Rule of thirds (diving) – Rule of thumb for scuba gas management
- Sidemount diving – Diving using an equipment configuration where the scuba sets are clipped to the sides of the harness
- Solo diving – Recreational diving without a dive buddy
- Surface-supplied diving skills – Skills and procedures required for the safe operation and use of surface-supplied diving equipment
- Underwater searches – Techniques for finding underwater targets
Underwater diving, by environment

Underwater diving environment – The underwater environment to which a diver may be exposed
- Open-water diving – Diving in unrestricted water when the diver has unrestricted vertical access to the surface
- Altitude diving – Underwater diving at altitudes above 300 m
- Cave diving – Underwater diving in water-filled caves
- Deep diving – Underwater diving to a depth beyond the norm accepted by the associated community
- Ice diving – Underwater diving under ice
- Muck diving – Recreational diving on a loose sedimentary bottom
- Night diving – Underwater diving during the hours of darkness
- Recreational dive sites – Specific places that recreational divers go to enjoy the underwater environment or are used for training purposes
- Wreck diving – Recreational diving on wrecks
Occupational diving




_2%252C_maneuvers_a_sunken_ship's_scr.jpg.webp)


Professional diving, also known as Occupational diving – Underwater diving where divers are paid for their work
- Ama (diving) – Japanese pearl divers
- Aquarium diving – Occupational diving in large aquariums
- Commercial diving – Professional diving on industrial projects
- Commercial offshore diving – Professional diving in support of the oil and gas industry
- Hyperbaric welding – Welding metal at elevated pressure
- Nondestructive testing – Evaluating the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage
- Diver training – Processes by which people develop the skills and knowledge to dive safely underwater
- Diving instructor – Person who trains and assesses underwater divers
- Diving school – Establishment for training and assessing underwater divers – A venue for training underwater divers
- Occupational diver training – Processes by which people develop the skills and knowledge to dive safely for diving at work
- Commercial diver training – Processes by which people develop the skills and knowledge to dive safely for industrial applications
- Military diver training – Training of underwater divers for service in the armed forces – Processes by which people develop the skills and knowledge to dive effectively for military applications
- Public safety diver training – Training divers for public safety services – Processes by which people develop the skills and knowledge to dive safely for public safety purposes
- Scientific diver training – Training divers who will be doing scientific work underwater – Processes by which people develop the skills and knowledge to dive safely for scientific projects
- Recreational diver training – Processes by which people develop the skills and knowledge to dive safely for recreational purposes
- Technical diver training – Processes by which people develop the skills and knowledge to dive safely for recreational technical diving
- Diver certification – Certification as competent to dive to a specified standard
- List of diver certification organizations – Agencies which issue certification for competence in diving skills
- Diamond Reef System – System for training divers in buoyancy, trim and maneuvering skills
- Divemaster, also known as Dive guide – Recreational dive leader certification and role
- Diving contractor – The legal persona responsible for professional diving operations for a client – A legal entity responsible for professional diving work
- Haenyeo – Female occupational divers in the Korean province of Jeju
- Hazmat diving – Underwater diving in a known hazardous materials environment
- Media diving – Underwater diving in support of the media industries
- Military diving – Underwater diving in a military context by members of an armed force
- Anti-frogman techniques
- Army engineer diver – Members of national armies who are trained to undertake reconnaissance, demolition, and salvage tasks underwater
- Clearance diver – Navy diver specialist with explosives
- List of military diving units – A list of links to articles on notable military diving units
- Army Ranger Wing – Special operations force of the Irish Defence Forces
- British commando frogmen – The Special Boat Service, whose members are drawn largely from the Royal Marines
- Canadian armed forces divers
- Clearance Diving Branch (RAN) – Diving unit of the Royal Australian Navy
- Comando Raggruppamento Subacquei e Incursori Teseo Tesei – Italian special forces diving unit
- Commandos Marine – Special operations forces of the French Navy
- Decima Flottiglia MAS – Italian naval commando frogman unit of the Fascist era
- French commando frogmen – Combat swimmer unit of the French Navy
- Frogman – Tactical scuba diver
- GRUMEC, also known as Brazilian commando frogmen – Brazilian Navy special forces diving unit
- INSFOC – Indonesian Navy Special Force and Operations Command
- Kommando Spezialkräfte Marine – German postwar commando amphibious warfare force
- KOPASKA – Indonesian Navy special operations and demolition unit
- Marine Commandos – Special operations group of the Lebanese Navy
- Minedykkerkommandoen – Norwegian Navy clearance diver unit
- Minentaucher – Mine clearance divers of the German Navy
- PASKAL – Special operations force of the Royal Malaysian Navy
- Naval Service Diving Section – Diving unit of the Irish Naval Service
- Naval Special Warfare Command (Thailand) – Special operations force within the Military of Thailand
- Röjdykare – Clearance divers of the Swedish Navy
- Russian commando frogmen – Tactical scuba diving unit
- Shayetet 13 – Special operations unit of the Israeli Navy
- Special Boat Service – Special forces unit of the Royal Navy. Formed originally from the RMBPD
- Special Service Group (Navy) – Pakistan Navy special operations force
- Taifib – Indonesian amphibious reconnaissance unit
- Underwater Defence (Turkish Armed Forces) – Special operations unit of the Turkish Navy
- Underwater Demolition Command – Special warfare unit of the Greek Navy
- Underwater Offence (Turkish Armed Forces) – Special operations Forces of the Turkish Navy
- United States military divers – Underwater divers employed by the US armed forces, including navy, army, marines, air force and coast guard
- Master diver (United States Navy) – Senior diver rating in US Navy
- Navy diver (United States Navy) – US Navy personnel qualified in underwater diving and salvage
- Explosive ordnance disposal (United States Navy) – US Navy personnel who render safe or detonate unexploded ordnance
- Underwater Demolition Team – US Navy special operations group
- United States Marine Corps Combatant Diver Course – Military diver training for the US Marines
- United States Navy SEALs – US Navy special operations force
- List of United States Navy SEALs – Notable current and former members of the United States Navy SEALs and Underwater Demolition Teams
- United States Navy SEAL selection and training – Selection and training procedures and criteria
- National Navy UDT-SEAL Museum – Museum recording the history of US Navy UDT and SEAL teams and their members
- Underwater warfare – One of the three operational areas of naval warfare
- Nuclear diving – Diving in an environment where there is a risk of exposure to radioactive materials
- Pearl hunting – Collecting pearls from wild molluscs
- Public safety diving – Underwater work done by law enforcement, rescue and search and recovery teams
- Police diving – A branch of professional diving carried out by police services
- Special Duties Unit – Hong Kong Police tactical unit
- Police diving – A branch of professional diving carried out by police services
- Salvage diving – The diving work associated with the recovery of vehicles, cargo and structures
- Scientific diving – The use of diving techniques in the pursuit of scientific knowledge
- Ships husbandry diving – Diving related to the maintenance and upkeep of ships
- Sponge diving – Diving to gather natural sponges
- Underwater archaeology – Archaeological techniques practiced at underwater sites
- Underwater demolition – The deliberate destruction or neutralization of man-made or natural underwater obstacles
- Underwater photography – Genre of photography
- Underwater search and recovery – Locating and recovering underwater objects
- Underwater videography – The branch of electronic underwater photography concerned with capturing moving images
Recreational diving

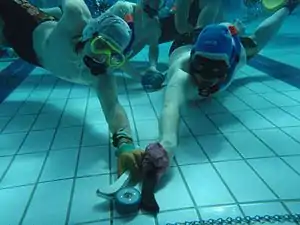


Recreational diving – Diving for the purpose of leisure and enjoyment, usually when using scuba equipment
- Technical diving – Extended scope recreational diving
- Cave diving – Underwater diving in water-filled caves
- Doing It Right (scuba diving) – Technical diving safety philosophy
- Shark tourism – Tourism industry based on viewing sharks in their natural habitat
- Shark cage diving – Diving inside a protective cage to observe sharks in the wild
- Shark-proof cage – A metal structure to protect divers and snorkellers from potentially dangerous sharks
- Shark baiting – Attracting sharks by chumming the water
- Shark cage diving – Diving inside a protective cage to observe sharks in the wild
- Underwater photography – Genre of photography
- Underwater sports – Competitive underwater recreational activities
- Aquathlon (underwater wrestling) – Competitive underwater wrestling
- Competitive apnea – Competitive breathhold diving
- Constant weight apnea – Freediving discipline in which the diver descends and ascends only by swimming with the use of fins
- Constant weight without fins – Freediving discipline in which the diver descends and ascends only by swimming without the use of fins
- Dynamic apnea – Freediving disciplines where the breath-hold diver swims horizontally under water with or without fins
- Free immersion apnea – Freediving discipline in which no propulsion equipment is used, but pulling on the rope during descent and ascent is permitted
- No-limits apnea – Freediving discipline in which the diver descends and ascends using their method of choice
- Variable weight apnea – Deep freediving using a weighted sled for descent, pulling along the depth rope for ascent
- Static apnea – A discipline in which the diver holds their breath underwater for as long as possible, and does not need to swim any distance
- Skandalopetra diving – Freediving using a stone weight at the end of a rope to the surface
- Finswimming – Competitive watersport using swimfins for propulsion
- 2016 Finswimming World Championships – International competition in Volos, Greece
- 2018 Finswimming World Championships – International competition in Belgrade, Serbia
- Apnea finswimming – Underwater swimming in a swimming pool using mask, monofin and holding one's breath.
- Finswimming at the 2009 Asian Indoor Games – Competition held in Mỹ Đình National Aquatics Sports Complex, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Immersion finswimming – Underwater swimming using mask, monofin and underwater breathing apparatus in a swimming pool
- Spearfishing – Hunting for fish using a spear
- Sport diving (sport) – Underwater sport using recreational open circuit scuba equipment in a swimming pool
- Underwater football – Underwater team sport using snorkeling equipment and an American football
- Underwater hockey – Underwater sport of pushing a puck into the opposing goal
- Underwater ice hockey – A variant of ice hockey played upside-down underneath frozen pools or ponds on breath-hold
- Underwater orienteering – Underwater compass navigation and speed competition on scuba.
- Underwater photography (sport) – Competitive underwater digital photography on scuba
- Underwater rugby – Game where two teams try to score a negatively buoyant ball into the opponents’ goal at the bottom of a swimming pool on breath-hold
- Underwater target shooting – Breathhold underwater sport of target shooting with a speargun in a swimming pool.
- Wreck diving – Recreational diving on wrecks
Diving and support equipment, tools and weapons







%252C_is_fitted_with_a_Kirby_Morgan_37_Dive_Helmet.jpg.webp)



_prepare_to_dive.jpg.webp)

Diving equipment
Diving equipment – Equipment used to facilitate underwater diving
- Autonomous underwater vehicle – Unmanned underwater vehicle with autonomous guidance system
- Breathing gas – Gas used for human respiration
- Buoyancy control device – Diving equipment for controlling buoyancy by volume adjustment
- Decompression equipment – Equipment used by divers to facilitate decompression
- Dive light – Light used underwater by a diver
- Diver propulsion vehicle – Powered device for diver mobility and range extension
- Diving bell – Chamber for transporting divers vertically through the water
- Diving mask – Watertight air-filled face cover with view-ports for improving underwater vision
- Anti-fog – Chemicals that prevent the condensation of water as small droplets on a surface
- Full face diving mask
- Integrated Diver Display Mask – Diving half-mask with integrated head-up instrument display
- Diving safety equipment – Equipment carried or worn by a diver or provided by the dive team to reduce risk or mitigate incidents
- Diving suit – Garment or device designed to protect a diver from the underwater environment
- Atmospheric diving suit – Articulated pressure resistant anthropomorphic housing for an underwater diver
- Dry suit – Watertight clothing that seals the wearer from cold and hazardous liquids
- Hot water suit – A wetsuit with a supply of heated water to keep a diver warm
- Rash vest – Stretch garment for protection from abrasion, UV and stings
- Wetsuit – Garment for water activities, providing thermal insulation but not designed to prevent water entering
- Standard diving dress – Rubberised canvas diving suit with copper helmet and weighted boots
- Diving weighting system – Ballast carried by underwater divers and diving equipment to counteract excess buoyancy
- Weight belt – A ballasted waist belt worn by a diver
- Diving weight – Ballast carried by a diver to counteract buoyancy or adjust trim
- Remotely operated underwater vehicle – A tethered underwater mobile device operated by a remote crew
- Snorkeling – Swimming while breathing through a snorkel represented by Snorkeling#Snorkel – Short curved tube used for face-down breathing at the surface
- Swimfin – Finlike accessories worn on the feet, used for swimming, snorkeling and diving propulsion
- Monofin – Single blade swimfin attached to both feet
- Towboard – Underwater survey equipment used to tow a diver
- Underwater breathing apparatus – Equipment which provides breathing gas to an underwater diver
- Scuba set – Self contained underwater breathing apparatus
- Diving cylinder – High pressure compressed gas cylinder used to store and supply breathing gas for diving
- Diving regulator – Mechanism that controls the pressure of a breathing gas supply for diving
- Rebreather – Apparatus to recycle breathing gas
- Surface-supplied diving equipment – Equipment used specifically for surface supplied diving
- Diving helmet – Rigid head enclosure with breathing gas supply worn for underwater diving
- Diver's umbilical – A hose and cable bundle which supplies breathing gas, communications and other services to a diver
- Scuba set – Self contained underwater breathing apparatus
Autonomous underwater vehicles
Autonomous underwater vehicle – Unmanned underwater vehicle with autonomous guidance system
- Autonomous Robotics Ltd – UK company developing an autonomous underwater vehicle
- AUV-150 – An unmanned underwater vehicle in development in by Central Mechanical Engineering Research Institute
- AUV Abyss – An autonomous underwater vehicle for mapping of the seabed and water column data collection
- Boaty McBoatface – Autonomous underwater vehicle, named from an online poll
- DeepC – Autonomous underwater vehicle powered by a fuel cell
- DEPTHX – Autonomous underwater vehicle for exploring sinkholes in Mexico
- Echo Ranger – A marine autonomous underwater vehicle built by Boeing
- Eelume – Autonomous underwater vehicle being developed by Eelume AS
- Explorer AUV – Autonomous underwater vehicle from People's Republic of China
- Intelligent Water class AUV – Autonomous underwater vehicle for the People's Liberation Army Navy
- Intervention AUV – Type of autonomous underwater vehicle capable of autonomous interventions
- iRobot Seaglider – Deep diving autonomous underwater vehicle for long term missions
- Maya AUV India – Autonomous underwater vehicle from National Institute of Oceanography, India
- Nereus (underwater vehicle) – Hybrid remotely operated or autonomous underwater vehicle
- REMUS (AUV) – Autonomous underwater vehicle series
- Sentry (AUV) – Autonomous underwater vehicle made by Woods Hole Oceanographic institution
- Spindle (vehicle) – Ice penetrating two-stage autonomous underwater vehicle
- SPURV – Self propelled underwater research vehicle built in 1957 for the US Navy
- SPURV II – Special purpose underwater research vessel built to srudy submarine wakes
- Theseus (AUV) – Large autonomous underwater vehicle for laying fibre optic cable
- Petrel HUG – A Chinese hybrid underwater glider
Breathing gas
Breathing gas – Gas used for human respiration
- Bailout gas – Emergency breathing gas supply carried by the diver
- Bottom gas – Gas breathed during the deep part of a dive
- Breathing air – Air quality suitable for safe breathing
- Decompression gas – Oxygen-rich gas used for accelerated decompression
- Emergency gas supply – Alternative independent breathing gas supply carried by a diver
- Heliox – A breathing gas mixed from helium and oxygen
- Nitrox – Breathing gas, mixture of nitrogen and oxygen
- Oxygen – Chemical element with atomic number 8
- Travel gas – Gas breathed during the descent part of a dive
- Trimix (breathing gas) – Breathing gas consisting of oxygen, helium and nitrogen
- Electro-galvanic oxygen sensor – Device which produces a voltage by a chemical reaction with oxygen proportional to partial pressure
- Gas blending – Producing special gas mixtures to specification
- Gas blending for scuba diving – Mixing and filling cylinders with breathing gases for use when scuba diving
- Oxygen compatibility – Use of equipment and materials that are suitable for service with a high partial pressure of oxygen
Decompression equipment
Decompression equipment – Equipment used by divers to facilitate decompression
- Decompression buoy – Inflatable surface marker buoy deployed from underwater
- Decompression cylinder – Scuba cylinder carrying decompression gas
- Decompression trapeze – Horizontal bars suspended at decompression stop depths
- Dive computer, also known as Decompression computer – Instrument to record dive profile and calculate decompression obligations in real time
- Dive tables – Tabulated data that allow divers to determine a decompression schedule for a given dive profile and breathing gas
- Diving bell – Chamber for transporting divers vertically through the water
- Diving chamber – Hyperbaric pressure vessel for human occupation used in diving operations
- Diving shot, also known as Shot line – Substantial weighted near-vertical line with buoy
- Diving stage – A platform on which one or two divers stand which transports them vertically through the water
- Jonline – A short line used by scuba divers to clip themselves to something
- Recreational dive planner
- Saturation system – A surface hyperbaric complex including a living chamber, transfer chamber, closed diving bell and the infrastructure to operate them
Diver propulsion vehicles
Diver propulsion vehicle – Powered device for diver mobility and range extension
- Advanced SEAL Delivery System – Former Navy SEAL mini-sub deployed from submarines
- Shallow Water Combat Submersible – A manned submersible and a type of swimmer delivery vehicle
- Wet sub – Ambient pressure diver propulsion vehicle
- Cosmos CE2F series – Italian swimmer delivery vehicles
- Human torpedo – Early form of diver propulsion vehicle
- Motorised Submersible Canoe – WWII British frogman delivery vehicle
- Necker Nymph – A DeepFlight Merlin class positively-buoyant open-cockpit 3-seater wet sub
- R-2 Mala-class swimmer delivery vehicle – 2-man wet sub swimmer delivery vehicle class of the Yugoslavian, and later, Croatian, Navies
- SEAL Delivery Vehicle – Manned wet submersible for deploying Navy SEALS
- Siluro San Bartolomeo – Italian manned torpedo design of late WWII
- Wet Nellie – 1976 car-shaped submarine from the James Bond film The Spy Who Loved Me
Diving safety equipment
Diving safety equipment – Equipment carried or worn by a diver or provided by the dive team to reduce risk or mitigate incidents
- Alternative air source – Emergency supply of breathing gas for an underwater diver
- Buddy line – A line physically tethering two scuba divers together underwater to avoid separation in low visibility conditions
- Decompression buoy, also known as DSMB – Inflatable surface marker buoy deployed from underwater
- Distance line, also known as dive reel or guide line – Line deployed by scuba divers for navigation
- Diver surface detection aids – Equipment to make a surfaced diver easier to find
- Diver's cutting tool – A tool to assist in extricating the diver from entrapment by lines or nets
- Diver's knife – A tool to assist in extricating the diver from entrapment by lines or nets
- Diving safety harness, also known as bell harness – A harness by which the diver can safely be lifted
- Jonline – A short line used by scuba divers to clip themselves to something
- Lifeline, also known as tether – A rope connecting the diver to an attendant, usually at the surface
- Line marker – Marker used on cave guide lines to provide safety information to divers
- Shotline – Substantial weighted near-vertical line with buoy
- Surface marker buoy – A buoy towed by a scuba diver to indicate the diver's position
Rebreathers
Rebreather – Apparatus to recycle breathing gas
- Carbon dioxide scrubber – Device which absorbs carbon dioxide from circulated gas
- Carleton CDBA – Military rebreather by Cobham plc
- Clearance Divers Life Support Equipment – British military electronically controlled closed circuit rebreather
- Cis-Lunar – Manufacturer of electronically controlled closed-circuit rebreathers for scuba diving
- Counterlung – Variable volume component in a rebreather to take up and release gas during a breathing cycle
- Cryogenic rebreather – Rebreather that removes CO2 by freezing it out using heat exchange with liquid oxygen
- CUMA – Canadian military diving rebreather
- Davis Submerged Escape Apparatus – Early submarine escape oxygen rebreather also used for shallow water diving.
- Dräger Dolphin – Semi-closed circuit recreational diving rebreather
- Dräger Ray – Semi-closed circuit recreational diving rebreather designed to use standard nitrox breathing gas mixtures
- FROGS
- Halcyon RB80 – Non-depth-compensated passive addition semi-closed circuit rebreather
- Halcyon PVR-BASC – Semi-closed circuit depth compensated passive addition diving rebreather
- IDA71 – Russian military rebreather for underwater and high altitude use
- Interspiro DCSC – Military semi-closed circuit passive addition diving rebreather
- KISS
- LAR-5, LAR-6, and LAR-V represented by Drägerwerk
- Lambertsen Amphibious Respiratory Unit – Early closed circuit oxygen diving rebreather
- Porpoise – Australian scuba manufacturer
- Siebe Gorman CDBA – A type of diving rebreather used by the Royal Navy
- Siva
- Viper
Remotely operated underwater vehicles
Remotely operated underwater vehicle – A tethered underwater mobile device operated by a remote crew
- 8A4-class ROUV – A Chinese work class remotely operated underwater vehicle
- ABISMO – Japanese remotely operated underwater vehicle for deep sea exploration
- Atlantis ROV Team – A high-school underwater robotics team from Whidbey Island, Washington, United States
- CURV – Early remotely operated underwater vehicle
- Épaulard – A French remotely operated underwater vehicle of the Ifremer
- Global Explorer ROV – A deep water science and survey remotely operated vehicle
- Goldfish-class ROUV – A light class of Chinese remotely operated underwater vehicle
- Kaikō ROV – Japanese remotely operated underwater vehicle for deep sea exploration
- Long-Term Mine Reconnaissance System – An American torpedo tube-launched underwater search and survey unmanned undersea vehicle
- Mini Rover ROV – A small, low cost observation class remotely operated underwater vehicle
- OpenROV – Open-source remotely operated underwater vehicle
- ROV KIEL 6000 – A remotely operated vehicle built by Schilling Robotics, Davis, California for scientific tasks
- ROV PHOCA – A remotely operated underwater vehicle of the COMANCHE type
- Scorpio ROV – A work class remotely operated underwater vehicle
- Sea Dragon-class ROV – A Chinese deep diving work class remotely operated underwater vehicle
- Seabed tractor – A special purpose class of remotely operated underwater vehicle
- Seafox drone – A remotely operated anti-mine marine drone
- Seahorse ROUV – A Chinese scientific and maintenance remotely operated underwater vehicle
- SeaPerch – A remotely operated underwater vehicle educational program
- SJT-class ROUV – A series of Chinese remotely operated underwater vehicles
- T1200 Trenching Unit – A remotely operated seabed trenching unit
- VideoRay UROVs – A series of inspection class remotely operated underwater vehicles
Underwater breathing apparatus
Underwater breathing apparatus – Equipment which provides breathing gas to an underwater diver
- Scuba set – Self contained underwater breathing apparatus
- Alternative air source – Emergency supply of breathing gas for an underwater diver
- Bailout bottle, also known as bailout cylinder – Emergency gas supply cylinder carried by a diver
- Emergency gas supply – Alternative independent breathing gas supply carried by a diver
- Pony bottle – Small independent scuba cylinder usually carried for emergency gas supply
- Backplate and wing – Type of back-mount scuba harness
- Diving cylinder – High pressure compressed gas cylinder used to store and supply breathing gas for diving
- Burst disc – A non-closing over-pressure relief device
- Cylinder valve alias Pillar valve represented by Diving cylinder#The cylinder valve – A valve to control gas flow to and from a cylinder and to connect with the regulator or filling hose
- Hydrostatic test – Non-destructive test of pressure vessels
- Sustained load cracking – Metallurgical failure mode of cracking under a prolonged static load
- Testing and inspection of diving cylinders – Periodical inspection and testing to revalidate fitness for service
- Diving regulator – Mechanism that controls the pressure of a breathing gas supply for diving
- Breathing performance of regulators – Measurement and requirements of function of breathing regulators
- Rebreather – Apparatus to recycle breathing gas
- Scuba manifold – Scuba component used to functionally connect diving cylinders
- Sidemount diving – Diving using an equipment configuration where the scuba sets are clipped to the sides of the harness
- Alternative air source – Emergency supply of breathing gas for an underwater diver
- Surface-supplied diving equipment – Equipment used specifically for surface supplied diving
- Air line, also known as air-line – A tube or hose carrying a compressed air supply
- Bailout cylinder – Emergency gas supply cylinder carried by a diver
- Bailout block – Valve block on diver's equipment for switching a diver's gas supply between main and emergency gas supply
- Diving helmet – Rigid head enclosure with breathing gas supply worn for underwater diving
- Diver's umbilical – A hose and cable bundle which supplies breathing gas, communications and other services to a diver
- Diving stage – A platform on which one or two divers stand which transports them vertically through the water
- Pneumofathometer – Gauge on the gas panel for indicating the depth of a surface-supplied diver
- Sea Trek (diving system) – Recreational underwater diving system using helmets
- Snuba – Limited depth airline breathing apparatus towed by the diver
- Standard diving dress – Rubberised canvas diving suit with copper helmet and weighted boots
Diving support equipment
Diving support equipment – Equipment used in the support of an underwater diving operation
- Booster pump – Machine to increase pressure of a fluid
- Cascade filling system – Filling pressurised gas from a series of storage cylinders
- Communications panel, also known as Diver's telephone – Surface control panel for underwater diving voice communications system
- Diver down flag – Flag signal indicating divers are in the water nearby
- Diver's pump – Manually powered surface air supply for divers
- Diving air compressor, also known as Diving compressor – Machine used to compress breathing air for use by underwater divers
- Diving chamber – Hyperbaric pressure vessel for human occupation used in diving operations
- Hyperbaric stretcher – Portable pressure vessel to transport a person under pressure.
- Diving spread – The topside base for commercial diving operations
- Air spread – The topside base for surface-supplied air diving operations
- Saturation spread – The topside base for saturation diving operations
- Saturation system – A surface hyperbaric complex including a living chamber, transfer chamber, closed diving bell and the infrastructure to operate them
- Diving support vessel – A ship used as a floating base for professional diving projects
- HMS Challenger – Royal Navy saturation diving support vessel
- Liveaboard – Way of using a boat
- Dive boat – Boat used for the support of scuba diving operations
- Combat Rubber Raiding Craft – Rubberised fabric tactical inflatable boat used by the US Navy
- Diving ladder – Ladder to facilitate egress from the water by divers
- Diving platform (scuba) – Low freeboard platform on a dive boat to give divers easy access to the water
- Moon pool – An opening in the base of a hull, platform, or chamber giving access to the water below
- Echo sounder, also known as fish finder – Measuring the depth of water by transmitting sound waves into water and timing the return
- Gas panel, also known as Diving gas distribution manifold – Breathing gas distribution panel for surface-supplied diving
- Helium analyzer – Instrument to measure the concentration of helium in a gas mixture
- Marine VHF radio – Radios operating in the very high frequency maritime mobile band
- Nitrox production – Methods of producing nitrox mixtures
- Membrane gas separation – Technology for splitting specific gases out of mixtures
- Pressure swing adsorption – method of gas concentration using selective adsorbtion under pressure
- Proton magnetometer, also known as metal detector – Instrument which measures very small variations in the Earth's magnetic field
- Recreational Dive Planner (RDP) – A PADI no-decompression dive table also available as a circular slide rule and electronic calculator
- Remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) – A tethered underwater mobile device operated by a remote crew
- Satellite navigation – Use of satellite signals for geo-spatial positioning
- Global Positioning System (GPS) – United States satellite navigation system
- Subsurface (software)
- Trongle – Device used on submarines to help swimmers to locate a submerged submarine
Underwater work tools and equipment

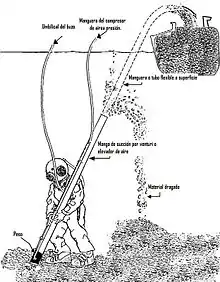

Underwater work tools and equipment – Tools and equipment used for underwater work
- Airlift (dredging device) – Dredging device using injected air to move water and entrained load up a pipe
- High-pressure water jetting – The use of very high pressure water for removing contamination and coatings from hard surfaces
- Lifting bag – Airtight bag used for underwater buoyant lifting when filled with air
- Remotely operated underwater vehicle – A tethered underwater mobile device operated by a remote crew
- Snoopy loop – Rubber band made from inner tube
- Tremie – Equipment for underwater concrete placement
Underwater weapons
Underwater weapons – Weapons that are intended for use underwater
- Limpet mine – A type of naval mine which is attached to a target by magnets
- Speargun – Underwater fishing implement
- Hawaiian sling – Simple form of underwater speargun
- Polespear – Basic rubber launched underwater fishing spear
- Underwater firearm – Firearms that can be effectively fired underwater
- Gyrojet – Firearm that fires small rocket projectiles
- Mk 1 Underwater Defense Gun – Underwater firearm developed by the United States during the Cold War
- Powerhead (firearm) – Specialized firearm used underwater that is fired when in direct contact with the target
- Underwater pistols
- Heckler & Koch P11 – Five-barreled underwater rocket dart pistol
- SPP-1 underwater pistol – Soviet four-barreled underwater dart pistol
- Underwater revolvers
- AAI underwater revolver – Six-round amphibious revolver for naval use
- Underwater rifles
- ADS amphibious rifle – Russian bullpup assault rifle for combat divers
- APS underwater rifle – Soviet underwater assault firearm firing unrifled steel flechettes
- ASM-DT amphibious rifle – Russian folding stock underwater firearm
Science of underwater diving
Physics of underwater diving

Physics of underwater diving – Aspects of physics which affect the underwater diver
- Buoyancy – Upward force that opposes the weight of an object immersed in fluid
- Archimedes' principle – Buoyancy principle in fluid dynamics
- Neutral buoyancy – Equilibrium between buoyancy and weight of an immersed object
- Diffusion – movement of molecules, atoms, or ions from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
- Molecular diffusion – The thermal motion of liquid or gas particles at temperatures above absolute zero
- Permeation – The penetration of a liquid, gas, or vapor through a solid
- Force – Any action that tends to maintain or alter the motion of an object
- Weight – Force on a mass due to gravity
- Ideal gas law – The equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas
- Combined gas law – Combination of Charles', Boyle's and Gay-Lussac's gas laws
- Amontons' law – Relationship between pressure and temperature of a gas at constant volume.
- Boyle's law – Relationship between pressure and volume in a gas at constant temperature
- Charles's law – Relationship between volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure
- Gay-Lussac's law – Relationship between pressure and temperature of a gas at constant volume.
- Pressure – Force distributed continuously over an area
- Ambient pressure – Pressure of the surrounding medium
- Atmospheric pressure – Static pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere
- Hydrostatic pressure – The static pressure exerted by the weight of the fluid column above the point
- Metre sea water – Unit of pressure equal to one tenth of a bar
- Partial pressure – Pressure attributed to a component gas in a mixture
- Dalton's law – Gas law describing pressure contributions of component gases in a mixture
- Oxygen fraction – Volumetric proportion of oxygen to other constituents in a breathing gas
- Torricellian chamber – An air space in a cave chamber with pressure below atmospheric
- Psychrometric constant – Relation of the partial pressure of water in air to temperature
- Solubility – Capacity of a substance to dissolve in a solvent in a homogeneous way
- Henry's law – Relation of equilibrium solubility of a gas in a liquid to its partial pressure in the contacting gas phase
- Solution – Homogeneous mixture of a solute and a solvent
- Supersaturation – State of a solution that contains more solute than can be dissolved at equilibrium
- Surface tension – Tendency of a liquid surface to shrink to reduce surface area
- Hydrophobe – molecule or surface that has no attraction to water
- Surfactant – Substance that lowers the surface tension between a liquid and another material
- Underwater vision – Effects of the underwater environment on (human) vision
- Snell's law, also known as Law of refraction – The relation between the angles of incidence and refraction of waves crossing the interface between isotropic media
- Work of breathing (WoB) – The energy expended to inhale and exhale a breathing gas
The diving environment



Underwater diving environment – The underwater environment to which a diver may be exposed
- List of diving environments by type – The variety of environments that people may dive in
- Underwater environment – The aquatic or submarine environment
- Open-water diving – Diving in unrestricted water when the diver has unrestricted vertical access to the surface
- Altitude diving – Underwater diving at altitudes above 300 m
- Cave diving – Underwater diving in water-filled caves
- Deep diving – Underwater diving to a depth beyond the norm accepted by the associated community
- Ice diving – Underwater diving under ice
- Muck diving – Recreational diving on a loose sedimentary bottom
- Night diving – Underwater diving during the hours of darkness
- Recreational dive sites – Specific places that recreational divers go to enjoy the underwater environment or are used for training purposes
- Wreck diving – Recreational diving on wrecks
- Physical and biological aspects of the diving environment
- Algal bloom – Rapid increase or accumulation in the population of planktonic algae
- Breaking wave, also known as Surf – A wave that becomes unstable as a consequence of excessive steepness
- Ocean current – Directional mass flow of oceanic water generated by external or internal forces
- Current (stream) – Flow of water in a river due to gravity
- Ekman transport – Net transport of surface water perpendicular to wind direction
- Halocline – Stratification of a body of water due to salinity differences
- Hazards of the aquatic environment represented by List of diving hazards and precautions#The aquatic environment –
- Hazards of the specific diving environment represented by List of diving hazards and precautions#The specific diving environment –
- List of diving hazards and precautions – List of the hazards to which an underwater diver may be exposed, their possible consequences and the common ways to manage the associated risk
- Longshore current – A current parallel to the shoreline caused by waves approaching at an angle to the shoreline
- Overfall current – A turbulent area of water caused by a strong current over an underwater ridge, or by currents meeting.
- Rip current – Narrow current of water that moves directly away from the shore, cutting through the lines of breaking waves
- Stratification – Stable water layers of different properties that act as a barrier to vertical mixing
- Surge (wave action) currently represented by Waves and shallow water – the component of wave motion close to and parallel with the bottom
- Thermocline – A distinct layer in a large body of fluid in which temperature changes more rapidly with depth than it does in the layers above or below
- Tidal race – A fast-moving tidal flow passing through a constriction, forming waves, eddies and strong currents
- Tide – Rise and fall of the sea level under astronomical gravitational influences
- Turbidity – The cloudiness of a fluid caused by large numbers of particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye
- Undertow (water waves) – Return flow below (nearshore) water waves.
- Upwelling – The replacement by deep water moving upwards of surface water driven offshore by wind
Physiology of underwater diving
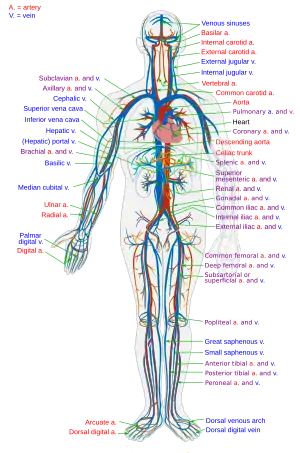
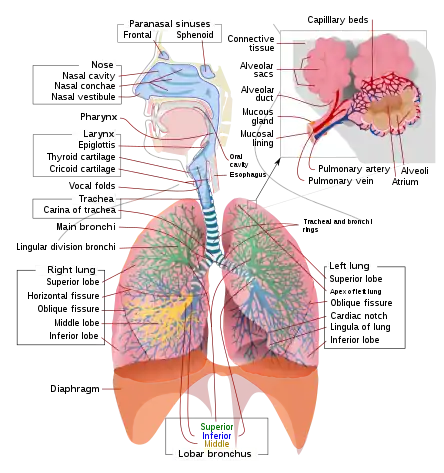
Human physiology of underwater diving – Influences of the underwater environment on the physiology of human divers
- Circulatory system – Organ system for circulating blood in animals
- Patent foramen ovale – A congenital heart defect in which blood can flow through an opening between the atrial chambers of the heart
- Blood–air barrier – Membrane separating alveolar air from blood in lung capillaries
- Blood shift – Blood flow to the extremities redistributed to the head and torso during a breathhold dive
- Perfusion – Passage of fluid through the circulatory or lymphatic system to an organ or tissue
- Pulmonary circulation – The part of the circulatory system which carries blood from heart to lungs and back to the heart
- Systemic circulation – The portion of the cardiovascular system which transports oxygenated blood away from the heart (between heart and body cells)
- Cold shock response – Physiological response to sudden exposure to cold
- Dead space (physiology) – The volume of inhaled air that does not take part in the gas exchange
- Diving reflex – The physiological responses to immersion of air-breathing vertebrates
- Metabolism – The set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of organisms
- Physiology of decompression – The physiological basis for decompression theory and practice
- Decompression theory – Theoretical modelling of decompression physiology
- Bühlmann decompression algorithm, also known as Buhlmann algorithm – Algorithm for modelling of inert gases entering and leaving body tissues in solution as pressure changes
- Equivalent air depth – Method of comparing decompression requirements for air and a given nitrox mix
- Gradient factor in decompression modelling – A way for users to adjust the conservatism of a decompression algorithm in software
- Haldane's decompression model – Decompression model developed by John Scott Haldane
- Lipid – A substance of biological origin that is soluble in nonpolar solvents
- Oxygen window in diving decompression – Physiological effect of oxygen metabolism on the total dissolved gas concentration in venous blood
- Reduced gradient bubble model – An algorithm by Bruce Wienke for modelling inert gases leaving the body during decompression in mixed dissolved and bubble phases
- Thalmann algorithm – Recent US Navy algorithm for modelling of inert gases entering and leaving body tissues as pressure changes
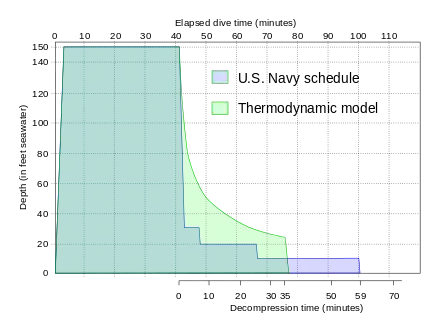
- Thermodynamic model of decompression – Early model in which decompression is controlled by the volume of gas bubbles coming out of solution
- Uncontrolled decompression – An unplanned drop in the pressure of a sealed system
- Varying Permeability Model – Decompression model and algorithm based on bubble physics
- Decompression theory – Theoretical modelling of decompression physiology
- Respiration (physiology) – Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between environment and tissues
- Artificial gills (human) – Hypothetical devices to allow a human to take in oxygen from surrounding water
- Breathing – Process of moving air into and out of the lungs
- Carbon dioxide retention – A tendency to retain abnormally high tissue carbon dioxide levels
- Gas exchange – The process by which gases diffuse through a biological membrane
- Hypocapnia – A state of reduced carbon dioxide in the blood
- Normocapnia – Normal arterial carbon dioxide levels
- Respiratory exchange ratio – The ratio between the amount of carbon dioxide produced in metabolism and oxygen used
- Respiratory quotient – Ratio of carbon dioxide produced by the body to oxygen consumed by the body
- Respiratory system – Biological system in animals and plants for gas exchange
- Tissue (biology) – Cellular organization level between cell and organ
- Underwater vision – Effects of the underwater environment on (human) vision
Diving medicine, disorders and treatment

Diving medicine
Diving medicine – Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disorders caused by underwater diving
- Fitness to dive, also known as Medical fitness to dive – Medical fitness of a person to function safely underwater under pressure
- Diving medical examiner – A medical practitioner registered to assess medical fitness to dive
- Diving medical practitioner – A medical practitioner registered to assess medical fitness to dive, manage diving accidents, plan safety for professional diving operations, provide advanced life support, acute trauma care and general wound care.
- Diving medical technician – a member of a dive team who is trained in advanced first aid and fit to provide treatment in a hyperbaric chamber in an emergency
- Hyperbaric medicine – Medical treatment at raised ambient pressure
Diving disorders and treatment

Diving disorders – Physiological disorders resulting from underwater diving
- List of signs and symptoms of diving disorders – The signs and symptoms of physiological disorders resulting from underwater diving
- Drowning – Respiratory impairment resulting from being in or underneath a liquid
- Laryngospasm – Involuntary contraction of the vocal folds restricting inhalation
- Dysbarism – Medical conditions resulting from changes of ambient pressure.
- Barotrauma – Injury caused by pressure
- Arterial gas embolism – Vascular blockage by gas bubbles
- Pulmonary barotrauma – Lung over-pressure and squeeze injuries
- Compression arthralgia – Joint pain caused by fast compression to high ambient pressure
- Decompression illness – Disorders arising from ambient pressure reduction
- Decompression sickness – Disorder caused by dissolved gases in the tissues forming bubbles during reduction of the surrounding pressure
- Dysbaric osteonecrosis – Ischemic bone disease caused by decompression bubbles
- Avascular necrosis – Death of bone tissue due to interruption of the blood supply
- Isobaric counterdiffusion – Diffusion of gases into and out of biological tissues under a constant ambient pressure after a change of gas composition
- Taravana – Decompression sickness after breath-hold diving
- Therapeutic recompression – Recompression to reduce symptoms of decompression illness
- Hyperbaric treatment schedules – Planned sequences of hyperbaric pressure exposure using a specified breathing gas as medical treatment
- In-water recompression – In-water treatment for decompression sickness
- Dysbaric osteonecrosis – Ischemic bone disease caused by decompression bubbles
- Decompression sickness – Disorder caused by dissolved gases in the tissues forming bubbles during reduction of the surrounding pressure
- Barotrauma – Injury caused by pressure
- Hypercapnia – Abnormally high tissue carbon dioxide levels
- Hypothermia – A human body core temperature below 35.0 °C
- Hypoxia (medical) – Medical condition caused by lack of oxygen in the tissues
- Freediving blackout – Loss of consciousness caused by cerebral hypoxia towards the end of a breath-hold dive
- Latent hypoxia – Tissue oxygen concentration which is sufficient to support consciousness at depth, but not at surface pressure
- Motion sickness, also known as seasickness – Nausea caused by motion
- Oxygen therapy – Use of oxygen as a medical treatment
- Built-in breathing system (BIBS) – System for supply of breathing gas on demand within a confined space
- Surfer's ear – The common name for an abnormal bone growth within the external ear canal
- Toxicity – The ability of a chemical to cause damage to life
- Carbon monoxide poisoning – Toxic effects of carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen narcosis – Reversible narcotic effects of respiratory nitrogen at elevated partial pressures
- Equivalent narcotic depth – Method for comparing the narcotic effects of a trimix diving gas with air
- Oxygen toxicity – Toxic effects of breathing in oxygen at high concentrations
- Maximum operating depth – Depth of seawater at which a specified breathing gas mixture will have a limiting maximum oxygen partial pressure
- High-pressure nervous syndrome – A reversible diving disorder that occurs when a diver descends below about 150 m using a breathing gas based on helium
- Hydrogen narcosis – Psychotropic state induced by breathing hydrogen at high partial pressures
- Hydrogen sulfide – Poisonous, corrosive and flammable gas
- Vertigo – Type of dizziness where a person has the sensation of moving or surrounding objects moving
- Alternobaric vertigo – Dizziness resulting from unequal pressures in the middle ears
Diving safety related articles
_listen_to_a_safety_brief_from_their_dive_supervisor.jpg.webp)




Diving safety
Diving safety – Safety of underwater diving activities
- Checklist – An aide-memoire to ensure consistency and completeness in carrying out a task
- Code of practice (CoP) – A set of written rules which specifies how people working in a particular occupation should behave
- Dive team – A group of people working together to enhance dive safety and achieve a task
- Professional diving – Underwater diving where divers are paid for their work
- Diving supervisor – Professional diving team leader responsible for safety
- Stand-by diver – A member of a dive team who is ready to assist or rescue the working diver
- Bellman (diving) – The member of a dive team who acts as stand-by diver and tender from the diving bell
- Diver's attendant – The member of a dive team who assists the diver at the surface and tends the diver's umbilical or lifeline
- Life support technician – A member of a saturation diving team who operates the surface habitat
- Chamber operator – A person who operates a diving chamber
- Diving systems technician – A competent person who maintains and repairs diving life-support equipment
- Divemaster – Recreational dive leader certification and role
- Diving hazards – The agents and situations that pose a threat to the underwater diver
- Silt out – Reduction of underwater visibility by disturbing silt deposits
- Task loading – The relationship between operator capacity and the accumulated activities that must be done
- Diver rescue – Rescue of a distressed or incapacitated diver
- Rescue Diver – Recreational scuba certification emphasising emergency response and diver rescue
- Doing It Right (scuba diving) (DIR) – Technical diving safety philosophy
- Human factors in diving safety – The influence of physical, cognitive and behavioral characteristics of divers on safety
- Hazardous Materials Identification System – A numerical hazard rating using colour coded labels
- Occupational safety and health, also known as Occupational health and safety – Field concerned with the safety, health and welfare of people at work
- Safety culture – The attitude, beliefs, perceptions and values that employees share in relation to risks in the workplace
- Operations manual – Authoritative document of how things should be done in an organisation
- Emergency response plan
- Evacuation plan – Removal of personnel from a high risk area or a developing incident to a safer place
- Standard operating procedure (SOP) – A set of detailed instructions compiled by an organization Or a manager to help workers carry out operations safely and effectively
- Risk management – Set of measures for the systematic identification, analysis, assessment, monitoring and control of risks
- Hazard identification and risk assessment (HIRA)
- Hazard analysis (HAZID) – The identification of present hazards as the first step in a process to assess risk
- Job safety analysis (JSA) – Procedure to integrate safety practices into a particular task
- Risk assessment – Estimation of risk associated with exposure to a given set of hazards
- Risk control – Process in which identified risks are reduced or mitigated
- Hierarchy of hazard controls – System used in industry to eliminate or minimize exposure to hazards
- Incident pit – Conceptual model for explaining incident development and recovery
- Lockout–tagout (LOTO) – Isolation of dangerous machinery
- Permit To Work
- Redundancy – Duplication of critical components to increase reliability of a system
- Safety data sheet, also known as Material safety data sheet – System for cataloging information, potential hazards and instructions for safe use associated with a material or product
- Hazard identification and risk assessment (HIRA)
- Scuba diving fatalities – Deaths occurring while scuba diving or as a consequence of scuba diving.
- Single point of failure – A part of a system that, if it fails, will stop the entire system from working
- Water safety – Human safety in the vicinity of bodies of water
Notable diving incidents rescues and fatalities
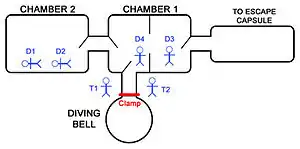
- Early diving incidents
- John Day (carpenter) – First recorded death in a diving chamber
- Charles Spalding – Scottish confectioner and amateur diving bell designer
- Ebenezer Watson – nephew of Charles Spalding and died in the same accident
- Freediving incidents
- Loïc Leferme – French freediving record breaker
- Audrey Mestre – French world record-setting freediver
- Nicholas Mevoli – American freediver who died while attempting to set a record
- Natalia Molchanova – Russian multiple world record holding freediver
- Professional diving incidents
- Johnson Sea Link accident – Manned submersible incident in which two divers died
- Offshore diving incidents
- Byford Dolphin#Diving bell accident – Semi-submersible offshore drilling rig
- Drill Master diving accident – Fatal diving bell accident off Norway in 1974
- Star Canopus diving accident – Fatal offshore diving bell accident in 1978
- Venture One diving accident – Saturation diving fatality in the North Sea in 1977
- Waage Drill II diving accident – Fatal saturation diving accident in the North Sea in 1975
- Wildrake diving accident – Fatal offshore diving accident in Scotland, 1979
- Rescues involving diving
- Tham Luang cave rescue – International operation to rescue a group of 12 boys and 1 adult from a flooded cave in Thailand in 2018
- Harrison Odjegba Okene
- Professional diving fatalities
- Roger Baldwin (diver) represented by Waage Drill II diving accident – Fatal saturation diving accident in the North Sea in 1975
- John Bennett (diver) – British technical diver and former record holder lost in commercial diving incident
- Victor F. Guiel Jr. represented by Wildrake diving accident – Fatal offshore diving accident in Scotland, 1979
- Craig M. Hoffman represented by Venture One diving accident – Saturation diving fatality in the North Sea in 1977
- Peter Henry Michael Holmes represented by Waage Drill II diving accident – Fatal saturation diving accident in the North Sea in 1975
- Edwin Clayton Link represented by Johnson Sea Link accident – Manned submersible incident in which two divers died
- Gerard Anthony Prangley represented by Star Canopus diving accident – Fatal offshore diving bell accident in 1978
- Pier Skipness represented by Drill Master diving accident – Fatal diving bell accident off Norway in 1974
- Robert John Smyth represented by Drill Master diving accident – Fatal diving bell accident off Norway in 1974
- Albert D. Stover represented by Johnson Sea Link accident – Manned submersible incident in which two divers died
- Richard A. Walker represented by Wildrake diving accident – Fatal offshore diving accident in Scotland, 1979
- Lothar Michael Ward represented by Star Canopus diving accident – Fatal offshore diving bell accident in 1978
- Joachim Wendler – German aquanaut who died in a diving accident
- Death of Bradley Westell – Fatal diving accident in the North Sea in 1995
- Arne Zetterström – Diver involved in experimental work with Hydrox breathing gas
- Scuba diving fatalities – Deaths occurring while scuba diving or as a consequence of scuba diving.
- Ricardo Armbruster – Spanish ecologist, adventurer and entrepreneur
- Allan Bridge – American conceptual artist
- David Bright (diver) – Wreck diver
- Berry L. Cannon – American aquanaut who died in a diving incident.
- Cotton Coulson – Photographer known for his work for National Geographic magazine
- Cláudio Coutinho – Brazilian football manager and coach
- E. Yale Dawson – American botanist and taxonomist
- Deon Dreyer – South African scuba diver who died in Bushman's Hole
- Milan Dufek – Czech singer, composer, guitarist and flautist
- Sheck Exley – American cave and deep diving pioneer and record breaker
- Maurice Fargues – French navy diver. First scuba fatality using aqualung for a depth record attempt
- Guy Garman – Scuba diver who died in a depth record attempt
- Steve Irwin – Australian zookeeper, conservationist and television personality
- Jim Jones (American football, born 1935) – American football defensive back
- Henry Way Kendall – American particle physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics
- Artur Kozłowski (speleologist) – Polish cave diver
- Chris and Chrissy Rouse, represented by The Last Dive – Non-fiction book by Bernie Chowdhury about a double wreck diving fatality
- Kirsty MacColl – English singer and songwriter
- Agnes Milowka – Australian cave diver
- François de Roubaix – French film score composer
- Dave Shaw (diver) – Australian technical diver and former record holder killed in a diving incident
- Wesley C. Skiles – American cave diver and underwater cinematographer.
- Dewey Smith – American aquanaut. Died in diving accident.
- Rob Stewart (filmmaker) – Canadian photographer, filmmaker and conservationist
- Esbjörn Svensson – Swedish jazz pianist
- Josef Velek – Czech journalist, author and environmentalist
Legal aspects of diving
Legal aspects of diving – how underwater diving and divers are affected by law
- Civil liability in recreational diving – Legal duty of care, negligence and liability in recreational diving
- Diving regulations – Legislation regulating diving activity, usually a branch of occupational health and safety.
- Duty of care – legal obligation to provide a standard of reasonable care when performing an activity that could foreseeably harm others
- Investigation of diving accidents – Forensic investigation of underwater diving accidents
- List of legislation regulating underwater diving – List of national and state legislation regulating underwater diving
Geography of diving

Recreational dive sites are specific places that recreational scuba divers go to enjoy the underwater environment. They include recreational diver training sites and technical diving sites beyond the range generally accepted for recreational diving. In this context all diving done for recreational purposes is included. Professional diving tends to be done where the job is, and with the exception of the recreational diving service industry, does not generally occur at specific sites chosen for their easy access, pleasant conditions or interesting features.
Recreational dive sites may be found in a wide range of bodies of water, and may be popular for various reasons, including accessibility, biodiversity, spectacular topography, historical interest and artifacts (such as shipwrecks), and water clarity. Tropical waters of high biodiversity and colourful sea life are popular recreational diving vacation destinations. South-east Asia, the Caribbean islands, the Red Sea and the Great Barrier Reef of Australia are regions where the clear, warm, waters and colourful and diverse sea life have made recreational diving an economically important tourist industry.
Recreational divers may accept a relatively high level of risk to dive at a site perceived to be of special interest. Wreck diving and cave diving have their adherents, and enthusiasts will endure considerable hardship, risk and expense to visit caves and wrecks where few have been before. Some sites are popular almost exclusively for their convenience for training and practice of skills, such as flooded quarries. They are generally found where more interesting and pleasant diving is not locally available, or may only be accessible when weather or water conditions permit. (Full article...)
History of underwater diving

History of underwater diving – History of the practice of descending below the water's surface to interact with the environment
- History of decompression research and development – A chronological list of notable events in the history of diving decompression.
- History of scuba diving – History of diving using self-contained underwater breathing apparatus
- Vintage scuba – Early model scuba equipment and the ongoing activity of diving with it
- Timeline of diving technology – A chronological list of notable events in the history of underwater diving equipment
Frogman operations

- 1982 invasion of the Falkland Islands – 1982 Argentine invasion of the Falklands
- Exercise Paddington Diamond – A joint Bolivian-British-Swiss scuba diving expedition to Lake Titicaca
- Raid on Algiers – Italian frogman raid on Allied ships in Algiers harbour in 1942
- Anti-frogman techniques
- Italian auxiliary ship Olterra – Salvaged Italian tanker used as support and base for WWII manned torpedo frogman raids on Allied shipping in Gibraltar
- Operation Algeciras – Argentine plan to sabotage a British warship in Gibraltar
- Operation Thunderhead – American amphibious mission during the civil war
- Raid on Alexandria (1941) – Italian frogman raid on British warships in Alexandria in 1941
- Sinking of the Rainbow Warrior – Covert attack by French military frogmen on a civilian ship in peacetime
- USS Westchester County (LST-1167) – US Navy tank landing ship built in 1952
Notable underwater salvage operations
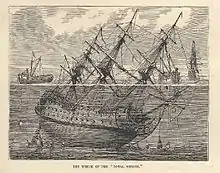
- HMS Royal George (1756)#Salvage attempts – Early salvage operation using bells and surface supplied divers
- SS Egypt#Salvage – Salvage of gold bullion from wreck using an armoured observation bell
- Kursk submarine disaster#Salvage operation – Raising the wreck of a Russian nuclear submarine
- USS Squalus represented by USS Sailfish (SS-192)#Sinking of Squalus and recommissioning – The successful rescue of the crew and later raising of the sunken vessel.
Diver training, certification, registration and standards

Diver training
- Diver training – Processes by which people develop the skills and knowledge to dive safely underwater
- Recreational diver certification represented by Diver certification – Certification as competent to dive to a specified standard
- Advanced Open Water Diver – Recreational scuba diving certification slightly above minimum entry level
- Autonomous diver – International minimum standard for entry level recreational scuba diver certification
- CMAS* scuba diver – Entry level recreational diving certification from CMAS
- Divemaster – Recreational dive leader certification and role
- Diving instructor – Person who trains and assesses underwater divers
- Open Water Diver – An entry-level autonomous diver certification for recreational scuba diving
- Master Instructor – A certificate given in recognition of a minimum level of experience in training divers after certification as a Diving Instructor, issued by PADI and SSI
- Master Scuba Diver – The highest non-leadership recreational scuba diver certification issued by some agencies
- Rescue Diver – Recreational scuba certification emphasising emergency response and diver rescue
- Supervised diver – Minimum requirements for a recreational diver to dive in open water under direct supervision
- Introductory diving – Non-certification scuba diving experience
- Universal Referral Program – A system to complete recreational scuba training with another instructor
Diver certification organisations
List of diver certification organizations – Agencies which issue certification for competence in diving skills
- Occupational diver certification authorities
- Australian Diver Accreditation Scheme (ADAS) – Australian based international occupational diver accreditation organisation
- Divers Institute of Technology – A private, commercial educational institution for the training of commercial divers
- Emergency Response Diving International (ERDI) – American organisation for training and certification of emergency response divers
- Health and Safety Executive (HSE) – Organisation responsible for the encouragement, regulation and enforcement of workplace health, safety and welfare in Great Britain
- South African Department of Employment and Labour – Department of the South African government responsible for matters related to employment
- Recreational diver certification agencies
- Freediver certification agencies
- AIDA International (AIDA) – Worldwide rule- and record-keeping body for competitive breath-hold events
- Confédération Mondiale des Activités Subaquatiques (CMAS) – International organisation for underwater activities in sport and science, and recreational diver training and certification
- Performance Freediving International (PI) – Freediver training agency
- Scuba Schools International (SSI) – Recreational scuba and freediving training and certification agency
- Recreational scuba certification agencies
- American Nitrox Divers International (ANDI) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- CEDIP members
- Association nationale des moniteurs de plongée (ANMP) – French recreational diver training and certification agency
- British Sub-Aqua Club (BSAC) – Recreational diving club, training and certification agency based in the UK
- Comhairle Fo-Thuinn (CFT) – governing body for recreational diving and underwater hockey in Ireland
- Confédération Mondiale des Activités Subaquatiques (CMAS) – International organisation for underwater activities in sport and science, and recreational diver training and certification
- CMAS Europe – Non-profit branch of the world underwater federation representing European affiliates – the branch of the world underwater federation representing European affiliates
- Fédération Française d'Études et de Sports Sous-Marins (FFESSM) – French diver training and certification agency
- Federazione Italiana Attività Subacquee (FIAS) – Italian non-profit recreational diver training organisation affiliated to CMAS
- Federación Española de Actividades Subacuáticas (FEDAS) – Spanish national federation for underwater activities, affiliated to CMAS
- Israeli Diving Federation (TIDF) – Israeli recreational diver training and certification agency
- Nederlandse Onderwatersport Bond (NOB)
- Sub-Aqua Association (SAA) – British recreational diver training and certification organisation
- Nederlandse Onderwatersport Bond (NOB)
- Scuba Educators International (SEI) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- Türkiye Sualtı Sporları Federasyonu (TSSF) – Turkish national governing body for underwater sport and lifesaving
- European Underwater Federation certification
- Israeli Diving Federation (TIDF) – Israeli recreational diver training and certification agency
- National Academy of Scuba Educators (NASE) – Recreational scuba training and certification agency
- Scuba Schools International (SSI) – Recreational scuba and freediving training and certification agency
- Global Underwater Explorers (GUE) – Recreational/technical scuba training and certification agency
- International Association for Handicapped Divers (IAHD) – Non-profit organisation based in the Netherlands
- International Association of Nitrox and Technical Divers (IANTD) – Recreational and technical scuba training and certification agency
- National Association for Cave Diving (NACD) – American non-profit organization for improving cave diving safety
- Scottish Sub Aqua Club (ScotSAC) – Scottish recreational diver training and certification agency
- United Diving Instructors (UDI) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- Unified Team Diving (UTD) – a recreational diver training and certification agency
- WRSTC and RSTC members
- American Canadian Underwater Certifications (ACUC) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- International Diving Educators Association (IDEA) – Recreational scuba training and certification agency
- National Association of Underwater Instructors (NAUI) – A non-profit training and certification agency association of scuba instructors
- Professional Association of Diving Instructors (PADI) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- Professional Diving Instructors Corporation (PDIC) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- Rebreather Association of International Divers (RAID) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- Scuba Diving International (SDI) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- Scuba Schools International (SSI) – Recreational scuba and freediving training and certification agency
- YMCA SCUBA Program – Defunct recreational diver training and certification agency.
- Technical diver certification agencies
- Cave diving certification agencies
- Cave Divers Association of Australia (CDAA) – Association to represent cave divers and administrate and support cave diving in Australia
- Cave Diving Group (CDG) – UK based cave diver training and certification agency
- National Association for Cave Diving (NACD) – American non-profit organization for improving cave diving safety
- American Nitrox Divers International (ANDI) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- British Sub-Aqua Club (BSAC) – Recreational diving club, training and certification agency based in the UK
- Diving Science and Technology (DSAT) – PADI affiliate and developer of recreational decompression planning tools
- Federazione Italiana Attività Subacquee (FIAS) – Italian non-profit recreational diver training organisation affiliated to CMAS
- Global Underwater Explorers (GUE) – Recreational/technical scuba training and certification agency
- International Association of Nitrox and Technical Divers (IANTD) – Recreational and technical scuba training and certification agency
- National Association of Underwater Instructors (NAUI) – A non-profit training and certification agency association of scuba instructors
- Professional Association of Diving Instructors (PADI) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- Professional Diving Instructors Corporation (PDIC) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- Rebreather Association of International Divers (RAID) – Recreational diver training and certification agency
- Technical Diving International (TDI) – Technical diver training and certification agency
- Trimix Scuba Association (TSA) – Recreational technical scuba training and certification agency
- Technical Extended Range (TXR) – Recreational scuba and freediving training and certification agency
- Unified Team Diving (UTD) – A recreational and technical diver training and certification agency
- Cave diving certification agencies
- Freediver certification agencies
- Scientific diver certification authorities
- American Academy of Underwater Sciences (AAUS) – Organization responsible for standards for American scientific diving certification and operation of scientific diving programs
- CMAS Scientific Committee – International organisation for underwater activities in sport and science, and recreational diver training and certification
- South African Department of Employment and Labour – Department of the South African government responsible for matters related to employment
Organisations setting international standards and codes of practice for diving and diver training
- Association of Diving Contractors International (ADCI)
- European Underwater Federation (EUF) – Umbrella organisation representing scuba diver training organisations in Europe
- International Diving Regulators and Certifiers Forum (IDRCF) – International forum of professional diver accreditation organisations
- International Diving Schools Association (IDSA) – Organisation to develop common standards for commercial diver training
- International Marine Contractors Association (IMCA) – International trade association for the marine contracting industry
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) – An international standard-setting body composed of representatives from national organizations for standards
- Rebreather Training Council (RTC)
- World Recreational Scuba Training Council (WRSTC) – Council of representatives of national or regional recreational diving councils to develop minimum diver training standards
- Scientific diving standards organizations
- American Academy of Underwater Sciences (AAUS) – Organization responsible for standards for American scientific diving certification and operation of scientific diving programs
- European Scientific Diving Panel – A panel of the European Network of Marine Research Institutes and Stations
Commercial diving schools
- Divers Academy International – A technical educational institution in New Jersey that offers training in commercial diving
Underwater diving organisations
Diver membership organisations
Diver membership organisations
- Freediver federations
- AIDA International (AIDA) – Worldwide rule- and record-keeping body for competitive breath-hold events
- AIDA Hellas – National representative of AIDA International in Greece
- British Freediving Association (BFA) – British affiliate to AIDA International
- Confédération Mondiale des Activités Subaquatiques (CMAS) – International organisation for underwater activities in sport and science, and recreational diver training and certification
- Recreational and technical scuba clubs and associations
- British Sub-Aqua Club (BSAC) – Recreational diving club, training and certification agency based in the UK
- Cave Divers Association of Australia (CDAA) – Association to represent cave divers and administrate and support cave diving in Australia
- Cave Diving Group (CDG) – UK based cave diver training and certification agency
- International Association for Handicapped Divers (IAHD) – Non-profit organisation based in the Netherlands
- National Association for Cave Diving (NACD) – American non-profit organization for improving cave diving safety
- Woodville Karst Plain Project (WKPP) – A project and organization to map the underwater cave systems of the Woodville Karst Plain
- Military services recreational diving organisations
- Naval Air Command Sub Aqua Club – An organisation within the Royal Navy for recreational and technical diving training for British naval aviation and fleet units
- Scientific, archaeological and historical diving organisations
- Historical Diving Society – UK based organisation to conserve diving heritage
- Nautical Archaeology Society (NAS) – British organisation to further research in nautical archaeology for the public benefit
- Save Ontario Shipwrecks (SOS) – A provincial heritage NGO in Ontario, Canada
- Sea Research Society – American non-profit educational society
- National underwater-sports federations
- Australian Underwater Federation (AUF) – The governing body for underwater sports in Australia
- British Octopush Association (BOA) – National body for underwater hockey in the United Kingdom
- British Underwater Sports Association (BUSA) – British affiliate to the world underwater federation sports committee.
- Comhairle Fo-Thuinn (CFT) – governing body for recreational diving and underwater hockey in Ireland
- Federación Española de Actividades Subacuáticas (FEDAS) – Spanish national federation for underwater activities, affiliated to CMAS
- Fédération Française d'Études et de Sports Sous-Marins (FFESSM) – French diver training and certification agency
- South African Underwater Sports Federation (SAUSF) – The official World Underwater Federation representative body in the Republic of South Africa.
- Türkiye Sualtı Sporları Federasyonu (TSSF) – Turkish national governing body for underwater sport and lifesaving
- Underwater Society of America (USOA) – American national representative organization for underwater sport.
- International underwater-sports federations
- AIDA International (AIDA) – Worldwide rule- and record-keeping body for competitive breath-hold events
- Confédération Mondiale des Activités Subaquatiques (CMAS) – International organisation for underwater activities in sport and science, and recreational diver training and certification
Diver nature conservation organisations
- Artificial Reef Society of British Columbia (ARSBC) – Canadian non-profit to create artificial reefs for habitat enhancement and recreation
- Green Fins – Organisation in South East Asia for preservation of coral reefs by improving diver behavior
- National Speleological Society – Cave Diving Section (NSS-CDS) – Organization for exploration, conservation, and study of caves in the United States
Diving industry trade associations
- Diving Equipment and Marketing Association (DEMA) – International trade association for the recreational diving equipment industry
Underwater environmental research organisations
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) – US government scientific agency
- Reef Life Survey (RLS) – Marine life monitoring programme based in Hobart, Tasmania
- South African Environmental Observation Network (SAEON) – A network to perform long-term ecological research in South Africa and surrounding waters
Diving medical research organisations
- Aerospace Medical Association – A professional organization in aviation, space, hyperbaric and environmental medicine
- Divers Alert Network (DAN) – International group of not-for-profit organizations for improving diving safety
- Diving Diseases Research Centre (DDRC) – British hyperbaric medical organisation
- Diving Medical Advisory Council (DMAC) – Independent organisation of diving medical specialists from Northern Europe
- European Diving Technology Committee (EDTC) – International organisation for improving professional diver safety
- European Underwater and Baromedical Society (EUBS) – Source of information for diving and hyperbaric medicine
- National Board of Diving and Hyperbaric Medical Technology – A non-profit organization for education and certification in diving and hyperbaric medicine
- Naval Submarine Medical Research Laboratory – Research unit for submarine and diving medicine
- Royal Australian Navy School of Underwater Medicine – Unit based in Sydney, Australia.
- Rubicon Foundation – Non-profit organization for promoting research and information access for underwater diving
- South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society (SPUMS) – A publisher for diving and hyperbaric medicine and physiology
- Southern African Underwater and Hyperbaric Medical Association (SAUHMA) – A special interest group of the Council of the South African Medical Association
- Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS) – US based organisation for research and education in hyperbaric physiology and medicine.
- United States Navy Experimental Diving Unit (NEDU) – The primary source of diving and hyperbaric operational guidance for the US Navy
Underwater diving publications
Books and manuals
- The Darkness Beckons – A history of UK cave diving by Martyn Farr
- Goldfinder – Autobiography of British diver and treasure hunter Keith Jessop
- The Last Dive – Non-fiction book by Bernie Chowdhury about a double wreck diving fatality
- Shadow Divers – Book by Robert Kurson recounting the discovery of a World War II German U-boat wreck
- The Silent World: A Story of Undersea Discovery and Adventure – Book by Jacques-Yves Cousteau and Frédéric Dumas
- Basic Cave Diving: A Blueprint for Survival – Book on cave diving safety by Sheck Exley
- Exploration and Mixed Gas Diving Encyclopedia
- Deep diving: an advanced guide to physiology, procedures and systems
- Diving manual A document providing extensive general information on the equipment, procedures and theoretical basis of underwater diving.
- NOAA Diving Manual – Training and operations manual for scientific diving Scientific diving manual published by the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration
- Professional Diver's Handbook John Bevan Ed. A manual of offshore diving
- U.S. Navy Diving Manual – Training and operations handbook
- Diving Medicine for Scuba Divers
- Bennett and Elliott's physiology and medicine of diving
- The Underwater Handbook: A Guide to Physiology and Performance for the Engineer
Legislation
- Diving at Work Regulations 1997
Codes of practice
(National or international codes of practice for diving)
- Code of practice – A set of written rules which specifies how people working in a particular occupation should behave
- IMCA Code of Practice for Offshore Diving A voluntary code of industry best practice followed by members of the International Marine Contractors Association.
- Code of Practice for Scientific Diving: Principles for the Safe Practice of Scientific Diving in Different Environments
Standards
(National or international standards relating to diving equipment or practices)
- EN 14143-2003 Respiratory equipment - Self-contained re-breathing diving apparatus
- BS EN 1802:2002 Transportable gas cylinders. Periodic inspection and testing of seamless aluminium alloy gas cylinders
- BS EN 1968:2002 Transportable gas cylinders. Periodic inspection and testing of seamless steel gas cylinders

- MIL-S-82258:1965 Military specification. Swim fins, rubber.
- GOST 22469:1977 Ласты резиновые для плавания. Общие технические условия. Swimming rubber flippers. General specifications.
- DIN 7876:1980 Tauchzubehör. Schwimmflossen. Maße, Anforderungen und Prüfung. Diving accessories for skin divers. Flippers. Dimensions, requirements and testing.
- BN-82/8444-17.02 Gumowy sprzęt pływacki - Płetwy pływackie (Rubber swimming equipment - Swimming fins).
- MS 974:1985 Specification for rubber swimming fins.
- ÖNORM S 4224:1988 Tauch-Zubehör; Schwimmflossen; Abmessungen, sicherheitstechnische Anforderungen, Prüfung, Normkennzeichnung. Diving accessories; fins; dimensions, safety requirements, testing, marking of conformity.
- MS 974:2002 Specification for rubber swimming fins. First revision.
- EN 16804:2015 Diving equipment. Diving open heel fins. Requirements and test methods.

- BS 4532:1969 Specification for snorkels and face masks. Amended 1977.
- GOST 20568:1975 Маски резиновые для плавания под водой. Общие технические условие. Rubber masks for submarine swimming. General specifications.
- DIN 7877:1980 Tauch-Zubehör. Tauchbrillen. Sicherheitstechnische Anforderungen und Prüfung. Diving accessories for skin divers. Diver's masks. Requirements and testing.
- BN-82/8444-17.01 Gumowy sprzęt pływacki - Maski pływackie (Rubber swimming equipment - Swimming masks).
- ANSI Z87.11:1985 Underwater Safety. Recreational Skin and Scuba Diving. Lenses for Masks.
- ÖNORM S 4225 Tauch-Zubehör; Tauchmasken (Tauchbrillen); Sicherheitstechnische Anforderungen, Prüfung, Normkennzeichnung. Diving accessories; divers’ masks; safety requirements, testing, marking of conformity.
- CNS 12497:1989 潛水鏡. Diving mask.
- CNS 12498:1989 潛水鏡檢驗法. Method of test for diving mask.
- EN 16805:2015 Diving equipment. Diving mask. Requirements and test methods.
- BS 4532:1969 Specification for snorkels and face masks. Amended 1977.
- DIN 7878:1980 Tauch-Zubehör; Schnorchel; Maße, Anforderungen, Prüfung. Diving accessories for skin divers. Snorkel. Technical requirements of safety, testing.
- ÖNORM S 4223:1988 Tauch-Zubehör; Schnorchel; Abmessungen, sicherheitstechnische Anforderungen, Prüfung, Normkennzeichnung. Diving accessories; snorkels; dimensions, safety requirements, testing, marking of conformity.
- DIN 7878:1991 Tauch-Zubehör; Schnorchel; Sicherheitstechnische Anforderungen und Prüfung. Diving accessories for skin divers. Snorkel. Safety requirements and testing.
- EN 1972:1997 Diving accessories. Snorkels. Safety requirements.
- EN 1972:2015 Diving equipment. Snorkels. Requirements and test methods.
- EN 1809:1998 Diving accessories. Buoyancy compensators. Functional and safety requirements, test methods.
- EN 1809:2014+A1:2016 Diving equipment. Buoyancy compensators. Functional and safety requirements, test methods.
- CNS 11251:1985 濕式潛水衣. Diving Wet Suit.
- EN 14225-1:2005 Diving suits. Wet suits. Requirements and test methods.
- EN 14225-1:2017 Diving suits. Wet suits. Requirements and test methods.
- EN 14225-2:2002 Diving suits. Dry suits. Requirements and test methods.
- EN 14225-2:2017 Diving suits. Dry suits. Requirements and test methods.
- EN 13319:2000 Diving accessories. Depth gauges and combined depth and time measuring devices. Functional and safety requirements, test methods.
- ISO 24801 Recreational diving services – Requirements for the training of recreational scuba divers
- ISO 21417 Recreational diving services – Requirements for training on environmental awareness for recreational divers
Recreational diving practices
- ISO 21416 Recreational diving services – Requirements and guidance on environmentally sustainable practices in recreational diving
Journals and magazines
- AquaCorps Magazine on technical diving, founded and edited by Michael Menduno
- Alert Diver Quarterly magazine of DAN om diving safety and recreational diving matters
- South Pacific Underwater Medical Society Journal
- Journal of Undersea and Hyperbaric Medicine
Repositories
- Rubicon Research Repository – On-line repository of documents relating to research on diving physiology, medicine, safety, equipment and procedures
Recreational dive site guides
Notable dive site guides with Wikipedia article.
- Index of recreational dive sites – Alphabetical listing of popular places for underwater diving
Authors of publications about diving

Authors of general non-fiction works on diving topics who are the subjects of Wikipedia articles.
- Michael C. Barnette – American underwater diver, author and founder of the Association of Underwater Explorers
- Victor Berge – Swedish diving pioneer and author
- Philippe Diolé – French author and undersea explorer
- Gary Gentile – American author and pioneering technical diver
- Bob Halstead – Underwater photographer, author, journalist and commentator on the recreational diving industry.
- Jarrod Jablonski – Pioneer American cave diver, author and previous cave diving record holder
- Trevor Jackson (diver) – Australian technical diver and author
- Richie Kohler – American technical diver and shipwreck historian
- Steve Lewis (diver) – Technical scuba diver and author
- John Mattera – American wreck diver and author
- Tom Mount – Pioneering technical and cave diver
Documentaries
Documentary movies focused on underwater diving.
- World Without Sun – 1964 film by Jacques Cousteau
- Voyage to the Edge of the World – 1976 French nature documentary
Underwater diving in popular culture
Movies, novels, TV series and shows, comics, graphic art, sculpture, games, myths, legends, and misconceptions. Fiction in general relating to all forms of diving, including hypothetical and imaginary methods, and other aspects of underwater diving which have become part of popular culture.
- Underwater diving in popular culture – Any aspects of underwater diving in fiction and popular culture
Researchers in diving medicine and physiology


- Arthur J. Bachrach – American psychologist and administrator
- Albert R. Behnke – US Navy physician and diving medicine researcher
- Paul Bert – French zoologist, physiologist and politician
- George F. Bond – US Navy physician and diving medicine and saturation diving researcher
- Robert Boyle – Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, and inventor
- Albert A. Bühlmann – Swiss physician and decompression researcher
- John R. Clarke – American scientist and underwater breathing apparatus authority
- William Paul Fife – US Air Force officer and hyperbaric medicine researcher
- John Scott Haldane – Scottish physiologist and decompression researcher
- Robert William Hamilton Jr. – American physiologist and researcher in hyperbaric physiology.
- Leonard Erskine Hill – British physiologist and diving physiology researcher
- Brian Andrew Hills – Physiologist who worked on decompression theory
- Felix Hoppe-Seyler – German physiologist and chemist
- Christian J. Lambertsen – American environmental and diving medicine specialist
- Simon Mitchell – New Zealand physician and author on diving medicine
- Charles Momsen – American pioneer in submarine rescue for the United States Navy
- John Rawlins R.N. – Royal Navy officer and pioneer in the field of diving medicine
- Charles Wesley Shilling – US Navy physician and decompression and hyperbaric medicine researcher
- Edward D. Thalmann – American hyperbaric medicine specialist and decompression researcher
- Jacques Triger – French geologist who invented the pressurised caisson
Underwater divers
Underwater divers are people who take part in underwater diving activities – Underwater diving is practiced as part of an occupation, or for recreation, where the practitioner submerges below the surface of the water or other liquid for a period which may range between seconds to order of a day at a time, either exposed to the ambient pressure or isolated by a pressure resistant suit, to interact with the underwater environment for pleasure, competitive sport, or as a means to reach a work site for profit or in the pursuit of knowledge, and may use no equipment at all, or a wide range of equipment which may include breathing apparatus, environmental protective clothing, aids to vision, communication, propulsion, maneuverability, buoyancy and safety equipment, and tools for the task at hand. (Full article...)
- Outline of underwater divers – Hierarchical outline list of biographical articles about underwater divers
- Index of underwater divers – Alphabetical listing of articles about underwater divers
- List of underwater divers – List of underwater divers whose exploits have made them notable.
Pioneers of diving
.jpg.webp)
- James F. Cahill – American scuba diving pioneer
- Alphonse and Théodore Carmagnolle – French inventors of the first anthropomorphic armoured diving suit
- Charles Condert – Inventor of an unsuccessful early scuba system
- Jacques Cousteau – Inventor of scuba-diving apparatus and film-maker
- Charles Anthony Deane – Pioneering diving engineer and inventor of a surface supplied diving helmet
- Guglielmo de Lorena – Italian inventor of a diving bell used for archaeological work on the Roman ships of lake Nemi
- Auguste Denayrouze – French inventor of a demand air supply regulator for underwater diving
- Frédéric Dumas – French pioneer of scuba diving
- Ted Eldred – Australian inventor of the single hose diving regulator
- Maurice Fernez – French inventor and pioneer in underwater breathing apparatus
- Émile Gagnan – French engineer and co-inventor of the open circuit demand scuba regulator
- Bret Gilliam – Pioneering technical diver and author.
- Edmond Halley – English astronomer, geophysicist, mathematician, meteorologist, and physicist
- Hans Hass – Austrian biologist, film-maker, and underwater diving pioneer
- Stig Insulán – Inventor of an adjustable automatic exhaust valve for variable volume dry suits
- Jim Jarret – Diver who test dived the first successful atmospheric diving suits
- Yves Le Prieur – French naval officer and inventor of a free-flow scuba system
- John Lethbridge – English wool merchant who invented a diving machine in 1715
- William Hogarth Main – Cave diver and scuba configuration experimentalist
- Phil Nuytten – Canadian deep-ocean explorer, scientist, and inventor of the Newtsuit
- Joseph Salim Peress – pioneering British diving engineer
- Benoît Rouquayrol – French inventor of an early diving demand regulator
- Dick Rutkowski – American pioneer in hyperbaric and diving medicine and use of mixed breathing gases for diving
- Joe Savoie – Inventor of the neck dam for lightweight helmets
- Augustus Siebe – German-born British engineer mostly known for his contributions to diving equipment
- Charles Spalding – Scottish confectioner and amateur diving bell designer
- Robert Sténuit – Belgian journalist, writer, underwater archeologist and the first aquanaut.
- Arne Zetterström – Diver involved in experimental work with Hydrox breathing gas
Underwater art and artists

- Jason deCaires Taylor – British sculptor and creator of the world's first underwater sculpture park
- Christ of the Abyss – A submerged bronze statue of Jesus Christ in the Mediterranean Sea
Miscellaneous
- Environmental impact of recreational diving – Effects of scuba diving on the underwater environment
- Scuba diving tourism – Industry based on recreational diver travel
- Shark tourism – Tourism industry based on viewing sharks in their natural habitat
- Sinking ships for wreck diving sites – Scuttling old ships to produce artificial reefs suitable for recreational wreck diving
Awards and events
- Hans Hass Award – Award in recognition of contribution made to the advancement of our knowledge of the ocean
- International Scuba Diving Hall of Fame – Annual event recognizing recreational scuba industry contributors
- London Diving Chamber Dive Lectures – A series of public lectures that have been hosted at the Royal Geographical Society in London
- NOGI Awards – Annual awards by Academy of Underwater Arts and Sciences.
See also
- Glossary of underwater diving terminology – Definitions of technical terms, jargon, diver slang and acronyms used in underwater diving