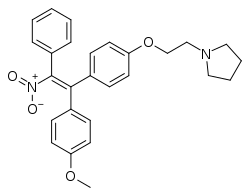
Nitromifene
Nitromifene (INN; also as the citrate salt nitromifene citrate (USAN), developmental code names CI-628, CN-5518, CN-55945) is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) related to triphenylethylenes like tamoxifen that was never marketed.[1] It is a mixture of (E)- and (Z)-isomers that possess similar antiestrogenic activity.[2] The drug was described in 1966.[1] Along with tamoxifen, nafoxidine, and clomifene, it was one of the earliest SERMs.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | CI-628; CN-5518; CN-55945 |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H28N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 444.531 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Nitromifene has been found to dissociate from the estrogen receptor 250-fold faster than estradiol.[4] This may be involved in its antagonistic activity at the estrogen receptor.[4]
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 880–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Raymond Eller Kirk; Donald Frederick Othmer (1980). Encyclopedia of chemical technology. Wiley. p. 676. ISBN 978-0-471-02065-3.
- Jordan VC, Morrow M (1999). "Tamoxifen, raloxifene, and the prevention of breast cancer". Endocr. Rev. 20 (3): 253–78. doi:10.1210/edrv.20.3.0368. PMID 10368771.
- De Boer W, Notides AC, Katzenellenbogen BS, Hayes JR, Katzenellenbogen JA (January 1981). "The capacity of the antiestrogen CI-628 to activate the estrogen receptor in vitro". Endocrinology. 108 (1): 206–12. doi:10.1210/endo-108-1-206. PMID 7007019.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.