Ecopipam
Ecopipam (SCH-39166) is a synthetic benzazepine derivative drug that acts as a selective dopamine D1/D5 receptor antagonist, with little affinity for either dopamine D2-like or 5-HT2 receptors.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
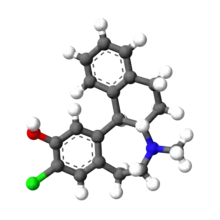
| Formula | C19H20ClNO |
| Molar mass | 313.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Clinical trials
Based on its profile in animal models, ecopipam was first studied as a treatment for schizophrenia but showed no activity.[2][3] Side effects including sedation, restlessness, emesis and anxiety were generally rated mild. There were no reports of Parkinsonian-like extrapyramidal symptoms typically seen with D2 antagonists.
Human clinical studies also showed that ecopipam was an effective antagonist of the acute euphoric effects of cocaine.[4] However, the effect did not persist following repeated administration.[5]
Researchers have postulated that dopamine via D1 receptors in the mesolimbic system is involved with rewarded behaviors and pleasure.[6] One such behavior is eating, and ecopipam has been shown in a large clinical study to be an effective treatment for obesity.[7] However, reports of mild-to-moderate, reversible anxiety and depression made it unsuitable for commercialization as an anti-obesity drug, and its development was stopped.[8]
Recent (2014) open label studies have shown ecopipam to reduce gambling behaviors in subjects with pathological gambling[9] and to decrease the motor and vocal tics in adults with Tourette’s Syndrome.[10] A subsequent double-blind placebo-controlled study in pediatric subjects confirmed ecopipam's ability to ameliorate the motor and vocal symptoms seen in patients with Tourette's. (Ecopipam, a D1 Receptor Antagonist, for Treatment of Tourette Syndrome in Children: A Randomized, Placebo-controlled Crossover Study, Gilbert et al., Movement Disorders, Volume33 (8):August 2018, Pages 1272-1280). Ecopipam is currently in a Phase 2/3 clinical trial for the treatment of Tourette's syndrome in children ages 7–17 conducted by the biotechnology company Emalex Bioscineces (who purchased Psyadon Pharmaceuticals in 2018) https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04007991?term=ecopipam&cond=Tourette+Syndrome+in+Children&draw=2&rank=1.
References
- Chipkin RE, Iorio LC, Coffin VL, McQuade RD, Berger JG, Barnett A (December 1988). "Pharmacological profile of SCH39166: a dopamine D1 selective benzonaphthazepine with potential antipsychotic activity". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 247 (3): 1093–102. PMID 2905002.
- Karlsson P, Smith L, Farde L, Härnryd C, Sedvall G, Wiesel FA (October 1995). "Lack of apparent antipsychotic effect of the D1-dopamine receptor antagonist SCH39166 in acutely ill schizophrenic patients". Psychopharmacology. 121 (3): 309–16. doi:10.1007/bf02246068. PMID 8584611.
- Den Boer JA, van Megen HJ, Fleischhacker WW, Louwerens JW, Slaap BR, Westenberg HG, Burrows GD, Srivastava ON (October 1995). "Differential effects of the D1-DA receptor antagonist SCH39166 on positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia". Psychopharmacology. 121 (3): 317–22. doi:10.1007/bf02246069. PMID 8584612.
- Haney M, Ward AS, Foltin RW, Fischman MW (June 2001). "Effects of ecopipam, a selective dopamine D1 antagonist, on smoked cocaine self-administration by humans". Psychopharmacology. 155 (4): 330–7. doi:10.1007/s002130100725. PMID 11441422.
- Nann-Vernotica E, Donny EC, Bigelow GE, Walsh SL (June 2001). "Repeated administration of the D1/5 antagonist ecopipam fails to attenuate the subjective effects of cocaine". Psychopharmacology. 155 (4): 338–47. doi:10.1007/s002130100724. PMID 11441423.
- Baik JH (October 11, 2013). "Dopamine signaling in reward-related behaviors". Front Neural Circuits. 7: 152. doi:10.3389/fncir.2013.00152. PMC 3795306. PMID 24130517.
- Astrup A, Greenway FL, Ling W, Pedicone L, Lachowicz J, Strader CD, Kwan R, Ecopipam Obesity Study Group (2007). "Randomized controlled trials of the D1/D5 antagonist ecopipam for weight loss in obese subjects". Obesity. 15 (7): 1717–31. doi:10.1038/oby.2007.205. PMID 17636090.
- Coulter AA, Rebello CJ, Greenway FL. Centrally Acting Agents for Obesity: Past, Present, and Future. Drugs. 2018;78(11):1113-1132. doi:10.1007/s40265-018-0946-y
- Grant JE, Odlaug BL, Black DW, Fong T, Davtian M, Chipkin R, Kim SW (August 2014). "A single-blind study of 'as-needed' ecopipam for gambling disorder". Ann Clin Psychiatry. 26 (3): 179–86. PMID 25166480.
- Gilbert DL, Budman CL, Singer HS, Kurlan R, Chipkin RE (January–February 2014). "A D1 receptor antagonist, ecopipam, for treatment of tics in Tourette syndrome". Clin Neuropharmacol. 37 (1): 26–30. doi:10.1097/WNF.0000000000000017. PMID 24434529.
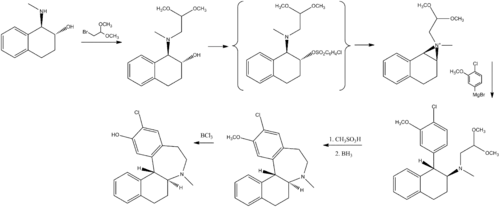
- Hou, D; Schumacher, D (2001). "The selection of a commercial route for the D1 antagonist Sch-39166". Current Opinion in Drug Discovery & Development. 4 (6): 792–9. PMID 11899619.