Urapidil
Urapidil is a sympatholytic antihypertensive drug. It acts as an α1-adrenoceptor antagonist and as an 5-HT1A receptor agonist.[1] Although an initial report suggested that urapidil was also an α2-adrenoceptor agonist,[2] this was not substantiated in later studies that demonstrated it was devoid of agonist actions in the dog saphenous vein and the guinea-pig ileum.[3] Unlike some other α1-adrenoceptor antagonists, urapidil does not elicit reflex tachycardia, and this may be related to its weak β1-adrenoceptor antagonist activity,[4][5] as well as its effect on cardiac vagal drive.[6] Urapidil is currently not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, but it is available in Europe.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.377 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
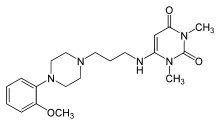
| Formula | C20H29N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 387.484 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
See also
References
- Ramage AG (April 1991). "The mechanism of the sympathoinhibitory action of urapidil: role of 5-HT1A receptors". Br. J. Pharmacol. 102 (4): 998–1002. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12290.x. PMC 1917978. PMID 1855130.
- Eltze M (1979). "Investigations on the mode of action of a new antihypertensive drug, urapidil, in the isolated vas deferens". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 59 (1–2): 1–9. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(79)90018-9. PMID 228944.
- Verberne AJM, Rand MJ (1984). "Pharmacological activities of the antihypertensive drug urapidil in the rat". Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 11 (4): 407–412. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.1984.tb00289.x. PMID 6097380.
- Schoetensack W, Bruckschen EG, Zech K (1983). Urapidil. New Drugs Annual: Cardiovascular Drugs. p. 19.
- Verberne AJM, Rand MJ (1985). "Effect of urapidil on β-adrenoceptors of rat atria". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 108 (2): 193–196. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(85)90725-3. PMID 2984023.
- Ramage AG (1990). "Influence of 5-HT1A receptor agonists on sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve activity". J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 15: S75–S85. doi:10.1097/00005344-199001001-00010. PMID 1702490.
| Sympatholytics (antagonize α-adrenergic vasoconstriction) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other antagonists |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simple piperazines (no additional rings) | |
|---|---|
| Phenylpiperazines |
|
| Benzylpiperazines | |
| Diphenylalkylpiperazines (benzhydrylalkylpiperazines) |
|
| Pyrimidinylpiperazines | |
| Pyridinylpiperazines | |
| Benzo(iso)thiazolylpiperazines | |
| Tricyclics (piperazine attached via side chain) |
|
| Others/Uncategorized | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.