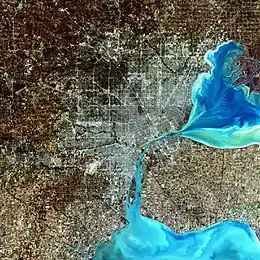
St. Clair County, Michigan
St. Clair County is a county located in the U.S. state of Michigan and bordering the west bank of the St. Clair River. As of the 2010 census, the population was 163,040.[3] It is the 13th-most populous county in the state. The county seat is Port Huron, located at the north end of the St. Clair River at Lake Huron.[1][4] The county was created September 10, 1820, and its government was organized in 1821.[1]
St. Clair County | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Seal | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Michigan | |
 Michigan's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 42°56′N 82°40′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | March 28, 1820 (created) 1821 (organized)[1][2] |
| Named for | St. Clare of Assisi |
| Seat | Port Huron |
| Largest city | Port Huron |
| Area | |
| • Total | 837 sq mi (2,170 km2) |
| • Land | 721 sq mi (1,870 km2) |
| • Water | 115 sq mi (300 km2) 14%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2019) | 159,128 |
| • Density | 226/sq mi (87/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Area code | 810 |
| Congressional district | 10th |
| Website | www |
Located northeast of Detroit, St. Clair County is part of the Detroit-Warren-Dearborn, MI Metropolitan Statistical Area. Geographically, it lies in the Thumb area of eastern Michigan.
Etymology
French explorer René Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle led an expedition to this area on August 12, 1679. These Roman Catholic men named the lake as Lac Sainte-Claire, because it was the feast day of Sainte Clare of Assisi, whom they venerated.[1][5] English mapmakers adopted the French name, identifying the lake feature as Saint Clare on maps dated as early as 1710. By the Mitchell Map of 1755, the spelling was given as St. Clair, which is the current version.[6] Located along the western shores of Lake St. Clair and the St. Clair River, the county was named for them by European-American settlers.
The name is sometimes mistakenly attributed to honoring Arthur St. Clair, an American Revolutionary War General and Governor of the Northwest Territory, but it was established long before he was considered a notable figure.[7] The earlier spelling of the lake's name may have been conflated with English practice and the name of the general, as several political jurisdictions near the lake and the river, such as St. Clair County, St. Clair Township, and the cities of St. Clair and St. Clair Shores, share this spelling. See also, List of Michigan county name etymologies.
The name has sometimes been mistakenly attributed to honoring Patrick Sinclair, a British officer who purchased land on the St. Clair River at the mouth of the Pine River. In 1764, he built Fort Sinclair there, which was in use for nearly 20 years before being abandoned.[8] As noted, the name was established before he was active in the area.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 837 square miles (2,170 km2), of which 721 square miles (1,870 km2) is land and 115 square miles (300 km2) (14%) is water.[9] St. Clair County is one of five counties that form the peninsula, known as the Thumb, that projects into Lake Huron. St. Clair County is closely connected in terms of economy with its neighbors, Metropolitan Detroit and Sanilac County in Michigan, and Lambton County across the river in Ontario, Canada. Saint Clair County is the principal county in The Blue Water Area, a sub-region of the Thumb.
Adjacent counties
- Sanilac County (north)
- Lapeer County (west)
- Macomb County (south)
- Lambton County, Ontario (east)
Major highways
 I-69 enters the county from the west, coming from Lansing and Flint, terminating at the approach to the Blue Water Bridge in Port Huron. (Once fully completed, the mainline of I-69 will span from Brownsville, Texas to Port Huron, Michigan.)
I-69 enters the county from the west, coming from Lansing and Flint, terminating at the approach to the Blue Water Bridge in Port Huron. (Once fully completed, the mainline of I-69 will span from Brownsville, Texas to Port Huron, Michigan.) I-94 enters St. Clair County from the southwest, having traversed the entire Metro Detroit region, and terminates at the approach to the Blue Water Bridge in Port Huron. On the Canadian side of the border, in Sarnia, Ontario, the route heads easterly designated as Highway 402.
I-94 enters St. Clair County from the southwest, having traversed the entire Metro Detroit region, and terminates at the approach to the Blue Water Bridge in Port Huron. On the Canadian side of the border, in Sarnia, Ontario, the route heads easterly designated as Highway 402. BL I-69
BL I-69 BL I-94
BL I-94 M-19
M-19 M-25 follows the Lake Huron–Saginaw Bay shoreline, beginning in Bay City and ending at a junction with |I-94/|I-69, and BL I-94/BL I-69 on the north side of Port Huron.
M-25 follows the Lake Huron–Saginaw Bay shoreline, beginning in Bay City and ending at a junction with |I-94/|I-69, and BL I-94/BL I-69 on the north side of Port Huron. M-29
M-29 M-136
M-136 M-154 serves Harsen's Island, in Lake St. Clair.
M-154 serves Harsen's Island, in Lake St. Clair.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1830 | 1,114 | — | |
| 1840 | 4,606 | 313.5% | |
| 1850 | 10,420 | 126.2% | |
| 1860 | 26,604 | 155.3% | |
| 1870 | 36,661 | 37.8% | |
| 1880 | 46,197 | 26.0% | |
| 1890 | 52,105 | 12.8% | |
| 1900 | 55,228 | 6.0% | |
| 1910 | 52,341 | −5.2% | |
| 1920 | 58,009 | 10.8% | |
| 1930 | 67,563 | 16.5% | |
| 1940 | 76,222 | 12.8% | |
| 1950 | 91,599 | 20.2% | |
| 1960 | 107,201 | 17.0% | |
| 1970 | 120,175 | 12.1% | |
| 1980 | 138,802 | 15.5% | |
| 1990 | 145,607 | 4.9% | |
| 2000 | 164,235 | 12.8% | |
| 2010 | 163,040 | −0.7% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 159,128 | [10] | −2.4% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[11] 1790-1960[12] 1900-1990[13] 1990-2000[14] 2010-2019[3] | |||
The 2010 United States Census[15] indicates St. Clair County had a 2010 population of 163,040. This is a decrease of -1,195 people from the 2000 United States Census. Overall, the county had a -0.7% growth rate during this ten-year period. In 2010 there were 63,841 households and 44,238 families in the county. The population density was 226.1 per square mile (87.3 square kilometers). There were 71,822 housing units at an average density of 99.6 per square mile (38.5 square kilometers). 93.9% were White, 2.4% Black or African American, 0.5% Asian, 0.4% Native American, 0.7% of some other race and 2.0% of two or more races. 2.9% were Hispanic or Latino (of any race). 25.9% identified as of German, 10.2% Polish, 9.3% Irish, 8.5% English, 6.5% French, 6.5% American, and 5.1% Italian ancestry.[15]
There were 63,841 households, out of which 31.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.9% were opposite-sex families, 11.4% had a female householder with no husband present, 30.7% were non-families, and 25.5% were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.52 and the average family size was 3.01.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 23.7% under age of 18, 8.0% from 18 to 24, 23.8% from 25 to 44, 30.1% from 45 to 64, and 14.5% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 41 years. For every 100 females, there were 98.1 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 95.7 males.
The 2010 American Community Survey 1-year estimate[15] indicates the median income for a household in the county was $44,369 and the median income for a family was $53,207. Males had a median income of $30,056 versus $16,771 for females. The per capita income for the county was $22,390. About 10.4% of families and 15.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 22.7% of those under the age 18 and 6.8% of those age 65 or over.
Government
The county government operates the jail, maintains rural roads, operates the major local courts, keeps files of deeds and mortgages, maintains vital records, administers public health regulations, and participates with the state in the provision of welfare and other social services. The county board of commissioners controls the budget but has only limited authority to make laws or ordinances. In Michigan, most local government functions — police and fire, building and zoning, tax assessment, street maintenance, etc. — are the responsibility of individual cities and townships.
Elected officials
- Prosecuting Attorney: Michael D. Wendling
- Sheriff: Mat King
- County Clerk/Register of Deeds: Jay DeBoyer
- County Treasurer: Kelly M. Roberts-Burnett, CPA
- Drain Commissioner: Robert Wiley
- County Commissioner District 2: Karl S. Tomion (R)
- County Commissioner District 4: Harry Dunn (R)
- 31st Circuit Court: Hon. Daniel Kelly; Hon Cynthia Lane; Hon. Michael West
- 72nd District Court: Hon. Michael Hulewicz; Hon. John Monaghan; Hon. Cynthia Platzer
- 74th Probate Court: Hon. Elwood Brown; Hon. John Tomlinson
(information as of November 2018)
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 64.2% 59,185 | 34.0% 31,363 | 1.8% 1,654 |
| 2016 | 62.9% 49,051 | 31.5% 24,553 | 5.6% 4,399 |
| 2012 | 52.9% 39,271 | 45.8% 33,983 | 1.3% 927 |
| 2008 | 47.6% 38,536 | 50.3% 40,677 | 2.1% 1,687 |
| 2004 | 53.6% 42,740 | 45.4% 36,174 | 1.0% 829 |
| 2000 | 49.0% 33,571 | 48.2% 33,002 | 2.8% 1,943 |
| 1996 | 37.4% 22,495 | 48.0% 28,881 | 14.5% 8,742 |
| 1992 | 36.7% 24,508 | 35.0% 23,385 | 28.3% 18,939 |
| 1988 | 60.3% 32,336 | 39.0% 20,909 | 0.8% 413 |
| 1984 | 67.6% 36,114 | 31.8% 16,998 | 0.5% 287 |
| 1980 | 55.6% 31,021 | 36.6% 20,410 | 7.8% 4,348 |
| 1976 | 52.7% 26,311 | 45.6% 22,734 | 1.7% 844 |
| 1972 | 63.1% 28,471 | 34.8% 15,712 | 2.2% 976 |
| 1968 | 49.4% 21,084 | 38.1% 16,251 | 12.5% 5,334 |
| 1964 | 40.8% 17,011 | 59.1% 24,662 | 0.2% 62 |
| 1960 | 59.8% 27,366 | 40.1% 18,332 | 0.2% 76 |
| 1956 | 69.5% 29,116 | 30.4% 12,753 | 0.1% 51 |
| 1952 | 69.3% 27,894 | 30.5% 12,268 | 0.2% 94 |
| 1948 | 61.8% 17,883 | 36.8% 10,647 | 1.4% 412 |
| 1944 | 61.6% 19,175 | 38.0% 11,813 | 0.4% 135 |
| 1940 | 60.2% 18,635 | 39.6% 12,259 | 0.3% 82 |
| 1936 | 45.9% 12,760 | 45.6% 12,663 | 8.5% 2,359 |
| 1932 | 53.1% 14,883 | 45.6% 12,776 | 1.4% 382 |
| 1928 | 71.6% 18,177 | 28.2% 7,151 | 0.3% 71 |
| 1924 | 76.5% 17,435 | 15.8% 3,600 | 7.7% 1,745 |
| 1920 | 75.1% 14,938 | 23.0% 4,566 | 1.9% 375 |
| 1916 | 57.4% 6,538 | 40.5% 4,617 | 2.1% 237 |
| 1912 | 27.5% 2,958 | 28.0% 3,008 | 44.6% 4,798 |
| 1908 | 62.2% 7,287 | 32.1% 3,756 | 5.7% 666 |
| 1904 | 69.0% 8,305 | 27.0% 3,248 | 4.0% 482 |
| 1900 | 61.4% 7,432 | 36.4% 4,403 | 2.2% 268 |
| 1896 | 56.9% 7,160 | 40.7% 5,130 | 2.4% 303 |
| 1892 | 48.8% 5,371 | 47.7% 5,248 | 3.5% 382 |
| 1888 | 49.0% 5,419 | 47.8% 5,286 | 3.1% 346 |
| 1884 | 44.2% 4,017 | 51.4% 4,668 | 4.4% 401 |
Parks
St. Clair County is home to five county parks: Columbus County Park, Fort Gratiot County Park, Fort Gratiot Light station, Goodells County Park, and Woodsong County Park. St. Clair County also operates the Wadhams to Avoca Trail and works with local units of government to develop the Bridge to Bay Trail.[17]
Communities
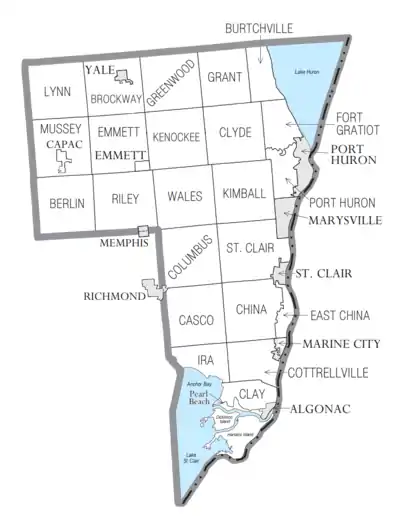
Cities
- Algonac
- Marine City
- Marysville
- Memphis (partial)
- Port Huron (county seat)
- Richmond (partial)
- St. Clair
- Yale
Charter townships
Civil townships
- Berlin Township
- Brockway Township
- Burtchville Township
- Casco Township
- Clay Township
- Clyde Township
- Columbus Township
- Cottrellville Township
- Emmett Township
- Grant Township
- Greenwood Township
- Ira Township
- Kenockee Township
- Kimball Township
- Lynn Township
- Mussey Township
- Riley Township
- St. Clair Township
- Wales Township
Census-designated place
Other unincorporated communities
- Abbottsford
- Adair
- Allenton
- Anchorville
- Atkins
- Avoca
- Avalon Beach
- Bedore
- Belle River
- Berville
- Blaine
- Broadbridge Station
- Brockway
- Casco
- Cherry Beach
- Clays Landing
- Columbus
- Copeland Corner
- Fair Haven
- Fargo
- Forster
- Gardendale
- Grande Pointe
- Goodells
- Hawthorne
- Jeddo
- Kimball
- Keewahdin
- Lakeport
- Lambs
- Lesterville
- Maple Leaf
- Martindale Beach
- Miller
- Muirs
- Muttonville
- North Lakeport
- North Street
- Perch Point
- Peters
- Pointe aux Tremble
- Rattle Run
- Riley Center
- Riverside
- Roberts Landing
- Ruby
- Sans Souci
- Smiths Creek
- Snyderville
- South Park
- Sparlingville
- Starville
- Tappan
- Thornton
- Wadhams
- Wales
- West Tappan
See also
References
- "Bibliography on St. Clair County". Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University. Retrieved January 29, 2013.
- "St. Clair County", Michigan History MagazineArchived April 17, 2003, at the Wayback Machine
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 29, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Jenks, p. 22
- Jenks, pp. 23-24
- Michigan County Names
- Fuller, pp. 21-22
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on November 13, 2013. Retrieved September 28, 2014.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved May 21, 2020.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 28, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved September 28, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 28, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 28, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 11, 2012.
- http://uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS
- "Columbus Park Overview" (PDF). Retrieved 2014-01-02.
References
- Fuller, George Newman (2005) [1926?]. "Indians and Explorations". Local history and personal sketches of St. Clair and Shiawassee counties. Ann Arbor, Mich.: University of Michigan Library. pp. 17–27. Retrieved 2007-11-23.
- Jenks, William Lee (2005) [1912]. "Origin of Name". St. Clair County, Michigan, its history and its people. Ann Arbor, Mich.: University of Michigan Library. pp. 20–24. Retrieved 2007-11-23.