2012 United States Senate election in Tennessee
The 2012 United States Senate election in Tennessee took place on November 6, 2012, as part of the general election including the 2012 U.S. presidential election, elections to the House of Representatives and various state and local elections. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator Bob Corker won a second term. Corker easily won the Republican primary with 85% of the vote. He faced Democratic Party nominee Mark E. Clayton[2] as well as several third-party candidates and several independents.
| |||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 52.2% (voting eligible)[1] | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
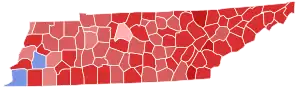 County results Corker: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% Clayton: 50–60% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Tennessee |
|---|
 |
|
|
Clayton won the Democratic nomination with 30% of the vote, despite raising no money and having a website that was four years out of date.[3] The next day Tennessee's Democratic Party disavowed the candidate over his active role in the Public Advocate of the United States, which they described as a "known hate group". They blamed his victory among candidates for whom the TNDP provided little forums to become known on the fact that his name appeared first on the ballot, and said they would do nothing to help his campaign, urging Democrats to vote for "the write-in candidate of their choice" in November.[4] One of the Democratic candidates, Larry Crim, filed a petition seeking to offer the voters a new primary in which to select a Democratic nominee among the remaining candidates the party had affirmed as bona fide and as a preliminary motion sought a temporary restraining order against certification of the results, but after a judge denied the temporary order Crim withdrew his petition.[5]
Background
The incumbent in the race, former Chattanooga mayor Bob Corker, was elected in 2006 with 50.71% of the vote in a win against U.S. representative Harold Ford, Jr..
Republican primary
Declared
- Fred R. Anderson
- Mark Twain Clemens, unemployed
- Bob Corker, incumbent U.S. Senator
- James Durkan, businessman
- Brenda Lenard, businesswoman & doctoral student
- Zach Poskevich, technology consultant
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Bob Corker (incumbent) | 389,483 | 85.1 | |
| Republican | Zach Poskevich | 28,299 | 6.2 | |
| Republican | Fred Anderson | 15,942 | 3.6 | |
| Republican | Mark Twain Clemens | 11,788 | 2.6 | |
| Republican | Brenda Lenard | 11,378 | 2.5 | |
| Total votes | 456,890 | 100 | ||
Democratic primary
Declared
- Mark E. Clayton, Vice President of the nonprofit organization Public Advocate of the United States and candidate for the U.S. Senate in 2008
- Larry Crim, nonprofit executive
- Gary Gene Davis
- Dave Hancock
- Park Overall, actress
- Thomas K. Owens
- Benjamin Roberts
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Mark E. Clayton | 48,126 | 30.0 | |
| Democratic | Gary Gene Davis | 24,789 | 15.4 | |
| Democratic | Park Overall | 24,263 | 15.1 | |
| Democratic | Larry Crim | 17,383 | 11.0 | |
| Democratic | Benjamin Roberts | 16,369 | 10.2 | |
| Democratic | David Hancock | 16,167 | 10.0 | |
| Democratic | Thomas Owens | 13,366 | 8.3 | |
| Total votes | 160,331 | 100 | ||
General election
Candidates
- Bob Corker (Republican), incumbent U.S. Senator
- Mark E. Clayton (Democratic)[7]
- Shaun Crowell (Libertarian)
- Martin Pleasant (Green)[8][9]
- Kermit Steck (Constitution)[9][10]
- David Gatchell (Independent)
- James Higdon (Independent)
- Michel Joseph Long (Independent)
- Troy Stephen Scoggin (Independent)
- Jacob Maurer (Write-In)[11]
Predictions
| Source | Ranking | As of |
|---|---|---|
| The Cook Political Report[12] | Solid R | November 1, 2012 |
| Sabato's Crystal Ball[13] | Safe R | November 5, 2012 |
| Rothenberg Political Report[14] | Safe R | November 2, 2012 |
| Real Clear Politics[15] | Safe R | November 5, 2012 |
Polling
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Bob Corker (R) |
Mark Clayton (D) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Issues and Answers Network Inc. | October 16–21, 2011 | 609 | ±4% | 59% | 21% | 4% | 15% |
Results
Despite the TN Democratic Party encouraging write-in voting, the general election only saw 0.05% cast write-in votes. Clayton significantly underperformed compared to Barack Obama, running for re-election to the Presidency on the same day. He got about 9% and 254,827 votes fewer than the President.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Bob Corker (incumbent) | 1,506,443 | 64.89% | +14.18% | |
| Democratic | Mark Clayton | 705,882 | 30.41% | -17.59% | |
| Green | Martin Pleasant | 38,472 | 1.66% | +1.52% | |
| Independent | Shaun Crowell | 20,936 | 0.90% | N/A | |
| Constitution | Kermit Steck | 18,620 | 0.80% | N/A | |
| Independent | James Higdon | 8,085 | 0.35% | N/A | |
| Independent | Michael Joseph Long | 8,080 | 0.35% | N/A | |
| Independent | Troy Stephen Scoggin | 7,148 | 0.31% | N/A | |
| Independent | David Gatchell | 6,523 | 0.28% | N/A | |
| n/a | Write-ins | 1,288 | 0.05% | N/A | |
| Total votes | '2,321,477' | '100.0%' | N/A | ||
| Republican hold | |||||
See also
References
- Dr. Michael McDonald (February 9, 2013). "2012 General Election Turnout Rates". George Mason University. Archived from the original on April 24, 2013. Retrieved April 6, 2013.
- "2012's worst candidate? With Mark Clayton, Tennessee Democrats hit bottom." by David A. Fahrenthold, Washington Post, October 22, 2012, Retrieved 2012-10-23, ""If there are people who don't believe that there's a campaign here, then guess what? They can come to Tennessee, if they're a voter, and they can see Mark E. Clayton, and next to Mark E. Clayton there's going to be a 'D,' " he said on the phone. "Like it or not, Mark Clayton is the Democratic nominee in Tennessee.""
- Murphy, Tim (August 3, 2012). "Dems Nominate Anti-Gay Conspiracy Theorist for Senate". Mother Jones. Retrieved August 21, 2012.
- Cass, Michael (August 3, 2012). "Tennessee Democratic Party disavows Senate nominee". The Tennessean. Retrieved August 4, 2012.
- Sisk, Chas (August 17, 2012). "Mark Clayton victory in Democratic primary upheld by Nashville judge". The Tennessean. Retrieved August 21, 2012.
- "Tennessee Secretary of State Unofficial Election Results". Secretary of State of Tennessee. Retrieved August 2, 2012.
- Mark Clayton website
- http://greenpartyoftennessee.org/candidates/
- Winger, Richard (February 3, 2012). "Tennessee Ballot Access Law for New and Minor Parties Struck Down". Ballot Access News. Retrieved August 4, 2012.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on October 21, 2012. Retrieved August 4, 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on June 6, 2013. Retrieved September 27, 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "2012 Senate Race Ratings for November 1, 2012". The Cook Political Report. Retrieved September 20, 2018.
- "2012 Senate". Sabato's Crystal Ball. Retrieved September 20, 2018.
- "2012 Senate Ratings". Senate Ratings. The Rothenberg Political Report. Retrieved September 20, 2018.
- "2012 Elections Map - Battle for the Senate 2012". Real Clear Politics. Retrieved September 20, 2018.
- http://sharetngov.tnsosfiles.com.s3.amazonaws.com/sos/election/results/2012-11/USSenateCountyTotals.pdf
External links
- Tennessee Department of Elections Board
- Campaign contributions at OpenSecrets.org
- Outside spending at Sunlight Foundation
- Candidate issue positions at On the Issues
- Official campaign websites
.jpg.webp)
