Nueva Ecija
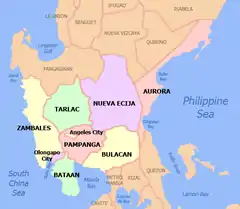
Nueva Ecija (PSGC: 034900000;[6] ISO: PH-NUE) (Filipino: Lalawigan ng Nueva Ecija [ˈnwɛba ˈɛsiha], also [ˈnwɛva- ]; Ilocano: Probinsia ti Nueva Ecija; Kapampangan: Lalawigan ning Nueva Ecija; Pangasinan: Luyag na Nueva Ecija) is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is the city of Palayan. Nueva Ecija borders, from the south clockwise, Bulacan, Pampanga, Tarlac, Pangasinan, Nueva Vizcaya and Aurora. The province is nationally known as the Rice Granary of the Philippines, producing the largest rice yield in the country.
Nueva Ecija | |
|---|---|
| Province of Nueva Ecija | |
 Nueva Ecija Provincial Capitol | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Nickname(s): Rice Bowl of the Philippines Milk Capital of the Philippines Heart of Inland Luzon | |
| Anthem: Awit ng Nueva Ecija (Song of Nueva Ecija) | |
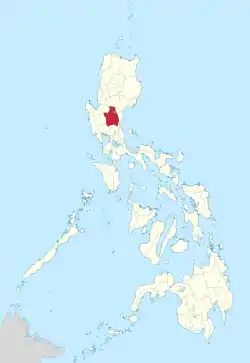 Location in the Philippines | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
| Coordinates: 15°35′N 121°00′E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Central Luzon (Region III) |
| Founded | April 25, 1801[1] (1848 on old sources) |
| Named for | Écija, Spain |
| Capital | Palayan |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlalawigan |
| • Governor | Aurelio Umali |
| • Vice Governor | Emmanuel Umali |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,751.33 km2 (2,220.60 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 12th out of 81 |
| Highest elevation | 1,673 m (5,489 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 2,151,461 |
| • Estimate (2020) | 2,355,416[4] |
| • Rank | 10th out of 81 |
| • Density | 370/km2 (970/sq mi) |
| • Density rank | 16th out of 81 |
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Divisions | |
| • Independent cities | 0 |
| • Component cities | |
| • Municipalities | |
| • Barangays | 849 |
| • Districts | 1st to 4th districts of Nueva Ecija |
| Demographics | |
| • Ethnic groups |
|
| • Languages | |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PHT) |
| ZIP code | 3100–3133 |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)44 |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-NUE |
Etymology
Nueva Ecija was named by the Spanish colonisers after the small town of Écija, Spain. Its indigenous names, such as Pinagpanaan, meaning the place where the arrow hit - defining the precolonial artistry in archery in the area, were abolished and changed by the government during the post-colonial period after World War II, sparking outrage from scholars and indigenous communities. Nevertheless, the name-change of some municipalities into colonial names during the post-colonial period was continued by the national government.
History
The sprawling and varied geological features of the land now known as Nueva Ecija, includes plains, mountains and rivers, all the requisites for the birth and sustenance of life itself. The land's very first settlers came upon three mountain ranges to the East, North and West and vast southern plains. All these were sustained by a great flowing river, one whose earliest name was spoken in a now lost tongue, and which was called the Rio Grande de Pampanga by the Spanish people later on. The Great Pampanga River nourished wild, fruit-bearing trees, served as home to an abundance of fish and made possible lush, teeming woodlands that sheltered animals.[7] All these combined must have been paradise in whatever language for the land's earliest settlers, who were able to not only survive but thrive in the surrounding abundance, all within easy reach.
Precolonial era
These first settlers included tribes of Ilongots (Egungot) or Italons, Abaca and Buquids.[8] Settlements were built along the banks following the river's undulations. The Ilongots, meaning people of the forest, were the fierce headhunters and animist tribes who occupied Carranglan and the mountainous terrain of Sierra Madre and Caraballo.[9] The head hunting communities were nestled along the riverbanks of Rio Grande's tributaries in the north. Abaca and Italon were subgroups of Ilongots meaning river settlers. Ilongots survived mainly by fishing and hunting. Food production was a secondary occupation. The agriculture-based community of Caraclans and Buquids[10] were settled in Bongabon and Pantabangan along the riverbanks of Rio Grande's tributaries in the northeast.[11]
When the waves of Malay migrations took place between 300 and 200 B.C., intrepid travelers and traders set up settlements along Luzon's western coast. These early settlements formed the nucleus of the Pampango Empire that was consolidated by Balagtas. The flatlands of the southern portion of Upper Pampanga was a hospitable place for these new Malay settlers. The indigenous tribes were forced to take to the hills in the face of the Malays' superior technology.[12]
Barter trade flourished among communities that settled along the great river. The constant riverside trading resulted in both a commercial and cultural exchange between the settlements in vast plains upstream of the Rio Grande de Pampanga. Settlements in Carranglan, Pantabangan, Bongabon and Puncan prospered and grew into more stable communities.
The Kingdom of Tondo, headed from what is now central Manila, invaded the area and took hold of the southern portions of Nueva Ecija. Eventually, more areas in northern Nueva Ecija were absorbed by the Kingdom of Tondo, to a point where even present-day Nueva Viscaya was conquered by Tondo. Even the northwest areas of Nueva Ecija, which was ruled by the Kaboloan of Pangasinan, was captured by Tondo.
Spanish attacks
When the Spanish arrived in Manila and destroyed the territorial powers of the Tondo monarchy, much of Nueva Ecija became a de facto free land. At the time, the Pampango crown has waned and had little resistance from Spanish invasion. When the Pampango Empire fell into the hands of Spanish forces under the command of Martin de Goiti in 1572, the conquistadores began their long upward trek towards Cagayan Valley and Mountain Province. Their forces passed through the settlement areas of the Upper Pampanga River. They also attacked the Kaboloan of Pangasinan, effectively capturing more territories from local kingdoms.
Because of growing territorial domain and evangelical missions, a command outpost or Commandancia in the Upper Pampanga River area was established. Then Governor-General[13] Fausto Cruzat y Góngora (July 25, 1690 to December 8, 1701) had most likely spent much of his time in the northern outpost in Carranglan and Pantabangan and, baking in the fiercely hot climate, probably waxed nostalgic about his hometown in Ecija, Andalusia in Spain. Ecija, Andalusia was also known as la sarten or the frying pan because of its intensely hot summers. Thus the Governor-General hit upon the notion to name the outpost Nueva Ecija. Both the New and Old Ecija were washed by navigable rivers- the former, by Rio Grande de Pampanga and the latter, by the river Genil.
Conversion to Christianity
Consistent with the history of Hispanization in the rest of Philippine archipelago, Nueva Ecija was established by Augustinian missionaries. The first mission was established in Gapan in 1595. The Augustinians abandoned their missionary work in 1636, maintaining only the mission in Bongabon.[14]
At the turn of the 18th century, the missionaries resumed their evangelical work and redirected their efforts to the northeast, towards rough, mountainous terrain inhabited by Ilongots.
On September 1, 1759, King Carlos III of Spain issued a Royal Decree that ended the founding missions of Augustinians and transferred all Augustinian responsibilities in the settlements of Nueva Ecija to Franciscan friars. Through tribute collections and polo y servicio or rendering of force labor, the Franciscans constructed churches, convents, parochial schools and tribunals. They also constructed roads and bridges to connect other settlements. In 1781, a simple irrigation system was constructed in Pantabangan. This new farming technology contributed to the promotion of agriculture in the province.
New province
To make possible the establishments of settlements, military force became necessary to protect the friars and whatever basic settlement structures were beginning to emerge. Thus military outposts were of utmost importance, especially with the friars trying to convert fierce head-hunting tribes with spears and bladed weapons. It was around this time, during the term of Governor General Fausto Cruzat y Gongora (July 25, 1690 to December 8, 1702), that he established the military outpost he named Nueva Ecija. At this time, however, Nueva Ecija was still part of upper Pampanga.
In 2016, researchers of the National Historical Commission of the Philippines (NHCP) and the provincial government found documents showing that in 1799, Carlos IV ordered the separation of towns and parishes of Upper Pampanga, near the Sierra Madre range, as well as coastal towns of Tayabas, along the Pacific Ocean and their organization into a corregimiento (political-military administrative unit). Royal directives were implemented on April 25, 1801, and the corregimiento was named Nueva Ecija after the Spanish hometown of that period's Governor General Rafael Maria de Aguilar, with Baler as its capital.[15]
Since then, the province had undergone numerous changes in territorial composition. The progressive towns of Gapan, San Isidro, Cabiao and Aliaga were all annexed to Nueva Ecija, resulting in an economic as well as population boom for inhabitants. While Nueva Ecija only had a population of 9,165 in 1845,[16] the annexation of new territories three years later pegged the population at 69,135.
Other changes occurred in the following years until, in 1901, Nueva Ecija's northern municipalities of Balungao, Rosales, San Quintin and Umingan were annexed to Pangasinan. Nueva Ecija's shifting political boundaries in fact necessitated transferring its provincial capital four times. Still, these changes proved ultimately beneficial to Nueva Ecija, as they resulted in a territory with rich land resources nourished by an excellent river system composed of the Rio Grande de Pampanga, Talavera and Penaranda rivers. This would help lay the foundation for Nueva Ecija's abundant agricultural economy starting with the American Occupation in the early 20th century.
Cry of Nueva Ecija

The "Cry of Nueva Ecija" is the 1896 revolutionary battle led by General Mariano Llanera, manned and assisted by General Manuel Tinio and Pantaleon Valmonte of Gapan City, Nueva Ecija and Colonel Alipio Tecson of Cabiao, Nueva Ecija who later on became Brigadaire General. The battle was fought in Cabiao, Nueva Ecija. Alipio Tecson would eventually become Governadorcillo of Cabiao, Nueva Ecija.[17]
Tobacco monopoly
Maintaining the Philippines as a colony became a challenge for the Spanish Empire. Expenses incurred in running the colony were usually paid for by a yearly subsidy (called real situado) sent from the Philippines' sister colony in Mexico. This financial support from the Spanish royal court was often insufficient, especially with expenditures in the Philippine colony growing each year.
This prompted the royal fiscal assigned in Manila to devise a plan to allow the colony itself to raise revenues on its own and thus be able to supplement the Spanish subsidy. This royal fiscal was Francisco Leandro de Vianna, who first proposed creating a tobacco monopoly. De Vianna reasoned, tobacco was a product widely consumed throughout the islands, with a market of roughly one million. He projected earnings of as much as P400,000 from the venture. The first time the proposal was made, however, both King Carlos III of Spain and colonial officials didn't give the idea much importance.
All that would change during the term of Governor-General Jose Basco y Vargas. Basco had plans to develop and promote Philippine agriculture, and de Vianna's proposal seemed attractive to him. After studying the proposal, Basco sent his plan to establish a large-scale tobacco production in the colony under complete ownership and management by the colonial government of Spain. What probably perked up the ears of the Spanish king about Basco's plan to make the Philippine colony financially self-sufficient, thus removing a huge financial burden from the Spanish crown. The King of Spain issued a royal decree on February 9, 1780 setting in motion Basco's plan.[18]
Almost two years to the date of that royal decree, Basco ordered local officials and military commanders to prevent unnecessary losses of tobacco revenues. By March 2, 1782 tobacco production was established in Luzon, with La Union, Ilocos, Abra, Cagayan Valley and Nueva Ecija (still part of Pampanga at the time) as the centers for planting, growing, harvesting and processing tobacco.
This made a drastic and extreme change in the lives of all Novo Ecijanos. Where farmland used to bear rice, tobacco was now the only crop allowed to grow. These included the towns of Gapan, San Isidro, Jaen, Cabiao, Cabanatuan, Talavera, Santor and Bongabon. Each farming family was given a quota of tobacco plant to grow.
By 1850 the tobacco monopoly was producing immense financial gain for the colonial government. Some reports at the time pegged the earnings by as much as $500,000. One account in 1866 reported a much higher amount, as earnings rose to $38,418,939 that year.
Novo Ecijanos suffered a lot from the system. Nueva Ecija was more often able to meet production quotas compared to the other districts. Despite this, tobacco policy imposed a lower price on tobacco from areas closer to Manila. That meant that first-class tobacco leaf grown and harvested from Nueva Ecija was priced lower by one dollar, compared to those from Ilocos, La Union and Cagayan Valley.
The tobacco monopoly did not spur Novo Ecijanos to revolt, unlike the Ilocanos who staged an uprising over injustices in the system. Some tobacco growers in Nueva Ecija resorted to smuggling their own harvests in order to get some profit. But getting caught entailed harsher fines and penalties. Even sympathetic local officials had no choice but to enforce the unjust policies under pain of arrest and hard labor, once laxity on their part resulted in low production.
The flourishing tobacco industry coupled with the rich agricultural lands in central and northeastern Nueva Ecija also attracted migrants from neighboring Pampanga, Pangasinan, Ilocos and Tagalog areas. This made Nueva Ecija a melting pot of cultures and influences, the results of which are still evident in present-day Novo Ecijano culture.
As the tobacco monopoly fuelled further unrest, Spain finally abolished the monopoly on December 3, 1882. It was only then that they could all once again grow rice for food.[19]
Rebellion against Spain

One distinct feature of the 1896 revolution against Spain in Nueva Ecija was that it was led by the elite, ruling class instead of the masses. Leaders of the revolt in Nueva Ecija were municipal officials and prominent citizens, who refused to collaborate with the Spanish authorities when armed struggle broke out. Despite being in the ruling class and enjoying positions in the colonial government, these prominent Novo Ecijanos proved their patriotism and love for fellow Filipinos.[20] In fact, one of the founding members of the reform movement La Liga Filipina[21] was lawyer and Novo Ecijano Mamerto Natividad. By the time the Katipunan, the revolutionary movement against Spain, was formed, Novo Ecijanos were actively yet secretly joining it. Even local officials in Nueva Ecija secretly allied with the illustrados and farmers in forming the underground revolutionary society.[22]
Once the Spanish authorities learned of the Katipunan's existence, those perceived as sympathizers of the movement, and even those who were falsely accused of being members of it, were arrested. Mamerto Natividad was among those arrested for sedition, tortured and killed by guardia civil. He was one of the first Novo Ecijano martyrs[23] for freedom. His death however, would result in bigger problems for the Spanish authorities.
Mamerto Natividad's two sons, Mamerto Jr. and Benito Natividad, later joined the Katipunan. The Spaniards burned their house and sugar mills in Jaen. Mamerto Jr. was later jailed for shooting a Spanish judge who had slapped his younger brother. As the Revolution gained ground, Mamerto Jr. was released and he was able to join the revolutionary army of General Emilio Aguinaldo in Cavite. By August 30, 1896 a state of war was declared by the Spanish colonial government in several Luzon provinces including Nueva Ecija, Bulacan, Pampanga, Tarlac, Batangas, Laguna, Cavite and Manila.[24]
Novo Ecijanos immediately proved themselves worthy of the fight for freedom. On September 2, 1896, Novo Ecijanos led by Gen. Mariano Llanera, capital municipal of Cabiao and Gen. Pantaleon Valmonte, capitan municipal of Gapan attacked San Isidro, the provincial capital. Their 3,000-strong army attacked San Isidro in distinct Novo Ecijano fashion: accompanied by music played by the Banda de Cabiao or Cabiao band. It seems that in love or war, music is integral to Novo Ecijanos.

Novo Ecijanos like Llanera, Valmonte, Mamerto Natividad, Jr. and Manuel Tinio conducted themselves heroically during the revolution. They were allied with Aguinaldo's Magdalo[25] group. Aguinaldo was in fact so impressed, he appointed Natividad and Llanera to the two highest-ranking posts in the revolutionary army. Natividad became General Mamerto Natividad, commanding general of the revolutionary army, while General Llanera was vice-commander with the rank of Lieutenant-General. General Natividad proved himself worthy of the position by scoring victories against the Spanish in Tayug, Pangasinan and San Rafael, Bulacan.

On November 11, 1897, Natividad's life would end after he was killed in action in Cabiao, Nueva Ecija. His death precipitated the Pact of Biak-na-Bato,[26] a peace treaty that sought to end hostilities between Spanish authorities and the Filipino rebels. The treaty provided for a payment of P800,000 to the rebels who would then be exiled to Hong Kong. Five Novo Ecijanos would accompany Aguinaldo's exile.[27] They were General Mariano Llanera, Benito Natividad, General Manuel Tinio,[28] and Joaquin Natividad.
Later on, Novo Ecijanos would continue to participate in the drama of war, revolution and the fight for freedom. They would fight when the revolt against Spain continued after the peace treaty broke down and the United States, after declaring war on Spain, promised to help Filipinos fight for freedom. Then, Novo Ecijanos again joined General Emilio Aguinaldo in the Philippine–American War (after it became evident the United States wanted to make the Philippines their own colony).[29]
Then when the Japanese tried to make the Philippines their own colony[30] at the outbreak of the Second World War in the Pacific, Novo Ecijanos would also make history by participating in guerilla activities. The exploits of the Novo Ecijano guerillas have in fact been made into literature, through the World War II novel Ghost Soldiers by Hampton Sides[31] and in Hollywood cinema, in the war film The Great Raid[32] based on the book.
American period
History records how the Philippine–American War began after American troops killed a Filipino soldier who was crossing the San Juan bridge on February 4, 1899.[33] One could also say however that hostilities and mistrust really began as early as August 13 the previous year. On that day, the Spanish colonial government in Intramuros surrendered to American forces instead of the Filipino soldiers that surrounded the Walled City. Thus began the United States own effort to have her own colonies, with the Philippines served, as it were, on a silver platter by the dying Spanish Empire thanks to the Treaty of Paris.[34][35]
When the war between Filipinos and Americans finally began, the fate of the infant Republic of the Philippines again lay in the hands of General Aguinaldo and his most trusted men who included Novo Ecijanos like General Llanera and General Tinio. And, as guerilla warfare became an effective tactic for the Filipinos, Novo Ecijanos were among the most feared guerillas around. Both the Novo Ecijanos and Americans were willing to resort to brutal tactics, torture and even atrocious killings in the course of the war. Two nove ecijanos were deported and exiled in Guam for not taking allegiance to the American government, they were General Mariano Llanera and Col. Alipio Tecson.
By the time the war ended on April 1, 1901 with Aguinaldo's surrender to the Americans,[36] Novo Ecijano guerillas who had fought so fiercely and bravely against two sets of foreign invaders reluctantly gave up. Still that was not the end of the association between them and the Americans. The end of the Philippine–American War also signaled a new beginning for Nueva Ecija and its people.
The railway
Before the American occupation, Nueva Ecija was already a hub of trade and commerce. Since Nueva Ecija in the 19th century had neither excellent roads nor the ideal land transport system, trading activities were done mainly through the waterways.
While we moderns consider rivers as obstacles that need to be crossed, people in the 19th century valued rivers not just as sources of food and water but as passages for trading barges and boats. Thus, Nueva Ecijas early trading settlements sprouted along riverbanks.
Commercial, interprovincial trade was carried out using the Rio Grande de Pampanga as main waterway, with trade outposts in San Isidro and Talipapa. Traders from Bulacan, Tondo and Manila regularly came to Nueva Ecija to carry back rice, palay, tobacco, sugar, corn and livestock.
The Americans, however, wanted to shift from water-borne trade to a land-based trade system. Their idea for establishing this depended on something they were masters at: building railways. The American colonial government thought a railway could help boost Nueva Ecija's economic growth, in the same way that the US railway system helped unite and develop the economy of the North American continent.
What made the railway project attractive was that it was less expensive than building roads. At first run by a private company, the US colonial government[37] took over the ownership and management of the railway system by 1917.
The Americans were soon proven right: trade conducted through the railways boosted Nueva Ecija's income by 25% while transport costs went down by 25% to as much as 75%. With the train able to transport more goods and more people at a cheaper rate, the railway helped spark a rice boom in Gapan, San Isidro, Cabanatuan, Santa Rosa and Penaranda. Farmers could devote more land to growing rice and even secondary crops like onions and watermelons.
More rice mills, farmers and farmer settlers came to Nueva Ecija. By 1936, there were 42 rice mills in Nueva Ecija, owned mostly by Chinese.[38]
The agriculture-based economic boom brought about by the train's huge load capacity and greater speed (compared to boats) encouraged waves of migrations to Nueva Ecija from places like Ilocos, Pampanga, Pangasinan, Tarlac and Bulacan.
The railway brought other changes to Nueva Ecija. While trade was still being done by waterways, settlements by necessity had to be established close to the rivers, where people's basic necessities came from. When the trains became the main mode of transporting goods and people, and with the influx of migrants, it became not only possible but crucial to build more communities further inland. This meant roads and irrigation systems were needed.[39]
Roads and irrigation
As communities expanded inward, first along the rivers and then along the railways, the need for roads and irrigation systems leading to communities in the plains became more urgent. These made it possible for the more remote towns—those farther away from both rivers and railroads—to grow crops and participate in trade, ending what was until then a very slow pace of economic development. By 1912 Governor Benito Natividad had appropriated funds to fast-track the building of roads and bridges linking these remote towns and municipalities to then provincial capital Cabanatuan.
The American government also constructed three major irrigation facilities: 1) The Talavera Irrigation System in 1924; 2) Penaranda River Irrigation System in 1930 and 3) Pampanga River Irrigation System in 1939.
By the time these irrigation systems went in full swing, combined with the railway system and the many rice mills, Nueva Ecija had been established as the "Rice Granary of the Philippines." From 1930 to 1939, rice production in Nueva Ecija was averaging more than 9 million cavans of rice.[40]
Homesteading and US-style tenancy
Unlike the American pioneers of the Old West, Filipinos were not so willing to occupy remote, unsettled and undeveloped areas. So when the American colonial government introduced homesteading, there were few takers among Filipinos. Essentially, homesteading happens when someone lays claim on, harnesses the resources and develops a parcel of land, even if it's still wilderness and far from population centers, for economic use. Homesteading could be done through a legal process of acquiring a land title, or even without a title at all. In the latter case however, the lack of a title makes the informal homesteader vulnerable to any legal action attempting to take the land away from him.[41]
When the Philippine Bill of 1902 was passed by the US Congress, the US colonial government was formally established in the Philippine islands. This meant the colonial government now had the authority to dispose of public lands on its own, without having to seek the approval of the President of the United States. Based on an earlier survey of public lands by the Philippine Commission, the new American colonial government offered public lands to settlers through homesteading, sale, purchase or lease.[42]
Under the American regime's homesteading system, an individual could get up to 16 hectares of land, while a corporation could get as much as 1,024 hectares. This did not result in a wide settlement of lands throughout the country, however. Nueva Ecija was one exception, as more settlers opted to homestead its lands. A 1928 Statistical Bulletin records nearly 70,000 hectares were given to more than five thousand homestead applicants.[43]
Among the immigrant-settlers of Nueva Ecija, the Ilocanos were mainly responsible for opening up through their homesteads, the once sparsely populated, remote areas of the province. Much like the early American pioneers, the Ilocanos tamed the land and turned what was once hostile wilderness into habitable and productive land.
However, the homesteading effort under the American regime resulted in a drop in tenancy in 1918, it ultimately failed in succeeding decades. This was due to two major factors. First, the new farmer-settlers did not have enough capital to sustain farming costs. Without any financial assistance available from the government that granted them the land, farmer-settlers accumulated huge debts at very high interest rates from usurious moneylenders. Most of these homesteaders were later forced to sell their land and become tenant farmers instead.
Civil government in the American period
The civil governments established in various provinces in the Philippines under the American Occupation were supposed to teach Filipinos the basic principles of democracy, following US military rule. In general, each provincial government presided over local governments in each town or municipality. In turn, each municipality would have a president, vice-president and municipal councillors. These were elected by a select group of qualified electors for two-year terms.[44]
The second Philippine Commission went to what was then Nueva's provincial capital, San Isidro, on June 8, 1901 to begin proceedings for establishing the local and provincial governments. 16 out of Nueva Ecija's 19 towns were represented in the meeting. Elections of various representatives from the different towns were carried out successfully.
However, there was still the thorny problem of deciding whether or not to move the provincial capital. The dilemma was caused by events related to the Philippine–American War. First, Nueva Ecija had been a hotbed of resistance against the American Occupation, and was therefore in a state of siege. Four of its towns, Balungao, Rosales, San Quentin and Umingan, which were further away from the capital and already considered pacified by US forces, had been annexed to the province of Pangasinan.
The newly elected Nueva Ecija representatives were of the view that since a civil government under the Americans was already being established, it was time to return the four towns to Nueva Ecija. This would benefit the province as the four town were rich in natural resources. The fact that the towns were quite far from the capital, one of the representatives suggested, was no obstacle: the provincial capital could simply be moved to Cabanatuan. Other representatives objected to this proposal, pointing out that Cabanatuan had no infrastructures wherein to house the provincial government.
The matter was not resolved until two years later, when the US governor-general signed Act No. 1748,[45] ordering the transfer of the capital to Cabanatuan by 1912.
The civil provincial government of Nueva Ecija was formally established by the Taft Commission[46] on June 11, 1901. The very first governor under this new system was Epifanio de los Santos. The main artery connecting most of Metro Manila has been named after Governor de los Santos, which is Epifanio de los Santos Avenue or simply, EDSA.
Education during the American period
It was the Americans who succeeded in making education widely available to Filipinos. While the Spanish government did, rather belatedly in their rule (in the middle of the 19th century), decide to establish public schools, it was the Americans who were able to improve it.[47]
A report of the United States' Philippine Commission in 1900 showed, only 10 out of 23 municipalities in Nueva Ecija had a public school established during the Spanish times and according to the Philippine Commission figures by 1902, 37 public primary schools were established, and 63 Novo Ecijano teachers supported by 16 American "Thomasites", part of the larger group of some 500 pioneer American teachers who arrived aboard the USAT Thomas in September 1901, to help establish an American public school system in the Philippines.
The Education Act No. 74 approved by the Philippine Commission in 1901[48] proved to be the catalyst that made Novo Ecijanos rally behind the local and American teachers to make sure as many children as possible benefitted from the public school system.
People contributed in the form of cash, construction materials or labor, and even vacant lots for the building of schools. Community support for the building of schools was such that by 1906, there were already 99 schools in Nueva Ecija. The Novo Ecijanos' high regard for the value of an education is a trait that persists until today.
The public schools system was still hampered by a lot of problems, however. Relying only on local support, Nueva Ecija (and other places in the Philippines as well) could simply not meet the increasing needs of a growing number of schools, teachers and students. Given the high premium placed by Novo Ecijanos on education, a legislator from Nueva Ecija took the crucial step to compel the American colonial government to allot funding for public education via a legislative act.
Assemblyman Isauro Gabaldon of Nueva Ecija filed an education bill before the 1907 Philippine Assembly, which would later be approved and known as the Gabaldon Education Act. The bill required government to earmark P1,000,000 for public schools throughout the Philippine islands.[49]
Nueva Ecija benefitted tremendously from the new education law. By 1908 Nueva Ecija had 144 primary schools, 11 non-sectarian private schools, 18 sectarian private schools, nine intermediate schools, one vocational school and one agricultural school, the Central Luzon Agricultural School, which is currently now operating as Central Luzon State University.
World War II


During World War II the Imperial Japanese Army entered the province and Nueva Ecija was taken in 1942. On March 29, 1942, under the leadership of Luis Taruc the Hukbalahap (Hukbo ng Bayan Laban sa Hapon-People's Army Against the Japanese) was organized in Sitio Bawit, Barrio San Julian in the town of Cabiao. It was perceived to be the military arm of the Partido Komunista ng Pilipinas (Communist Party of the Philippines), that brought about the beginning of the early organized resistance of the Filipino people.[50]
During World War II under the Japanese occupation, The Philippine Commonwealth Army has the re-establishment of the Military General Headquarters, Military Bases and Camps here in the province of Nueva Ecija on January 3, 1942 to June 30, 1946 before the engagements of the Anti-Japanese Imperial Military Operations in Central Luzon include Nueva Ecija, Pampanga, Tarlac, Zambales, Bulacan and Northern Tayabas (now. Aurora) from 1942 to 1945 and aided the local recognized guerrillas and the Hukbalahap Communist guerrillas against the Japanese Imperial forces since the Japanese Counter-Insurgencies (1942-1944) and the Allied Liberation (1944-1945).
In January to August 1945, combined American and Filipino soldiers liberated Nueva Ecija with the recognized guerrillas continuing to harass the Japanese at every opportunity. When Filipino soldiers of the 2nd, 22nd, 23rd, 25th and 26th Infantry Division of the Philippine Commonwealth Army and the 2nd Constabulary Regiment of the Philippine Constabulary was re-invading launches to entering liberated the province of Nueva Ecija and helping recognized guerrilla resistance fighter units, the Hukbalahap Communist guerrillas and the American troops against the Japanese Imperial forces during the Invasion of Nueva Ecija. On January 30, 1945 American Army Rangers, Alamo scouts and Filipino guerrillas conducted a raid to liberate Allied civilians and prisoners of war in Cabanatuan, this was successful with over 516 rescued.[51] By January 31, 1945, the liberated civilians and POWs reached Talavera, the rescue is commemorated in Talavera.
Contemporary era
After the war, much rebuilding was made at the urban areas of the province, specifically Cabanatuan and Gapan. This became the focus of the administrations of Quezon, Roxas, Quirino, Magsaysay, Garcia, and Macapagal. The city of Palayan was formally established by law and became the new capital of the province. Much of the rebuilding and establishment of economic centers in the province spiraled down due to the declaration of martial law by Marcos, which was toppled by the EDSA People Power Revolution, where the namesake came from a Novo Ecijano. Repairing the economy was continued by the Aquino and Ramos governments. The Estrada government led to a decline in agriculture in the province. The Arroyo and Aquino governments swayed the losses and regained vitality in the province. The Duterte government accession made wary ups and downs in the provincial economy.
Geography
The province is the largest in Central Luzon, covering a total area of 5,751.33 square kilometres (2,220.60 sq mi)[6]. Its terrain begins with the southwestern marshes near the Pampanga border. It levels off and then gradually increases in elevation to rolling hills as it approaches the mountains of Sierra Madre in the east, and the Caraballo and Cordillera Central ranges in the north.
Nueva Ecija is bordered on the northeast by Nueva Vizcaya, east by Aurora, south by Bulacan, southwest by Pampanga, west by Tarlac, and northwest by Pangasinan. The province has four distinct districts. The first district (northwest) has a mixture of Ilokano, Pangasinense, and Tagalog cultures. The second district (northeast) is the most complex as it has at least 10 different ethnic groups. The third district (central) has a metropolitan culture, coming from a majority of Tagalog culture, as Cabanatuan City is within it. And the fourth district (southwest) has a mixture of Kapampangan and Tagalog cultures.
Flora and fauna

The species of flora and fauna in the province is diverse on its north and east borders, which exhibit a shared ecosystem with the Caraballo mountains in the north and the Sierra Madre mountains in the east. The southeast areas are also known for its diverse fauna and flora due to the presence of the Minalungao National Park. The ceratocentron fesselii orchid, which can only be found in the Pantabangan–Carranglan Watershed Forest Reserve in Carranglan, is considered as one of the most critically endangered orchid species in the entire Southeast Asian region. It is endangered due to illegal gathering from the wild and due to the illegal black market trade. The forest reserve is also home to the endemic Rafflesia consueloae, which is the smallest rafflesia in the world and is found nowhere else. Philippine deer, Philippine warty pig, cloud rats, and other indigenous mouse species are also present in the province. In a recent activity, the presence of a Philippine Eagle couple was discovered in the Sierra Madre side of Nueva Ecija. The couple are now protected by the local government units in that area. Snakes, lizards, and various amphibian species are also present, especially in wetter months.
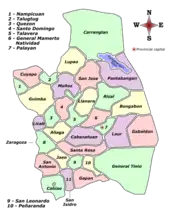
Administrative divisions
The province is divided into four congressional districts comprising 27 municipalities and 5 cities. The province has the most number of cities in the Central Luzon region.
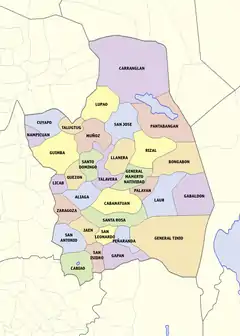
- † Provincial capital and component city
- ∗ Component city
- Municipality
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Climate
| Climate data for Nueva Ecija | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 32.1 (89.8) |
32.8 (91.0) |
34.4 (93.9) |
36.2 (97.2) |
35.3 (95.5) |
34.0 (93.2) |
32.8 (91.0) |
32.1 (89.8) |
32.4 (90.3) |
32.8 (91.0) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.0 (89.6) |
33.3 (91.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 21.1 (70.0) |
21.6 (70.9) |
22.7 (72.9) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.6 (76.3) |
24.5 (76.1) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.7 (74.7) |
22.9 (73.2) |
21.9 (71.4) |
23.3 (73.9) |
| Average rainy days | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 13 | 16 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 10 | 8 | 4 | 122 |
| Source: Storm247 [53] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority [3] [52] [52] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The population of Nueva Ecija in the 2015 census was 2,151,461 people, [3] with a density of 370 inhabitants per square kilometre or 960 inhabitants per square mile.
| Population percentage (2015 Census) [3] |
|---|
|
| Total population: 2,151,461 |
Ethinicity
According to the Atlas Filipinas published by the National Commission for Culture and the Arts of the Philippines, 11 local ethnic languages with living ethnic speakers are present in Nueva Ecija, namely, Tagalog (in the entire province), Abellan (in a small part in the centre), Kapampangan (in the southwest-most section), Kankanaey (in the east central), Ilokano (northern areas and a small section in the centre), Alta (in the east central), Ayta Mag-antsi (in the centre and the north-central), Bugkalut (in Carranglan), Ibaloy (in Carranglan), Kalanguya' and 'Isinay (in Carranglan).[54]
Religion
The province is predominantly Roman Catholic (about 82.43%). Other Christian groups are Iglesia ni Cristo (5.55%), Born-again Christians, Philippine Independent Church (2.50%), Evangelical (1.70%) & Methodists(1.62%).[55] The remaining minorities (6.2%) are The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints, Jehovah's Witnesses and Seventh-day Adventist & Muslims. Anitists, and animists are also represented in the province practiced by indigenous ethnic groups.[56]
Economy


Nueva Ecija is considered the main rice growing province of the Philippines and the leading producer of onions in the country.
Major industries
Nueva Ecija is one of the top producers of agricultural products in the country. Its principal crops is mainly rice but corn and onion are produced in quantity. The province is often referred to as the "Rice Granary of the Philippines."[64][65] Other major crops are mango, calamansi (calamondin orange), banana, garlic, and vegetables. The municipality of Bongabon at the eastern part of the province at the foot of the Sierra Madre mountains and its neighbouring Laur and Rizal are the major producers of onion and garlic. Bongabon is called the "onion capital of the country". A sunflower farm is housed inside the Central Luzon State University campus in Science City of Muñoz.
Education is very well established as a major industry in the province. The leading educational institutions are the Central Luzon State University in Science City of Munoz and Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology, Wesleyan University-Philippines, the only internationally accredited school in Central Luzon; College of the Immaculate Conception; La Fortuna College and Araullo University in Cabanatuan City. There are 18 tertiary level institutions in Cabanatuan City alone.
Health services is a notable industry. Hospitals cater to patients from Nueva Ecija and some from neighbouring provinces. There are schools of nursing and midwifery, mostly in Cabanatuan City.
There are poultry farms in a number of towns, most notably, the Lorenzo poultry farms in San Isidro which is one of the largest in the country. Duck raising and egg production is an important livelihood. Fishponds are unevenly distributed throughout the province but the largest concentrations are in San Antonio, Santa Rosa, and Cuyapo.
Fabrication of tricycle "sidecars" is widespread in the province, notably in Santa Rosa, where prices are as low as PhP 7,000 which is practically the cheapest in the country.
Several areas have mineral deposits. Copper and manganese have been found in General Tinio, Carranglan, and Pantabangan. The upper reaches of Carranglan and Palayan City are said to contain gold.[66]
In June 2008, it received the title "Milk Capital of the Philippines" because Nueva Ecija gathers more milk from cows and carabaos (water buffaloes) than any other place in the Philippines.[67] The Philippine Carabao Center is in the CLSU compound in Science City of Munoz.
Tourism
Tourism in Nueva Ecija is focused on gatherings in churches, parks, and festivals. Some of these heritage areas are the Gapan Church, a Byzantine architecture church built from 1856 to 1872 which has been declared as a National Cultural Treasure, the first in the entire province; the Quezon Family Rest House in Bongabon which was also the place of death of former First Lady Aurora Quezon; Centuries-old brick walls of the Tabacalera in San Isidro remain as witness to the Novo Ecijanos' 100-year oppression, from 1782 to 1882, when the province became the center of the tobacco monopoly in Central Luzon and was thus restricted from raising other crops; the statue of Philippine hero General Antonio Luna astride a horse stands at the Cabanatuan plaza in front of the cathedral on the exact spot where the brave general was assassinated in 1899 in the city that adopted him subsequently; Site of the arrest of Philippine hero Apolinario Mabini, known as "the sublime paralytic," by the Americans on December 10, 1899 in Cuyapo; the Triala House of General Manual Tinio, built during the early Commonwealth period, it features ornately designed turn-of-the-century furniture and a life-size figure of esteemed Nove Ecijano Don Kapitan Berong in stained glass; The Grand Sedeco house in San Isidro, which General Emilio Aguinaldo frequented, marks this gallant town that has proven time and again to be cradle of Filipino heroes - it was here that General Frederick Funston planned the capture of Aguinaldo, first President of the Philippine republic, during the Philippine–American War; Wright Institute of San Isidro, of the first high schools established outside Metro Manila during the American period; the Dalton Pass located in Capintalan, Carranglan, the five-hectare area blessed with a cool climate houses the monument of General Dalton and a tower that borders the provinces of Nueva Ecija and Nueva Vizcaya - uphill is a World War II memorial in black marble where a historical account of the war had been etched in English and Japanese; the WWII Concentration Camp in Cabanatuan City; Nampicuan Church; Carranglan Church; Pantabangan Church; the grand Minalungao National Park,[68] known for its high limestone formations sculpted by the Penaranda river; General Luna Fall in Rizal; Mount Olivete in Bongabon, which is frequented by pilgrims due to its holy spring; the Capintalan, which is a reserve known for its WWII tunnels, forests, rivers, and artifacts and has been maintained by the only Ifugao community in Nueva Ecija, located in Carranglan; Palaspas Falls in San Jose City; Gabaldon Falls in Gabaldon which is within the Sabani Estate Agricultural College; Peñaranda Church, which is one of the oldest in the province, built initially in 1887; Diamond Park in San Jose City; Pantabangan Dam, built in 1947, is the first and only rubber dam in Asia; the campus of the Philippine Rice Research Institute in Muñoz which is the main research and experimentation arm of the government for rice and other crops; Central Luzon State University, which is the most academically excellent in the province and the only Novo Ecijano university to be declared a cultural property of the nation; CLSU Agricultural Museum; Living Fish Museum in Muñoz; the Philippine Carabao Center in Muñoz, which is the main arm of the national government on carabao research and development; Mount Mapait in Palayan City; and the Philippine Eagle Exclusive Area in the Nueva Ecija Sierra Madres.
Tourist attractions:
- Minalungao Park
- Pantabangan Lake
- Lupao Pinsal Falls
- Nabao Lake
- Fort Magsaysay Dam (Pahingahan)
- Tanawan

 Landscape at Carranglan
Landscape at Carranglan Pantabangan Dam
Pantabangan Dam Central Luzon State University main gate
Central Luzon State University main gate
Politics
The Governor of Nueva Ecija is the highest-ranking official in the province, after the President of the Philippines. The province is divided into four congressional districts, which consists of 27 municipalities and five cities, namely: Cabanatuan, San Jose, Palayan, Gapan and Science City of Muñoz. The provincial capital is Palayan City. Each district has a specialization, where district 1 is known for its organic agriculture, district 2 is known for its highlands and protected forests, district 3 is known for its urban and economic settings, and district 4 is known for its diverse cultural celebrations. Each district is under a congressperson, whom represents the district at the House of Representatives in Congress. Political alliances in the province is extremely strong, with the ruling party, the Liberal Party of the Philippines, staying in power since the post-martial law era. Being an agricultural province, the main political agenda for the province is agricultural and aquacultural advancements, along with high level education, health, and job and business generation. The current governor of the province is Aurelio Umali and its vice governor is Anthony Umali.


Culture
Novo Ecijano culture is a mixture of Tagalog, Kapampangan, Pangasinense, Ilokano, and other indigenous cultures within the province. A melting pot of culture, the province has a varied of festivals, traditions, and beliefs that constitute Novo Ecijano heritage, along with tangible heritage structures, scenes, and objects.
Cosmopolitanism
Novoecijano architecture is based on indigenous Filipino types, Spanish colonial types, American colonial types, and modernist types. In rural areas, the bahay kubo is still present, but has decreased significantly. Spanish and American colonial architecture, like those in the National Capital Region, have slowly been demolished one after the other, signaling a destruction of colonial heritage. Despite this, there are still colonial structures preserved and conserved such as town churches and some houses surrounding them. The current architectural trend in the province is modernist architecture, signaling an end to colonial architecture in the province.
Music
The music of the Neocijano is more concentrated on the Tagalog traditional and international music. The province shares the music heritage of other Tagalog provinces such as Rizal, Batangas, Bataan, Bulacan, Quezon, and Laguna.
Visual arts
Many Novo ecijanos have been internationally known for their visual arts. The mediums are diverse, from garlic oil, blood, hair, threads, clays, pastels, leaves, mud, bronze, marble, cotton, pina, and paints which introduced as Indigenous Materials or Indigenouism movement started by Internationally known Hair and Blood Painter of the Philippines.
Values
As a general description, the distinct value system of Filipinos is rooted primarily in personal alliance systems, especially those based in kinship, obligation, friendship, religion, and commercial relationships.
Filipino values are, for the most part, centered around maintaining social harmony, motivated primarily by the desire to be accepted within a group.[496] The main sanction against diverging from these values are the concepts of "Hiya", roughly translated as 'a sense of shame', and "Amor propio" or 'self-esteem'.[496] Social approval, acceptance by a group, and belonging to a group are major concerns. Caring about what others will think, say or do, are strong influences on social behavior among Filipinos.
Other elements of the Filipino value system are optimism about the future, pessimism about present situations and events, concern and care for other people, the existence of friendship and friendliness, the habit of being hospitable, religious nature, respectfulness to self and others, respect for the female members of society, the fear of God, and abhorrence of acts of cheating and thievery.
Dance
A very Tagalog hotpot of culture, the novoecijano dance scheme is ruled by the carinosa, tinikling, and other Tagalog traditional dances.
Cuisine
Neoeciajno cuisine is varied. In its northwest, seafood and vegetable dishes with a lot of salt is prevalent due to its proximity with Pangasinan. In its northwest, highland crops are much prized. In its central and southern areas, food is very diverse due to its proximity with numerous sources of ingredients.
Literature
Novo Ecijano literature is defined by a strong nationalistic approach and a strong ethnically grounded scheme. The literature of the province is honed by the two literature departments of the Central Luzon State University, among others.
The best known Tagalog novelist of the province is Lázaro Francisco. His novels depicted life in an agrarian society that gave rise to the social unrest of his period (1950s and 1960s). One of his novels was serialized by Liwayway Magazine, the most popular Tagalog magazine at that time until the 1970s.[69] But unlike the Partido Komunista ng Pilipinas, Lazaro advocated for the peaceful resolution of the agrarian problem, relying on the benevolence of the government and the landlords.[70]
Lázaro Francisco was from Tarlac. As a child, her parents immigrated to Nueva Ecija. He practically grew up and studied in Cabanatuan. One of the elementary schools in Cabanatuan has been named after him.[70] He was named a National Artist in 2012. He was also a Freemason, and one of the distinguished Master of Masonic Lodge 53 in Cabanatuan City. He was named a National Artist in 2012.
Media
Nueva Ecija has many of its own television channels and radio stations. Almost all towns have their own radio stations.
Sports
The most prevalent sport in the province, like in other provinces in the country, is basketball. Volleyball, badminton, cockfighting, and sepak takraw are the other big sports in the province.
Games
Traditional Novo Ecijano games are mainly Tagalog in nature. These games include luksong baka, patintero, piko, and tumbang preso. The novo ecijano art group "Makasining" is also a main author of "Laro ng Lahi" or Philippine Indigenous Games preservation advocacy.
Festivals
One of the most historic provinces of the Philippines, festivals and fiestas are celebrated in different places in Nueva Ecija. Local history, customs and traditions can be witnessed in the province's festivals of locality.[71][72]
| Festival | City/Municipality | Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Banatu | Cabanatuan City | January 29 – February 4 | “Banatu Festival,” takes its name from “banatu” which means “vine” |
| Taong Putik Festival | Aliaga | June 24 | At the crack of dawn, scores of mud-covered, barely dressed devotees make their appearance, asking for alms and candles form the wide awake town folks.This practice mimics a biblical myth about St. John the Baptist |
| Ragragsak Ti Guimba | Guimba, Nueva Ecija | February to March | - |
| Holy Week Rituals of Puncan | Carranglan | Holy Week | The unique Holy Week rites of (Puncan)Carranglan one of the oldest towns in Nueva Ecija |
| Kariton Festival | Licab | March 28 | Celebrated during the annual celebration of the founding anniversary of Licab |
| Baybayanting Festival | Lupao | July 25 | Honoring the town's patron – Señor Santiago. or Saint James |
| Araquio Festival | Penaranda | May | The festival dramatized the spread of Christianity in the country and the war between Christians and Muslims |
| Tanduyong Festival | San Jose City | 4th Sunday of April | The people of San Jose dance through the main street in a colorful, enchanting celebration of the blessing of the harvest of onion. The streets are filled with contingents of dancers outfitted in striking, multi-hued native costumes |
| Pagibang Damara | San Jose City | April or May | A celebration for a bountiful harvest of the city |
| Pandawan Festival | Pantabangan | April | The word “Pandaw” means assurance of an abundant fresh-water catch each time the festival is celebrated |
| Sibuyas Festival | Bongabon | April 1–10 | Celebrated as a form of thanksgiving and a way to show that Bongabon is one of the largest producers of onion in Asia |
| Tsinelas Festival | Gapan | August 6–25 | Commemorates Gapan's major industry with the Tsinelas Festival on the anniversary of their cityhood. |
| Paistima Festival | Cabiao | February 5–11 | Commemorate the founding anniversary of the town |
| Kabyawan Festival | Cabiao | May 8–16 | Thanks giving to the feast of patron's town proper Saint John Nepomocene |
| Kalamay Festival | San Leonardo | August 25 | Thanksgiving for the abundance of harvest using rice as main ingredients of kalamay is the town's major cultural activity. |
| Papaya Festival | General Tinio | March | Holy Mass and religious activities are celebrated to honor the town's patron saint, San Isidro de Labrador. Papaya is the town's former name after a fruit tree abundant in the town. |
Health
The health issues facing the province are minimal because of the health establishments dotting all over the province. National health issues such as dengue, and malaria are on rise during rainy seasons, while HIV/AIDS is still low, but 2015 annual growth rate is unarguably high.
Education
The level of literacy in the province is very high. The top four universities in the province, collectively known as the 'Four Knowledge Eagle Universities of Nueva Ecija' or 4-KEUN, are Central Luzon State University at Science City of Muñoz, Wesleyan University Philippines, Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology and Araullo University, all located at Cabanatuan City. The universities offer a diverse range of specializations. Every municipality also has local colleges. Central Luzon State University, a national cultural property, has also been accredited as being the twenty first to the sixth most academically excellent in the entire country. The university has also been cited as one of the 100 most significant educational institutions in Asia, overwhelming most schools in Metro Manila and other metropolitan areas in the country.
Notable people
- General Mariano Llanera † (1855–1942) — fought in the provinces of Bulacan, Tarlac, Pampanga, and Nueva Ecija.
- Engr. Ponciano A. Bernardo † (December 2, 1905 — April 28, 1949) was the 2nd Mayor of Quezon City. Ponciano Bernardo was born in Santa Rosa, Nueva Ecija, whose father immigrated from Pandi, Bulacan to PAPAYA now called General Tinio, Nueva Ecija. Ponciano Bernardo School and Ponciano Bernardo Park in Cubao, Quezon City is a memorial for him. Ponciano was killed in an ambush by Hukbalahap with the Philippine First Lady Aurora Quezon on their route to Aurora. Ponciano was appointed by the 2nd Philippine President Manuel Quezon, prior to being Mayor he was Secretary of Department of Public Works and Highways. Ponciano was a Filipino engineer and politician who served as mayor of Quezon City, holding the position from 1947 until his death in 1949. It was during his tenure that Quezon City was designated as the capital city of the Philippines.
- Juan Pajota (c.1914 – 1976) was involved in the Raid at Cabanatuan, an action which took place in the Philippines on 30 January 1945 by US Army Rangers and Filipino guerrillas and resulted in the liberation of more than 500 American prisoners of war (POWs) from a Japanese POW camp near Cabanatuan City
- Epifanio de los Santos † (April 7, 1871 — April 18, 1928) — Epifanio de los Santos y Cristóbal, sometimes known as Don Pañong or Don Panyong he was born in 1871 in Malabon, province of Rizal, (now an independent city) to Escolastico de los Santos of Nueva Ecija and musician Antonina Cristóbal of Malabon. He was a noted Filipino historian, literary critic, art critic, jurist, prosecutor, antiquarian, archivist, scholar, painter, poet, musician, musicologist, philosopher, philologist, bibliographer, translator, journalist, editor, publisher, paleographer, ethnographer, biographer, researcher, civil servant, patriot and hero. He was appointed Director of the Philippine Library and Museum by Governor General Leonard Wood in 1925. He was appointed district attorney of San Isidro, Nueva Ecija. He was later elected as governor of Nueva Ecija in 1902 and 1904. His election victory made him the first democratically elected provincial governor and head of the Federal Party in Nueva Ecija.
- Heber Gonzalez Bartolome (born November 4, 1948) — a Filipino folk and folk rock singer, songwriter, composer, poet, guitarist, bandurria player, bluesman, and painter. His music was influenced by the "stylistic tradition" of Philippine folk and religious melodies.
- Catalino "Lino" Ortiz Brocka, also known as Lino Brocka (April 3, 1939 – May 22, 1991) born in Pilar, Sorsogon but he grew up in San Jose City, Nueva Ecija. He was a Filipino film director, widely regarded as one of the most influential and significant Filipino filmmakers in the history of Philippine cinema. In 1983, he founded the organization Concerned Artists of the Philippines (CAP), dedicated to helping artists address issues confronting the country.
- Dorothy Acueza Jones, also known as Nida Blanca † (January 6, 1936 – November 7, 2001) — Nida Blanca as popularly known by her stage name, was a Filipina actress. She starred in over 163 movies and 14 television shows and received over 16 awards for movies and six awards for television during her 50-year film career. She was named one of 15 Best Actress of all Time by YES magazine.
- Deo Macalma — news anchor currently working at DZRH in the Philippines. Live in Gapan City
- Jaime de los Santos (born April 1946, Nueva Écija — is a retired military general in the Philippines. He joined the Philippine Army in 1969 after graduating from the Philippine Military Academy with a degree Bachelor of Science in Military Engineering. De los Santos later on served as a Brigade Commander, Chief of Staff and Commanding General of an Infantry Division and Superintendent of the Philippine Military Academy.
- Frankie Evangelista † (July 24, 1934 — February 18, 2004) — A former radio and television broadcaster of ABS-CBN since 1953.
- Josepina "Josie" Padiermos Fitial (born November 25, 1962) — The current First Lady of the Northern Mariana Islands and the wife of Governor Benigno Fitial. She became First Lady upon the inauguration of her husband as the 6th Governor of the Northern Mariana Islands on January 9, 2006.[1]
- Fred Panopio † (February 2, 1939 — April 22, 2010) — A Filipino singer and actor who rose to fame in the 1970s.
- Rogelio R. Sikat (Also known as Rogelio Sícat) (1940–1997) — A Filipino fictionist, playwright, translator and educator. He was born to Estanislao Sikat and Crisanta Rodriguez on June 26, 1940 in Alua, San Isidro, Nueva Ecija. He is the sixth of eight children. Sicat graduated with a B.Litt. in Journalism from the University of Santo Tomas and an M.A. in Filipino from the University of the Philippines.
- Néstor de Villa † (July 6, 1928 – February 21, 2004) — was a Filipino actor frequently cast in musical films. He was a gifted dancer often paired with frequent onscreen partner Nida Blanca in both movies and television. His dancing talent led some to call him the "Fred Astaire of the Philippines", though the same moniker had also been given to Bayani Casimiro.
- Francisco Lazaro is one of the finest Tagalog novelist. One of his novels has been serialized by Liwayway magazine, the most popular Tagalog magazine in the 1950s-1970s. A Freemason and one of the distinguished Master of Masonic Lodge 53 of Cabanatuan City, he was named National Artist in 2012.
- Felipe Padilla de León a Filipino classical music composer, conductor, and scholar. He was a 1997 National Artist of Philippines for Music.
- Oscar A. Solis (October 13, 1953) — Oscar Azarcon Solis was born in San Jose City, Philippines. He studied at Christ the King Seminary of the Society of the Divine Word in Quezon City, Philippines, and at the Pontifical Royal Seminary, University of Santo Tomas, in Manila. After migrating to the United States in 1984, Father Solis served as associate pastor of St. Rocco's parish, New Jersey, 1984–1988. With permission from his Ordinary in the Philippines, he went to the Diocese of Houma-Thibodaux in 1988 where he was appointed associate pastor of St. Joseph Co-Cathedral. He was incardinated into the Diocese of Houma-Thibodaux in 1992, and was named pastor of St. Joseph Co-Cathedral in 1999. He has been a member of the Diocesan Priests' Council, the Personnel Committee and the College of Consultors. Solis is the first Filipino-American to be consecrated a bishop.[73]
- Joe Taruc (September 18, 1946 - September 30, 2017) - Born in Gapan City, Jose Malgapo Taruc, Jr. is his full name. He is a longtime radio broadcaster of DZRH and also a host of his radio programs Pangunahing Balita and Damdaming Bayan.
- Anthony Taberna (January 16, 1975) — Born in San Isidro, Nueva Ecija, Anthony "Tunying" Taberna is a Filipino television news anchor and radio broadcaster. At ABS-CBN, Taberna has hosted television and radio programs covering news and public affairs. He is currently hosting Umagang Kay Ganda (where he gained popularity in the segment "Punto por Punto") and XXX: Exklusibong, Explosibong, Exposé. As a DZMM broadcaster, Taberna is one of the lead anchors for Dos Por Dos, a late afternoon show, along with Gerry Baja.
- Kathryn Bernardo (March 26, 1996) — Born in Cabanatuan City, Kathryn Chandria Manuel Bernardo is her full name. She is a Filipina actress and her career started in 2003. She is best known for her role as Mara in the primetime Filipino drama, Mara Clara. Kathryn is currently a contract artist of Star Magic and ABS-CBN and most recently starred as Ana Bartolome in the 2011 drama film, Way Back Home. She currently plays the main protagonist, Christina Charlota Tampipi, in the primetime series Got to Believe.
- Ameurfina Melencio-Herrera, Filipino lawyer and jurist who served as Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines from 1979 to 1992. Herrera is a granddaughter of Emilio Aguinaldo.
- Willie Revillame (January 27, 1961) — A Novo Ecijano with roots from Cabanatuan City but he was born in Manila, Philippines. He started his career in 1986. He is a television host, actor, comedian and a recording artist in the Philippines.
- Elito Circa (January 28, 1970) — A Novo Ecijano from Pantabangan, Nueva Ecija better known as "Amangpintor", is a Filipino painter and folk artist, known for his indigenous human hair and blood medium for paintings with mythologism and mythicalism subject matters. He is noted as the "First Hair and Blood Painter" of his generation and known for his signature subject of Legend of Minggan. He also popularized Hand Painting performances done within five (5) to ten (10) minutes in a canvas of 432 square inches using the three (3) primary colors.
- Jose "Kaka" Balagtas — A film director, writer, and actor. He is the Vice Mayor of San Antonio, Nueva Ecija.
- Joanna Cindy Miranda — A Filipina model and host from Rizal, Nueva Ecija, who won the Binibining Pilipinas-Tourism 2013 crown and will represent the country in Miss Tourism Queen International in Lhasa, Tibet in the first week of September, 2013.
- Paolo Ballesteros — (born November 29, 1982 in Cabanatuan City, is a Filipino actor, TV host and model. He has appeared in films and several TV shows. He has won numerous international awards, all portraying the struggles of the LGBT community.
- John Paul Lizardo — Also known as Japoy Lizardo, is a Filipino Taekwondo Asian Games Bronze medalist, Actor and commercial model from Cabanatuan City.
- Yen Santos — A Filipina actress and dancer. Part of ABS-CBN Star Magic. Had appeared in Growing Up and teleserye Pure Love. From Cabanatuan City.
- Jason Abalos — An actor, dancer and commercial model. Part of ABS-CBN Star Magic from Pantabangan, Nueva Ecija.
- Rommel Padilla — An politician, businessman, actor and endorser from Cuyapo, Nueva Ecija and Father of Daniel Padilla and Brother of Robin Padilla known for starring in the Philippine movies Lorenzo's Time (2012), Totoy Golem (1996) and Kahit Demonyo Itutumba Ko (2000).
- Ramon Valmonte— An writer and founder of Nueva Ecija Journal. Professor from Wesleyan University Philippines descendant of Pantaleón Valmonte y Rufino, sometimes referred to as Pantaleón Belmonte a capitan municipal (mayor) of Gapan and a general during the Philippine Revolution against Spain.
- Anselmo Roque— An agricultural columnist. Multiawarded journalist and educator Anselmo Roque. One of the longest-serving provincial writers of the Inquirer, Roque joined the paper in 1986 as its correspondent in Nueva Ecija province.
- Ryza Cenon — A Filipina actress born on December 21, 1987 in Gapan City, as Rhiza Ann Cenon Simbulan. She is an actress, known for Lovestruck (2005), Mr. & Mrs. Cruz (2018) and Sana ay ikaw na nga (2012).
- Renato Bautista — He was born in 1980 in Nueva Ecija, Philippines as Renato M. Bautista Jr. He is an assistant director and director, known for 'Di natatapos ang gabi (2010), Palitan (2012) and Expressway (2016).
- Bert Matias — He was born on July 6, 1937 in Cabanatuan City, Philippines as Lamberto I. Matias. He is an actor, known for Fred Claus (2007), Book of Swords (1996) and Renegade Force (1998).
- Ameurfina Melencio-Herrera, Filipino lawyer and jurist who served as Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines from 1979 to 1992. Herrera is a granddaughter of Emilio Aguinaldo.
- Vic Sotto — Multi-awarded Filipino actor, television host, comedian.
- Ruel S. Bayani — Filipino film and television director, writer, producer, who is best known for directing movies like One More Try, and No Other Woman and co-directing television shows like Budoy, Kokey, Mula Sa Puso.
- Samboy de Leon — Filipino professional basketball player who last played for the Star Hotshots of the Philippine Basketball Association (PBA). National Athletic Association of Schools, Colleges and Universities (NAASCU), where he was awarded the league MVP in 2014 played for CEU Scorpions.
- Coleen Perez — (born Coleen Nicole Perez Borgonia on 26 January 1995 in Gapan City, (Formerly known as Maricris Garcia and also known as Faye Lorenzo) is a Filipina commercial model and actress, known for her roles such as Molly Rivera in GMA Network's More Than Words.
- Nikki Brianne F. Samonte — better known as Nikki "Nikz" Samonte (born March 1, 2000) in Nueva Ecija is a Filipina child actress, singer and model. She is currently handled and managed by ABS-CBN's talent agency, Star Magic.
- Manuel Chua — (born October 29, 1980) in Cabanatuan City is a Filipino male model and actor.He was discovered in the Filipino version of the reality game show Pinoy Fear Factor which was aired on ABS-CBN, from November 2008 to February 2009. Chua currently is a member of ABS-CBN's elite circle of homegrown talents, Star Magic. Chua is currently a freelance artist.
- Fred Panopio — (February 2, 1939 – April 22, 2010) was a Filipino singer and actor who rose to fame in the 1970s. This particular kind of music is evident is many of his hits, such as "Pitong Gatang," "Markado," and "Tatlong Baraha". He was also an occasional actor, and appeared in several movies alongside Jess Lapid and Fernando Poe, Jr. He is also known sing the Poe's movie's theme songs.In 1999, Panopio and Victor Wood released an album and became part of the OPM legends.
- Kurt Isaiah Perez — (born December 1, 1997) in Cabanatuan City is a Filipino former child actor. He became famous for being the Ultimate Male Survivor of StarStruck Kids, the reality-based talent search show of GMA in the Philippines.
See also
References
- "N. Ecija founding date April 25, not Sept. 2". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on 30 May 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Archived from the original on 21 January 2013. Retrieved 17 October 2013.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region III (Central Luzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "POPULATION PROJECTIONS BY REGION, PROVINCE, CITIES AND MUNICIPALITIES, 2020-2025". www.doh.gov.ph. Department of Health. August 27, 2020. Retrieved October 16, 2020.
- "Dependency Ratio Down by Three Persons in Nueva Ecija". Philippine Statistics Authority. September 2, 2002. Retrieved 15 December 2015.
- "Province: Nueva Ecija". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- "Pampanga River Basin". rbco.denr.gov.ph.
- Census, United States Bureau of the; Commission (1900-1916), United States Philippine (1905). Census of the Philippine Islands: Taken Under the Direction of the Philippine Commission in the Year 1903, in Four Volumes ... U.S. Government Printing Office. Retrieved 17 August 2019.
- Barrows, Dr. David P. (1910). The Ilongot or Ibilao of Luzon. Popular Science Monthly.
- Mozo, Antonio (1763). En Que Se Da Cuenta. googlebooks.com. p. 247.
- "The Ilongot". Daniel Strouthes.
- "Pre Colonial Period". oocities.org.
- Barrows, David P. (1916). "The Governor-General of the Philippines Under Spain and the United States". The American Historical Review. 21 (2): 288–311. doi:10.2307/1835051. JSTOR 1835051.
- "The Augustinian Friars (Order of Saint Augustine)". sanagustinchurch.org.
- "N. Ecija founding date April 25, not Sept. 2". inquirer.net.
- "About Cabanatuan City". fnetravel.com.
- "HISTORY OF "UNANG SIGAW NG NUEVA ECIJA"". Ginto ang Inaani.
- Edilberto C de Jesus. "Tobacco Monopoly in Philippines". The Reading Life.
- "History of the Province". visitmyphilippines.com.
- "True Version of the Philippine Revolution". authorama.com.
- Agoncillo & Guerrero (1977). "The Constitution of the Old La Liga Filipina(1892)". History of the Filipino People (5th ed.). pp. 164–168. Archived from the original on 2012-08-03.
- "La Solidaridad and La Liga Filipina". philippine-history.org.
- "About Gapan". cityofgapan.gov.
- "Philippine Revolution of 1896". About Philippines. Archived from the original on 2013-10-21. Retrieved 2012-05-29.
- "Magdiwang and Magdalo". tripod.com.
- "Pact of Biak na Bato". philippine-history.org.
- "Emilio Aguinaldo y Famy". Library of Congress.
- Arnaldo Dumindin. "Philippine–American War, 1899–1902". philippineamericanwar.webs.com.
- "The World of 1898: The Spanish–American War". Hispanic Division Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 2011-06-29. Retrieved 2017-12-29.
- "Japanese Occupation". philippine-history.org.
- "Ghost Soldiers". Hampton Sides.
- "Great Raid". Carole D. Bos.
- Arnaldo Dumindin. "Fil-Am War Breaks Out". philippineamericanwar.webs.com.
- "The Philippines under Spanish and American Rules". Forbes-Lindsay, C. H.
- "The Treaty of Paris" (PDF). law.upd.edu.ph. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-26.
- "The Last Holdouts". Arnaldo Dumindin.
- American Colonial Period (Philippines)
- Edgar Wickberg. Early Chinese Economic Influence in the Philippines, 1850–1898 (PDF). upf.edu. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-02-20.
- "Railways in The Philippines". Trade Chakra.
- "The Rice Granary of the Philippines". kylian74.
- "Agrarian Reform History". Department of Agrarian Reform. Archived from the original on 2013-05-14. Retrieved 2012-06-24.
- "THE PHILIPPINE BILL OF JULY 1, 1902". chanrobles.com.
- "The United States and Its Territories (1870–1925:The Age of Imperialism)". quod.lib.umich.edu.
- Henry F. Funtecha (August 18, 2006). "The Government During the American Regime". The News Today.
- "Act No. 1748". philippinelaw.info.
- "The Taft Commission". philippine-history.org.
- "American Government Gave Importance to Education". etravelpilipinas.com.
- "Education Act of 1901". philippinelaw. Archived from the original on 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2012-05-29.
- 1st Philippine Legislature
- Kerkvliet, Benedict J. (1977). The Huk Rebellion: A Study of Peasant Revolt in the Philippines. ISBN 9780742518681.
- "1945 Great Raid on Cabanatuan Prison". Olive-Drab.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region III (Central Luzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- "Weather forecast for Nueva Ecija, Philippines". Storm247.com. StormGeo AS, Nordre Nøstekaien 1, N-5011 Bergen, Norway: StormGeo AS. Retrieved 23 April 2016.CS1 maint: location (link)
- Atlas Filipinas | kwf.gov.ph
- "2000 Census on Population and Housing/" (PDF). PSA.gov. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- Tan, Michael L.; Tan, Michael T. (2008). Revisiting Usog, Pasma, Kulam. UP Press. p. 154. ISBN 9789715425704. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/NSCB_LocalPovertyPhilippines_0.pdf; publication date: 29 November 2005; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2009%20Poverty%20Statistics.pdf; publication date: 8 February 2011; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Updated%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%20with%20Measures%20of%20Precision%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province_2015%20and%202018.xlsx; publication date: 4 June 2020; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- "RICE GRANARY OF THE PHILIPPINES". Ginto ang Inaani.
- "Nueva Ecija, Still the Country's Top Palay Producing Province". National Statistical Coordination Board. June 2008. Archived from the original on 2008-07-27.
- Estimation of the Geologic Mineral Reserve of the small-scale Gold Mines in the Philippines. National Statistical Coordination Board.
- TV Patrol North Central Luzon
- "Best Places to Visit in Minalungao National Park". Indi Newz. 2019-09-05. Retrieved 2019-09-27.
- Cruz, Neni Sta Romana. "Remembering Lazaro Francisco". opinion.inquirer.net. Retrieved 17 August 2019.
- "Francisco, Lazaro". CulturEd: Philippine Cultural Education Online. Retrieved 17 August 2019.
- Romulo, Liana (2012). Filipino Celebrations: A treasury of Feasts and Festivals. Tuttle Publishing. ISBN 9781462908622. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- "Famous and Notable Traditionally Celebrated Socio-cultural and Religious Festivals of Nueva Ecija". Knoji. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
- "Louisiana Pastor Named Auxiliary Bishop Of Los Angeles". United States Conference of Catholic Bishops. Archived from the original on 2013-04-16.
External links
 Media related to Nueva Ecija at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Nueva Ecija at Wikimedia Commons Geographic data related to Nueva Ecija at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Nueva Ecija at OpenStreetMap- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- Local Governance Performance Management System
- Nueva Ecija Now and Beyond