Santa Rosa, Laguna
Santa Rosa, officially the City of Santa Rosa (Tagalog: Lungsod ng Santa Rosa), is a first-class component city in the province of Laguna, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 353,767 people. [3]
Santa Rosa | |
|---|---|
Component city | |
| City of Santa Rosa | |
      (From left, clockwise): Santa Rosa Arch, Enchanted Kingdom, Santa Rosa de Lima Parish Church, Nuvali, Cuartel de Santo Domingo, Downtown Santa Rosa | |
 Seal | |
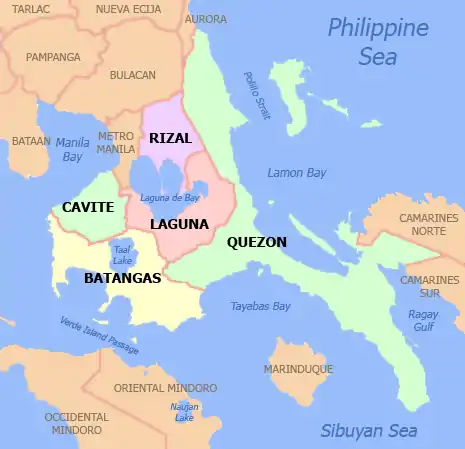
 Map of Laguna with Santa Rosa highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png.webp) Santa Rosa Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 14°19′N 121°07′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Calabarzon (Region IV-A) |
| Province | Laguna |
| District | 1st District |
| Founded | January 18, 1792 |
| Cityhood | July 10, 2004 |
| Named for | St. Rose of Lima |
| Barangays | 18 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlungsod |
| • Mayor | Arlene B. Arcillas |
| • Vice Mayor | Arnel DC. Gomez |
| • Representative | Danilo Ramon S. Fernandez |
| • Electorate | 213,913 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 54.84 km2 (21.17 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 70 m (230 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 353,767 |
| • Rank | 2 out of 30 (in Laguna)[4] |
| • Density | 6,500/km2 (17,000/sq mi) |
| • Households | 94,323 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 1st city income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 2.37% (2015)[5] |
| • Revenue | ₱2,302,416,040.75 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 4026 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)49 |
| Climate type | tropical monsoon climate |
| Native languages | Tagalog |
| Website | www |
It is the second largest local government unit in Laguna after Calamba. [3] On August 28, 2019, President Rodrigo Duterte signed Republic Act No. 11395,[6] which separated the city from the first district, allowing it to elect its separate representative beginning in the 2022 elections. However, for the purposes of electing Sangguniang Panlalawigan members, Santa Rosa will remain part of the province's first Sangguniang Panlalawigan District.
Santa Rosa was initially known for the Coca-Cola and Toyota manufacturing plants in its industrial estates. Recently, it has become popular for being the site of Enchanted Kingdom, a local theme park, and several housing developments.
History

In 1571, Spanish conquistador Juan de Salcedo, the grandson of Miguel López de Legazpi, founded the town of Biñan which was annexed as a barrio to Tabuco (now Cabuyao) while exploring the region of Laguna de Bay.
In 1688, Biñan, together with Barrio Bukol (Santa Rosa, before separation from Biñan) separated from Cabuyao. After a series of renaming and separating barrios to become independent towns, Barrio Bukol was politically emancipated as the municipality of Santa Rosa, which was named after Saint Rose of Lima. The municipality of Santa Rosa was founded on January 18, 1792.
During the revolutionary period in 1898, the town was instrumental in the proclamation of Philippine independence from Spain when the country signed the Act of Independence on June 12, 1898. Later on, the town's local revolutionaries fought alongside the forces of Pío del Pilar during the Philippine–American War.
On February 5, 1945, the town was abandoned by Japanese soldiers when the local guerrilla resistance movement, with support from the American and Filipino military contingent, entered the town, where skirmishes, torture, and deaths occurred.
During the postwar era up until the 1970s, the townspeople primarily depended on basic agriculture and family-owned enterprises for their livelihood. The influence of industrialization grew in the 1980s with the entry of local and foreign investors who were responsible for the fast-paced economic and social transformation of the town and the province.
Cityhood and present
On July 10, 2004, Santa Rosa was converted into a city by Republic Act 9264,[7] which was approved by voters in the plebiscite. Leon Arcillas, who was sworn in for his third and final term ten days before, became its first city mayor.
Arcillas was assassinated at the former city hall by two gunmen, Arnold David and Herminigildo Vidal Jr. They were convicted and sentenced to life imprisonment in 2013. Jose Catindig Jr., who served as vice mayor, became mayor to serve out the remainder of his term.
On May 14, 2007, Catindig, who ran for his full term as mayor, was defeated by Arcillas' daughter, Arlene B. Arcillas.
Geography
Santa Rosa's land area is approximately 54.13 square kilometers (20.90 sq mi). It is located west of Laguna de Bay.
The western half of the city occupies the numerous commercial, industrial, and business establishments, while the other is primarily composed of residential areas and subdivisions, schools, industrial zones, and various business establishments.
Barangays
Santa Rosa is politically subdivided into 18 barangays:

- Aplaya
- Balibago
- Caingin
- Dila
- Dita
- Don Jose
- Ibaba
- Kanluran (Barangay Poblacion Uno)
- Labas
- Macabling
- Malitlit
- Malusak (Barangay Poblacion Dos)
- Market Area (Barangay Poblacion Tres)
- Pooc
- Pulong Santa Cruz
- Santo Domingo
- Sinalhan
- Tagapo
Climate
| Climate data for Santa Rosa City, Laguna | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 29 (84) |
30 (86) |
32 (90) |
34 (93) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
30 (87) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 21 (70) |
20 (68) |
21 (70) |
22 (72) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
22 (72) |
21 (70) |
23 (73) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 10 (0.4) |
10 (0.4) |
12 (0.5) |
27 (1.1) |
94 (3.7) |
153 (6.0) |
206 (8.1) |
190 (7.5) |
179 (7.0) |
120 (4.7) |
54 (2.1) |
39 (1.5) |
1,094 (43) |
| Average rainy days | 5.2 | 4.5 | 6.4 | 9.2 | 19.7 | 24.3 | 26.9 | 25.7 | 24.4 | 21.0 | 12.9 | 9.1 | 189.3 |
| Source: Meteoblue [8] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
The population of Santa Rosa is fast-growing with an intercensal growth rate of 7% from 1990 to 1995, exponentially increasing in subsequent decades (except between the 2007 and 2010 censuses).
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority [3] [9] [10][11] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | Density |
|---|---|
| 1990 | 1,730/km2 |
| 1995 | 2,520/km2 |
| 2000 | 3,400/km2 |
| 2007 | 4,900/km2 |
| 2010 | 5,200/km2 |
| 2015 | 6,500/km2 |
Some inhabitants of Santa Rosa today erroneously refer to themselves as "Rosanians"; since Santa Rosa is a Spanish name, the correct demonym should be "Rosaños".
Ethnic groups
Like other places in Metro Manila, the original settlers are Tagalogs. Throughout the centuries, there has been constant migration of Spaniards, Visayans, Bikolanos, Ilokanos, Chinese, and Americans.
Languages
The main language is Filipino, which is based on Tagalog. In addition, due to continuous development of the city, English is used in education, business and information technology.
Religion
(2018-08-26).jpg.webp)
Most people are Roman Catholics. Other religious groups represented include the Aglipayans (members of the Iglesia Filipina Independiente – a breakout group from the Catholic Church in 1902 headed by the Union Obrera Democratica), the Church of God International, the United Church of Christ in the Philippines, Jesus Is Lord Church, Baptist, Jehovah's Witness, and Iglesia Evangelica Unida de Cristo (Unida Evangelical Christian Church). In 1994, some migrants and expats have formed the Saint Nicholas Orthodox Church (under the canonical jurisdiction of The Orthodox Metropolitanate of Hong Kong/Philippines- Ecumenical Patriarchate) in Golden City Subdivision under the pastoral care of Rev. Fr. Philemon Castro, M.Div.
Economy
Santa Rosa is considered to be the premier city and hub of South Luzon. It is also known as the Lion City of South Luzon. According to the 2013 COA AFR report, the city has an annual income of 2.3 billion pesos, surpassing the income of Calamba and Batangas City. Santa Rosa is now the richest city in Luzon outside of Metro Manila in terms of annual income.
Special economic zones and industrial parks in Santa Rosa include:
- Laguna Technopark Inc.
- Greenfield Automotive Park
- Toyota Special Economic Zone
- Lakeside Evozone Nuvali
- Daystar Santa Rosa Industrial Park
- Santa Rosa Commercial Complex
- Meridian Industrial Complex
Banking
Major commercial banks in the Philippines operate in the city. Currently, the city hosts banking institutions that offer banking services to businesses and residents. Most of these are concentrated in barangays Balibago, Don Jose, Macabling, Pulong Santa Cruz, Santo Domingo, and Tagapo.
Car dealerships
A number of car brands have put up dealerships in Santa Rosa. Prominent car dealerships include Toyota, Chevrolet, Ford (Borromeo), Foton, Honda (ANC), Hyundai, Isuzu (Gencars), JMC, Kia, Mazda (Borromeo), MG Motor (Greenfield), Mitsubishi (Amcar), Nissan (Greenfield), Subaru (ANC), and Volkswagen (Greenfield).
Furthermore, the Borromeo's Ford and Mazda have recently set up shops while two of the six ANC Group brands, Honda and Subaru, have branches in Santa Rosa.
Shopping malls
.jpg.webp)
The city host various shopping malls: SM City Santa Rosa, Robinsons Place Santa Rosa, Ayala Malls Solenad, Walter Mart Santa Rosa, Walter Mart Santa Rosa Bel-Air, Victory Mall Santa Rosa, Vista Mall Sta. Rosa, Paseo de Santa Rosa, and Target Mall.
Industries and manufacturing
Dubbed as the "Motor City of the Philippines" or "Detroit City of the Philippines", Santa Rosa is host to multinational automotive giants Nissan Motors Co., Ltd., Toyota Motor Corporation, and Mitsubishi – all contributing 95 percent of the country's automotive production. It is also the location for the headquarters of Santarosa Motor Works, Inc.
Food conglomerate Monde Nissin Corporation, which manufactures Lucky Me! instant noodles and Monde biscuits, has a plant here in its 14-hectare manufacturing facility. Santa Rosa is also home to the largest plant of The Coca-Cola Company in the Philippines, situated right across the Santa Rosa Exit of the South Luzon Expressway. In 2018, Santa Rosa became the new home of HAMBURG Trading Corporation's 7000 sqm facility that houses the company's warehouse, administration office, and state-of-the-art demo kitchen - all in one roof.
Information technology
Santa Rosa is aiming to be the next hub for the BPO industry. It is currently ranked 82nd in the world for its competitiveness in the Information Technology and Business Process Outsourcing services (IT-BPO) by the leading strategic advisory firm, THOLONS. BPO companies present in Santa Rosa are IQor, KGB, Teletech, IBM, and Concentrix.
Infrastructure
Transportation

Santa Rosa is serviced by South Luzon Expressway (SLEX) and Cavite–Laguna Expressway (CALAX). Two exits of SLEX are located in the city: Santa Rosa Exit and Eton City (Malitlit) Exit. The city is also accessible through Greenfield City (Mamplasan) Exit in Biñan, which provides access to CALAX, SM City Santa Rosa, and the Santa Rosa city proper. Two exits of CALAX directly serve the city, namely: Sta. Rosa City Exit, located in Barangay Carmen, Silang, Cavite, and Laguna Boulevard Exit, located within the city. A four-lane national highway from Alabang, Muntinlupa up to Calamba, Laguna passes through the city. Another road, Santa Rosa-Tagaytay Road, acts as the main route for people going up to Tagaytay from Metro Manila, especially on weekends and vacation periods.
Public transportation within the city, like in most of the urban areas in the Philippines, is facilitated mostly using inexpensive jeepneys. Tricycles are also used for short distances. The Santa Rosa railway station is located in barangay Labas, near the city center. The city is also the location of the Santa Rosa Commercial Complex, a well-known intermodal transport and commercial hub in barangay Balibago, and the Santa Rosa Integrated Terminal, a provincial bus station serving Metro Manila and eventually other parts south of Metro Manila.
Utilities and communication
Santa Rosa's source of electricity is partly from the Manila Electric Company and Meralco. Its water supply is provided by the Laguna Water Inc. Santa Rosa's communication system is powered by Philippine Long Distance Telephone (PLDT) and Globe Telecom, and the cellular network in the Philippines, particularly in metropolitan areas, is increasing due to the low cost of calls and text messaging. Globe Telecom and Smart Communications (PLDT), which has acquired Sun Cellular, provide cellular networks in Santa Rosa. Cable & Satellite Television access is provided by SkyCable, G Sat, Cignal Digital TV, and Royal Cable. Internet Digital Subscriber Line or DSL coverage is provided by PLDT, cable internet is serviced by SkyCable's ZPDee and Global Destiny. Fiber Internet Wireless broadband is provided by Globelines Broadband and Smart Communications.
Health
The Santa Rosa Community Hospital is the primary public hospital of Santa Rosa. The city also hosts at least seven other private hospitals: New Sinai MDI Hospital and Medical Center, Marian Hospital, Balibago Polyclinic and Hospital, St. James Hospital in Dita, Santa Rosa Hospital, Medical Center along RSBS Boulevard, The Medical City South Luzon in Greenfield City, and QualiMed Hospital – Sta. Rosa in Nuvali.
City government

Santa Rosa City is governed primarily by the city mayor, the vice mayor, and the city councilors. The mayor acts as the chief executive of the city while the city councilors act as its legislative body. The vice mayor, besides taking on mayoral responsibilities in case of a temporary vacancy, acts as the presiding officer of the city legislature. The legislative body is composed of 10 regular members and representatives from the barangay and the youth council.
| Position | Name | Party | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mayor | Arlene B. Arcillas | PDP–Laban | |
| Vice Mayor | Arnel D.C. Gomez | NPC | |
| Councilors | Sonia U. Algabre | PDP–Laban | |
| Mythor C. Cendaña | PDP–Laban | ||
| Ina Clariza B. Cartagena | PDP–Laban | ||
| Laudemer A. Carta | PDP–Laban | ||
| Roy M. Gonzales | PDP–Laban | ||
| Ma. Theresa C. Aala | PFP | ||
| Rodrigo B. Malapitan | PDP–Laban | ||
| Antonio M. Tuzon, Jr. | PDP–Laban | ||
| Wilfredo A. Castro | PDP–Laban | ||
| Jose Joel L. Aala | PDP–Laban | ||
| Ex Officio City Council Members | |||
| ABC President | Aldrin M. Lumague (Tagapo) | ||
| SK President | Domel Jenson Ian M. Barairo | ||
Former mayors
The following is the list of chief executives of Santa Rosa, Laguna.[12]
- Francisco Arambulo (1890-1894)
- Basilio B. Gonzales (1899-1900)
- Pedro Teaño Perlas (1900-1901)
- Pablo Monsod Manguerra, Sr. (1900-1901)
- Celerino Castillo Tiongco (1905-1907)
- Feliciano Arambulo Gomez (1908-1911)
- Honorio Tiongco (1912-1916)
- Lorenzo Cartagena Tatlonghari (1916-1922)
- Jose Vallejo Zavalla (1922-1925)
- Aquilino Carballo (1925-1926)
- Felixberto Castro Tiongco (1926-1928)
- Benito Lijauco delos Reyes(1928-1931)
- Hermenegildo Regalado delos Reyes (1931-1937)
- Celso Gonzaga Carteciano (1938-1940)
- Valentin Regalado delos Reyes (1941-1942)
- Jose Alumno Alinsod (1942-August 1943)
- Valentin Regalado delos Reyes (August–December 1943)
- Eduardo de Leon Marcelo (1944)
- Angel Z. Tiongco (1944 - March 6, 1945)
- Jose Alumno Alinsod (March 7, 1945)
- Francisco Gomez Arambulo Jr. (1946-1947)
- Felimon delos Trinos de Guzman (1948-1951)
- Gervacio Almira de Guzman (1952-1955)
- Angel Z. Tiongco (1960-1978)
- Cesar E. Nepomuceno (February 3, 1978 – December 3, 1987)
- Zosimo B. Cartaño (February 3 - December 3, 1987)
- Leo T. Bustamante (OIC, December 3, 1987 - February 2, 1988)
- Roberto R. Gonzales (1988 – June 30, 1998)
- Leon C. Arcillas (June 30, 1998 – May 10, 2005)
- Jose B. Catindig, Jr. (May 10, 2005 – June 30, 2007)
- Arlene B. Arcillas (June 30, 2007 – June 30, 2016)
- Danilo Ramon S. Fernandez (June 30, 2016 – June 30, 2019)
- Arlene B. Arcillas (June 30, 2019 – present)
Education
STI College, Sta. Rosa
| Schools/Colleges | Location |
|---|---|
| San Geronimo Emiliani School of Santa Rosa | San Lorenzo South, Barangay Malitlit Santa Rosa |
| Our Lady of Fatima University - Santa Rosa Campus | Barangay Macabling |
| University of Santo Tomas – Santa Rosa Campus (U/C) | Sta. Elena City, Barangay Don Jose |
| University of the East – Laguna Campus (U/C) | Eton City, Barangay Malitlit |
| Polytechnic University of the Philippines – Santa Rosa Campus | Barangay Tagapo |
| Santa Rosa Science and Technology High School | J.P Rizal Blvd., Barangay Market Area, Santa Rosa, Laguna |
| Laguna Eastern Academy of Santa Rosa, Inc. | Ambrocia Subd. Barangay Ibaba, Santa Rosa Laguna |
| Laguna BelAir Science School | Laguna BelAir 1, Barangay Don Jose |
| Seven Pillars Catholic School | Laguna BelAir 2, Barangay Don Jose |
| Dominican College of Santa Rosa | RSBS Boulevard, San Lorenzo South, Barangay Balibago |
| Holy Rosary College | Bartolazo Compound., Barangay Tagapo |
| Holy Rosary College - Center for Child Development | F. Gomez Street., Barangay Kanluran |
| Canossa School | Zavalla Street., Barangay Kanluran |
| Our Lady of Assumption College, Santa Rosa | RSBS Boulevard., San Lorenzo South, Barangay Malitlit |
| Santa Rosa Educational Institution | Tatlong Hari St., Barangay Market Area |
| Green Fields Integrated School of Laguna | San Lorenzo South, Villa Segovia, Barangay Dita |
| Colegio de Santa Rosa de Lima | Rizal Boulevard, Barangay Labas |
| Asia Technological School of Science and Arts | Barangay Dita, Santa Rosa, Laguna |
| Systems Technology Institute (STI) | Balibago Complex, Santa Rosa, Laguna |
| Aplaya National High School | Purok 3 Brgy Aplaya, Santa Rosa, Laguna |
| Emmanuel Christian School - Main Campus | San Lorenzo South, Barangay Malitlit |
| Emmanuel Christian School - Ciudad Grande Campus | Ciudad Grande, Barangay Market Area |
| Meridian Educational Institute | Golden City Subd. Barangay Dila |
| Dita SpEd Center | Barangay Dita |
| Santa Rosa Central III SpEd Center | Barangay Kanluran |
| Balibago SpEd Center | Barangay Balibago |
| St. Ignatius Technical Institute of Business and Arts Inc. | Balibago, Santa Rosa, Laguna |
Notable people
- Mark Herras, actor and Starstruck Season 1 Ultimate Survivor
- Alden Richards, actor and former Ginoong Santa Rosa
- Jason Fernandez, former vocalist of Rivermaya, singer
- Koreen Medina, actress, model and StarStruck Avenger
- Jef Gaitan, former Rosas ng Santa Rosa and Banana Split mainstay
- Nadine Samonte, actress and StarStruck Avenger
- Jodi Sta. Maria, actress
- Juancho Triviño, actor
References
- City of Santa Rosa | (DILG)
- "Province: Laguna". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved November 12, 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- Laguna (province)#Administrative divisions
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved January 1, 2020.
- Republic Act No. 11395 (August 28, 2019), An Act Separating the City of Santa Rosa from the First Legislative District of the Province of Laguna to Constitute the Lone Legislative District of Santa Rosa (PDF)
- Republic Act No. 9264 (March 10, 2004), An Act Converting the Municipality of Santa Rosa in the Province of Laguna into a Component City to be Known as the City of Santa Rosa
- "Santa Rosa: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved May 11, 2020.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Laguna". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
- "Local Chief Executive". City Government of Santa Rosa.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Santa Rosa. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Santa Rosa, Laguna. |