1976 United States presidential election
The 1976 United States presidential election was the 48th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 2, 1976. Democrat Jimmy Carter of Georgia defeated incumbent Republican President Gerald Ford from Michigan. Carter's win represented the lone Democratic victory in a period of Republican dominance at the presidential level; he was the first Democrat to win a presidential election since 1964 and the last until 1992.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 53.5%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
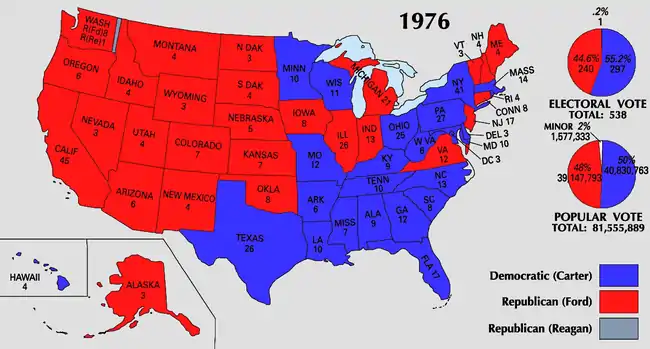
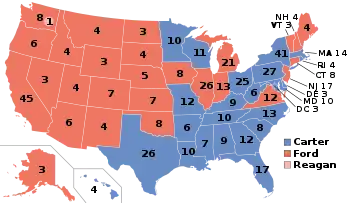 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Carter/Mondale and red denotes those won by Ford/Dole. Pink is the electoral vote for Ronald Reagan by a Washington faithless elector. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes cast by each state and the District of Columbia. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
President Richard Nixon had won the 1972 election with Spiro Agnew as his running mate, but in 1973 Agnew resigned and Ford was appointed as vice president via the 25th Amendment. When Nixon resigned in 1974 in the wake of the Watergate scandal, Ford ascended to the presidency, becoming the first president to take office without having been elected as either president or vice president. He faced a strong challenge from conservative former governor and future president Ronald Reagan of California in the Republican primaries, but Ford narrowly prevailed at the convention. Carter was little-known at the start of the Democratic primaries, but the former governor of Georgia emerged as the front-runner after his victories in the first set of primaries. Campaigning as a political moderate and Washington outsider, Carter defeated opponents such as Jerry Brown and Mo Udall to clinch the Democratic nomination.
Ford pursued a "Rose Garden strategy" in which he sought to portray himself as an experienced leader focused on fulfilling his role as chief executive. Carter emphasized his status as a reformer who was "untainted" by Washington. Saddled with a poor economy, the fall of South Vietnam and his unpopular pardon of Nixon, Ford trailed by a wide margin in polls taken after Carter's formal nomination in July 1976. Ford's polling rebounded after a strong performance in the first presidential debate, and the race was close on election day.
Carter won a majority of the popular and electoral vote. He carried every state in the South except Virginia, while Ford dominated the Western states. Carter remains the only Democratic candidate since 1964 to win a majority of the Southern states. Ford won 27 states, the most states ever carried by a losing candidate. Both of the major party vice-presidential nominees, Walter Mondale in 1984 and Bob Dole in 1996, would later win their respective party's presidential nominations, but lose in the general election.
As of 2020, this was the last time that Alabama, Mississippi, South Carolina, and Texas voted for the Democratic candidate in a presidential election, as well as the last election where the winning candidate did not win a majority of the 51 jurisdictions (the 50 states plus the District of Columbia). However, it was not the last time a candidate won the popular vote without winning the majority of states. Al Gore in 2000 and Hillary Clinton in 2016 both won the popular vote but did not carry the electoral vote.
Nominations
Democratic Party
Democratic candidates
- Jimmy Carter, former governor of Georgia
- Morris Udall, U.S. Representative from Arizona
- Jerry Brown, Governor of California
- George Wallace, Governor of Alabama
- Ellen McCormack, housewife from New York
- Frank Church, U.S. Senator from Idaho
- Henry M. Jackson, U.S. Senator from Washington
- Fred R. Harris, former U.S. Senator from Oklahoma
- Robert Byrd, U.S. Senator from West Virginia
- Milton Shapp, Governor of Pennsylvania
- Sargent Shriver, former U.S. Ambassador to France, from Maryland
- Birch Bayh, U.S. Senator from Indiana
- Lloyd Bentsen, U.S. Senator from Texas
- Terry Sanford, former governor of North Carolina
- Walter Fauntroy, U.S. Delegate from Washington, D.C.
| Jimmy Carter | Walter Mondale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.jpg.webp) |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 76th Governor of Georgia (1971–1975) |
U.S. senator from Minnesota (1964–1976) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The surprise winner of the 1976 Democratic presidential nomination was Jimmy Carter, a former state senator and governor of Georgia. When the primaries began, Carter was little-known at the national level, and many political pundits regarded a number of better-known candidates, such as Senator Henry M. Jackson from Washington, Representative Morris Udall from Arizona, Governor George Wallace of Alabama, and California Governor Jerry Brown, as the favorites for the nomination. However, in the wake of the Watergate scandal, Carter realized that his status as a Washington outsider, political centrist, and moderate reformer could give him an advantage over his better-known establishment rivals. Carter also took advantage of the record number of state primaries and caucuses in 1976 to eliminate his better-known rivals one-by-one.
Senator Jackson made a fateful decision not to compete in the early Iowa caucus and New Hampshire primary, which Jimmy Carter won after liberals split their votes among four other candidates. Though Jackson went on to win the Massachusetts and New York primaries, he was forced to quit the race on May 1 after losing the critical Pennsylvania primary to Carter by twelve percentage points. Carter then defeated Governor Wallace, his main conservative challenger, by a wide margin in the North Carolina primary, thus forcing Wallace to end his campaign. Representative Udall, a liberal, then became Carter's main challenger. He finished second to Carter in the New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Wisconsin, New York, Michigan, South Dakota, and Ohio primaries, and won the caucuses in his home state of Arizona, while running even with Carter in the New Mexico caucuses. However, the fact that Udall finished second to Carter in most of these races meant that Carter steadily accumulated more delegates for the nomination than he did.
As Carter closed in on the nomination, an "ABC" (Anybody But Carter) movement started among Northern and Western liberal Democrats who worried that Carter's Southern upbringing would make him too conservative for the Democratic Party. The leaders of the "ABC" movement – Idaho Senator Frank Church and California Governor Jerry Brown – both announced their candidacies for the Democratic nomination and defeated Carter in several late primaries. However, their campaigns started too late to prevent Carter from gathering the remaining delegates he needed to capture the nomination.
By June 1976, Carter had captured more than enough delegates to win the Democratic nomination. At the 1976 Democratic National Convention, Carter easily won the nomination on the first ballot; Udall finished in second place. Carter then chose Minnesota Senator Walter Mondale, a liberal and political protégé of Hubert Humphrey, as his running mate.
Republican Party
Republican candidates
- Gerald Ford, President of the United States
- Ronald Reagan, former governor of California
| Gerald Ford | Bob Dole | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
.jpg.webp) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 38th President of the United States (1974–1977) |
U.S. senator from Kansas (1969–1996) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

The contest for the Republican Party's presidential nomination in 1976 was between two serious candidates: incumbent president Gerald Ford from Michigan, a member of the party's moderate wing, and former governor of California, Ronald Reagan, a member of the party's conservative wing. The presidential primary campaign between the two men was hard-fought and relatively even; by the start of the Republican Convention in August 1976, the race for the nomination was still too close to call. Ford defeated Reagan by a narrow margin on the first ballot at the 1976 Republican National Convention in Kansas City, and chose Senator Bob Dole from Kansas as his running mate in place of incumbent Vice President Nelson Rockefeller, who had announced the previous year that he was not interested in being considered for the Vice Presidential nomination.[3] Since Rockefeller was the second vice president to assume the office as ruled by the Section 2 of the 25th Amendment and the other one who achieved this feat was Ford who was nominated in 1976, this made Rockefeller the only vice president never contested in the general election both as presidential and vice presidential nominee. All presidents had contested for the office, either as president or vice president, with the exception of Ford who appeared only after being president and all other vice presidents other than Ford had contested for the office. The 1976 Republican Convention was the last political convention to open with the presidential nomination still being undecided until the actual balloting at the convention.
Others
- Roger MacBride, who had gained fame in the 1972 election as a faithless elector, ran as the nominee of the Libertarian Party.
- Eugene McCarthy, a former Democratic Senator from Minnesota, ran as an independent candidate.
- Ben Bubar, Prohibition Party nominee.
- Frank Zeidler, former mayor of Milwaukee, Wisconsin, ran as the nominee of Socialist Party USA, which was founded in a split with Socialist Party of America.
- Gus Hall, four-time Communist Party candidate[4]
General election
Fall campaign

One of the advantages Ford held over Carter as the general election campaign began was that as president he was privileged to preside over events dealing with the United States Bicentennial; this often resulted in favorable publicity for Ford. The Washington, D.C., fireworks display on the Fourth of July was presided over by the president and televised nationally.[5] On July 7, 1976, the President and First Lady served as hosts at a White House state dinner for Elizabeth II and Prince Philip of the United Kingdom, which was televised on the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) network. These events were part of Ford's "Rose Garden" strategy to win the election, meaning that instead of appearing as a typical politician, Ford presented himself as a "tested leader" who was busily fulfilling the role of national leader and chief executive. Not until October did Ford leave the White House to campaign actively across the nation.
Jimmy Carter ran as a reformer who was "untainted" by Washington political scandals,[6] which many voters found attractive in the wake of the Watergate scandal that had led to President Richard Nixon's resignation. Ford, although personally unconnected with Watergate, was seen by many as too close to the discredited Nixon administration, especially after he granted Nixon a presidential pardon for any crimes he might have committed during his term of office. Ford's pardon of Nixon caused his popularity, as measured by public-opinion polls, to plummet. Ford's refusal to explain his reasons for pardoning Nixon publicly (he would do so in his memoirs several years later), also hurt his image.
Ford unsuccessfully asked Congress to end the 1950s-era price controls on natural gas, which caused a dwindling of American natural gas reserves after the 1973 Oil Crisis.[7] Carter stated during his campaign that he opposed the ending of the price controls and thought such a move would be "disastrous".[8]
After the Democratic National Convention, Carter held a 33-point lead over Ford in the polls.[9] However, as the campaign continued, the race greatly tightened. During the campaign Playboy magazine published a controversial interview with Carter; in the interview, Carter admitted to having "lusted in my heart" for women other than his wife and used the word "screw," which cut into his support among women and evangelical Christians.[10] On September 23, Ford performed well in what was the first televised presidential debate since 1960. Polls taken after the debate showed that most viewers felt that Ford was the winner. Carter was also hurt by Ford's charges that he lacked the necessary experience to be an effective national leader, and that Carter was vague on many issues.

However, Ford also committed a costly blunder in the campaign that halted his momentum. During the second presidential debate on October 6, in a response to Max Frankel, Ford stumbled when he asserted that "there is no Soviet domination of Eastern Europe and there never will be under a Ford administration". He added that he did not "believe that the Poles consider themselves dominated by the Soviet Union" and made the same claim with regard to Yugoslavia and Romania (Yugoslavia was not a Warsaw Pact member).[11] Ford refused to retract his statement for almost a week after the debate; as a result his surge in the polls stalled and Carter was able to maintain a slight lead in the polls.
A vice-presidential debate, the first ever formal one of its kind,[12] between Bob Dole and Walter Mondale also hurt the Republican ticket when Dole asserted that military unpreparedness on the part of Democratic presidents was responsible for all of the wars the U.S. had fought in the 20th century. Dole, a World War II veteran, noted that in every 20th-century war from World War I to the Vietnam War, a Democrat had been president. Dole then pointed out that the number of U.S. casualties in "Democrat wars" was roughly equal to the population of Detroit. Many voters felt that Dole's criticism was unfairly harsh and that his dispassionate delivery made him seem cold. Years later, Dole would remark that he regretted the comment, having viewed it as hurting the Republican ticket.[13] One factor which did help Ford in the closing days of the campaign was a series of popular television appearances he did with Joe Garagiola Sr., a retired baseball star for the St. Louis Cardinals and a well-known announcer for NBC Sports. Garagiola and Ford appeared in a number of shows in several large cities. During the show Garagiola would ask Ford questions about his life and beliefs; the shows were so informal, relaxed, and laid-back that some television critics labelled them the "Joe and Jerry Show". Ford and Garagiola obviously enjoyed one another's company, and they remained friends after the election was over.
Presidential debates
There were three presidential debates and one vice presidential debate during the 1976 general election.[14][15]
| No. | Date | Host | City | Moderator | Panelists | Participants | Viewership (Millions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Thursday, September 23, 1976 | Walnut Street Theatre | Philadelphia, Pennsylvania | Edwin Newman | Elizabeth Drew James P. Gannon Frank Reynolds |
Governor Jimmy Carter President Gerald Ford |
69.7[14] |
| P2 | Wednesday, October 6, 1976 | Palace of Fine Arts | San Francisco, California | Pauline Frederick | Max Frankel Henry Trewhitt Richard Valeriani |
Governor Jimmy Carter President Gerald Ford |
63.9[14] |
| VP | Friday, October 15, 1976 | Alley Theatre | Houston, Texas | James Hoge | Marilyn Berger Hal Bruno Walter Mears |
Senator Bob Dole Senator Walter Mondale |
43.2[14] |
| P3 | Friday, October 22, 1976 | Phi Beta Kappa Memorial Hall[16] | Williamsburg, Virginia | Barbara Walters | Joseph Kraft Robert Maynard Jack Nelson |
Governor Jimmy Carter President Gerald Ford |
62.7[14] |
Results
Despite his campaign's blunders, Ford managed to close the remaining gap in the polls and by election day, the race was judged to be even. It took most of that night and the following morning to determine the winner. It was not until 3:30 am (EST), that the NBC television network was able to declare that Carter had carried Mississippi and had thus accumulated more than the 270 electoral votes needed to win (seconds later, ABC News also declared Carter the winner based on projections for Carter in Wisconsin and Hawaii while CBS News announced Carter's victory at 3:45 am).[17] Carter defeated Ford by two percentage points in the national popular vote.
The electoral vote was the closest since 1916; Carter carried 23 states with 297 electoral votes, while Ford won 27 states with 240 electoral votes (one elector from Washington state, pledged to Ford, voted for Reagan). Carter's victory came primarily from his near-sweep of the South (he lost only Virginia and Oklahoma) and his narrow victories in large Northern states, such as New York, Ohio, and Pennsylvania. Ford did well in the West, carrying every state in that region except for Hawaii. The most tightly contested state in the election was Oregon; Ford won that state by under 2,000 votes.
A switch of 3,687 votes in Hawaii and 5,559 votes in Ohio, or 144,384 votes from New York from Carter to Ford would have triggered the first contingent election since 1825, as Ford would have received 269 electoral votes and Carter would have received 268, or 282 for Ford and 256 for Carter.[18] By percentage of the vote, the states that secured Carter's victory were Wisconsin (1.68% margin) and Ohio (.27% margin). Had Ford won these states and all other states he carried, he would have won the presidency. The 27 states he won were and still are the most states ever carried by a losing candidate for president. Had Ford won the election, the provisions of the 22nd amendment would have disqualified him from running in 1980, as he served more than two years of Nixon's second term.
Carter was the first Democrat since John F. Kennedy in 1960 to carry the states of the Deep South (Bill Clinton is the only Democrat since 1976 to carry more than one state from the Deep South, doing so in both 1992 and 1996) and the first since Lyndon B. Johnson in 1964 to carry a majority of all southern states. Carter performed very strongly in his home state of Georgia, carrying 66.7% of the vote and every county in the state. His winning of 23 states was only the first time since the 1960 election and the second time in history that the winner of the election won fewer than half the states. His 50.1% of the vote was the only time since 1964 that a Democrat managed to obtain an absolute majority of the popular vote in a presidential election until Barack Obama won 52.9% of the vote in 2008. Carter is one of six Democrats since the American Civil War to obtain an absolute majority of the popular vote, the others being Samuel J. Tilden, Franklin D. Roosevelt, Lyndon B. Johnson, Barack Obama and Joe Biden.
This election represents the last time to date that Texas, Mississippi, Alabama, or South Carolina would vote Democratic, and the last time North Carolina would vote Democratic until 2008, as well as the last time Florida voted Democratic until 1996, the last time Arkansas, Delaware, Kentucky, Louisiana, Missouri, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Tennessee voted Democratic until 1992. It is also the last time in which Shasta, Yuba, Placer, El Dorado and Madera Counties in California, Adams and Brown in Ohio, Brazoria, Williamson and McLennan Counties in Texas, Madison County in Alabama, Duval and Brevard Counties in Florida, Warren County, Kentucky and St. Mary's County, Maryland would vote Democratic. Cobb and Gwinnett Counties in Georgia would never again vote Democratic until 2016.[19] This election was the last time that a Democrat won the presidency without winning California, Connecticut, Illinois, Iowa, Maine, Michigan, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, Oregon, Vermont and Washington.
It was the first time in exactly 100 years (since 1876) when Florida and Virginia supported different candidates. This would happen again in 1996, 2016 and 2020. It was also the first time since Oklahoma statehood in 1907 when the Sooner State and Tennessee supported different candidates, an occurrence replicated only in 1992 and 1996.
Statistics
Source (Popular Vote): Leip, David. "1976 Presidential Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved August 7, 2005.
Source (Electoral Vote): "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved August 7, 2005.
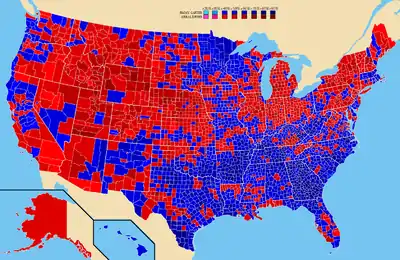
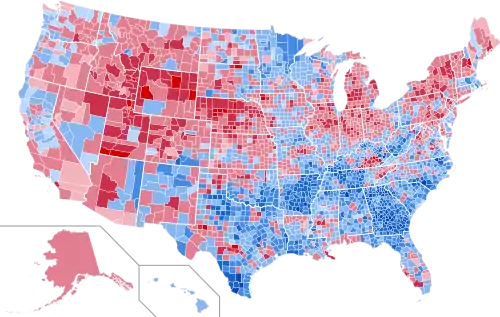 Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
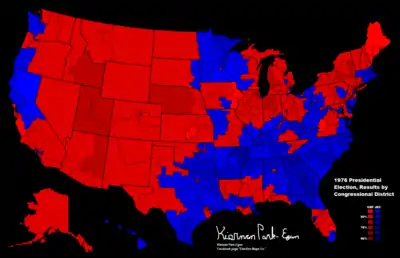
Results by state
This election represents the second time that the winning candidate has received a majority of the electoral votes, although the second-place candidate carried a majority of the states. It had previously happened in the 1960 election. The "margin" column shows the difference between the two leading candidates, and the "swing" column shows the margin swing from the respective party's nominee from 1972 to 1976.
| States/districts won by Carter/Mondale |
| States/districts won by Ford/Dole |
| Jimmy Carter Democratic |
Gerald Ford Republican |
Eugene McCarthy Independent |
Roger MacBride Libertarian |
Margin | Swing | State Total | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | # | ||
| Alabama | 9 | 659,170 | 55.73 | 9 | 504,070 | 42.61 | - | - | - | - | 1,481 | 0.13 | - | 155,100 | 13.11 | 60.00 | 1,182,850 | AL |
| Alaska | 3 | 44,058 | 35.65 | - | 71,555 | 57.90 | 3 | - | - | - | 6,785 | 5.49 | - | -27,497 | -22.25 | 1.26 | 123,574 | AK |
| Arizona | 6 | 295,602 | 39.80 | - | 418,642 | 56.37 | 6 | 19,229 | 2.59 | - | 7,647 | 1.03 | - | -123,040 | -16.57 | 14.69 | 742,719 | AZ |
| Arkansas | 6 | 499,614 | 64.94 | 6 | 268,753 | 34.93 | - | 647 | 0.08 | - | - | - | - | 230,861 | 30.01 | 68.12 | 769,396 | AR |
| California | 45 | 3,742,284 | 47.57 | - | 3,882,244 | 49.35 | 45 | 58,412 | 0.74 | - | 56,388 | 0.72 | - | -139,960 | -1.78 | 11.68 | 7,867,117 | CA |
| Colorado | 7 | 460,353 | 42.58 | - | 584,367 | 54.05 | 7 | 26,107 | 2.41 | - | 5,330 | 0.49 | - | -124,014 | -11.47 | 16.54 | 1,081,135 | CO |
| Connecticut | 8 | 647,895 | 46.90 | - | 719,261 | 52.06 | 8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -71,366 | -5.17 | 13.27 | 1,381,526 | CT |
| Delaware | 3 | 122,596 | 51.98 | 3 | 109,831 | 46.57 | - | 2,437 | 1.03 | - | - | - | - | 12,765 | 5.41 | 25.82 | 235,834 | DE |
| D.C. | 3 | 137,818 | 81.63 | 3 | 27,873 | 16.51 | - | - | - | - | 274 | 0.16 | - | 109,945 | 65.12 | 8.58 | 168,830 | DC |
| Florida | 17 | 1,636,000 | 51.93 | 17 | 1,469,531 | 46.64 | - | 23,643 | 0.75 | - | 103 | 0.00 | - | 166,469 | 5.28 | 49.40 | 3,150,631 | FL |
| Georgia | 12 | 979,409 | 66.74 | 12 | 483,743 | 32.96 | - | 991 | 0.07 | - | 175 | 0.01 | - | 495,666 | 33.78 | 84.17 | 1,467,458 | GA |
| Hawaii | 4 | 147,375 | 50.59 | 4 | 140,003 | 48.06 | - | - | - | - | 3,923 | 1.35 | - | 7,372 | 2.53 | 27.49 | 291,301 | HI |
| Idaho | 4 | 126,549 | 37.12 | - | 204,151 | 59.88 | 4 | - | - | - | 3,558 | 1.04 | - | -77,602 | -22.76 | 15.44 | 340,932 | ID |
| Illinois | 26 | 2,271,295 | 48.13 | - | 2,364,269 | 50.10 | 26 | 55,939 | 1.19 | - | 8,057 | 0.17 | - | -92,974 | -1.97 | 16.55 | 4,718,833 | IL |
| Indiana | 13 | 1,014,714 | 45.70 | - | 1,183,958 | 53.32 | 13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -169,244 | -7.62 | 25.15 | 2,220,362 | IN |
| Iowa | 8 | 619,931 | 48.46 | - | 632,863 | 49.47 | 8 | 20,051 | 1.57 | - | 1,452 | 0.11 | - | -12,932 | -1.01 | 16.12 | 1,279,306 | IA |
| Kansas | 7 | 430,421 | 44.94 | - | 502,752 | 52.49 | 7 | 13,185 | 1.38 | - | 3,242 | 0.34 | - | -72,331 | -7.55 | 30.60 | 957,845 | KS |
| Kentucky | 9 | 615,717 | 52.75 | 9 | 531,852 | 45.57 | - | 6,837 | 0.59 | - | 814 | 0.07 | - | 83,865 | 7.19 | 35.79 | 1,167,142 | KY |
| Louisiana | 10 | 661,365 | 51.73 | 10 | 587,446 | 45.95 | - | 6,588 | 0.52 | - | 3,325 | 0.26 | - | 73,919 | 5.78 | 42.75 | 1,278,439 | LA |
| Maine | 4 | 232,279 | 48.07 | - | 236,320 | 48.91 | 4 | 10,874 | 2.25 | - | 10 | 0.00 | - | -4,041 | -0.84 | 22.14 | 483,208 | ME |
| Maryland | 10 | 759,612 | 53.04 | 10 | 672,661 | 46.96 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 86,951 | 6.07 | 29.97 | 1,432,273 | MD |
| Massachusetts | 14 | 1,429,475 | 56.11 | 14 | 1,030,276 | 40.44 | - | 65,637 | 2.58 | - | 135 | 0.01 | - | 399,199 | 15.67 | 6.70 | 2,547,557 | MA |
| Michigan | 21 | 1,696,714 | 46.44 | - | 1,893,742 | 51.83 | 21 | 47,905 | 1.31 | - | 5,406 | 0.15 | - | -197,028 | -5.39 | 9.00 | 3,653,749 | MI |
| Minnesota | 10 | 1,070,440 | 54.90 | 10 | 819,395 | 42.02 | - | 35,490 | 1.82 | - | 3,529 | 0.18 | - | 251,045 | 12.87 | 18.38 | 1,949,931 | MN |
| Mississippi | 7 | 381,309 | 49.56 | 7 | 366,846 | 47.68 | - | 4,074 | 0.53 | - | 2,787 | 0.36 | - | 14,463 | 1.88 | 60.45 | 769,360 | MS |
| Missouri | 12 | 998,387 | 51.10 | 12 | 927,443 | 47.47 | - | 24,029 | 1.23 | - | - | - | - | 70,944 | 3.63 | 28.22 | 1,953,600 | MO |
| Montana | 4 | 149,259 | 45.40 | - | 173,703 | 52.84 | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -24,444 | -7.44 | 12.64 | 328,734 | MT |
| Nebraska | 5 | 233,692 | 38.46 | - | 359,705 | 59.19 | 5 | 9,409 | 1.55 | - | 1,482 | 0.24 | - | -126,013 | -20.74 | 20.26 | 607,668 | NE |
| Nevada | 3 | 92,479 | 45.81 | - | 101,273 | 50.17 | 3 | - | - | - | 1,519 | 0.75 | - | -8,794 | -4.36 | 23.00 | 201,876 | NV |
| New Hampshire | 4 | 147,635 | 43.47 | - | 185,935 | 54.75 | 4 | 4,095 | 1.21 | - | 936 | 0.28 | - | -38,300 | -11.28 | 17.84 | 339,618 | NH |
| New Jersey | 17 | 1,444,653 | 47.92 | - | 1,509,688 | 50.08 | 17 | 32,717 | 1.09 | - | 9,449 | 0.31 | - | -65,035 | -2.16 | 22.64 | 3,014,472 | NJ |
| New Mexico | 4 | 201,148 | 48.28 | - | 211,419 | 50.75 | 4 | - | - | - | 1,110 | 0.27 | - | -10,271 | -2.47 | 22.02 | 416,590 | NM |
| New York | 41 | 3,389,558 | 51.95 | 41 | 3,100,791 | 47.52 | - | 4,303 | 0.07 | - | 12,197 | 0.19 | - | 288,767 | 4.43 | 21.77 | 6,525,225 | NY |
| North Carolina | 13 | 927,365 | 55.27 | 13 | 741,960 | 44.22 | - | - | - | - | 2,219 | 0.13 | - | 185,405 | 11.05 | 51.63 | 1,677,906 | NC |
| North Dakota | 3 | 136,078 | 45.80 | - | 153,470 | 51.66 | 3 | 2,952 | 0.99 | - | 256 | 0.09 | - | -17,392 | -5.85 | 20.43 | 297,094 | ND |
| Ohio | 25 | 2,011,621 | 48.92 | 25 | 2,000,505 | 48.65 | - | 58,258 | 1.42 | - | 8,961 | 0.22 | - | 11,116 | 0.27 | 21.87 | 4,111,873 | OH |
| Oklahoma | 8 | 532,442 | 48.75 | - | 545,708 | 49.96 | 8 | 14,101 | 1.29 | - | - | - | - | -13,266 | -1.21 | 48.49 | 1,092,251 | OK |
| Oregon | 6 | 490,407 | 47.62 | - | 492,120 | 47.78 | 6 | 40,207 | 3.90 | - | - | - | - | -1,713 | -0.17 | 9.95 | 1,029,876 | OR |
| Pennsylvania | 27 | 2,328,677 | 50.40 | 27 | 2,205,604 | 47.73 | - | 50,584 | 1.09 | - | - | - | - | 123,073 | 2.66 | 22.64 | 4,620,787 | PA |
| Rhode Island | 4 | 227,636 | 55.36 | 4 | 181,249 | 44.08 | - | 479 | 0.12 | - | 715 | 0.17 | - | 46,387 | 11.28 | 17.47 | 411,170 | RI |
| South Carolina | 8 | 450,825 | 56.17 | 8 | 346,140 | 43.13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 104,685 | 13.04 | 55.70 | 802,594 | SC |
| South Dakota | 4 | 147,068 | 48.91 | - | 151,505 | 50.39 | 4 | - | - | - | 1,619 | 0.54 | - | -4,437 | -1.48 | 7.15 | 300,678 | SD |
| Tennessee | 10 | 825,879 | 55.94 | 10 | 633,969 | 42.94 | - | 5,004 | 0.34 | - | 1,375 | 0.09 | - | 191,910 | 13.00 | 50.95 | 1,476,346 | TN |
| Texas | 26 | 2,082,319 | 51.14 | 26 | 1,953,300 | 47.97 | - | 20,118 | 0.49 | - | 263 | 0.01 | - | 129,019 | 3.17 | 36.13 | 4,071,884 | TX |
| Utah | 4 | 182,110 | 33.65 | - | 337,908 | 62.44 | 4 | 3,907 | 0.72 | - | 2,438 | 0.45 | - | -155,798 | -28.79 | 12.46 | 541,198 | UT |
| Vermont | 3 | 81,044 | 43.14 | - | 102,085 | 54.34 | 3 | 4,001 | 2.13 | - | 4 | 0.00 | - | -21,041 | -11.20 | 15.00 | 187,855 | VT |
| Virginia | 12 | 813,896 | 47.96 | - | 836,554 | 49.29 | 12 | - | - | - | 4,648 | 0.27 | - | -22,658 | -1.34 | 36.38 | 1,697,094 | VA |
| Washington | 9 | 717,323 | 46.11 | - | 777,732 | 50.00 | 8 | 36,986 | 2.38 | - | 5,042 | 0.32 | - | -60,409 | -3.88 | 14.40 | 1,555,534 | WA |
| West Virginia | 6 | 435,914 | 58.07 | 6 | 314,760 | 41.93 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 121,154 | 16.14 | 43.36 | 750,674 | WV |
| Wisconsin | 11 | 1,040,232 | 49.50 | 11 | 1,004,987 | 47.83 | - | 34,943 | 1.66 | - | 3,814 | 0.18 | - | 35,245 | 1.68 | 11.35 | 2,101,336 | WI |
| Wyoming | 3 | 62,239 | 39.81 | - | 92,717 | 59.30 | 3 | 624 | 0.40 | - | 89 | 0.06 | - | -30,478 | -19.49 | 19.05 | 156,343 | WY |
| TOTALS: | 538 | 40,831,881 | 50.08 | 297 | 39,148,634 | 48.02 | 240 | 740,460 | 0.91 | - | 172,557 | 0.21 | - | 1,683,247 | 2.06 | 25.21 | 81,531,584 | US |
Close states



States where margin of victory was under 1% (35 electoral votes):
- Oregon, 0.16%
- Ohio, 0.27%
- Maine, 0.84%
States where margin of victory was under 5% (264 electoral votes):
- Iowa, 1.01%
- Oklahoma, 1.21%
- Virginia, 1.34%
- South Dakota, 1.48%
- Wisconsin, 1.68% (tipping point state)
- California, 1.78%
- Mississippi, 1.88%
- Illinois, 1.97%
- New Jersey, 2.16%
- New Mexico, 2.47%
- Hawaii, 2.53%
- Pennsylvania, 2.66%
- Texas, 3.17%
- Missouri, 3.63%
- Washington, 3.88%
- Nevada, 4.36%
- New York, 4.43%
States where margin of victory was more than 5%, but less than 10% (105 electoral votes):
- Connecticut, 5.16%
- Florida, 5.29%
- Michigan, 5.39%
- Delaware, 5.41%
- Louisiana, 5.78%
- North Dakota, 5.86%
- Maryland, 6.08%
- Kentucky, 7.18%
- Montana, 7.44%
- Kansas, 7.55%
- Indiana, 7.62%
Statistics
Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Democratic)
- Banks County, Georgia 87.85%
- Starr County, Texas 87.25%
- Brantley County, Georgia 86.50%
- Duval County, Texas 86.36%
- Wilcox County, Georgia 86.15%
Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Republican)
- Jackson County, Kentucky 79.80%
- Owsley County, Kentucky 77.03%
- Hooker County, Nebraska 76.35%
- Ottawa County, Michigan 74.12%
- Arthur County, Nebraska 73.66%
Voter demographics
| Social groups and the presidential vote, 1976 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size[A 1] | Carter | Ford | ||||
| Party | ||||||
| Democratic | 43 | 77 | 22 | |||
| Independent | 23 | 43 | 54 | |||
| Republican | 28 | 9 | 90 | |||
| Ideology | ||||||
| Liberal | 18 | 70 | 26 | |||
| Moderate | 51 | 51 | 48 | |||
| Conservative | 31 | 29 | 69 | |||
| Ethnicity | ||||||
| Black | 10 | 82 | 16 | |||
| Hispanic | 2 | 74 | 24 | |||
| White | 88 | 47 | 51 | |||
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | 48 | 50 | 48 | |||
| Male | 52 | 50 | 48 | |||
| Religion | ||||||
| Protestant | 46 | 44 | 55 | |||
| White Protestant | 41 | 42 | 57 | |||
| Catholic | 25 | 54 | 44 | |||
| Jewish | 5 | 64 | 34 | |||
| Family income | ||||||
| Less than US$10,000 | 13 | 58 | 40 | |||
| $10,000–$14,999 | 15 | 55 | 43 | |||
| $15,000–$24,999 | 29 | 48 | 50 | |||
| $25,000–$50,000 | 24 | 36 | 62 | |||
| Over $50,000 | 5 | — | — | |||
| Occupation | ||||||
| Professional or manager | 39 | 41 | 57 | |||
| Clerical, sales, white-collar | 11 | 46 | 53 | |||
| Blue-collar | 17 | 57 | 41 | |||
| Farmer | 3 | — | — | |||
| Unemployed | 3 | 65 | 34 | |||
| Education | ||||||
| Less than high school | 11 | 58 | 39 | |||
| High school graduate | 28 | 54 | 44 | |||
| Some college | 28 | 50 | 49 | |||
| College graduate | 27 | 43 | 55 | |||
| Union membership | ||||||
| Labor union household | 28 | 59 | 39 | |||
| No member of household in union | 62 | 43 | 55 | |||
| Age | ||||||
| 18–21 years old | 6 | 48 | 50 | |||
| 22–29 years old | 17 | 51 | 46 | |||
| 30–44 years old | 31 | 49 | 49 | |||
| 45–59 years old | 23 | 47 | 52 | |||
| 60 years or older | 18 | 47 | 52 | |||
| Region | ||||||
| East | 25 | 51 | 47 | |||
| South | 27 | 54 | 45 | |||
| White South | 22 | 46 | 52 | |||
| Midwest | 27 | 48 | 50 | |||
| Far West | 19 | 46 | 51 | |||
| Community size | ||||||
| City over 250,000 | 18 | 58 | 40 | |||
| Suburb/small city | 53 | 51 | 47 | |||
| Rural/town | 29 | 47 | 51 | |||
Source: CBS News/New York Times interviews with 12,782 voters as they left the polls, as reported in The New York Times, November 9, 1980, p. 28, and in further analysis. The 1976 data are from CBS News interviews.
- "Size" = share of 1980 national total.
Characteristics
- As of 2021, the 1976 election was the most recent time that a Democratic candidate carried any of the following states: Alabama, Mississippi, South Carolina and Texas. North Carolina did not vote for a Democratic candidate again until Obama in 2008. Obama also carried Virginia, the only state in the South that Carter did not win.[22]
- As of 2021, the 1976 election is the earliest election with a living nominee (Carter) and both living vice presidential nominees (Mondale and Dole).
- As of 2021, the 1976 election was the most recent time that a Democratic candidate won the White House without carrying California, Connecticut, Illinois, Michigan, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, Oregon, Maine, Vermont, and Washington.
- This election was the first time since 1908 that Nevada did not back the winning candidate, something that would happen again in 2016.
- This is the last election that Missouri voted Democratic and Iowa voted Republican in the same election.
- This is the last election that Georgia voted Democratic along with North Carolina and Florida in the same election.
- This is the only election that New Mexico did not back the winner of the national popular vote since it had achieved statehood in 1912 (and the first of three where it didn't back the winner of the electoral vote).
- Ford carried 27 out of 50 states, the most ever won by a losing candidate. He became the second and as of 2016 the last person not to win the presidency while carrying more than half the states. The first was Nixon in 1960, who won in 26 states.
- This election marks the only time in U.S. history that the two major candidates and their running mates would all win their respective party's nomination for President and lose, coming second in the general election: Ford in 1976, Carter in 1980, Mondale in 1984 and Dole in 1996.
- With the triumph of Jimmy Carter, the 1976 presidential election was the last time in which a winning presidential candidate from the Democratic Party would win the presidency at the same time their party won majorities in both chambers of Congress and eventually go on to see that party retain control of both houses in the following midterm election (although Carter's party still lost seats in both houses). The subsequent victorious Democrats, Bill Clinton and Barack Obama, witnessed the House of Representatives and Senate switch to Republican control during Clinton's in 1994 and Obama losing the House and several seats in the Senate in 2010 (though Clinton and Obama would both go on to be reelected and this would turn out to be Carter's only midterm election).
- Carter carried 1,711 counties, to Ford's 1,403. Since this election, only Bill Clinton in both 1992 and 1996 carried more than 1,000 counties, and no Democrat since 1976 has won more counties than their Republican opponent.[23]
- This is the first time in American history where both candidates eventually would become the longest lived president in the history of the United States. Gerald Ford held the record from November 12, 2006 to November 25, 2017. Jimmy Carter got the record on March 22, 2019. This happened once more, in 1980, which also involved Carter.
- This is the most recent presidential election when the Democratic candidate would emerge victorious with less than 300 electoral votes.
See also
Notes
- Mike Padden, a Republican faithless elector from Washington, gave Ronald Reagan one electoral vote.
- The running mate of McCarthy varied from state to state.
- Research has not yet determined whether Anderson's home state was Tennessee or Texas at the time of the 1976 election.
References
- "1976 Presidential Election Statistics". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved August 9, 2020.
- A faithless Republican elector voted for Reagan for president. The same elector voted for Dole for vice president as pledged.
- "The President and the Vice President have a complete understanding between them regarding the Vice President's decision. The letter speaks for itself. The initiative was the Vice President's" (PDF). Fordlibrarymuseum.gov. Retrieved March 4, 2016.
- "1976 Presidential General Election Results". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved July 24, 2018.
- "Election of 1976: A Political Outsider Prevails". Archived from the original on August 2, 2003. Retrieved August 2, 2003.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) C-SPAN. Retrieved on June 20, 2012.
- "Commercials - 1976 - Essence". The Living Room Candidate. August 9, 1974. Archived from the original on August 25, 2012. Retrieved March 4, 2016.
- Frum, David (2000). How We Got Here: The '70s. New York, New York: Basic Books. pp. 321–322. ISBN 0-465-04195-7.
- Frum, David (2000). How We Got Here: The '70s. New York, New York: Basic Books. pp. 321–322. ISBN 0-465-04195-7.
- "Gerald Ford Retrospective". Gallup. December 29, 2006. Retrieved October 6, 2019.
- Chapter three The Bicentennial election. Archived May 2, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- "Debating Our Destiny: The Second 1976 Presidential Debate – October 6, 1976". Pbs.org. October 6, 1976. Retrieved January 30, 2016.
- "The First VP Debate: Dole-Mondale, 10-15-76". Janda.org. October 15, 1976. Retrieved March 4, 2016.
- Bob Dole interview, November 10, 1999. PBS.org.
- "CPD: 1976 Debates". www.debates.org. Retrieved January 8, 2019.
- "1976 Debates Overview". AllPolitics. CNN. 1996. Retrieved April 24, 2019.
- "The Daily Diary of President Gerald R. Ford - October 22, 1976" (PDF). Gerald R. Ford Presidential Museum. Retrieved April 24, 2019.
- Jules Witcover. Marathon: The Pursuit of the Presidency, 1972–1976 (New York: Viking), p. 11.
- "How Close Were U.S. Presidential Elections?". Archived from the original on August 25, 2012. Retrieved August 25, 2012.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- Sullivan, Robert David; 'How the Red and Blue Map Evolved Over the Past Century'; America Magazine in The National Catholic Review; June 29, 2016
- "1976 Presidential General Election Data - National". Retrieved March 18, 2013.
- "1976 Presidential General Election Data - National". Retrieved March 18, 2013.
- "1976 Presidential General Election Results - Virginia". Uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved May 28, 2010.
- "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". Uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved October 21, 2012.
Further reading
- Chester, Edward W A guide to political platforms (1977) online
- MacDougall, Malcolm D. (1977). We Almost Made It. New York: Crown. ISBN 0-517-52933-5.
- Roessner, Amber (2020). Jimmy Carter and the Birth of the Marathon Media Campaign. Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 978-0807170793.
- Shirley, Craig (2005). Reagan's Revolution: The Untold Story of the Campaign That Started It All. Nashville, Tennessee: Thomas Nelson. ISBN 0-7852-6049-8.
External links
- The Election Wall's 1976 Election Video Page
- 1976 popular vote by counties
- 1976 popular vote by states (with bar graphs)
- Campaign commercials from the 1976 election
- How close was the 1976 election? at the Wayback Machine (archived August 25, 2012) — Michael Sheppard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (archived)
- Election of 1976 in Counting the Votes

.jpg.webp)


.jpg.webp)

