Homochlorcyclizine
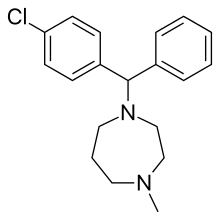
Homochlorcyclizine (INN) is an antihistamine of the diphenylmethylpiperazine group which has been marketed in Japan since 1965.[1] It is used in the treatment of allergies and other conditions. It also has some anticholinergic, antidopaminergic, and antiserotonergic properties.[2][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.545 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H23ClN2 |
| Molar mass | 314.86 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
See also
References
- "Homoclomin Tablets 10 mg" (PDF). Eisai Co. December 2007. Retrieved 2008-07-29.
- Haraguchi K, Ito K, Kotaki H, Sawada Y, Iga T (June 1997). "Prediction of drug-induced catalepsy based on dopamine D1, D2, and muscarinic acetylcholine receptor occupancies". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 25 (6): 675–84. PMID 9193868.
- KIMURA ET, YOUNG PR, RICHARDS RK (1960). "Pharmacologic properties of N-p-chloro-benzhydryl-N'-methyl homopiperazine dihydrochloride (homochlorcyclizine; SA-97), a serotonin antagonist". Journal of Allergy. 31: 237–47. PMID 14409112.
| Benzimidazoles (*) | |
|---|---|
| Diarylmethanes |
|
| Ethylenediamines | |
| Tricyclics | |
| Others |
|
| For topical use | |
| H1 |
|
|---|---|
| H2 |
|
| H3 |
|
| H4 |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors | |
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
