Dacemazine
Dacemazine (INN, also known as Ahistan and Histantine)[1] is a phenothiazine derivative which acts as a histamine antagonist at the H1 subtype. First described in 1951, it was never marketed as a drug on its own, although a combination of dacemazine and di-tert-butylnaphthalenesulfonate was sold as an antispasmodic and antitussive under the trade name Codopectyl.[1] It was also assessed as a possible anticancer drug.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
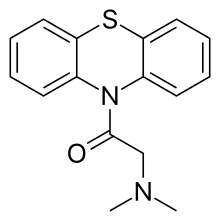
| Formula | C16H16N2OS |
| Molar mass | 284.38 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- Triggle DJ, Ganellin CR, MacDonald F (1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. 1. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. p. 711. ISBN 0-412-46630-9. Retrieved on August 2, 2008 through Google Book Search.
- Karolyhazy G, Havas I, Jansco G, Kapas L, Sellei C (August 1952). "[The anticarcinogenic effect of dimethylaminoacetyl-phentiazide (ahistan)]". Kiserletes Orvostudomany (in Romanian). 4 (4): 260–2. PMID 13023855.
| H1 |
|
|---|---|
| H2 |
|
| H3 |
|
| H4 |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors | |
| Classes | |
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (TCAs and TeCAs) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Others |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.