List of counties in West Virginia
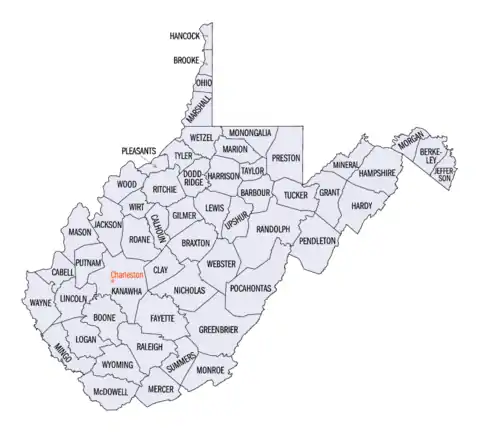
The U.S. state of West Virginia has 55 counties. Fifty of them existed at the time of the Wheeling Convention in 1861, before which West Virginia was part of the Commonwealth of Virginia.[1] The remaining five (Grant, Mineral, Lincoln, Summers, and Mingo) were formed within the state[1] after its admission to the United States on June 20, 1863.[2] At that time, Berkeley County and Jefferson County, the two easternmost counties of West Virginia, refused to recognize their inclusion in the state. In March 1866, the United States Congress passed a joint mandate assenting to their inclusion.[3]
| Counties of West Virginia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | State of West Virginia |
| Number | 55 |
| Populations | 5,717 (Wirt) – 193,063 (Kanawha) |
| Areas | 83 square miles (210 km2) (Hancock) – 1,040 square miles (2,700 km2) (Randolph) |
| Government | County government |
| Subdivisions | cities, towns, unincorporated communities, census designated place |
The West Virginia Constitution was ratified in 1872, replacing the state constitution created in 1863 when West Virginia became a state.[4] Article 9, Section 8, of the West Virginia Constitution permits the creation of additional counties if a majority of citizens in the proposed new county vote for its creation and the new county has a minimum area of 400 square miles (1,036 km2) and a population of at least 6,000. Creation of a new county is prohibited if it would bring another county below these thresholds.[5] Three counties (Greenbrier, Kanawha, and Randolph) have sufficient population and land area to allow a new county to be split off.[5][6][7] The remaining counties cannot be split, as either their land area would decrease to under 400 square miles, or their population would decrease to below 6,000.[5][6][7] Population figures are based on the 2010 United States Census.
The role of counties in local government had been minimized under the 1863 constitution, which vested most local government authority in a system of townships based on the New England model. The authors of the 1872 constitution chose to return to the system used in Virginia, in which each county was governed by a county court with combined authority for executive, legislative, and judicial functions of the county government.[8] In 1880, West Virginia amended its constitution and replaced the county court system with an arrangement that divides county government powers between seven county offices, each of which is independently elected: the county commission, county clerk, circuit clerk, county sheriff, county assessor, county prosecuting attorney, and county surveyor of lands.[9] Counties have only those powers that are expressly granted to them by the state Constitution or by state statute. These powers include, but are not limited to, maintaining the infrastructure of the state, funding libraries, maintaining jails and hospitals, and waste disposal.[9] Reforming public education became a county function in 1933. In May 1933, a county unit plan was adopted. Under this plan, the state's 398 school districts were consolidated into the current 55 county school systems. This enabled public schools to be funded more economically and saved West Virginia millions of dollars.[10]
Randolph County is the largest by area at 1,040 square miles (2,694 km2), and Hancock County is the smallest at 83 square miles (215 km2).[7] Kanawha County contributed land to the founding of 12 West Virginia counties[11] and has the largest population (193,063 in 2010). Wirt County has the smallest population (5,717 in 2010).[7] The oldest county is Hampshire, established in 1754, and the newest is Mingo, established in 1895.[1] Spruce Knob, located in Pendleton County, is the state's highest point at 4,863 feet (1,482 m).[12] Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) codes, which are used by the United States government to identify counties uniquely, are five-digit numbers. For West Virginia, they start with 54 and end with the three-digit county code (for example, Barbour County has FIPS code 54001). Each county's code is provided in the table below, linked to census data for that county.[13]
Counties
References
- Lewis, Virgil (1896). History and Government of West Virginia (1st ed.). New York: Werner School Book Company. pp. 264–270. (WV County Founding Dates and Etymology). Other editions available at ASIN B009CI6FRI and Google Books.
- Littlefield, Charles (1910). Commonwealth of Virginia, plaintiff vs. ... State of West Virginia, defendant (1st ed.). Charleston, WV: Lovett Printing Company. pp. 9–10. (WV Statehood). Other editions available at ISBN 9781274843111 and Google Books
- Rice, Otis & Brown, Stephen (1993). West Virginia, A History (2nd ed.). Lexington: University Press of Kentucky. p. 153. (WV State Boundaries). Other editions available: ISBN 9780813118543
- Bastress, Robert (1995). The West Virginia Constitution: A Reference Guide. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. p. 18. ISBN 0313274096.
- Warth, John (1887). The Code of West Virginia. Wheeling and Charleston WV: West Virginia Printing Company, Printers and Binders. pp. 271–273. Other editions available at ISBN 9781231066737 and Google Books.
- "Find A County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved February 4, 2013. (Find a county)
- "West Virginia QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 4, 2013. (2010 Census)
- Bastress (1995), p. 20.
- Brisbin, Richard (1996). West Virginia Politics and Government. University of Nebraska Press. pp. 142–146. ISBN 0803212712.
- Rice & Brown (1993), p. 247.
- "West Virginia Counties". West Virginia Division of Culture and History. Archived from the original on September 23, 2001. Retrieved February 4, 2013. (WV County Formation)
- Morton, Oren (1910). A History of Pendleton County, West Virginia (1st ed.). Dayton, VA: Ruebush-Elkins Company. p. 3. Other editions available at ISBN 9781165299102.
- "EPA County FIPS Code Listing". EPA.gov. Archived from the original on March 21, 2014. Retrieved February 4, 2013.
- McCulloch, Delia (1908). American Historical Magazine Volume 3. New York NY: Americana Society. pp. 628–629. Available at ISBN 1144825210 and Google Books.