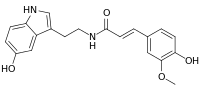
N-Feruloylserotonin
N-Feruloylserotonin an alkaloid and polyphenol found in safflower seed. Chemically, it is an amide formed between serotonin and ferulic acid. It has in vitro anti-atherogenic activity.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2E)-N-[2-(5-Hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)acrylamide | |
| Other names
Moschamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H20N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 352.390 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Takimoto, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Katsuya; Arisaka, Harumi; Murata, Takahisa; Ozaki, Hiroshi; Koyama, Naoto (2011). "Effect of N-(p-coumaroyl)serotonin and N-feruloylserotonin, major anti-atherogenic polyphenols in safflower seed, on vasodilation, proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells". Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 55 (10): 1561. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201000545.
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.