Prodiame
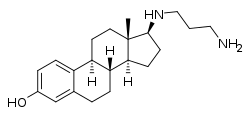
Prodiame, also known as 17β-((3-aminopropyl)amino)estradiol, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and a 17β-aminoestrogen with anticoagulant effects that was first described in 1983 and was never marketed.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 17β-((3-aminopropyl)amino)estradiol; 17β-[(3-Aminopropyl)amino]estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-3-ol; N-(3-Hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-1,3-17beta)-1,3-propylenediamine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H32N2O |
| Molar mass | 328.500 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 1023–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Rubio-Póo C, Mandoki JJ, Jayme V, Mendoza-Patiño N, Alvarado C, Silva G, Zavala E, Fernández-González JM, Rubio-Arroyo M (1983). "Prodiame: a new estrogen with sustained anticoagulant effect". Proc. West. Pharmacol. Soc. 26: 111–3. PMID 6889323.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.