Nakhon Si Thammarat Province
Nakhon Si Thammarat Province (Thai: จังหวัดนครศรีธรรมราช, pronounced [ná(ʔ).kʰɔ̄ːn sǐː tʰām.mā.râːt̚]; often shortened to Nakhon Si, Nakhon Si Thammarat or Nakornsrithammarach) is one of the southern provinces (changwat) of Thailand, on the western shore of the Gulf of Thailand. Neighboring provinces are (from south clockwise) Songkhla, Phatthalung, Trang, Krabi and Surat Thani.[5]
Nakhon Si Thammarat Province
จังหวัดนครศรีธรรมราช | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Nickname(s): Nakhon Si or Nakornsri (นครศรีฯ) Muangkhon (เมืองคอน) | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Nakhon Si Thammarat Province | |
| Coordinates: 8°25′7″N 99°57′49″E | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Nakhon Si Thammarat |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Siripat Phatthakun (since October 2019)[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 9,943 km2 (3,839 sq mi) |
| Area rank | Ranked 18th |
| Population (2018)[3] | |
| • Total | 1,560,433 |
| • Rank | Ranked 8th |
| • Density | 157/km2 (410/sq mi) |
| • Density rank | Ranked 26th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
| • HAI (2017) | 0.5687 "average" Ranked 55th |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 80xxx |
| Calling code | 075 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-80 |
| Website | www |
The name of the province derives from its Pali–Sanskrit name Nagara Sri Dhammaraja ('City of the Sacred Dharma King'), which in Thai pronunciation becomes "Nakhon Si Thammarat".
As of 2018, the population of the province was 1,560,433 persons.[3]
Geography
The province is on the Gulf of Thailand on the east side of the Malay Peninsula. The terrain is mostly rugged hilly forest. The province is home to south Thailand's highest peak, Khao Luang, at 1,835 metres (6,000 ft), now protected in Khao Luang National Park.[6]

Environment
Forested peat swamp forests cover more than 9,900 hectares on the borders of Nakhon Si Thammarat, Phatthalung, and Songkhla Provinces. About 800 hectares of the peat swamp were destroyed by 88 fires in the first half of 2019. The Royal Forest Department says that most of the fires in the Khuan Khreng peat swamp forest were man-made. Criminals clear the forest for the illegal expansion of rubber and oil palm plantations. Honey collectors and fishermen were also complicit as they burn grass to catch fish or to collect wild honey. Khuan Khreng peat swamp was hit by drought in what is normally the rainy season making it susceptible to arson. The forest is surrounded by oil palm plantations and surface water in the forest has been drained out to feed the plantations.[7]
The province is home to Khao Luang National Park and Hat Khanom–Mu Ko Thale Tai National Park.
Economy
Tourism has become a first-tier tourist province, as defined by the central government, joining 22 other first-tier provinces. In 2019, it is projected to receive four million tourists—80% of them domestic—largely attracted by religious sites. They contributed more than 11 billion baht to the provincial economy. The Airports Department plans to expand Nakhon Si Thammarat airport runways and terminal by 2022 to deal with an anticipated increase in international flights to support foreign visitor arrivals. The province has 320 hotels with 8,800 rooms, up from 310 hotels and 7,000 rooms in 2018.[8]
Symbols
The provincial seal shows the Phra Baromathat chedi of Wat Phra Mahathat Voramahavihan, one of the most important historical sites in southern Thailand. According to the city chronicle it was already built in 311, but archaeology dates it to the 13th century. The chedi was built by the ruler of Malay Buddha Kingdom of Tambralinga, named Chandrabhanu Sridhamaraja of The Patama Vamsa (Lotus Dynasty). The chedi is surrounded by the animals of the Chinese zodiac in the seal. The twelve animals represent the twelve Naksat cities or city-states which were tributary to the Nakhon Si Thammarat kingdom: the Rat of Saiburi; the Ox of Pattani; the Tiger of Kelantan; the Rabbit of Pahang (actually a city in Pahang which is said to be submerged by a lake now); the Dragon of Kedah; the Snake of Phatthalung; the Horse of Trang; the Goat of Chumphon; the Monkey of Bantaysamer (might be Chaiya, or a town in Krabi Province); the Rooster of Sa-ulau (unidentified city, might be Songkhla, Kanchanadit or Pla Tha); the Dog of Takua Pa and a Pig of Kraburi.[9]
The provincial flower is the Golden Shower Tree (Cassia fistula), and the provincial tree is Millettia atropurpurea.[10]
The provincial slogan is เมืองประวัติศาสตร์ พระธาตุทองคำ ชื่นฉ่ำธรรมชาติ แร่ธาตุอุดม เครื่องถมสามกษัตริย์ มากวัดมากศิลป์ ครบสิ้นกุ้งปู, which translates to "A historical town, the golden Phra That, plentiful minerals, three-metal nielloware, numerous temples, abundant shellfish."[10]
Administrative divisions
Provincial government
Nakhon Si Thammarat is divided into 23 districts (amphoes). The districts are further divided into 165 subdistricts (tambons) and 1428 villages (mubans).
Local government
As of 26 November 2019 there are:[11] one Nakhon Si Thammarat Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 54 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Nakhon Si Thammarat has (thesaban nakhon) status. Pak Phun, Thung Son and Pak Panang have town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 50 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 130 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[3]
Transport
Nakhon Si Thammarat is served by Nakhon Si Thammarat Airport and the Nakhon Si Thammarat Railway Station.
Education
Public universities
- Walailak University[12]
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Rajabhat University
- Rajamangala University of Technology Srivijaya
- College of Industrial Technology and Management
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Saiyai Campus
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Thungyai Campus
- Thaksin University
- Management for Development College, Nakhon Si Thammarat Education Center
- Mahachulalongkornrajavidyalaya University, Nakhon Si Thammarat Campus
- Mahamakut Buddhist University, Sithammasokkarat Campus
- Ramkhamhaeng University, Nakhon Si Thammarat Regional Campus in Honour of His Majesty the King
- Sukhothai Thammathirat Open University, Nakhon Si Thammarat Regional Distance Education Center
- Boromarajonani College of Nursing Nakhon Si Thammarat
Public vocational colleges
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Technical College
- Thung Song Technical College
- Sichon Technical College
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Seaboard Industrial College
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Polytechnic College
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Vocational College
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Arts and Crafts College
- Nakhon Si Thammarat College of Agriculture and Technology
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Industrial and Community Education College
- Hua Sai Industrial and Community Education College
- Phrom Khiri Industrial and Community Education College
- Nakhon Si Thammarat Colleges of Dramatic Arts
- Nakhon Si Thammarat College of Fine Arts
Private vocational colleges
- Innovation Technological College
- Jaruspichakorn College of Technology
- Satapat Nakhon Technological College
- Thurakit Bundit Technological College
- Nakhon Commercial Vocational College
- Prateesasana Business Administration College
- Thaksin Vocational Technological College
- Pakphanang Vocational College
- Southern Technological College
- Thungsong Commercial College
- Charoenmit Commercial Technological College
- Sichon Commercial Technological College
- Virasinpin Vocational College
- Sakdisilpin Commercial School
Human achievement index 2017
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 23 | 24 | 65 | 33 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |
 |
 |
 |
|
| 46 | 61 | 39 | 66 |
| Province Nakhon Si Thammarat, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.5687 is "somewhat low", occupies place 55 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the Human achievement index (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[4]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
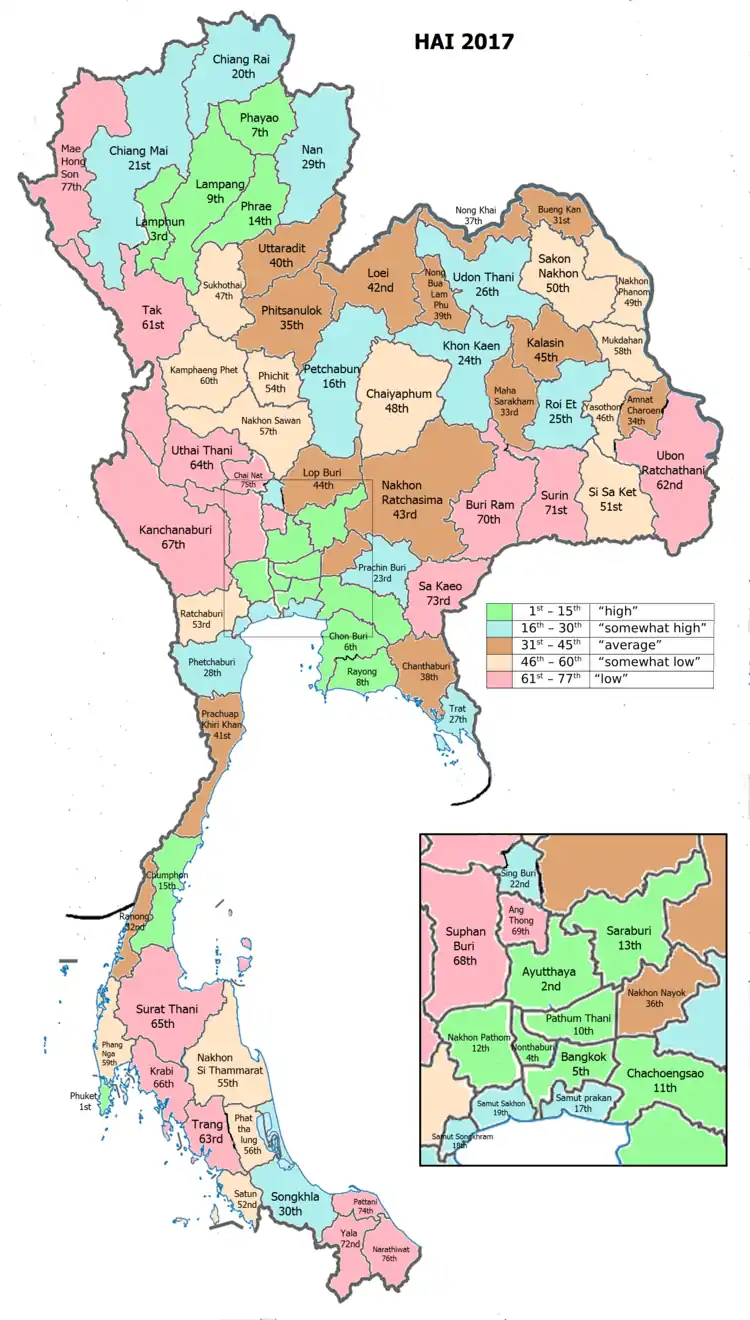 |
Sports
Football
Volleyball clubs
| Men's Volleyball Club | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Team | Leagues | Level | Years | Region | Position | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Supreme Nakhon Si Thammarat | Men's Volleyball Thailand League | Level 1 | 2010–11 | Thailand | 8th | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Women's Volleyball Club | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Team | Leagues | Level | Years | Region | Position | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Supreme Nakhon Si Thammarat | Women's Volleyball Thailand League | Level 1 | 2010–11 | Thailand | 5th | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011–12 | Thailand | 2nd | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012–13 | Thailand | 5th | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
Notes
Reports (data) from Thai government are "not copyrightable" (Public Domain), Copyright Act 2537 (1994), section 7.
References
- "ประกาศสำนักนายกรัฐมนตรี เรื่อง แต่งตั้งข้าราชการพลเรือนสามัญ" [Announcement of the Prime Minister's Office regarding the appointment of civil servants] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 136 (Special 242 Ngor). 10. 28 September 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.
- "รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ศ.2561" [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2018]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior (in Thai). 31 December 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- "About Nakhon Si Thammarat". Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT). Retrieved 2 August 2019.
- "Khao Luang National Park". Department of National Parks (DNP) Thailand. Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 24 May 2015.
- "More firefighters sent to Khuan Khreng swamp fire in Nakhon Si Thammarat". Thai PBS World. 1 August 2019. Retrieved 2 August 2019.
- Worrachaddejchai, Dusida (23 September 2019). "New province joins 1st-tier tourism ranks". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 23 September 2019.
- "Nakhon Sri Thammarat: Provincial Escutcheon". Thailex. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- "จังหวัดนครศรีธรรมราช". Nakhon Si Thammarat Provincial Administration (in Thai). Archived from the original on 2004-08-24. Retrieved 2015-07-31.
- "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
21 Nakhon Si Thammarat: 1 PAO, 1 City mun., 3 Town mun., 50 Subdistrict mun., 130 SAO.
- "Walailak University International College". Walailak University International College. Retrieved 21 June 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nakhon Si Thammarat Province. |
 Nakhon Si Thammarat travel guide from Wikivoyage
Nakhon Si Thammarat travel guide from Wikivoyage- Website of province (Thai)
- Nakhon Si Thammarat provincial map, coat of arms and postal stamp
- Everything in Nakhon Si Thammarat
- Tambralinga