List of territorial disputes
Territorial disputes have occurred throughout history, over lands around the world. Bold indicates one claimant's full control; italics indicates one or more claimants' partial control.
Ongoing disputes between UN member/observer states
Africa
| Territory | Claimants | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Abyei, Heglig, Jodha, Kafia Kingi and Kaka | Both Sudan and South Sudan have claimed the area after the civil war that led to South Sudan's independence. Heglig was controlled by South Sudan in mid-April 2012 but retaken by the Sudan. Abyei was taken in May 2012. | |
| Banc du Geyser | France claims the reef as a part of the Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean, a district of the French Southern Territories. | |
| Bassas da India, Europa Island and Juan de Nova Island | De facto a part of the French overseas territory of the French Southern Territories. | |
| Ceuta,[2] Melilla, other plazas de soberanía | Ceuta and Melilla are administered by Spain as autonomous cities.
An incident on Perejil Island happened in 2002, after which both countries agreed to return to status quo.[3] | |
| Chagos Archipelago | United Kingdom administers the archipelago as part of the British Indian Ocean Territory. An advisory opinion of the International Court of Justice has found the United Kingdom administration to be unlawful and called upon the United Kingdom to complete the process of decolonization with respect to Mauritius. | |
| Doumeira Mountain, Ras Doumeira and Doumeira Island | Basis of the Djiboutian–Eritrean border conflict of 2008. Disputed territory occupied by Eritrea following withdrawal of Qatari peacekeepers in June 2017.[5][6] Alternatively transliterated as the Dumaira Mountains.[5] | |
| Glorioso Islands | De facto a part of the French overseas territory of the French Southern Territories. | |
| Hala'ib Triangle | Previously under joint administration; Egypt now maintains full de facto control of the Hala'ib Triangle. The boundaries claimed by Egypt and Sudan both include the Hala'ib Triangle. | |
| Ilemi Triangle | De facto controlled by Kenya. Ethiopian tribes have used and made raids in the land, but the Ethiopian government has never made a claim to it, agreeing it was Sudanese in 1902, 1907 and 1972 treaties.[8][9][10] | |
| KaNgwane and Ingwavuma | Eswatini claims territories which it states were confiscated during colonial times.[11] The area claimed by Eswatini is the former bantustan of KaNgwane, which now forms the northern parts of Jozini and uMhlabuyalingana local municipalities in KwaZulu-Natal, and the southern part of Nkomazi, the southeastern part of Umjindi and the far eastern part of Albert Luthuli local municipalities in Mpumalanga. | |
| Koualou village and surrounding area | Burkina Faso and Benin retain a border dispute at this 68 km2 triangular area of land near the tripoint border with Togo.[12][13] In a 2008 meeting, it was declared that the territory was a neutral zone, neither Burkinabé nor Beninese.[12] According to the UN Refugee Agency in 2015, there were issues of children being born stateless in the area, however a Beninese civil registration office has taken control of registering births in the area.[14] | |
| Kpéaba village area (near Sipilou/Siquita) | The Guinean military occupied this village for 1 month from January to February 2013, before withdrawing in preparation of talks.[15] In December 2016, Guinea soldiers and civilians attacked the village, killing 1 and wounding several others, before returning to their side of the border.[16] According to the Guinean Minister of Defence, the Guinean army had been asked not to send any soldiers to this area and had no involvement in this incident.[17] | |
| Area near Logoba/Moyo District | [18] | |
| Border near Chiengi, Lunchinda-Pweto Province | Dormant dispute. | |
| Mayotte | Under the 2009 referendum, the population supported becoming an overseas department of France, and so became one on March 31, 2011. | |
| Islands in Mbamba Bay, Lake Nyasa | Lundo Is. and Mbambo Is. are claimed as part of the lake, as Malawi claims to the shore based on 1890 Anglo-German treaty. See Tanzania–Malawi dispute. | |
| Mbañie Island, Cocotiers and Congas Island | Contested islands in Corisco Bay, valuable for their oil.[19][20] | |
| Migingo Island vicinity, and, farther north, the vicinity of the islands of Lolwe, Oyasi, Remba, Ringiti and Sigulu, all a maritime rights dispute in Lake Victoria. | ||
| Several islands in the Congo River | ||
| Several islands in the Ntem River | ||
| Several villages near the Okpara River | ||
| Orange River border line | Namibia claims the border lies along the middle of the river, while South Africa claims it lies along the north bank. | |
| The Rufunzo Valley and Sabanerwa | ||
| Rukwanzi Island and the Semliki River valley | ||
| Sindabezi Island | ||
| Socotra Archipelago | Somalia, while not formally claiming the archipelago, asked for the United Nations to look into "the status" of the Socotran archipelago (i.e., whether or not it "should" belong to Yemen or rather Somalia).[22] | |
| Tromelin Island | De facto a part of the French overseas territory of the French Southern Territories. | |
| Wadi Halfa Salient | ||
| Western Sahara | Territory controlled by Morocco (80%) since 1975 outside of the international law, and classified by the UN as a Non-Self-Governing Territory. |
Asia
| Territory | Claimants | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Ashmore and Cartier Islands | Indonesia argues that the islands, known in Indonesian as Kepulauan Pasir, were first discovered and inhabited by local fishermen from Lesser Sunda Islands, which were then part of Dutch East Indies.[23][24][25] | |
| Aarsal, Deir El Aachayer, Kfar Qouq, Mazraat Deir al-Ashayer, Qaa, Qasr and Tuffah | ||
| Shatt al-Arab | ||
| Abu Musa | ||
| Greater and Lesser Tunbs | ||
| Zirku Island, Sir Abu Nu’ayr[26] | ||
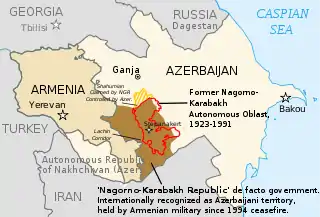
| Nagorno-Karabakh region | Internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan,[27] de facto controlled by the Nagorno-Karabakh supported by Armenia. | |
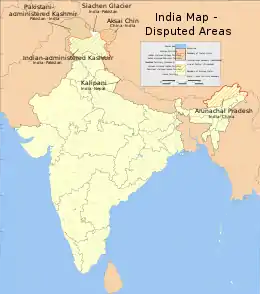
| Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan | Administered by Pakistan and claimed by India. Part of the Kashmir conflict. | |
| Hatay Province | Territory annexed by Turkey in 1939, ceded from Syria under the French Mandate of Syria; the annexation was never formally recognized by Syria after its independence. | |
| Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh | Part of the Kashmir conflict. Both India and Pakistan claim the former independent princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, leading to the Indo-Pakistani war of 1947. A UN-mediated ceasefire put a halt to the conflict in January 1949. The UN resolution called for both the countries to demilitarise the region, following which a plebiscite would be held. However, no demilitarisation plan acceptable to both the countries could be agreed. The countries fought two further wars in 1965 and 1971. Following the latter war, the countries reached the Simla Agreement, agreeing on a Line of Control between their respective regions and committing to a peaceful resolution of the dispute through bilateral negotiations. An armed insurgency broke out in 1989 in the Indian administered part of Kashmir, demanding "independence". Pakistan is believed to provide arms and training to the militants.[28][29][30][31] | |
| Ko Kut | ||
| David Gareja monastery complex boundary dispute | ||
| Doi Lang | ||
| Fasht Ad Dibal and Qit'at Jaradah | These were not included in the 2001 International Court of Justice judgement, as low-tide elevations. | |
| Several areas in the Fergana Valley | Kyrgyzstan: Barak is a tiny Kyrgyz village in the Fergana Valley region (where Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan meet). In August 1999, the area around Barak was occupied by Uzbekistan. Barak became a de facto enclave only 1.5 km from the shifted main border.[32][33][34] (Map) In August 2018 Kyrgyz and Uzbek authorities agreed to a land swap that would eliminate the exclave. The exchange process may take up to two years.[35] Tajikistan: There are three Tajik exclaves, all of them in the Fergana Valley. One of them, the village of Sarvan, is surrounded by Uzbek territory, whereas the remaining two, the village of Vorukh and a small settlement near the Kyrgyz railway station of Kairagach, are each surrounded by Kyrgyz territory. Uzbekistan: There are four Uzbek exclaves, all inside Kyrgyz territory in the Fergana Valley. Two of them are the towns of Sokh and Shakhimardan and the other two the tiny territories of Chon-Qora and Jani-Ayil. There may be a fifth Uzbek exclave inside of Kyrgyzstan.[36] Most of the border in the area is still not demarcated. | |
| Isfara Valley | ||
| Ambalat | ||
| 24-mile stretch of border at pass of the Kabaw[37] | India's government acknowledges that its border with Myanmar is not yet demarcated, but does not consider there to be a "dispute".[38] | |
| Golan Heights | Syrian territory captured by Israel in 1967 (the Six-Day War), and unilaterally annexed by Israel in 1981. In 2008, a plenary session of the United Nations General Assembly voted by 161–1 in favor of a motion on the "occupied Syrian Golan" that reaffirmed support for UN Resolution 497; United Nations, December 5, 2008). During the Syrian civil war period, Syrian Arab Republic had lost direct control of the Eastern Golan areas and retreated from cease-fire line with Israel (in favor of various rebel and Jihadist groups), though did regain the area in 2018. | |
| Israel within the Green Line | See Israeli–Palestinian conflict | |
| West Bank and East Jerusalem |
|
See Israeli occupation of the West Bank |
| Gaza Strip | See Blockade of the Gaza Strip | |
| Kalapani region, the smaller Susta River dispute and the smaller still Antudanda and Nawalparasi disputes | Kalapani is administered by India while Susta is administered by Nepal. The few remaining border disagreements with Nepal since delineation was announced 98% complete in 2019.[39] See Territorial disputes of India and Nepal. | |
| Artsvashen exclave of Gegharkunik province, de jure part of Armenia; Karki exclave of Nakhichevan Autonomous Republic, Yukhari Askipara and Barkhudarli, both exclaves of Qazakh Rayon de jure part of Azerbaijan; "Yaradullu" is controlled by Azerbaijan along with occupying the much larger de jure Armenian territory surrounding it. | Azerbaijan and Armenia have controlled these areas as part of the wider Nagorno-Karabakh conflict. | |
| Khuriya Muriya Islands | ||
| Korean Peninsula north of the Military Demarcation Line | The Democratic People's Republic of Korea administers North Korea, but Article 1 of the Constitution of North Korea reads: "The Democratic People's Republic of Korea is an independent socialist State representing the interests of all the Korean people." The Republic of Korea administers South Korea, but Article 3 of the Constitution of South Korea reads: "The territory of the Republic of Korea shall consist of the Korean peninsula and its adjacent islands." | |
| Korean Peninsula south of the Military Demarcation Line | The Democratic People's Republic of Korea administers North Korea, but Article 1 of the Constitution of North Korea reads: "The Democratic People's Republic of Korea is an independent socialist State representing the interests of all the Korean people." The Republic of Korea administers South Korea, but Article 3 of the Constitution of South Korea reads: "The territory of the Republic of Korea shall consist of the Korean peninsula and its adjacent islands." | |
| South Kuril Islands (Northern Territories)[1] | ||
| Dokdo/Takeshima | Incorporated into Korea in 1900 but claimed by Japan in 1905. And occupied by South Korea since 1952. | |
| Certain islands in the Naf River | ||
| Noktundo | In 1990, the former Soviet Union and the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) signed a border treaty which made the border run through the center of the Tumen river, leaving Noktundo in Russia. South Korea refused to acknowledge the treaty. | |
| "Pedra Branca"; several islets at the eastern entrance to the Singapore Strait | The International Court of Justice rendered its decision on 23 May 2008 that sovereignty over Pedra Branca belongs to Singapore; sovereignty over Middle Rocks belongs to Malaysia. It said sovereignty over South Ledge would remain disputed until the states could determine the ownership of the territorial waters in which it is located.[40] | |
| "Point 20"; a small area of land reclaimed from the sea by Singapore | Malaysia claims the land was reclaimed in its territorial waters. | |
| O'Tangav area (claimed as part of Stung Treng Province) | ||
| Part of Poipet commune | ||
| Prachinburi area | ||
| Area near Preah Vihear Temple (Khao Phra Wihan) | Temple complex awarded to Cambodia by an International Court of Justice ruling in 1962; "promontory" measuring 0.3 km2 immediately adjacent to temple awarded to Cambodia by ICJ ruling in 2013; both countries acknowledge continuing dispute over an additional 4.3 km2 immediately northwest of the 2013 ruling's area. | |
| Qaruh and Umm al Maradim | ||
| Part of Sabah (North Borneo) | The Philippines retains a claim on the eastern part of Sabah (see North Borneo dispute) on the basis claimed by the Government of the Philippines that the territory is only leased by the former Sultanate of Sulu to British North Borneo Company, of which the Philippines argued that it should be the successor state of all Sulu past territories.[1] | |
| Saudi Arabia–United Arab Emirates border dispute | ||
| Siachen Glacier and Saltoro Ridge area | Controlled by India after Operation Meghdoot in 1984.[41] | |
| Sir Creek | A dispute over where in the estuary the line falls; only small areas of marsh land are disputed, but significant maritime territory is involved. It is divided mid-creek. | |
| Parts of Three Pagodas Pass | ||
| The islands of Ukatnyy, Zhestky and Malyy Zhemchuzhnyy[42] | ||
| Ungar-Too (Ungar-Tepa) mountain[43][44] | ||
| Vozrozhdeniya Island (now a peninsula) | ||
| Limbang District | Limbang District was part of Brunei until it was forced to cede it to the Raj of Sarawak in 1890. Since then Brunei is divided territorially into two. It was claimed by Brunei in 1967 in order to reconnect the country. It forms the main part of the Brunei–Malaysia border#Disputes. Malaysia claimed to settle the issue in 2009, however this was disputed by Brunei. |
Europe
| Territory | Claimants | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Russia–Ukraine border | Since 2001 Russia delays an establishment of the border with Ukraine.[45] | |
| Tuzla Island and Strait of Kerch; Sarych | The conflict arose in 2003 when the Russian authorities started to build a dam towards the island. Ukraine then established a border garrison on the island for a closer surveillance. The reason for the conflict was the fact that Tuzla island's strategic location gave Ukraine full rights over the main channel in the Strait of Kerch and, thus, the access to the Sea of Azov. The conflict was based on the division of the Black Sea Fleet and a lease agreement of the Sevastopol Naval facilities. | |
| Sea of Azov | ("Mutual jurisdiction")[46] On 25 November 2018 Russia blocked three Ukrainian Navy vessels from entering Sea of Azov.[47] | |
| Crimea | In 2014, Russian forces occupied and annexed the Crimean peninsula, seizing it from Ukrainian territories. Russian claims to Crimea are not internationally recognized.[48] The United Nations, through General Assembly Resolution 68/262, affirmed that Crimea was part of Ukraine and that Russia's annexation is invalid.[49] Several nations imposed international sanctions on Russia in reaction to its action. | |
| Aegean dispute, Imia/Kardak | Broad number of delimitation disputes about a.o. national airspace, territorial waters and exclusive economic zones. Includes Imia/Kardak dispute. | |
| Mont Blanc summit dispute | France asserts that the principal peaks on the Mont Blanc massif—Dôme du Goûter, Punta Helbronner, and Mont Blanc lie in French territory, while Italy asserts that the summits are shared.[50] | |
| Carlingford Lough and Lough Foyle boundary dispute | Lough Foyle divides County Donegal, Republic of Ireland, and County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. Carlingford Lough divides County Louth, Republic of Ireland, and County Down, Northern Ireland.[51][52] | |
| Gibraltar | Dispute over the interpretation of the Treaty of Utrecht and the location of the border. | |
| Rockall Island | Disputed uninhabited island in the North Atlantic Ocean.[53] | |
| Dollart bay | The exact course of the border through this bay is disputed,[54] yet the countries have agreed to disagree by signing a treaty in 1960.[55] | |
| Lake Constance | Switzerland holds the view that the border runs through the middle of the lake. Austria is of the opinion that the contentious area belongs to all the states on its banks. | |
| Olivenza and Vila Real (including the municipality of Táliga) | In 1801, during the War of the Oranges, Spain, with French military support, occupied the territory of Olivenza (in Portuguese Olivença). During the Treaty of Vienna (1815), the signatory powers (including Spain) agreed with the Portuguese arguments concerning its claim on Olivença but Spain never fulfilled its duty of giving the city of Olivença and its territory back to Portugal. | |
| Croatia-Serbia border dispute | Limited areas along the Danube Parts of Osijek-Baranja and Vukovar-Syrmia Counties and West and South Bačka Districts | |
| Island of Šarengrad | ||
| Island of Vukovar | ||
| Croatia-Slovenia border disputes | ||
| Gulf of Piran | An agreement was signed (and ratified by Croatia's parliament on 20 November 2009) to pursue binding arbitration to both the land and maritime portions of this continuing dispute.
In 2015 collusion between the Slovenian judge on the arbitration panel and a representative from the Slovenian government was uncovered. The Croatian Sabor voted to withdraw from the arbitration, citing allegations of significant breaches of arbitration rules by Slovenia as the reason. Despite this the arbitration tribunal continued its work, issuing a ruling in 2017.[56] | |
| Military complex near Sveta Gera | The complex is in the area of Žumberak/Gorjanci | |
| Prevlaka | ||
| Sastavci | ||
| Tip of the Klek peninsula, and the islands of Veliki Školj and Mali Školj (near Neum) | ||
North America
| Territory | Claimants | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Aves Island | Dominica abandoned the claim to the island in 2007, but continues to claim the adjacent seas, as do some neighboring states. | |
| Bajo Nuevo Bank | Honduras has recognized the sovereignty of Colombia; other claimants have not. On November 19, 2012, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) ruled that Colombia has sovereignty over Bajo Nuevo.[57] | |
| Southern half of Belize | Guatemala formerly claimed all of Belize. | |
| Conejo Island | ||
| Navassa Island [1] | ||
| Sapodilla Cay | Guatemala formerly claimed all of Belize. | |
| Serranilla Bank | Jamaica has recognized the sovereignty of Colombia; other claimants have not. On November 19, 2012, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) ruled that Colombia has sovereignty over Serranilla.[57] | |
| Oyster Pond | Claimed by both The Kingdom of the Netherlands (on behalf of Sint Maarten) and France.[58][59][60][61] | |
| Hans Island | Claimed by both Canada and the Kingdom of Denmark (on behalf of Greenland). |
Territory disputed between Canada and the United States
| Territory | ||
|---|---|---|
| Machias Seal Island | New Brunswick | Maine |
| North Rock | New Brunswick | Maine |
| Strait of Juan de Fuca | British Columbia | Washington |
| Dixon Entrance | British Columbia | Alaska |
| Beaufort Sea | Northwest Territories, Yukon | Alaska |
| Northwest Passage and some other Arctic waters | Canadian territorial waters | U.S. claims navigation rights |
Oceania
| Territory | Claimants | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Matthew and Hunter Islands[1] | ||
| Minerva Reefs | Fiji claims that the entire reef is submerged at high tide, negating use of Minerva as a basis for any sovereignty or maritime EEZ claim by Tonga under the rules of UNCLOS. | |
| Swains Island[1] | Tokelau's claim is unsupported by New Zealand, of whom Tokelau is a dependency. New Zealand formally recognises the USA's sovereignty over Swains Island.[62] | |
| Wake Island[1] |
South America
| Territory | Claimants | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Guayana Esequiba (Guyana west of the Essequibo River) and Ankoko Island/Isla de Anacoco | Venezuela and Guyana have overlapping maritime area claims as well. Barbados and Guyana have since signed joint cooperation agreement over this area. | |
| Arroyo de la Invernada or Rincón de Artigas and Vila Albornoz | Dispute in the 237 km2 (92 sq mi) Invernada River region near Masoller, over which tributary represents the legitimate source of the Quaraí River/Cuareim River (the UN does not officially recognize the claim) | |
| Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands [1] | Including Shag Rocks. See Falkland Islands sovereignty dispute, South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands sovereignty dispute | |
| French Guiana west of the Marouini River | ||
| Tigri Area east of the Upper Courantyne River | The Tigri Area (Dutch: Tigri-gebied) is a wooded area that has been disputed since around 1840 by Suriname and Guyana. It involves the area between the Upper Corentyne River (also called New River), the Coeroeni River and the Kutari River. This triangular area is in Guyana known as the New River Triangle. In 1969 the conflict ran high on and since then the Tigri Area is controlled by Guyana and claimed by Suriname. In 1971 both governments in Trinidad agreed that they continue talks over the border issue and withdraw their military forces from the disputed Triangle. Guyana has never held upon this agreement. | |
| Isla Brasilera/Ilha Brasileira | Uruguayan officials claim that the island falls under their Artigas Department (the UN does not officially recognize the claim) | |
| Isla Suárez/Ilha de Guajará-mirim | An island in the river that serves as a border between Bolivia and Brazil, alongside others 80 island not assigned to any country, the island is closer to Bolivia but despite this, is economically dependent of the Brazilian city of Guajará-Mirim, both countries signed in 1958 a treaty that keep the island in a status quo | |
| Gulf of Venezuela and Los Monjes Archipelago surrounding waters | Dispute regarding the undefined sea border between both countries.[63] | |
| Southern Patagonian Ice Field between Monte Fitz Roy and Cerro Murallón[64] |
Parts of the border still officially undefined. |
Ongoing disputes involving states outside the UN
| Territory | Claimants | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Abkhazia | ||
| Village of Aibga and surrounding area[65][66] | ||
| Aksai Chin | ||
| Bakassi | While Nigeria transferred Bakassi to Cameroon in 2008, elements within Nigeria have declared the territorial cession unconstitutional | |
| Eastern part of Bhutan | ||
| Bhutanese enclaves in Tibet, namely Cherkip Gompa, Dho, Dungmar, Gesur, Gezon, Itse Gompa, Khochar, Nyanri, Ringung, Sanmar, Darchen, Doklam, and Zuthulphuk | ||
| Demchok sector | ||
| Depsang Plains, Demchok sector, Chumar, Kaurik, Shipki La, Barahoti, Jadhang, Lapthal, Nelang, Pulam Sumda and Sang | Disputed areas located between Aksai Chin and Nepal. | |
| James Shoal | ||
| North Cyprus | Northern Cyprus (a state with limited recognition) controls and administers the northern part of the island. Republic of Cyprus claims the whole island. | |
| Macclesfield Bank | ||
| Mainland China, Hainan, and other areas controlled by the PRC | ||
| Moldovan-controlled area of Dubăsari district | ||
| Kokkina/Erenköy exclave | Northern Cyprus controls and administers Kokkina, an area separated from the rest of the main land on Northern Cyprus via the land controlled by the Republic of Cyprus. | |
| Heixiazi / Bolshoy Ussuriysky Island (eastern half) |
Generally held to have been resolved in October 2004 by the Complementary Agreement between the People's Republic of China and the Russian Federation on the Eastern Section of the China-Russia Boundary. However, the settlement is not recognized by the Republic of China.[note 2] | |
| Heixiazi / Bolshoy Ussuriysky Island (western half) |
||
| Hong Kong | Former ROC president Lee Teng-hui claimed that Hong Kong should have been returned to the ROC instead of the PRC because the ROC government had the original manuscript of the Treaty of Nanking.[71] | |
| Northern part of Kachin State | North part west of the Gaoligong Mountains (高黎貢山) in western Yunnan, China, and the Division of Sagaing: Jiangxinpo (江心坡) and Nankan (南坎). | |
| 106.40 square kilometres of formerly Chinese territory in Kazakhstan | ||
| Kosovo | Kosovo is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Serbia and the self-proclaimed Republic of Kosovo. The latter declared independence on 17 February 2008, while Serbia claims it as part of its own sovereign territory. Its independence is recognized by 97 UN member states. | |
| Kula Kangri and mountainous areas to the west of this peak, plus the western Haa District of Bhutan | ||
| Kutuzov Island | ||
| Macau | Both the PRC and the ROC officially consider themselves to be the sole legitimate government over the entirety of China. | |
| Part of the EEZ generated by the Natuna Islands | The People's Republic of China claims the water off the Natuna Islands that fall under the nine-dash line claim are traditional Chinese fishing grounds. The Republic of China on Taiwan also claims the area.[72] | |
| Ladakh | Controlled by India, but Pakistan claims sovereignty as part of the Muslim populated state of Kashmir. | |
| Outer Mongolia | The Republic of China briefly recognized Mongolia's independence between 1945 and 1952, and from 2002 onwards; however, under the Constitution of the Republic of China, the ROC claim on Mongolia cannot be withdrawn without recourse to a referendum. | |
| Pamir Mountains | The Tajik Government ceded 1,158 square kilometres (447 sq mi) to the PRC, while PRC relinquished its 28,000 square miles (73,000 km2) claim over the remaining territory with final ratification of a treaty in January 2011.[73][note 2] However, the settlement is not recognized by the Republic of China.[note 2] | |
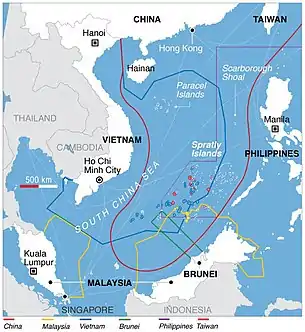
| Paracel Islands[1] | Entirely controlled by the People's Republic of China but claimed by the Republic of China and Vietnam.[74] | |
| Part of the Ryanggang Province | ||
| Part of the Rasŏn administrative division | ||
| Scarborough Shoal | Controlled by the PRC since the 2012 Scarborough Shoal standoff. | |
| Senkaku Islands (Diaoyu Tai or Diaoyu Dao)[1] | Controlled by Japan but claimed by the PRC and ROC.[75] | |
| Shaksgam Valley | Pakistan was originally a party to the dispute but relinquished its claim and accepted Chinese sovereignty over the area in 1963. | |
| Sixty-Four Villages East of the Heilongjiang River | ||
| Republic of Somaliland | ||
| South Ossetia | ||
| South Tibet | Controlled by India but claimed by the PRC and ROC who dispute the validity of the McMahon Line. | |
| Southern Cameroons | ||
| Spratly Islands | Each of the claimant countries except Brunei controls one or more of the individual islands. | |
| 'Border' checkpoint near Strovilia | Northern Cyprus controls and administers the border checkpoint near Strovilia. UK's claim in regard to its Sovereign Base Areas Technically, of course, this also involves | |
| Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu Islands, Pratas Island and the Vereker Banks |
The government of the People's Republic of China claims the entire island of Taiwan, as well as a number of minor islands, such as Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu, that are controlled by the Republic of China. See also: Anti-Secession Law, Legal status of Taiwan. | |
| Trans-Karakoram Tracts | ||
| Transnistria (including Bendery) | ||
| Tannu Tuva | Originally part of China during the Qing dynasty but came under Russian influence in the 20th century. Sovereignty over the area has not been officially relinquished by the ROC. However, the claim is not actively pursued by the ROC government. | |
| Varnita and Copanca | ||
| Western Sahara | The United Nations keeps the Western Sahara in its list of Non-Self-Governing Territories and considers the sovereignty issue as unresolved pending a final solution. To that end, the UN sent a mission in the territory to oversee a referendum on self-determination in 1991, but it never happened. Administration was relinquished by Spain in 1976. | |
| Yalu River (disputed sovereignty of certain islands)[1][note 3] | Generally held to have been resolved in 2005. North Korea is allocated all of the large islands in the lower Yalu River, including Pidan and Sindo at the mouth.[78] The river's maritime rights remain shared between North Korea and the PRC. However, the settlement is not recognized by the Republic of China.[note 2] |
Ongoing disputes within a state by internal entities
| Territory | Country | Internal claimants | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Several islands in the Paraná River | Islands: Isla de los Mástiles/La Carlota, Isla Ingeniero Sabino Corsi Norte/Sur and Isla General Juan Pistarini. | ||
| Put Point | The three states claim three different borders between them. | ||
| Mount Kerinci | |||
| Belgaum | Karnataka Maharashtra |
||
| As much as a 2,821 km2-wide area in and around the Ibiapaba mountain range | This dispute originated in an 1880 imperial decree. In 1920 a solution to the dispute was arbitrated but in practice it was never carried out. In 2008 there were new attempted negotiations, but they broke down in 2011, and as of 2013 it is pending either a supreme court decision, a referendum or a possible mutual agreement.[79] | ||
| The dispute dates from the colonial period.[80] | |||
| Disputed territories of Northern Iraq | Iraq's autonomous region of Iraqi Kurdistan claims and controls parts of the governorates of Nineveh, Arbil, Kirkuk and Diyala. | ||
| Lubicon traditional territory between the Peace River and Athabasca River and north of Lesser Slave Lake | Lubicon Lake Indian Nation (Cree) |
Northern Alberta | |
| Southern edge of Labrador | This was formerly an international dispute between Canada, which includes Quebec, and the Dominion of Newfoundland, then an independent country. Quebec has never accepted the border. | ||
| Songling District and Jiagedaqi District | Inner Mongolia Heilongjiang |
The two districts are owned by Inner Mongolia, but Jiagedaqi District(urban) was established as capital of Daxinganling Prefecture, Heilongjiang Province, resulting it and adjacent Songling District under effective control of Heilongjiang Province. Hulunbuir City(Prefecture), Inner Mongolia actively disputes these two districts, as they formerly belongs to Oroqen Autonomous Banner, Hulunbuir. | |
| Belén de Bajirá | Disputed since 2000, both Departments of Antioquia and Chocó have claimed the corregimiento as part of their own respective municipalities. In 2014, amidst a rise of tensions between the claimants, the National Government under the Geographic Institute Agustín Codazzi formally started a process to find a solution for the dispute.[81] | ||
| A wide section from the 35th parallel north to one mile south. | Due to an inaccurate measurement in 1818, Georgia claims the correct 35th latitude north, and does so in a chance of a drought, it would have access to the Tennessee River.[82] See Tennessee-Georgia water dispute. | ||
| California-Oregon border, 51,000 acres straddling the 42nd parallel north |
Location errors in an 1868–1870 survey to demarcate the Oregon-California border created a dispute between Oregon and California, which upon statehood had established the 42nd parallel north as its de jure border, based on the 1819 Adams–Onís Treaty between the U.S. and Spain. The dispute continues to this day, as Oregon has about 31,000 acres of California, while California has about 20,000 acres of Oregon.[83] The border should follow the 42nd parallel straight west from the 120th meridian west to the Pacific. Instead it zigzags, and only one of the many surveyor's markers put down in 1868 actually is on the 42nd parallel.[84][85][86] | ||
| New Mexico-Texas Panhandle border | The border was defined as the 103rd meridian but an 1859 survey marked it too far west, mistakenly putting present-day towns of Farwell, Texline, and a part of Glenrio in Texas. New Mexico's draft constitution used the 103rd meridian as intended. The New Mexico Senate passed a bill to file a lawsuit to recover the strip, but it has not become law.[87] The land and towns are administered by Texas. | ||
| Parts of Fort Bonifacio | Makati Taguig Pateros |
Disputed since 1983. Taguig claims more than 729 hectares of land in Fort Bonifacio, an area administered by Makati. On August 5, 2013, the Court of Appeals Sixth Division ruled that Makati has legal jurisdiction over the area, thus invalidating Taguig's claim.[88] Taguig has not abandoned its claims and will petition the Court of Appeals to have the decision revoked.[89] Pateros also claims the area and has filed a petition before the Taguig Regional Court Branch 271 in 2012 concerning its claim. Pateros reiterated its claims in 2013 following the decision of the Court of Appeals awarding Makati jurisdiction over the area.[90][91] | |
| Fiat Auto Poland factory and nearest areas | Tychy Bieruń |
The territory has historically been a part of the town of Bieruń. In years 1975–1991 Bieruń was a part of Tychy. The Fiat Auto Poland (formerly FSM factory) remaining in Tychy was a condition of Bieruń's separation. In the 90s, Bieruń has regained the Homera osiedle which was part of the disputed area.[92] | |
| Prigorodny District, North Ossetia–Alania | North Ossetia–Alania Ingushetia |
||
| Phuldungsei | Mizoram Tripura |
Antarctica
The Antarctic Treaty System, formed on 1 December 1959 and entered into force on 23 June 1961, establishes the legal framework for the management of Antarctica and provides administration for the continent, which is carried out through consultative member meetings. It prevents new territorial claims of all signatories (except the U.S. and Russia) for as long as the treaty is in force. However, it is not a final settlement; parties can choose to withdraw from the System at any time. Furthermore, only a minority of states have signed it, and it is not formally sanctioned by the United Nations. Thus, Antarctica remains the only part of the planet any (non-signatory) state can still lay claim to as terra nullius (on the grounds of it not having been part of any existing state's legal and effective territory).
| Territory | Claimants | Antarctic territory |
|---|---|---|
| Area between 25°W and 53°W | ||
| Area between 53°W and 74°W | ||
| Area between 74°W and 80°W |
Historical disputes, subsequently settled
Africa
| Territory | Former claimants | Dispute started | Dispute settled | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agacher Strip | c. 1960 | 1986 | Following repeated military clashes between Burkina Faso and Mali over the Agacher Strip, the International Court of Justice resolved the conflict in 1986 by dividing the disputed area approximately equally between the two countries.[93] | |
| Aouzou Strip | c. 1973 | 1994 | In 1994 the International Court of Justice decision found in favour of Chad sovereignty over the Aouzou strip, and ended the Libyan claim. | |
| Badme | 1993 | 2018 | Basis of the Eritrean-Ethiopian War which began in 1998. The territory was handed over to Eritrea following a joint statement at the Eritrea–Ethiopia summit in 2018. | |
| Bakassi | 1913 | 2006 | This area was handed over by Nigeria to Cameroon following an International Court of Justice ruling and the Greentree Agreement. | |
| Bure | 2002 | 2008 | Eritrea has accepted the decision and no longer disputes this location.[95] | |
| Burkina Faso–Niger border dispute | c. 1960 | 2013 | The International Court of Justice redefined the border between Burkina Faso and Niger in 2013. In 2015 the ruling was implemented by exchanging 18 towns between the two countries.[96] | |
| Part of the Kahemba region | 2007 | Following a March 2007 report on the disputed area on the joint border in the Kahemba region, the Congolese interior minister admitted the territory was in fact part of Angola and agreed to send a technical team to demarcate the border along colonial era lines.[97] The countries agreed to end the dispute in July 2007.[98] | ||
| Lété Island and nearby islands in the Niger River | c. 1960 | 2005 | In 2005 the International Court of Justice awarded Lété and 15 of the other disputed islands to Niger, and the remaining nine islands to Benin.[99] | |
| Sedudu | 1890 | 1999 | In 1999 the International Court of Justice awarded Sedudu to Botswana, ending the Namibian claim.[100] | |
| Tsorona-Zalambessa | 2002 | 2008 | Eritrea has accepted the decision and no longer disputes this location.[95] | |
| Yenga (border hamlet), and left bank of the Makona and Moa rivers | c. 1995 | 2013 | The two heads of state settled this dispute in 2013.[101] |
Americas
| Territory | Former claimants | Dispute started | Dispute settled | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska boundary dispute | 1821 | 1903 | Disputed between the United States and Canada (then a British Dominion with its foreign affairs controlled from London). The dispute had been going on between the Russian and British Empires since 1821, and was inherited by the United States as a consequence of the Alaska Purchase in 1867. It was resolved by arbitration in 1903 with a delegation that included 3 Americans, 2 Canadians, and 1 British delegate that became the swing vote. By a 4 to 2 vote, the final resolution favored the American position. Canada did not get an outlet from the Yukon gold fields to the sea. The disappointment and anger in Canada was directed less at the United States, and more at the British government for betraying Canadian interests in pursuit of a friendly relationship between Britain and the United States. | |
| Aroostook War | 1838 | 1842 | Disputed border between the state of Maine and the provinces of New Brunswick and Lower Canada. | |
| Atacama border dispute | 1879 | 1904 | ||
| Guaíra Falls | 1872 | 1980 | The disputed islands were submerged by the reservoir of Itaipú. | |
| Chamizal dispute | 1898 | 1963 | Disputed border within the El Paso/Ciudad Juárez region. | |
| Cresap's War | 1730 | 1767 | Dispute over the northern border of the Province of Maryland and southern border of Province of Pennsylvania, particularly west of the Susquehanna River. Settled by the drawing of the Mason–Dixon line. | |
| New Hampshire Grants/Vermont | New Hampshire | 1749 | 1791 | In 1664 King Charles II decided the west bank of the Connecticut River was the eastern boundary of New York, so that that province included all of what later became the state of Vermont. During 1749–64, Governor Benning Wentworth of New Hampshire issued well over a hundred "grants", offering lands for sale west of the river in what would become Vermont. In 1764, King George III attempted to end the dispute by ruling that the region belonged to New York. But New York would not recognize the property claims of numerous settlers whose claims were based on Wentworth's grants, so local governments and militias resisted New York's rule. In 1777, the politicians of the disputed territory declared it independent of New York, Britain, and New Hampshire, calling it the State of Vermont. Vermont existed for 14 years as an unrecognized de facto independent country, considered by New York to be a district in rebellion. Negotiations between New York and Vermont in 1790 removed impediments to Vermont's admission to the Union in 1791. |
| Delaware Wedge | 1750s | 1921 | A gore created when the borders of the colonies Maryland, Delaware, and Pennsylvania were defined. Dispute over the borders between the three colonies dates to the foundation of each during the middle 17th century. A series of defined lines and arcs were laid out by statute to settle the disputes, the most famous of which was the Mason–Dixon line. The Wedge was left out of all three colonies (and later U.S. states), and remained a matter of dispute until it was formally resolved to assign the Wedge to Delaware in 1921. | |
| Eastern shore of the Narragansett Bay | Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations Plymouth Colony (to 1691) Province of Massachusetts Bay (from 1691) |
1636 | 1898 | Claimed by both Rhode Island and Plymouth Colony. Plymouth's claim was inherited by the newly created Province of Massachusetts Bay when the latter was created in 1691 from the merger of earlier Massachusetts Bay and Plymouth Colonies. A royal decree in 1746 assigned the land to Rhode Island, but Massachusetts continued to press its claim until 1898. |
| New York – New Jersey Line War | 1701 | 1756 | Dispute over the southern border of Province of New York and the northern border of the Province of New Jersey. Raiding parties kidnapped and burned crops. | |
| Isla Martín García | 1879 | 1973 | After the Conquest of the Desert was formally launched in 1879, many indigenous leaders captured were confined there. The island was transferred to Argentine Navy jurisdiction in 1886. The island's distance from the Uruguayan territory is less than two miles, and its jurisdictional status was formally established by the Treaty of Río de la Plata between Uruguay and Argentina on November 19, 1973. | |
| Cordillera del Cóndor-Cenepa River | 1828 | 1998 | ||
| Cordillera of the Andes Boundary Case | 1881 | 1902 | After the signature of the Boundary treaty of 1881 between Chile and Argentina differing interpretations on whether the highest Andean peaks (favouring Argentina) or the continental divide (favouring Chile) was to be considered the boundary. | |
| Puna de Atacama dispute | 1889 | 1898 | ||
| Clipperton Island | 1897 | 1931 | Disputed between France and Mexico. On January 28, 1931, King Victor Emanuel, selected as a neutral arbitrator, finally declared Clipperton to be a French possession, and it has remained relatively undisputed ever since. | |
| Beagle conflict | 1898 | 1982 | ||
| Río Encuentro-Alto Palena dispute | 1913 | 1966 | ||
| Laguna del Desierto | 1949 | 1994 | ||
| Missouri | 1861 | 1865 | After the Missouri secession, the State of Missouri was claimed by both the United States and Confederate States until the defeat of the Confederacy in the American Civil War | |
| Border of New Hampshire and Canada | 1783 | 1842 | Ill-defined terms of the Treaty of Paris at the end of the Revolutionary War left the boundary of the state of New Hampshire and Canada in doubt. The lack of a precise definition of the "northwesternmost head of the Connecticut River" as defined by the Treaty of Paris left the land that is now the town of Pittsburg, New Hampshire within the conflicting jurisdiction of both the United States and Great Britain. In 1832 residents of the area established the short-lived Republic of Indian Stream in the area; the minuscule population of the putative nation never exceeded about 300. The boundary was finally settled definitively by the Webster–Ashburton Treaty of 1842. | |
| Sverdrup Islands | 1928 | 1930 | In 1928 Norway asserted its claim of sovereignty over the Sverdrup Islands. The islands are named after Norwegian explorer Otto Sverdrup, who explored and mapped them from 1898 to 1902 with the vessel Fram, although some were previously inhabited by Inuit people. Sverdrup claimed the islands for Norway, but the Norwegian government did not pursue the claim until 1928. At that point, the Norwegian government raised the claim, primarily to use the islands as bargaining chips in negotiations with the United Kingdom over the status of the Arctic island Jan Mayen and the Antarctic Bouvet Island. On November 11, 1930, Norway ceded the Sverdrup Islands to Canada, in exchange for British recognition of Norway's sovereignty over Jan Mayen.[102] | |
| San Andrés and Providencia | 1928 | 2012[103] | ||
| Tacna–Arica compromise | 1883 | 1929 | ||
| Pacific Ocean Sea border | 1985 | 2014[104] | ||
| Erik the Red's Land | 1931 | 1933[105] | ||
| Isla Portillos | 2010 | 2018 | On 2 Feb 2018, the ICJ rendered a decision in a border dispute between Nicaragua and Costa Rica regarding Isla Portillos. Nicaragua was left with just the Laguna Los Portillos and its short strip of beach. The court also decided that the sea just outside of the lagoon would be Costa Rican waters. The ICJ concluded that the whole beach is Costa Rican except for the part directly between the lagoon and the Caribbean Sea – now a tiny enclave of Nicaraguan territory separated from the rest of the country.[106] | |
Antarctica
| Territory | Former Claimants | Dispute Started | Dispute Settled | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bouvet Island | 1927 | 1929 | The United Kingdom claimed this Antarctic island as Lindsay/Liverpool Island based on sightings going back to 1808, but Norway landed there in 1927. In November 1929, Britain renounced its claim to the island.[107] |
Asia
| Territory | Former claimants | Dispute started | Dispute settled | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiran and Sanafir Islands | 1906 | 2017 | These islands were transferred to Saudi Arabia in 2017. | |
| Arabi Island and Farsi Island | 1968 | These islands were disputed between Iran and Saudi Arabia. In 1968 Iran and Saudi Arabia had an agreement that Farsi island be given to Iran and Arabi island be given to Saudi Arabia. | ||
| Bay of Bengal Maritime Boundary between Bangladesh and India | 1974 | 2014 | India and Bangladesh had engaged in eight rounds of bilateral negotiations starting 1974 but it remained inconclusive until 2009. In October 2009, Bangladesh served India with notice of arbitration proceedings under the UNCLOS .
The Arbitration Tribunal delivered the ruling on 7 July 2014 and settled the dispute. | |
| Indo-Bangladesh enclaves, adverse possessions and undemarcated land boundaries | 1947 | 2015 | Following Partition of Bengal (1947), the issues of adverse possessions, enclaves and unmarked boundary arose. Inside the main part of Bangladesh, there were 111 Indian enclaves (17,160.63 acres), while inside the main part of India, there were 51 Bangladeshi enclaves (7,110.02 acres). In 1974 Bangladesh approved a proposed treaty, Land Boundary Agreement, to exchange all enclaves within each other's territories, but India did not ratify it. Another agreement was agreed upon in 2011 to exchange enclaves and adverse possessions. With respect to adverse possessions, India received 2,777.038 acres of land and transferred 2,267.682 acres to Bangladesh. India ratified the agreement by constitutional amendment in May 2015.[108] | |
| Muhurichar river island | 1974 | 2011 | Historically controlled by India but claimed by Bangladesh, disputed from approximately 1974.[109] An agreement was reached on the demarcation of the border in the area in 2011,[110] and in 2019 the Indian government confirmed that it no longer had any outstanding boundary dispute with Bangladesh.[38] | |
| South Talpatti/New Moore/Purbasha Island | c. 1975 | 2010 | This former dispute over a small island never more than two meters above sea level was contested from the island's appearance in the 1970s to its disappearance, likely due to climate change,[111] in the first decade of the 2000s. Though land disputes no longer exist, the maritime boundary was not settled until 2014.[112][113][114][115] | |
| Sakhalin Island | 1845 | 1875 | Japan unilaterally proclaimed sovereignty over the whole island in 1845, but its claims were ignored by the Russian Empire. The 1855 Treaty of Shimoda acknowledged that both Russia and Japan had joint rights of occupation to Sakhalin, without setting a definite territorial demarcation. As the island became settled in the 1860s and 1870s, this ambiguity led to increasing friction between settlers. Attempts by the Tokugawa shogunate to purchase the entire island from the Russian Empire failed, and the new Meiji government was unable to negotiate a partition of the island into separate territories.
In 1875 by the Treaty of Saint Petersburg, Japan agreed to give up its claims on Sakhalin in exchange for undisputed ownership of the Kuril Islands. In 1905 under the Treaty of Portsmouth Japan gained Sakhalin to the 60th parallel, but lost it again in 1945. | |
| Palmas Island (modern-day Miangas Island) | 1906 | 1928 | Dispute between the United States and the Netherlands over the Palmas island located south of the Philippines, which was then American territory. The Netherlands believed that the islands were part of the Dutch East Indies. The territorial dispute was solved through the Island of Palmas case which decided that the Palmas Island belongs to the Netherlands. Palmas Island, now Miangas Island, is a part of modern Indonesia. | |
| Shaksgam Valley | (still claimed by: |
1947 | 1963 | Pakistan relinquished its claim to the People's Republic of China; India did not. |
| Sinai Peninsula | 1967 | 1982 | During the Six-Day War Israel claimed Sinai. It was returned in 1982 under the terms of the 1979 Egypt–Israel Peace Treaty. | |
| Taba | 1979 | 1989 | When Egypt and Israel were negotiating the exact position of the border in preparation for the 1979 peace treaty, Israel claimed that Taba had been on the Ottoman side of a border agreed between the Ottomans and British Egypt in 1906 and had, therefore, been in error in its two previous agreements. Although most of Sinai was returned to Egypt in 1982, Taba was the last portion to be returned. The issue was submitted to an international commission. In 1988, the commission ruled in Egypt's favour, and Israel returned Taba to Egypt in 1989. | |
| Phú Quốc island and Thổ Chu Islands area | 1982 | In 1939, Governor General of Indochina, Jules Brévié, sent a letter to the Governor of Cochinchina about “the issue of the islands in the Gulf of Siam whose is a matter of controversy between Cambodia and Cochin-China”. In this letter,“for administrative purposes”, he drew a line which defined the border between the waters of Cambodia and Cochin-China: all the islands north of the line are under Cambodian sovereignty, all the islands south of the line are ruled by Cochin-China. As a result, Phú Quốc was under Cochinchina administration. In 1949, Cochin-China became part of Vietnam, an Associated State in the French Union within the Indochinese Federation. After the Geneva Accords, in 1954, its sovereignty was handed over to the State of Vietnam. In 1964, then Head of State Prince Norodom Sihanouk proposed to the Vietnamese a map aimed at settling the issue. Cambodia offered to accept the colonial “Brévié Line” as the maritime boundary, thus abandoning its claim. That position of Cambodia was confirmed by maps given to the mission sent by the UN Security Council after the Chantrea incidents. On June 8, 1967, the Vietnamese issued a declaration that accepted the “Brévié Line” as the maritime border. On May 1, 1975, a squad of Khmer Rouge soldiers raided and took Phú Quốc, but Vietnam soon recaptured it. This was to be the first of a series of incursions and counter-incursions that would escalate to the Cambodian–Vietnamese War in 1979. Cambodia dropped its claims to Phú Quốc in 1976.[116] But the bone of contention involving the island between the governments of the two countries continued, as both have a historical claim to it and the surrounding waters. A July 1982 agreement between Vietnam and The People's Republic of Kampuchea ostensibly settled the dispute; however, it is still the object of irredentist sentiments. | ||
| Turtle Islands | 1930 | Dispute between the United States and the United Kingdom over the Turtle Islands located south of the Philippines, which was then American territory. In a 1930 treaty the United Kingdom acknowledge American sovereignty over the islands and was agreed upon that the British would remain administering the island until the United States express interest to take over control over the islands after a one-year notice. When the Philippines gained full independence from the United States in 1946, the Philippines invoked the treaty and the British turned over the islands to the Philippines in 1947. | ||
| West Bank, including East Jerusalem | 1967 | 1988 | During the Six-Day War Israel conquered these territories from Jordan. Jordan later renounced the claim on the territory, supporting instead its inclusion in a future Palestine. | |
| Ligitan and Sipadan | 1969 | 2002 | The 2002 International Court of Justice ruling awarded both islands to Malaysia, but left unsettled the maritime boundary immediately southwest and west of the islands between Malaysia and Indonesia. | |
| Hawar Islands | 1971 | 2001 | Formerly disputed between Qatar and Bahrain, it was settled by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in The Hague. In the June 2001 decision, Bahrain kept the Hawar Islands and Qit'at Jaradah but dropped claims to Janan Island and Zubarah on mainland Qatar, while Qatar retained significant maritime areas and their resources. The agreement has furthered the goal of definitively establishing the border with Saudi Arabia and Saudi-led mediation efforts continue. | |
| Batek Island | 2002 | 2004 | Ceded by Timor-Leste to Indonesia in August 2004. | |
| Saudi Arabia–Yemen border demarcation dispute | 1934 | 2000 | Settled by the Treaty of Jeddah (2000). |
Europe
| Territory | Former claimants | Dispute started | Dispute settled | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baltic Sea | 1978 | 2018 | Poland has decided to cede to Denmark 80 percent of disputed territory[117] | |
| Bregovo | 1885 | 1886 | Bulgaria and Serbia briefly had a war over a small border village called Bregovo and this has been the recognized border ever since then. | |
| Åland Islands | 1917 | 1920 | Sweden and Finland argued over the control of the Åland Islands (located between Sweden and Finland). The Åland movement (Ålandsrörelsen) wanted Åland to reunite with its old mother country Sweden (Finland and Åland belonged to Sweden before 1809). The movement gathered signatures from over 7000 inhabitants of legal age at the Åland Islands in 1917 (that was about 96% of the population) - they all supported a union with Sweden. When Finland became independent (December 6, 1917) Sweden wanted a plebiscite about the future of the Åland Islands to solve the problem. Finland refused and argued that the Åland Islands had always been a natural part of Finland - even when Finland was under Swedish rule. Sweden appealed to the League of Nations referring to the right of the population to determine which country they should belong to. After studying the matter closely the League of Nations decided Finland should retain sovereignty over the province but that the Åland Islands should be made an autonomous territory. The Swedish Prime Minister said he didn't accept the verdict but he also said that Sweden was not going to use military force to get their claims.[118] | |
| Graham Island | 1831 | 1831 | A dispute between the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, the British Crown Colony of Malta, the Kingdom of France and the Kingdom of Spain occurred after the volcanic island appeared in 1831. The British were the first to claim the island as part of Malta, and they were followed by the Two Sicilies and France, while Spain expressed their ambitions to control the island. The island disappeared by December 1831 and the dispute stopped. A Sicilian flag was lowered over the now submerged island in 2000 to show Italian claims to the area. It is no longer disputed by Britain, France, Spain or Malta. | |
| Lampedusa | 1800 | 1814 | The island was controlled by British troops as a de facto part of the Malta Protectorate from 1800 onwards. After a British royal commission was sent there in 1812, the new Governor of Malta Sir Thomas Maitland withdrew British troops and the island was returned to Sicily. | |
| Tenedos | 1920 | 1923 | On 11 August 1920, following World War I, the Treaty of Sèvres with the defeated Ottoman Empire granted the island to Greece, who joined the war in Allies' side in May 1917. The new Turkish Government of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, based in Ankara, which was not party to the treaty, overthrew the Ottoman government, which signed but did not ratify the treaty. After the Turkish War of Independence ended in Greek defeat in Anatolia, and the fall of David Lloyd George and his Middle Eastern policies after the Carlton Club meeting, the western powers agreed to the Treaty of Lausanne with the new Turkish Republic, in 1923. This treaty made Tenedos and Imbros part of Turkey, and it guaranteed a special autonomous administrative status there to accommodate the Greeks. | |
| Northern Ireland | 1920 | 1998 | Formerly disputed between Ireland and the United Kingdom since partition on 23 December 1920, it was settled by the Good Friday Agreement in 1998, when Ireland amended its constitutional claim. Both countries acknowledged that the territory can join the rest of Ireland if separate referendums in both Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland approve of the former's cession. | |
| Pytalovo (Abrene in Latvia) | 1991 | 2007 | Pytalovo was a village in the parish of Vyshgorogok, the westernmost part of the Ostrov uyezd, Governorate of Pskov that was ceded from RSFSR to Latvia under the Treaty of Riga (1920) along with parishes of Kachanovo and Tonkovo. In 1940 Latvian Republic was annexed by the Soviet Union and Latvian SSR was established, encompassing the above named territories until 1944 when they were transferred to the district of Ostrov, Pskov Oblast, RSFSR.[119] Since 1991 reestablished Republic of Latvia disputed Russian jurisdiction over the region until the border treaty with Russia was signed in 2007.[120] | |
| Ivangorod, Izborsk and Pechorsky District | 1991 | 2007 | As of 1916, Ivangorod, the eastern suburb of Narva, constituted the westernmost town of the St.Petersburg Governorate on the border with the Governorate of Estonia. The towns of Pechory and Izborsk with respective parishes were the westernmost parts of the Governorate of Pskov. Under the Treaty of Tartu, 1920 the above territories were ceded from RSFSR to the newly established Republic of Estonia that was annexed by the USSR in 1940 as the Estonian SSR. In 1944 with two decrees of the USSR supreme Council the city of Narva and vicinity was split along Narova river leaving Narva with Estonia and Ivangorod with the Leningrad oblast. Pechory, Izborsk and Panikovichi with respective parishes as well as certain areas of Slobodskaya parish were transferred to the Pskov Oblast. Exception was made for some rural areas of the borderland populated by ethnic Estonians leaving these with Estonian SSR.[119] After the fall of the Soviet Union this caused a territorial dispute that was resolved by the Russian-Estonian Border Treaty.[121][122] Some sources argue Estonia might have claims in the area.[123][124] | |
| Sevastopol | 1993 | 1997 | On July 28, 1993, one of the leaders of the Russian Society of Crimea, Viktor Prusakov, stated that his organisation was ready for an armed mutiny and establishment of the Russian administration in Sevastopol. In May 1997, Russia and Ukraine signed the Peace and Friendship Treaty, ruling out Moscow's territorial claims to Ukraine.[125] However, the dispute would be revived after the Russian military intervention in Ukraine and the annexation of Crimea in 2014. | |
| Black Sea and Snake Island | 2004 | 2009 | In 2004 Romania filed a case to International Court of Justice claiming that Ukraine's Snake Island was an uninhabitable rock under UNCLOS standards and thus not eligible to carry influence over determination of the maritime boundary between the two states. During the Soviet times the island was a small naval station with a lighthouse. In 2007 the Ukrainian parliament approved an establishment of a small hamlet (settlement) there, Bile, as part of Vylkove city Odessa Region. The maritime boundary issue was settled by the International Court of Justice in 2009. | |
| Vilnius Region | 1920 | 1945 | During the Polish-Soviet War Polish armies entered the Vilnius Region which was at the time part of the Soviet Lithuanian-Belorussian Soviet Socialist Republic. In 1920, Polish General Lucjan Zeligowski led a coup and established the Republic of Central Lithuania which was annexed to the Second Polish Republic after the war as part of the historic Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and due to ethnic Poles in the region. Lithuania moved its capital to Kaunas while never giving up its claim to Vilnius. The Lithuanians found support in the Soviet Union for their cause signing the Soviet-Lithuanian Mutual Assistance Treaty in 1939. Following the Soviet invasion of Poland, the region came under Soviet control and became part of the Lithuanian SSR after World War II which was followed by a large number of ethnic Poles being deported two times. Following the fall of the Soviet Union and Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania the Vilnius region became part of Lithuania again. | |
| Passetto di Borgo in the vicinity of the Vatican City | 1870 | 1991 | Pope John Paul II recognized the sovereignty of Italy over the Passetto on May 18, 1991.[126][127] |
Notes
- Since the end of the Chinese Civil War in 1949, the de facto territories of the Republic of China (ROC) are limited to the Taiwan Area.[67][68] Meanwhile, the People's Republic of China (PRC) controls mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau.[67] Officially, both the ROC and the PRC claim de jure sovereignty over all of China (including Taiwan), and regard the other government as being in rebellion.[67][69][70] In Taiwan, the ROC's constitutional claim is supported by the Pan-Blue Coalition led by the Kuomintang, while the Pan-Green Coalition led by the Democratic Progressive Party favors Taiwanese independence and does not actively pursue the claim.
- Relinquished by the People's Republic of China (PRC) but is still officially claimed by the Republic of China (ROC). Officially, both the PRC and the ROC claim de jure sovereignty over all of China (including Taiwan), and regard the other government as being in rebellion.[67][69][70] Therefore, the ROC does not recognize any territorial dispute settlement entered into by the PRC.
- The Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) and the Republic of Korea (South Korea) do not recognize each other.
See also
- Demilitarized zone
- Dependent territory
- Frozen conflict
- List of border conflicts
- List of countries and territories by land and maritime borders
- List of sovereign states
- Lists of active separatist movements
- Neutral territory
- List of administrative divisions by country
- Territorial claims in the Arctic
- Territorial disputes in the Persian Gulf
- List of internal boundary disputes in the Philippines
References
- Field Listing - Disputes - international, The World Factbook
- "Breaking News, World News & Multimedia". Retrieved 30 June 2017.
- "Comunicados y notas de prensa de la OID" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on September 27, 2007.
- "Maldives defends UN vote on Chagos Islands dispute". Maldives Independent.
- Maasho, Aaron (June 16, 2017). Dalgleish, James (ed.). "Djibouti, Eritrea in territorial dispute after Qatar peacekeepers leave". Reuters.
- Suckling, Chris. "Eritrea's alleged seizure of disputed Djiboutian territory increases likelihood of miscalculation leading to military escalation". Jane's Information Group. Archived from the original on 2017-06-25. Retrieved 2017-06-27.
Djibouti's foreign minister, Mahamoud Ali Youssouf, alleged in a televised address on 16 June that Eritrean forces had occupied the disputed Dumaira Mountains, immediately after Qatar withdrew a 500-strong contingent of peacekeepers without notification on 14 June.
- "Why are Egypt and Sudan in dispute over the Hala'ib Triangle?(Quizzical)(Brief Article)". Archived from the original on 2007-11-13.
- Brownlie, Ian (1979). African Boundaries: A Legal and Diplomatic Encyclopedia. Institute for International Affairs, Hurst and Co. pp. 867–884, 917–921.
- Collins, Robert O. (2004). The Ilemi Triangle in: Annales d'Éthiopie. Volume 20, année 2004. pp. 5–12. Retrieved 2011-06-17.
- The National Geographic Society in recent works has included an Ethiopian claim, later removed due to lack of sources. The World Factbook confirms that Ethiopia does not claim the territory
- "ESWATINI: Land claim falls on deaf SA ears". IRIN. June 16, 2003. Retrieved March 7, 2012.
- "Différend frontalier Burkina-Bénin : Kourou/Koalou déclarée zone (...) - leFaso.net, l'actualité au Burkina Faso". lefaso.net (in French). Retrieved 2017-10-12.
- "CIA World Factbook – Benin". Retrieved 12 October 2017.
- "UNHCR Newsletter – January–August 2015". p. 5. Retrieved 12 October 2017.
- "Guinea, Cote d'Ivoire Border Dispute Reportedly Resurfaces". Guinee News. Archived from the original on 2014-03-08.
- "Côte d'Ivoire : un civil tué par des militaires guinéens à Kpéaba dans l'ouest du pays, la Guinée dément – JeuneAfrique.com". JeuneAfrique.com (in French). 2016-12-23. Retrieved 2017-10-12.
- "Côte d'Ivoire/Guinée: un ancien litige frontalier ressurgit à Kpéaba - RFI". RFI Afrique (in French). Retrieved 2017-10-12.
- "Uganda, South Sudan should urgently settle border dispute". Daily Monitor. Retrieved 2017-10-12.
- Compte rendu du déplacement d'une délégation du groupe interparlementaire France-Afrique centrale au Gabon, en Guinée équatoriale et à Sao Tomé-et-Principe, parliamentary report of the Senate of France, 2003.
- "UN mediates dispute over Corisco Bay islands". IRIN. 2004-01-23. Retrieved 2017-10-12.
- Muntschick, Johannes (2017-10-09). The Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the European Union (EU): Regionalism and External Influence. ISBN 9783319453309.
- "For First Time in History, Somalia Claims Socotra as Its Own". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- Pike, John. "Ashmore and Cartier Islands [AU]". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2018-01-14.
- antaranews.com. "Fakta Sejarah Tunjukkan Pulau Pasir Milik Indonesia - ANTARA News". Antara News (in Indonesian). Retrieved 2018-01-14.
- Merdeka.com. "Pengakuan Kepemilikan Australia Atas Pulau Pasir Masih Lemah | merdeka.com". merdeka.com. Retrieved 2018-01-14.
- "New Iranian exaggeration over the Emirati demand for the recovery of its occupied islands". Al Mezmaah Studies & Research Centre. 26 Sep 2016. Retrieved 2020-08-01.
- "General Assembly adopts resolution reaffirming territorial integrity of Azerbaijan, demanding withdrawal of all Armenian forces". United Nations. 14 March 2008. Retrieved 23 Dec 2016.
- Korbel, Josef (1966), Danger in Kashmir, Princeton University Press
- Schofield, Victoria (2003) [First published in 2000], Kashmir in Conflict, London and New York: I. B. Taurus & Co, ISBN 978-1860648984
- Bose, Sumantra (2003), Kashmir: Roots of Conflict, Paths to Peace, Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0-674-01173-1
- Varshney, Ashutosh (1992), "Three Compromised Nationalisms: Why Kashmir has been a Problem" (PDF), in Raju G. C. Thomas (ed.), Perspectives on Kashmir: the roots of conflict in South Asia, Westview Press, pp. 191–234, ISBN 978-0-8133-8343-9
- "Kyrgyz In Exclave In Uzbekistan Want To Relocate To Kyrgyzstan". EurasiaNet. 12 May 2011. Archived from the original on 19 March 2014. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- Azizov, Demir (18 Feb 2014). "Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan intensify work on delimitation and demarcation of state border". Archived from the original on 19 March 2014. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- Борис ГОЛОВАНОВ (22 Feb 2002). "Продолжаются споры по линии прохождения узбеко-кыргызской границы. Неделимы Сох, Барак и Гавасай". Вечерний Бишкек. Archived from the original on 19 March 2014. Retrieved 2014-02-15.
- "Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan Agree To Work On Land Swap Near Border". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. Archived from the original on 2019-03-15. Retrieved 2019-01-17.
- "Enclaves III: The Fergana Valley". Archived from the original on October 17, 2013.
- "Myanmar aims to complete border demarcation". IBRU Boundary News. August 22, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2017.
- Territorial disputes of India and Nepal
- Pedra Branca case, operative clause; Sovereignty over Pedra Branca/Pulau Batu Puteh, Middle Rocks and South Ledge (Malaysia/Singapore), International Court of Justice, 23 May 2008, archived from the original on 27 May 2008, retrieved 25 October 2012. See also ICJ awards Pedra Branca's sovereignty to Singapore, Channel NewsAsia, 23 May 2008, retrieved 23 May 2008; "Court awards islet to Singapore", BBC News, 23 May 2008
- "OP MEGHDOOT". Indian Air Force. Retrieved 2020-09-17.
- "КАСПИЙСКИЙ САММИТ НЕ СОСТОЯЛСЯ". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- "Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan Deploy Troops In Dispute Over Border Mountain". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- "Uzbek side withdrew a police post from Ungar-Too". Kabar. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- Woronowycz, R. Ukraine and Russia move on border delimitation. Kyiv Press Bureau. "The Ukrainian Weekly". 25 November 2001
- McEwan, Alec. "Russia – Ukraine Boundary in the Sea of Azov and Kerch Strait" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 14, 2014.
- Osborn, Andrew. "Russia seizes Ukrainian ships near annexed Crimea after firing on them". Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- Maria Raquel Freire, "Ukraine and the Restructuring of East-West Relations" in The Russian Challenge to the European Security Environment (ed. Roger E. Kanet), p. 201.
- "Backing Ukraine's territorial integrity, UN Assembly declares Crimea referendum invalid". United Nations News. March 27, 2014.
- Michael Day (June 28, 2015). "Mont Blanc controversy: French suffer a fit of pique as Italy's Prime Minister 'reclaims' Europe's highest mountain". Independent.
- Kochenov, Dimitry; Basheska, Elena (2005). "Introduction: Good Neighbourliness Inside and Outside the Union". Good Neighbourliness in the European Legal Context. Brill Nijhoff. p. 4. ISBN 9789004299788.
- "Ireland-United Kingdom: Lough Foyle and Carlingford Lough" in Border Disputes: A Global Encyclopedia, Vol. 1 (ed. Emmanuel Brunet-Jailly, ABC-CLIO, 2015).
- "Who owns Rockall? A history of disputes over a tiny Atlantic island". The Irish Times. 8 June 2019. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- "Layer Nordsee - Ems-Dollart-Vertrag" (in German). State of Lower Saxony. Archived from the original on 2018-01-04. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
- "Verdrag tussen het Koninkrijk der Nederlanden en de Bondsrepubliek Duitsland tot [...] van de samenwerking in de Eemsmonding (Eems-Dollardverdrag), 's-Gravenhage, 08-04-1960" (in Dutch). Government of the Netherlands. 1 July 1978. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
- "Arbitration Between The Republic of Croatia and The Republic of Slovenia". Permanent Court of Arbitration. 29 June 2017.
- International Court of Justice (2012). "Territorial and maritime dispute (Nicaragua vs Colombia)" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-11-27.
- "Nederland en Frankrijk ruziën over grens Sint Maarten" (in Dutch). November 12, 2016. Retrieved April 10, 2020.
- "The border at Oyster Pond, the reason behind another conflict". November 2, 2016. Retrieved April 10, 2020.
- "Negotiations on Oyster Pond border to commence late 2019". August 15, 2019. Retrieved April 10, 2020.
- "Frankrijk belemmert herbouw Oyster Pond" (in Dutch). September 15, 2019. Retrieved April 10, 2020.
- "Treaty on the delimitation of the maritime boundary between Tokelau and the United States of America (with map). Signed at Atafu on 2 December 1980. Authentic texts: English and Tokelauan. Registered by the United States on 25 July 1991" (PDF) (in English and Tokelau). July 25, 1991. Retrieved August 28, 2011.
- "Colombia and Venezuela: The Border Dispute Over the Gulf". Council on Hemispheric Affairs. Retrieved 18 April 2018.
- "Acuerdo para precisar el recorrido del Límite desde el Monte Fitz Roy hasta el Cerro Daudet". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- "Moscow, Sokhumi Dispute Village in 'Border Talks'". Civil.ge. 2 April 2011. Archived from the original on 21 April 2018.
- Troiano, Luca (23 May 2011). "Russia e Abkhazia litigano per i confini". AgoraVox Italia (in Italian).
- Sarmento, Clara (2009). Eastwards / Westwards: Which Direction for Gender Studies in the 21st Century?. p. 127. ISBN 9781443808682.
- Henckaerts, Jean-Marie (1996). The International Status of Taiwan in the New World Order: Legal And Political Considerations. p. 117. ISBN 9789041109293.
- Hudson, Christopher (2014). The China Handbook. p. 59. ISBN 9781134269662.
- Rigger, Shelley (2002). Politics in Taiwan: Voting for Reform. p. 60. ISBN 9781134692972.
- "南京條約的正本在台灣 香港的主權屬於中華民國". 台灣綠黨. 1997-06-26. Archived from the original on 2014-05-09.
- Kivimäki, Timo (30 June 2017). War Or Peace in the South China Sea?. NIAS Press. ISBN 9788791114014. Retrieved 30 June 2017 – via Google Books.
- "Tajikistan cedes land to China". BBC News. 13 January 2011.
- "What does disputed Paracel island look like?". BBC News. 2016-02-17. Retrieved 2020-09-17.
- "Nation protests Japan's Diaoyutai move". Taipei Times. 2020-06-23. Retrieved 2020-09-15.
- Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China, Article 9, Section 2
- Constitution of the People's Republic of China, Preamble
- Even official Chinese maps award these islands to North Korea, such as the provincial map on p. 41 in the 2005 Chinese atlas "Zhonghua Renmin Gongheguo Jiaotong Dituji" ISBN 7-80104-652-8, (www.starmap.com.cn)
- "G1 – Ação no STF acirra disputa entre Ceará e Piauí por área de divisa – notícias em Ceará". Ceará. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- "Fernando de Noronha em meio a uma queda de braço". Folha de Pernambuco.
- "Antioquia pide respetar reglas en proceso de deslinde de Belén de Bajirá". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- Shaila Dewan, Georgia Claims a Sliver of the Tennessee River, The New York Times, February 22, 2008
- Barnard, Jeff (May 19, 1985). "California-Oregon Dispute : Border Fight Has Townfolk on Edge". Los Angeles Times. Associated Press.
Preliminary studies indicate that, as the result of an 1870 surveying error, Oregon has about 31,000 acres of California, while California has about 20,000 acres of Oregon.
- Turner, Wallace (March 24, 1985). "SEA RICHES SPUR FEUD ON BORDER". New York Times.
- Sims, Hank (June 14, 2013). "Will the North Coast Marine Protected Areas Spark a War With Oregon?". Lost Coast Outpost.
- California Department of Fish and Wildlife (1 Mar 2016). Map: Pyramid Point State Marine Conservation Area (PDF) (Map). California Department of Fish and Wildlife.
Available from: http://nrm.dfg.ca.gov/FileHandler.ashx?DocumentID=117182
- Daniel Gertson. "Border War Brewing?". Retrieved 2018-04-17.
- "CA rules Makati City, not Taguig, has jurisdiction over Fort Bonifacio". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- "Taguig to appeal CA decision on Fort Boni dispute". GMA News Online. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- "Pateros: Fort Bonifacio is ours". ABS-CBN News. Retrieved 22 October 2014.
- "Pateros joins the fray: 'Fort Bonifacio is ours'". Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- Tomczyk, Krzysztof (4 March 2010). "Tychy kontra Bieruń. Jak Kargul i Pawlak, ale z Fiatem w tle". Moje Miasto Silesia (in Polish). Media Regionalne. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- "International Court settles West African land dispute". Chicago Sun-Times. 1986. Archived from the original on 2015-03-28. Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- ABBINK, J (1 October 1998). "Briefing: The Eritrean-Ethiopian Border Dispute". African Affairs. 97 (389): 551–565. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.afraf.a007970. hdl:1887/9481. Retrieved 30 June 2017.
- "Eritrea accepts 'virtual' border with Ethiopia". Retrieved 2016-05-05.
- "International Court rules that main disputed island belongs to Niger not Benin". The Guardian. 8 May 2015. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
- "Congo Acknowledges Disputed Border Area Is In Angola Origin". Embassy Kinshasa cable. 16 March 2007. Archived from the original on 27 June 2012. Retrieved 19 July 2012.
- "Angola, DR Congo end border row". BBC. 31 Jul 2007. Retrieved 19 July 2012.
- "International Court rules that main disputed island belongs to Niger not Benin". IRIN. Dakar. 12 July 2005. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
- "Cases: Kasikili/Sedudu Island (Botswana/Namibia)". Archived from the original on 2011-06-05. Retrieved 30 June 2017.
- "Sierra Leone government takes media to disputed border with Guinea". News Kenya. Archived from the original on 2014-03-05.
- Berton, Pierre (1988). The Arctic Grail: the Quest for the North West Passage and the North Pole, 1818–1909. Viking. p. 629. ISBN 978-0-670-82491-5.
- Fallo de 2012 de la Corte Internacional de Justicia. "Territorial and maritime dispute (Nicaragua vs Colombia)" (PDF). Retrieved 23 November 2012.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-02-02. Retrieved 2014-01-30.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Legal Status of Eastern Greenland, Denmark v. Norway, Judgment, 5 September 1933, Permanent Court of International Justice (PCIJ)". Worldcourts.com. Retrieved 2015-11-11.
- "Costa Rica & Nicaragua Settle Border Dispute in Court". Political Geography Now. 3 Feb 2018. Archived from the original on 5 February 2018. Retrieved 2018-02-04.
- Barr, Susan (1987). Norway's Polar Territories. Oslo: Aschehoug. p. 63. ISBN 978-82-03-15689-2.
- India (2 December 2014). "Everything you need to know: Land swap in offing with Bangladesh to end disputes". The Indian Express. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- Shib Shankar Chatterjee (18 April 2012). "India-Bangladesh International Border Disputes - Muhuri River". NewsBlaze.
- "PROTOCOL TO THE AGREEMENT BETWEEN THE GOVERNMENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDIA AND THE GOVERNMENT OF THE PEOPLE's REPUBLIC OF BANGLADESH CONCERNING THE DEMARCATION OF THE LAND BOUNDARY BETWEEN INDIA AND BANGLADESH AND RELATED MATTERS" (PDF). South Asia Terrorism Portal.
- Wade, Matt (March 25, 2010). "Rising sea level settles border dispute". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- "Bay of Bengal island 'disappears'". BBC News. 2010-03-24.
- A. G. Noorani. "Of Indo-Bangladesh distrust". Archived from the original on 2001-09-08.
- George, Nirmala (March 24, 2010). "Disputed isle in Bay of Bengal vanishes".
- Hanns Jürgen Buchholz. Law of the Sea Zones in the Pacific Ocean. Retrieved 2015-10-09. p.41
- "Poland and Denmark sign agreement on maritime boundary in the Baltic Sea". 28 November 2018.
- "Disputes in the League of Nations in the 1920's". MacGregor is History. Archived from the original on 16 June 2012.
- "Указ Президиума ВС СССР от 23.08.1944 Об образовании Псковской области в составе РСФСР (Decree of the Supreme Council of USSR on establishing the Pskov Oblast within the RSFSR)". www.bestpravo.com. Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2018-12-18.
- "The Republic of Latvia and the Russian Federation Treaty On the State Border of Latvia and Russia". www.mfa.gov.lv. 4 April 2007.
- "After 20 years, Russia and Estonia sign border treaty". Reuters. 2014-02-18. Retrieved 2018-12-18.
- "The Estonian-Russian Border Treaty Between The Republic of Estonia and The Russian Federation" (PDF). vm.ee.
- "EIKI BERG: Milleks meile idapiir ja ilma lepinguta?". Eesti Päevaleht. 20 September 2007. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- "Enn Eesmaa: väide Petseri-soovist on ennekõike provokatiivne". Eesti Päevaleht. 21 August 2009. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- "Review of Ukraine base lease 'fatal,' Russia warns". People's Daily. Beijing, China. 28 December 2005. Archived from the original on 17 January 2006. Retrieved 12 June 2012.
- "ABC (Madrid) - 06/08/1991, p. 51 - ABC.es Hemeroteca". hemeroteca.abc.es. Retrieved 30 June 2017.
- "Catholic Herald". CatholicHerald.co.uk. Retrieved 5 October 2014.