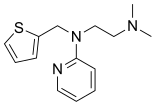
Methapyrilene
Methapyrilene is an antihistamine and anticholinergic of the pyridine chemical class which was developed in the early 1950s. It was sold under the trade names Co-Pyronil and Histadyl EC.[1] It has relatively strong sedative effects, to the extent that its primary use was as a medication for insomnia rather than for its antihistamine action. Together with scopolamine, it was the main ingredient in Sominex, Nytol, and Sleep-Eze. It also provided the sedative component of Excedrin PM. All of these products were reformulated in the late 1970s when methapyrilene was demonstrated to cause liver cancer in rats when given chronically.[2]
"Thionylan" redirects here. Not to be confused with thionyl halides: thionyl fluoride, thionyl chloride and thionyl bromide.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.714 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H19N3S |
| Molar mass | 261.39 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
See also
References
- The Birmingham Post Archive. thefreelibrary.com
- Lijinsky W, Reuber MD, Blackwell BN (August 1980). "Liver tumors induced in rats by oral administration of the antihistaminic methapyrilene hydrochloride". Science. 209 (4458): 817–9. Bibcode:1980Sci...209..817L. doi:10.1126/science.7403848. PMID 7403848.
| Benzimidazoles (*) | |
|---|---|
| Diarylmethanes |
|
| Ethylenediamines | |
| Tricyclics | |
| Others |
|
| For topical use | |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H1 |
|
|---|---|
| H2 |
|
| H3 |
|
| H4 |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.