Triphenylmethylethylene
Triphenylmethylethylene, also known as methyltriphenylethylene or as triphenylpropene, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the triphenylethylene group that is related to triphenylchloroethylene and was never marketed.[1][2] Along with diethylstilbestrol and triphenylchoroethylene, triphenylmethylethylene was studied in 1944 by Sir Alexander Haddow for the treatment of breast cancer, and this is historically notable in that it was the first time that high-dose estrogens were found to be effective in the treatment of breast cancer.[1][3] However, while diethylstilbestrol and triphenylchloroethylene were found to be significantly effective, triphenylmethylethylene was less effective and showed a favorable response in only 1 of 4 treated cases.[4][5]
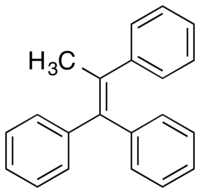 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Methyltriphenylethylene; Triphenylpropene |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal estrogen |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H18 |
| Molar mass | 270.375 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- V. Craig Jordan (2013). Estrogen Action, Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators, and Women's Health: Progress and Promise. World Scientific. pp. 42–43. ISBN 978-1-84816-958-6.
- Hormones and Breast Cancer. Elsevier. 25 June 2013. pp. 9–. ISBN 978-0-12-416676-9.
- D. J. Th. Wagener (13 July 2009). The History of Oncology. Bohn Stafleu van Loghum. pp. 189–. ISBN 978-90-313-6143-4.
- Obiorah I, Jordan VC (2013). "Scientific rationale for postmenopause delay in the use of conjugated equine estrogens among postmenopausal women that causes reduction in breast cancer incidence and mortality". Menopause. 20 (4): 372–82. doi:10.1097/GME.0b013e31828865a5 (inactive 2021-01-16). PMC 3740456. PMID 23921472.
Of 4 cases of breast cancer treated with triphenylmethylethylene, only one showed a favorable response.
CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2021 (link) - Sir James Hopwood Jeans (1928). The physics of the universe. Printed by R. & R. Clark, limited. p. 486.
Triphenylmethylethylene was less effective than either stilbcestrol or triphenylchloroethylene.