Tidewater (region)
Tidewater is a reference to the north Atlantic coastal plain region of the United States of America.
Definition
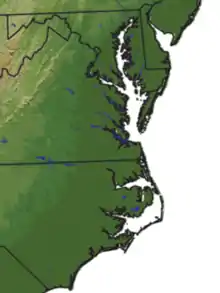
It includes the low-lying plains of southeast Virginia, northeastern North Carolina, southern Maryland and the Chesapeake Bay.[1] According to another definition geographically it covers about 50,000 square miles extending north from Long Island down south to the North Carolina-South Carolina border.[2] This would include the state of Delaware and the Delmarva Peninsula.
The area got its name from the effects of the changing tides on local rivers, sounds, and the ocean; it has a centuries-old cultural heritage that sets the Tidewater region apart from other parts of the United States, especially its distinctive dialects of English that are gradually disappearing,[3] along with islands and shoreline.[4]
Geography

.jpg.webp)
Tidewater region is generally flat and low flooded river plains composed of tidal marsh and large expanses of swamp. Much of the area is covered with pocosin and the higher areas are used for agricultural farmlands. Geographically, in North Carolina and Virginia the Tidewater area is the land between the Suffolk Scarp and the Atlantic Ocean. In Maryland the Tidewater area is the flooded river areas below the Fall Line. The Hampton Roads area of Virginia is considered to be a Tidewater region. Southern Maryland[5] and the Eastern Shore, parts of Delaware round out the northern part of the region on the Chesapeake and Delaware Bays.
The term tidewater may be correctly applied to all portions of any area, including Virginia, where the water level is affected by the tides (more specifically, where the water level rises when the tide comes in). In the case of Virginia, the Tidewater region includes the land east of the Fall Line, the natural border with the Piedmont Region. It includes Hampton Roads, the rest of the Virginia Peninsula, the Middle Peninsula, the Northern Neck, and the Eastern Shore.
Planters in the early American colonies extended their tobacco productions above the Fall Line, where waterfalls or rapids mark the end of the Tidewater and the beginning of the foothill region known as the Piedmont.
Tidewater is host to flora commonly associated with the South Atlantic pine forests and lower Southeast Coastal Plain maritime flora, the latter found primarily in southeastern Virginia.
See also
- Hampton Roads
- Inner Banks
- Southern Maryland
- Eastern Shore (Maryland)
- Eastern Shore (Virginia)
References
- Boon, John D. (2004). "Tidewater". Secrets of the Tide. Horwood. p. 1. ISBN 1-904275-17-6.
Geographically, Tidewater Virginia and Tidewater Maryland together form a triangle whose base extends from the Chesapeake Bay entrance westward through Hampton Roads and the lowlands south of the James River to Petersburg....
- Dickinson, Joanne (August 5, 2015). "Along the Tidewater Region–I Can See Clearly Now…". Our Unbounded Heritage: 12th Century & Beyond. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- Fahrenthold, David (February 19, 2005). "Bay's Dialects Slowly Dying; As City Encroaches and Watermen Leave, Linguists Try to Preserve Vernacular". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 16, 2018.
- Wernick, Adam (July 20, 2014). "An island in Chesapeake Bay is disappearing — and so is a British dialect and a piece of history". Public Radio International. Retrieved December 17, 2018.
- "Title unknown". Archived from the original on July 26, 2009.
Bibliography
- Colin Woodard: American Nations: A History of the Eleven Rival Regional Cultures in North America. 2011. ISBN 978-0143122029
External links
![]() Media related to Tidewater (region) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tidewater (region) at Wikimedia Commons




