U-90042
U-90042 is a sedative and hypnotic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to sedative-hypnotic benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
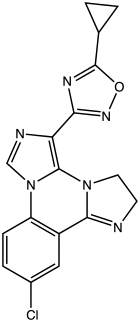
| Formula | C17H13ClN6O |
| Molar mass | 352.78 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
U-90042 is a GABAA agonist acting primarily at the α1, α3 and α6 subtypes, with a Ki of 7.8nM at α1, 9.5nM at α3 and 11.0nM at α6. It produces sedation and ataxia and prolongs sleeping time in mice, rats and monkeys, but does not produce amnesia and blocks the amnestic effect of diazepam, reflecting its different subtype affinity compared to benzodiazepine drugs.[1] It was developed by a team at Novo Nordisk in the 1980s.[2]
References
- Tang AH, Smith MW, Carter DB, Im WB, VonVoigtlander PF (November 1995). "U-90042, a sedative/hypnotic compound that interacts differentially with the GABAA receptor subtypes". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 275 (2): 761–7. PMID 7473164.
- US 5100895, "Heterocyclic compounds and their preparation and use"
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.