Foreign relations of Greece
As one of the oldest Euro-Atlantic member states in the region of Southeast Europe, Greece enjoys a prominent geopolitical role as a middle power, due to its political and geographical proximity to Europe, Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. Its main allies are the United States, France, Italy, Bulgaria, the other NATO countries, Cyprus and the rest of the European Union.
| This article is part of a series on |
| Politics of Greece |
|---|
 |
|
|
Greece also maintains strong diplomatic relations with Armenia, Serbia, Egypt, Albania, Romania, the United Arab Emirates, Russia and Israel, while at the same time focuses at improving further the good relations with the Arab World, Caucasus, China, India and Japan. As member of both the EU and the Union for the Mediterranean, Greece is a key player in the eastern Mediterranean region and has encouraged the collaboration between neighbors, as well as promoting the Energy Triangle, for gas exports to Europe. Greece also has the largest economy in the Balkans, where it is an important regional investor.
Prominent issues in Hellenic foreign policy include the claims in the Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean by Turkey and the Turkish occupation of Cyprus.
Overview
Greece has diplomatic relations with almost all the countries in the world, as shown in the map below.
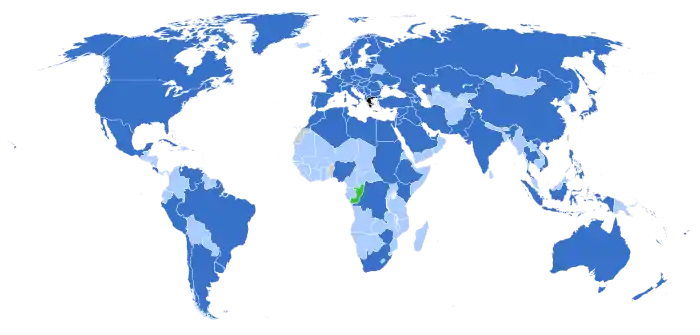
general consulate – no representation – Greece
Disputes
Cyprus dispute
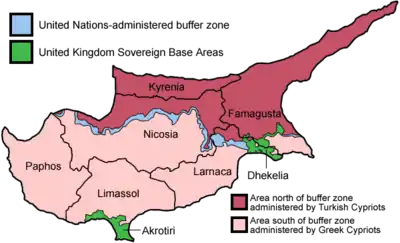
As the island of Cyprus was heading towards independence from the United Kingdom the Greek (82%) and Turkish (18%) communities became embroiled in bitter inter-communal fighting, partly sponsored by the two "motherlands". EOKA-B and the Turkish Resistance Organization (TMT) were responsible for many atrocities which resulted in cementing tensions and led to total isolation of the communities with Turkish Cypriots withdrawn into enclaves.
In 1974 the US-backed Greek junta – in power since 1967 – partly in a move to draw attention away from internal turmoil and partly unsatisfied with Makarios' policy in Cyprus, on 15 July attempted a coup to replace him with Nikos Sampson and declare union with Greece. Seven days later, Turkey launched an invasion of Cyprus allegedly to reinstate the constitution but which resulted in blooded conflict, partition of the island and mass ethnic cleansing. The overwhelming Turkish land, naval and air superiority against island's weak defenses led to the bringing of 37% of the land under Turkish control.
170,000 Greek Cypriots were evicted from their homes in the north with 50,000 Turks following the opposite path concluding the de facto division of Cyprus. In 1983 Turkish Cypriots proclaimed independence unilaterally with only Turkey recognizing them. As of today the north is under an embargo as a measure against the illegal partition of the island.
Ever since both countries along with the two communities of the island are engages into a vicious cycle of negotiations which led to little. In 2004 the Annan Plan for Cyprus was put to vote but whilst it was accepted by the north, it was rejected by the Greek-Cypriots as it meant in their eyes, endorsing a confederal state with a weak central government and considerable local autonomy. The Republic of Cyprus is a constitutional democracy which has reached great levels of prosperity, with a booming economy and good infrastructures, part of the United Nations, European Union and several others organizations by whom it is recognized as the sole legitimate government of the whole island.
Greece calls for the removal of Turkish troops from Cyprus and the restoration of a unified state. The Republic of Cyprus is receiving strong support from Greece in international forums with the latter maintaining a military contingent on the island, and Greek officers filling key positions in the Cypriot National Guard.
Aegean claims by Turkey
Other issues dividing Greece and Turkey involve the delimitation of the continental shelf in the Aegean Sea, territorial waters and airspace. In March 1987 a dispute concerning oil drilling rights, almost led to war between the countries with Greece advocating the dispute to be decided by the International Court of Justice. In early 1988, the Turkish and Greek Prime Ministers met at Davos, Switzerland, and later in Brussels. They agreed on various measures to reduce bilateral tensions and to encourage cooperation.
Tensions over the Aegean Sea surfaced again in November 1994, when Greece claimed under the Law of the Sea Treaty, which Turkey has not signed, that it reserved the right to declare an expansion of its continental shelf from 6 to 12 nautical miles (11–22 km; 7–14 mi) around its Aegean islands. Turkey which has itself expanded its continental shelf in the Black Sea shore, stated that it would consider any such action a cause for war. New technical-level bilateral discussions began in 1994 but soon fizzled-out.
In January 1996, Greece and Turkey came close to an armed confrontation over the question of which country had sovereignty over an islet in the Aegean. In July 1997, on the sidelines of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) summit in Madrid, Greek and Turkish leaders reached agreement on six principles to govern their bilateral relations. Within a few months, however, the two countries were again at odds over Aegean airspace and sovereignty issues. Tensions remained high for months, although various confidence-building measures were discussed to reduce the risk of military accidents or conflict in the Aegean, under the auspices of the NATO Secretary General.
Turkey and the EU
Greece has come out in support of Turkey's bid for European Union membership,[2] and supports its full integration to the union when conditions for its acceptance are met. On 6 May 2004, Turkey's Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdoğan became the first Turkish leader to visit Greece in fifty years.[3] On 24 January 2008, Greece's premier Costas Karamanlis visited Turkey a full 48 years after the last Greek premier and uncle of his Constantine Karamanlis had visited the neighboring country.
Turkish government arson admission
On Monday 23 December 2011, in an interview on Turkish newspaper BirGün discussing secret budgets, former Turkish Prime Minister Mesut Yılmaz admitted that Turkish secret agents intentionally started forest fires in Greece between 1995 and 1997 during the Prime Ministership of Tansu Çiller as part of state-sponsored sabotage, resulting in huge damage caused by major forest fires on the islands of the eastern Aegean and in Macedonia. Mesut Yılmaz's admission sparked political outrage in Greece on Monday, causing Greece's Foreign Ministry spokesman Grigoris Delavekouras to say that the claims were "serious and must be investigated," adding that Athens was awaiting a briefing from Ankara. Conservative New Democracy's shadow foreign minister Panos Panayiotopoulos said the revelations "cast heavy shadows over Greek-Turkish relations" and called on Turkey recompense Greece for losses incurred.[4][5]
Following an official complaint from Greece on 24 December seeking clarification over comments by former Prime Minister Mesut Yılmaz relating to forest fires in Greece in the mid-1990s, the Greek and Turkish foreign ministers, Stavros Dimas and Ahmet Davutoğlu, spoke on Wednesday 28 December. Dimas stressed how important it was that Ankara investigate the claims that in the past Turkey's intelligence services paid arsonists to set fire to forests in Greece. In addition to Greek Foreign Ministry meetings with Turkish officials, Greece's Supreme Court prosecutor Yiannis Tentes launched an emergency inquiry on 27 December, ordering the investigations into the mid-1990s wildfires blamed on arson to be reopened with regard to the initial claims reportedly made by Yılmaz.[6]
Former head of Greek intelligence service Leonidas Vasilikopoulos said they had received information from their agents in Turkey that Turkish agents or others were involved in the forest fires on Greek islands.[7] After making the comments in Turkish daily newspaper BirGün, Yilmaz said that his words had been distorted and that he was referring to Greek agents causing fires in Turkey.[8] However, on Thursday 29, Turkish daily Milliyet published an article referring to a secret report that seemed to support claims made in the interview by Mesut Yılmaz that secret agents had caused forest fires in Greece in the 1990s. According to Milliyet, an associate of Yılmaz's, Kutlu Savas, compiled a 12-page report that detailed the actions of Turkish agents in Greece. It described how the National Intelligence Organization of Turkey (MIT) had formed two teams: one which carried out bombings at tourist sites on Crete and other parts of Greece and another which was responsible for starting the wildfires. An attack on an army camp in Lamia, central Greece, is also mentioned.[9]
Bilateral relations
Africa
Greece enjoys close historic relations with many members of the African Union, such as South Africa, Sudan, and Ethiopia.
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
see Algeria–Greece relations
| ||
|
Greece is repreented in Namibia through its embassy in Pretoria, South Africa, and Namibia is represented in Greece through its embassy in London, United Kingdom.[11] | ||
See Democratic Republic of the Congo – Greece relations
| ||
| see Egypt–Greece relations
Both countries share relations since the years BC with the creation of Alexandria by Alexander the Great. Egypt has had a sizable Greek community which is mostly centered around Alexandria, Egypt's second largest city and the seat of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria. In the modern era, both countries enjoy very good and warm diplomatic relations since 1833 and especially after the Greek War of Independence, and both countries have signed several defense cooperation agreements, with the heads of states visiting each other in a regular basis.
| ||
See Ethiopia–Greece relations
| ||
See Greece–Kenya relations
| ||
| 1952 |
| |
| ||
| see Greece–Nigeria relations
Nigeria has an embassy in Athens.[22] Greece established a diplomatic mission in Nigeria in 1970, and today has an embassy in Abuja and a consulate in Lagos. Trade between the two countries is imbalanced, with imports from Greece to Nigeria exceeding exports. Greek-owned tankers have an important role in shipping Nigerian oil and natural gas, its main exports. Recently a Greek tanker was involved a dispute over crude oil smuggling.[23] Greek-controlled companies have invested US$5 billion in the Nigerian economy. There is a small Greek business community in Lagos.[24] | ||
Greece-Somalia relations | ||
See Greece–South Africa relations
| ||
|
Greece and Sudan have long enjoyed a very cordial and friendly relationship spanning decades. The two countries enjoy strong and productive relations in the areas of diplomacy, economic reciprocity, and also there are large concentrations of Sudanese (both students and immigrants) in Greece, and numerous Greek nationals who have resided in Sudan since the early 20th century. The two countries are on very good terms with each other, notwithstanding Sudan's close ties with Greece's historical rival, Turkey. Greece has an embassy in Khartoum, whilst Sudan is represented in Greece through the parallel accreditation of its embassy in Athens. The Hellenic country also deeply supports peaceful stability in Sudan's western region, Darfur. | ||
| See Greece–Tunisia relations | ||
| see Greece–Zimbabwe relations
Greece has an embassy in Harare. Due to the economic situation, Zimbabwe has neither an embassy nor an honorary consulate in Greece.[32] |
The Americas
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| see Argentina–Greece relations
Both countries are represented by an embassy in the other one's capital. At least 30,000 persons of Greek descent live in Argentina with about 5,000 with Greek passports. The majority of Greeks live in Buenos Aires.[33]
| ||
| ||
See Greece–Brazil relations
| ||
| 1942 | See Canada–Greece relations
| |
see Chile–Greece relations
| ||
| 1942 |
| |
See Cuba–Greece relations
| ||
| 2005[39] |
Diplomatic relations were established on 15 November 2005. Greece is represented in Dominica via parallel accreditation of its embassy in Caracas. Dominica has appointed an ambassador accredited to Greece, based in Roseau, Dominica.[39] | |
| 1979 | ||
| 17 May 1938 | See Greece–Mexico relations
| |
| see Greece–Nicaragua relations
Greece–Nicaragua relations are foreign relations between Greece and Nicaragua. Diplomatic relations were officially established on 2 July 1965.[1] Greece is represented in Nicaragua through its embassy in Mexico City.[1] Nicaragua is represented in Greece through its embassy in Rome. | ||
| 1956 |
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 7 May 1956.[44] | |
| 1966 | See Greece–Peru relations | |
| see Greece–United States relations
The United States and Greece have long-standing historical, political, and cultural ties based on the shared democratic values, history of Greek immigration to the States and participation as Allies during World War II, the Korean War, and the Cold War. Previously, the US helped the reconstruction of post-war Greece through the Marshall plan and various other aids culminating at about $11.1 billion in economic and security assistance since 1946. The current mutual defense cooperation agreement (MDCA) provides for continued U.S. military assistance to Greece and the operation by the U.S. of a military facility at Souda Bay, Crete. About three million Americans are of Greek ancestry.[46] Greek-Americans are an established, well-organized community in the U.S. (several notable politicians, including former Vice-President Spiro Agnew, and Senators Olympia Snowe and Paul Sarbanes are of Greek ancestry), and they help cultivate close political and cultural ties with Greece. Greece has the seventh-largest population of U.S. Social Security beneficiaries in the world. However, there is also a strong sentiment against USA policies towards Greece and the Balkans in general. Critics also charge the United States for supporting the 1967–1974 military junta in Greece, a fact that was acknowledged by Bill Clinton in his visit to Athens "When the junta took over in 1967 here, the United States allowed its interests in prosecuting the Cold War to prevail over its interests – I should say its obligation – to support democracy, which was, after all, the cause for which we fought the Cold War. It is important that we acknowledge that." This American support for the military regime led to left-wing terrorist groups, most notably 17 November, attacking US targets such as the killing of the Central Intelligence Agency's station chief in Athens, Richard Welch in 1975. The populist PASOK leader Andreas Papandreou had also a very strong anti-Western rhetoric, fueling the negative sentiments towards USA, even though it wasn't followed by actions. The backing of Turkish invasion of Cyprus by Henry Kissinger, the Kosovo war and the invasion of Iraq[47] have tarnished the image of the United States in the eyes of their European ally. More recently, the strong support of President George W. Bush towards the Republic of Macedonia in the naming dispute, evident in his recognition of the state as Macedonia in 2004 and in his full backing to the country's accession to NATO further tarnished America's image. | ||
See Greece–Uruguay relations
| ||
See Greece–Venezuela relations
|
Asia
Greece has a special interest in Middle East and North Africa because of its geographic position and its economic and historic ties to the area. The country cooperated with allied forces during the 1990–1991 Gulf War. Since 1994, Greece has signed defense cooperation agreements with Israel and Egypt and in recent years, Greek leaders have made numerous trips to the region in order to strengthen bilateral ties and encourage the Middle East Peace Process. In July 1997, December 1997, and July 1998 Greece hosted meetings of Israeli and Palestinian politicians to contribute to the peace process. Greece also maintains diplomatic relations with the General Palestinian Delegation while enjoying cordial relations with Syria.
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes
Greece-Afghanistan relations |
|---|---|---|
| 2004[48] | See Afghanistan–Greece relations | |
| 21 September 1991 | see Armenia–Greece relations
Greece was one of the first countries to recognize Armenia's independence on 21 September 1991 and one of those that have officially recognized the Armenian Genocide. Since the independence of Armenia the two countries have been partners within the framework of international organizations (United Nations, OSCE, Council of Europe, BSEC), whilst Greece firmly supports the community programs aimed at further developing relations between the EU and Armenia. Continuous visits of the highest level have shown that both countries want to continue to improve the levels of friendship and cooperation (Visit by the President of Armenia Levon Ter-Petrossian to Greece in 1996, visit by the President of the Hellenic Republic Costis Stephanopoulos in 1999, visit by the President of Armenia Robert Kocharyan to Greece in 2000 and 2005 and visit by Greek president Karolos Papoulias to Armenia in June 2007). Greece is, after Russia, the major military partner of Armenia. Armenian officers are trained in Greek military academies, and various technical assistance is supplied by Greece. Since 2003, an Armenian platoon has been deployed in Kosovo as part of KFOR, where they operate as a part of the Greek battalion of KFOR. | |
| 1992 | see Azerbaijan–Greece relations
Azerbaijan-Greece relations today are friendly. Each state maintains a full embassy, Azerbaijan in Athens and Greece in Baku. Recently in February 2009, Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev visited Greece in order to boost bilateral relations.[49] The leader met with Greek President Karolos Papoulias, as well as the Greek Prime Minister Costas Karamanlis.[49] At the meeting between the officials, the two nations agreed that they must work more closely to get Azeri gas into Greece to help ease recent security issues.[50][51] In the past the two nations have made many deals related to the oil industry. In 2007 Greek Development Minister Dimitris Sioufas signed a "memorandum of cooperation" in the sectors of natural gas and oil while in Baku.[52][53] Sioufas referred to this memorandum as a "new page in economic and energy relations of the two countries."[53] Greece supports Azerbaijan's bid to join to European Union and is the first EU member that wanted directly gas important from Azerbaijan.[54] | |
| 28 August 1973 |
| |
| ||
| ||
| 6 June 1972 | see China–Greece relations
| |
| 20 April 1992 | See Georgia–Greece relations
| |
| 1950 | see Greece-India relations
| |
| 1960s |
| |
See Greece–Iran relations
 Cartoon on the establishment of diplomatic relations between Greece and the then-ruling Qajar dynasty of Persia in 1902
| ||
| see Greece-Iraq relations, Greece–Kurdistan Region relations
Relations of the Greek and Iraqi peoples are deeply rooted in history, both have developed cultures that have influenced the course of humanity. They date as far back as when Alexander the Great ruled Mesopotamia (which name is of Greek origin, meaning "land between rivers") and eventually died in Babylon, Iraq. Greece firmly and consistently supports the independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity of Iraq. Greece traditionally maintained good and friendly relations with Iraq due to strong historical and cultural bonds, dating back to ancient times.[59] Greece has an embassy in Baghdad, and Iraq is represented by her embassy in Athens. | ||
see Greece–Israel relations
| ||
| 1899 | see Greece–Japan relations
| |
| 1 October 1992 | See Greece–Kazakhstan relations
| |
see Greece-Kyrgyzstan relations
| ||
| see Greece–Lebanon relations
The relation between both people dates back to early antiquity, with the early trading activities between the ancient Greeks and the Phoenicians. In modern times, Greek-Lebanese bilateral relations are very good at all levels. Both countries are members of the Union for the Mediterranean and the Francophonie.
| ||
see Greece–Malaysia relations
| ||
| 6 December 1983 | ||
| 21 February 1986 |
| |
| 8 March 2001[72] | ||
| See Greece–Pakistan relations
In modern times, Pakistan's first embassy in Athens was opened in 1975. Greece established an embassy in Islamabad in 1987. There are around 32,500 Pakistani people living and working in Greece. However, Islamabad has stated it will not accept Greek sovereignty over Cyprus and it should withdraw its bulk of armed forces from the southern part of the island to restore the independence of the Cypriots, which it continues to have diplomatic relations with Nicosia. | ||
See Greece–Palestine relations
| ||
| ||
| 1973 | see Greece–Qatar relations | |
See Greece–Saudi Arabia relations
| ||
| ||
| 5 April 1961[75] | See Greece–South Korea relations
| |
| 1957 | ||
See Greece–Syria relations
| ||
| 26 May 1958 | ||
| see above, and see Greece–Turkey relations
After more than a century of strained relations and intermittent fighting, Greece and Turkey agreed under the Treaty of Lausanne (1923) to a population exchange as an attempt to reduce tensions between the two countries in the future. A significant 300,000 strong Greek community in Istanbul and a 100,000 Muslim one in Western Thrace were excluded from the transfer, with each one supposed to be working as counter-weights to any anti-minority policy that either Turkey or Greece may sought to apply in the future, however that counter-weight came to an end before the Cyprus dispute because of the Varlik Vergisi and Istanbul pogrom. In 1942 a wealth tax called the Varlık Vergisi was imposed on non-Muslims including Greeks, this resulted in financial ruin for many Greeks and another exodus of Greeks from Anatolia once World War II had come to an end. Again in 1955 an anti-Greek Istanbul pogrom was initiated by Turkish mobs against the Greek community of Istanbul, which led to the final gradual extinction of the Greek community in Anatolia. These two events were a major factor when the Cyprus problem surfaced as Greece and Turkey nearly came to a full-out war after Turkey's invasion of Cyprus. Similar disputes occurred for the islands of Imbros and Tenedos. Up to late 1990s strained relations almost led to an open war in 1974, 1987 and 1996. Since the earthquake diplomacy in 1999 relations have once again begun improving. | ||
| 1971 | See Greece–United Arab Emirates relations
| |
| April 1975 | See Greece–Vietnam relations
|
Europe
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1912, 1971 and 1991 | see Albania–Greece relations
Greece and Albania – even though diplomatic relations were restored in 1971[86][87] – normalized relations only in 1987 as till then both countries were officially – in a cease-fire – but nevertheless under the state of war since Albania and Italy had declared war on Greece on 28 October 1940. During rule of dictator Enver Hoxha relations were strained because of the part that Albania played during World War II against Greece and also because of the material help that they provided to Greek communists during the Greek civil war. In addition there was controversy about the treatment of the Greek minority in southern Albania, the historic region of Northern Epirus and the Cham issue. After the fall of the Albanian socialist regime in 1991, relations between the two countries got better but soon begun to deteriorate with accusations about mistreatment of minorities vice versa. To the latter problem it was added the widespread phenomenon of waves of illegal immigration from Albania towards Greece. High criminality numbers from one hand and alleged police brutality from the other became familiar subjects on the news of both neighbors, increasing eventually tensions. According to official Greek data around 450,000 Albanian immigrants work in Greece and it is believed the number will almost double if illegal immigrants are accounted too. This is a brand new situation for both countries, as Greece for the first time become a destination country for immigrants and Albanians for the first time got out of their country after the total isolation that the communist regime had imposed. Today, relations between the two countries are very close and are regarded as excellent, and, at the Albanian Government's request, about 250 Greek military personnel are stationed in Albania to assist with the training and restructuring the Albanian Armed Forces. Albania's economy is overdependent to the money immigrants from Greece sent back home, while Greece is the second larger trading partner, with more than US$400 million worth of investments. Moreover, Greek products account for 21% of Albania's imports, with Greece absorbing 12% of its neighboring country's exports.[88] At the same time, low cost labor from Albania propelled the growth of the Greek economy, especially in the construction and agriculture sectors. Albania is home to 300,000 or more Greeks, with about 650,000 Greeks in total being linked to Albania[89] while between 400,000 and 600,000 Albanians live and work in Greece, the vast majority of them post-1991 economic migrants.
| |
| See Austria–Greece relations
Both countries have had diplomatic relation since the 19th century, after Greece's independence. Greece has an embassy in Vienna and an honorary consulate in Salzburg. Austria has an embassy in Athens and six honorary consulates (in Heraklion, Hermoupolis, Korfu, Patras, Rhodes and Thessaloniki). Both countries are full members of the European Union. There is also a Greek community living in Austria. | ||
| 1992 |
| |
| 1874 | See Belgium–Greece relations
| |
| 30 November 1995 |
| |
| 1908 | See Bulgaria–Greece relations
Since the Second World War, relations between Greece and Bulgaria have been flourishing, and as the Greek President Konstantinos Tsatsos said during the Bulgarian leader Todor Zhivkov's visit to Athens in April 1976, "the old controversies have been forgotten and the hatchet buried forever".[103] Greece became a firm supporter of Bulgaria's European Union membership and was the fifth EU member state and the first old member state to ratify the Accession Treaty.[104] Since Bulgaria joined NATO in May 2004, Greek-Bulgarian relations have been developing on all fronts, and the Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs describes relations between Greece and Bulgaria as "excellent".[104]
| |
see Croatia–Greece relations
| ||
see Cyprus–Greece relations
| ||
| 1 January 1993 | see Czech Republic–Greece relations
| |
| 21 May 1928 | see Denmark–Greece relations
| |
See Estonia–Greece relations
| ||
| 5 January 1918 | See Finland–Greece relations
| |
| 1833 | see France–Greece relations
| |
See Germany–Greece relations
| ||
| 1980 | see Greece–Holy See relations
| |
| 23 July 1956 | See Greece–Hungary relations
| |
| see Greece–Iceland relations | ||
see Greece–Ireland relations
| ||
| 1861 | see Greece–Italy relations
| |
| 23 May 1922 | See Greece–Latvia relations
| |
| 7 January 1922 | See Greece–Lithuania relations
| |
| ||
See Greece–Malta relations
| ||
| 18 December 2006 | See Greece–Montenegro relations
| |
| 27 March 1992 | see Greece–Moldova relations
| |
| 13 September 1995[117] | See Greece–North Macedonia relations
| |
see Greece–Norway relations
| ||
| 1919 | see Greece–Poland relations
| |
| ||
| see Greece–Romania relations
Diplomatic relations were established on 20 February 1880, at the legation level, and were raised to embassy-level on 1 January 1939. There has been a Greek presence in Romania for at least 27 centuries.
| ||
| 1828 | see Greece–Russia relations
Diplomatic relations were established in 1828. Greece has an embassy in Moscow, and two general consulates (Saint Petersburg and Novorossiysk). Russia has an embassy in Athens, a general consulate in Thessaloniki and in 2012 announced to open honorary consulate in Alexandroupolis. Greece also opened another consulate general in Yekaterinburg. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe.[62] Despite historical sentiments of cultural and religious affinity between the two peoples, the countries′ official relationship has largely been adverse. Russia and Greece share stance on the Kosovo Declaration of Independence. Relations deteriorated drastically in the summer of 2018.[123] | |
| 1878 | see Greece–Serbia relations
The two nations are traditionally, historically, religiously and culturally close and their friendly relations are confirmed by a regular political dialogue. Greece is supporting quick implementation of the Stabilisation and Association Agreement (SAA) between the EU and Serbia and easing visa regime EU towards Serbia. Greece is among the states that have not recognized the Kosovo Unilateral Declaration of Independence. Greece recognizes Kosovo as a part of Serbia. Greece is one of the most important economic investors in Serbia, mainly in financial, telecommunication, energy and construction sector. Greece will participate in financing construction of the Corridor 10 highway in Serbia with 100 mil. EUR in total which is a part of its Hellenic Plan for the Economic Reconstruction of the Balkans. | |
| 1 January 1993 |
| |
| July 1992 |
| |
See Greece–Spain relations
| ||
See Greece–Sweden relations
| ||
| 1992 | See Greece–Ukraine relations
| |
see Greece–United Kingdom relations
The UK and Greece were also allies during both World Wars and the Korean War, and they continue to maintain a warm relationship to the present day, having never been adversaries of each other. |
Australia and Oceania
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| See Australia–Greece relations
Relations between the two states are close: both country were allies during both World Wars, there are a large Greek community in Australia (dating back from the 1950s and 1960s). Both countries have an embassy in the each other's capital. Greece also has consulates general in Sydney, Melbourne and Adelaide, as well as a consulate in Perth, honorary consulates general in Brisbane and Darwin, and honorary consulates in Newcastle and Hobart. | ||
| 1978[132] | ||
|
Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1984.[134] | ||
| see Greece–New Zealand relations
In 1999, Greece opened an embassy in Wellington; however, it has since closed and Greece is accredited to New Zealand from its embassy in Canberra, Australia. There is a Greek Honorary Consulate in Auckland. As part of an effort to redeploy resources in Europe, New Zealand closed its embassy in Athens in 1991, since when it has been represented in Greece through its embassy in Rome, Italy which is accredited accordingly. It does still retain an honorary consulate general in Athens. On the level of political cooperation, the two countries have a like-minded approach to international crises and current issues of international interest. There is particularly close cooperation in offering mutual support within international organizations, such as the Human Rights Commission, the Universal Postal Union, etc. New Zealand also supported Greece's candidacy for a seat on the UN Security Council. The prevailing climate in political relations between Greece and New Zealand was demonstrated in 2002 by the visit of the President of the Hellenic Republic to Wellington, which confirmed the excellent state of relations between the two countries. | ||
| 3 April 1981 |
Both countries established diplomatic relations on April 3, 1981.[135][136] | |
| 1984[139] |
|
Terms
North Macedonia
Greece rejected the use of the term Macedonia or "Republic of Macedonia" to refer to its northern neighbour after its independence from the former Yugoslavia in 1991.[140] The Greek government opposed the use of the name without any qualification such as 'Republic of Northern Macedonia' to the post-1991 constitutional name of its northern neighbour,[140] citing historical and territorial concerns resulting from the ambiguity between the terms Republic of Macedonia, the Greek region of Macedonia and the ancient kingdom of Macedon,[140] which falls within Greek Macedonia.
Greece also objected to the use of the terms "Macedonian" to denote ethnic Macedonians and the Macedonian language,[140] as these terms have a different meaning in Greece (inhabitants of the Greek region of Macedonia and the Macedonian dialect of Greek). The dispute has escalated to the highest level of international mediation, involving numerous attempts to achieve a resolution, notably by the United Nations.
The provisional reference the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (FYROM)[117] was used in relations involving states which do not recognise the constitutional name, Republic of Macedonia. Nevertheless, all the United Nations member-states have agreed to accept any final agreement resulting from negotiations between the two countries. The dispute has not prevented the two countries from enjoying close trade links and investment levels (especially from Greece), but it has generated a great deal of political and academic debate on both sides.
On 13 September 1995 the two countries signed the Interim Accord,[117] whereby Greece recognized the Republic of Macedonia under its provisional reference.[117] As of August 2011 negotiations aimed at resolving the dispute are ongoing. Under Greek pressure, the European Union and NATO agreed that in order for the Republic of Macedonia to receive an invitation to join these institutions the name dispute must be resolved first.[141][142][143] This resulted in a case at the International Court of Justice against Greece for violation of the Interim Accord.[144] The Court deemed Greece was wrong to block its neighbour's bid to join NATO.[145] No penalties were imposed[146] but the result made it politically more difficult for Greece to object to any of its neighbour's future applications to either NATO or the EU.
On 12 June 2018 the Prespes agreement was signed between the two countries which changed the constitutional name of "Macedonia" to Republic of North Macedonia. Opposition arose in both countries but in the end the agreement was mutually ratified. The Prespes agreement went into force 12 February 2019. Greece officially endorsed North Macedonia's accession to NATO on 15 February 2019, being the first country in the defense alliance to do so.[147]
Northern Epirus
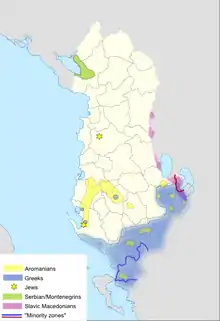
Northern Epirus is the name used generally by Greeks to refer to the southern part of Albania, home to a Greek minority[148] which after 1989 keeps reducing due to immigration to Greece. The Greek minority was subject to oppression and harassment during Enver Hoxha's communist rule and along with the rest of Albanians was hit hardly by the isolation that the regime imposed and from the economic hardship that followed the fall of communism as well. The treatment of the minority by the Albanian government is strongly linked with the status of Greco-Albanian relations.
The Greek minority is organized under the Unity for Human Rights Party which is the continuation of the former banned party called "Omonoia" (Unity in Greek) and has since 1997 joined the Socialist coalition. At the last elections the Greek minority party received 4.1% of the vote and two seats in parliament. The party leader is Vangjel Dule, while party member Vasilis Bolanos is the current mayor of the town of Himara. The party is represented in the ELDR group in the Council of Europe. Strong Greek presence exists in Gjirokastër (Argyrocastro), Korçë (Korytsa), Sarandë (Ag.Saranta), Himara (Xeimara) and the nearby areas. The former CIA director George J. Tenet, Pyrros Dimas, Sotiris Ninis and former Greek president Kostis Stefanopoulos have ancestral links to the Greek minority.
Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople

The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, protected under the treaty of Lausanne is a point of controversy between Greece and Turkey as the latter refuses to recognize the Ecumenical character of the Patriarchate thus requiring the Patriarch himself to be a Turkish citizen. Moreover, the biggest part of the Patriarchate's property – known as Vakoufia – had been confiscated by Turkish authorities and the Theological school of Halki which is the traditional school out of which the Eastern Orthodox Church, draws its clergy is closed since 1971. To no avail numerous Greek, European Union and USA officials have criticized Turkey's attitude and even president Bill Clinton during his visit in Greece asked for the theological school to open. During Greek prime-minister's Kostas Karamanlis historic visit to Turkey in 2007, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan promised to reconsider his country's stance on the matter.
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a region heavily colonized by Greeks throughout history. It used to have a significant presence of Greeks up until the population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923. Nowadays there remains Greek presence on the shores of Black Sea mainly in Mariupol (Ukraine), Crimea, Russia and Georgia despite emigration to Greece during and after the dissolution of Soviet Union. Today Greeks in the region are estimated to be around 215,000 according to official Greek diaspora figures. Greece is a founding member of the Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation.
International organization participation
Greece is a major participant in most large-scale international bodies, with the geographic significance of the region proving advantageous for diplomatic, trade and political crossroads.
In 1967, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and the Netherlands brought the Greek Case against the Greek junta regime for human rights violations. As a result, Greece left the Council of Europe in 1969, returning in 1976. It is the only country to have left the Council of Europe.[149][150]
BIS, BSEC, CCC, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECA (associate), ECE, ECLAC, EIB, EMU, EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, ILO, IMF, International Maritime Organization, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, NATO, OECD, OSCE, UN, UN Security Council, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, WEU, WHO, WIPO, WMO.
Greece was elected by the United Nations General Assembly to the United Nations Security Council, on 15 October 2004, as a non-permanent member for 2005 and 2006.
See also
References
- "Αρχές του Εξωτερικού (Missions Abroad)". Hellenic Republic Ministry of Foreign Affairs (in Greek). www.mfa.gr. Archived from the original on 21 May 2011. Retrieved 2 July 2011.
- Lucas, Dimitrios (4 January 2006). "Greece's Shifting Position on Turkish Accession to the EU Before and After Helsinki (1999)". MA in European Studies. Catholic University of Leuven. Retrieved 14 August 2008.
[Greece has become] one of Turkey's most ardent supporters within the EU.
- "Turkish PM visits Greek Muslims". BBC News. London. 8 May 2004. Retrieved 14 August 2008.
- Mesut Yilmaz told BirGün about the dark years Archived 18 July 2013 at the Wayback Machine, BirGün, Monday 23 December 2011 (in Turkish)
- Former Turkish PM's arson admission fuels anger, Kathimerini, Tuesday 27 December 2011
- Greece demands official response from Ankara on forest fires Archived 31 December 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Zaman, Wednesday 28 December 2011
- Turk-Greek Ties Strained by Arson Row Archived 31 May 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Journal of Turkish Weekly, Friday 30 December 2011
- Greek, Turkish foreign ministers discuss fire comment, Kathimerini, Saturday 31 December 2011
- Turkish daily cites report supporting wildfire claims, Kathimerini, Saturday 31 December 2011
- Greek Foreign Affairs Ministry about relations with Algeria
- "Greece is represented in Namibia via parallel accreditation of its Embassy in Pretoria. Namibia maintains an Honorary Consulate in Athens, and the Namibian Ambassador to London has parallel accreditation in Athens".
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- "Nigerian Missions Overseas". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Nigeria. Archived from the original on 6 February 2009. Retrieved 22 April 2009.
- "Row over tanker held in Nigeria". BBC News. London. 30 November 2008. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- "Nigeria". Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 22 April 2009.
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- "Greek consulate in Johannesburg". Archived from the original on 12 June 2009. Retrieved 25 June 2009.
- "Default Parallels Plesk Panel Page". Archived from the original on 18 December 2014. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- "Zimbabwe". Retrieved 14 April 2009.
Greece has an Embassy in Harare, whereas Zimbabwe does not have an Embassy and is not able to afford one. Zimbabwe does not have an Honorary Consulate in Greece either.
- "Framework of Treaties". Greece. Retrieved 7 May 2009.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 December 2017. Retrieved 30 December 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 25 July 2017. Retrieved 13 December 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "- Cancillería". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Ministry Foreign Affairs of Greece".
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 March 2016. Retrieved 16 July 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Greek Ministry of foreign affairs
- "Η Ελλάδα στο Μεξικό". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Embajada de México en Grecia". Archived from the original on 7 October 2016. Retrieved 24 September 2016.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 August 2020. Retrieved 7 January 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- United States Department of State: Background Note: Greece
- "Greeks angered by NATO strikes clash with riot police". CNN. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- "Azerbaijan, Greece aim to boost relations". Southeast Europe Times. February 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- "Greece, Azerbaijan to work closer on energy security". EUbusiness. February 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- "Azerbaijan plans to export gas to Europe via Greece: Azerbaijani president". Trend Capital. 16 February 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- "Greece, Azerbaijan sign energy cooperation memorandum". Athens News Agency. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- "Greece and Azerbaijan sign energy cooperation agreement". Journal of Turkish Weekly (JTW). August 2007. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- Greece "wants to be first" EU member to directly import Azeri gas
- "Bilateral Relations: Cambodia". Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Greece). 2009. Retrieved 2 May 2009.
- "Membres" (in French). L'Organisation internationale de la Francophonie. 2009. Archived from the original on 16 April 2009. Retrieved 2 May 2009.
- D. J. Mosley,Archipresbeutai, Hermes, Vol. 94, No. 3 (1966), pp. 377–381.
- Iranian embassy in Athens Archived 13 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "Greece and Gulf War II'" (PDF). lse.ac.uk. Retrieved 23 August 2008.Author:George Tzogopoulos, PhD researcher on U.S. foreign policy and the media, Loughborough University.
- "Ελληνική Δημοκρατία – Υπουργείο Εξωτερικών". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Tajikistan". Greece. Retrieved 21 May 2009.
Greece and Tajikistan established diplomatic relations in 1992. The stabilization of the country following the civil war and its increasing presence as part of the international community are expected to offer an opportunity for substantially developing its bilateral relations with Greece.
- "Bilateral relations between Russia and Greece". Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- "Kyrgyz president in Greece". BBC. 1 November 2004. Archived from the original on 19 October 2012. Retrieved 22 May 2009.
Kyrgyz President Askar Akayev left for Greece on an official visit on 31 October
- "Kyrgyzstan: The Greek Community". Hellenic Republic: Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 4 May 2009. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "General Information". General Secretariat For Greeks Abroad. Archived from the original on 16 July 2008. Retrieved 7 May 2009.
- "Greece, Kyrgyzstan sign bilateral accords". ANA. 2004. Retrieved 22 May 2009.
Greece and Kyrgyzstan on Monday signed three bilateral accords in the sectors of air transports, tourism and diplomacy, during a meeting between President of the Republic Costis Stephanopoulos and his Kyrgyz counterpart Askare Askayev, who is in Athens on a state visit.
- "Kyrgyzstan, Greece sign cooperation accords". BBC. 1 November 2004. Retrieved 22 May 2009.
Kyrgyz President Askar Akayev met Greek President Konstandinos Stefanopoulos in a narrow circle in Athens as part of an official visit to Greece on 1 November 2004. There was an exchange of views on a wide range of issues of cooperation...
- Greek Foreign Affairs Ministry about relations with Malaysia
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 12 September 2015. Retrieved 12 September 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Wertz, Daniel; Oh, JJ; Kim, Insung (August 2016). Issue Brief: DPRK Diplomatic Relations (PDF). The National Committee on North Korea. p. 8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 December 2016. Retrieved 4 February 2018.
- "Website of Former Ambassador Rigoberto Tiglao". Archived from the original on 6 January 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs about relations with Qatar
- http://www.mofa.go.kr/ENG/countries/europe/countries/20070818/1_24613.jsp?menu=m_30_40%5B%5D
- 외교부. "외교부 홈페이지에 오신것을 환영합니다". Archived from the original on 20 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- http://blog.naver.com/lynnk_01/200255239
- http://map.naver.com/local/siteview.nhn?code=11631470
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 21 February 2017. Retrieved 26 January 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Syrian embassy in Athens". Archived from the original on 10 June 2009. Retrieved 25 June 2009.
- "Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs about relations with Thailand". Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- "Thai embassy in Athens". Embassy Thailand. Archived from the original on 9 April 2009. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- "Thai deputy premier, UN sec. gen. candidate, meets with premier Karamanlis". Foreign Ministry. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- "Greece". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 1 November 2008.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Bilateral Relations Between Greece And Albania
- Stella Tsolakidou. ""Omonoia" Proceeds With Census of Greek Minority in Albania". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Βορειοηπειρώτης". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Albeu.com – Greece supports EU candidate status for Albania". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Maria Papathanasiou. "Karolos Papoulias visits Albania - GreekReporter.com". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Archbishop Anastasios of Albania
- Origin of the Albanians
- ""Northern Epiros": The Greek Minority in Southern Albania". Cultural Survival. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Languages of Albania
- Albanian communities in Greece
- "Pelasgians – Greeks – Albanias – Greeks – Albanians". Pelasgians – Greeks – Albanias. Archived from the original on 20 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Omonoia
- "Albanian official: 'We are much more pro-European than several EU members'". EurActiv – EU News & policy debates, across languages. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Belgian embassy in Athens". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "IU Webmaster redirect". Archived from the original on 10 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Bulgaria and its neighbors: a hundred years after independence Archived 11 March 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs: Bilateral relations between Greece and Bulgaria Archived 5 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- "greekembassy-cy.org". Archived from the original on 9 July 2009. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Czech embassy in Athens". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs about relations with Czech Republic
- "france 24 - Greece hails 'special relationship' with France on Hollande visit - France 24". France 24.
- The French Ministry of Foreign affairs. "Greece". France Diplomatie :: The French Ministry of Foreign affairs. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs about relations with France Archived 30 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "Ambassade de France en Grèce – Πρεσβεία της Γαλλίας στην Ελλάδα – La France en Grèce". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Nouvelle page 2". Archived from the original on 22 July 2017. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Chiara Teofili. "Presidenza: Italia-Grecia: una faccia, una razza". Archived from the original on 5 June 2015.
- Dizaino Kryptis. "Ministry of Foreign Affairs – Ministry of Foreign Affairs". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Welcome to nginx on Debian!". Archived from the original on 20 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Embassy of Greece in Moldova". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "GREECE and THE FORMER YUGOSLAV REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA – Interim Accord (with related letters and translations of the Interim Accord in the languages of the Contracting Parties). Signed at New York on 13 September 1995" (PDF). untreaty.un.org. 13 September 1995. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 December 2008. Retrieved 27 August 2011.
- "Πρώην Γιουγκοσλαβική ∆ημοκρατία της Μακεδονίας" [the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia]. www.mfa.gr. Archived from the original on 25 September 2011. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- "Diplomatic Missions". www.mfa.gov.mk. Archived from the original on 30 September 2011. Retrieved 28 August 2011.
- Norway's embassy in Athens
- "greece.pl". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Placówki Dyplomatyczne Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej". Archived from the original on 28 June 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Russia expels Greek diplomats in retaliatory move Reuters, 6 August 2018.
- "Greece.sk". Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Athens – SwedenAbroad". Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Greek embassy in Stockholm". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Ýëåêòðîííàÿ áèáëèîòåêà LibOk.Net – ÷èòàòü è ñêà÷àòü êíèãè áåñïëàòíî". Archived from the original on 9 September 2016. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Посольство України у Грецькій Республіці". Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Greece's Bilateral Relations". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Worldwide organisations". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "British Embassy Athens – GOV.UK". Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Fiji
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece
- "FYROM Name Issue". www.mfa.gr. Archived from the original on 15 October 2011. Retrieved 27 August 2011.
- "Bucharest Summit Declaration Issued by the Heads of State and Government participating in the meeting of the North Atlantic Council in Bucharest on 3 April 2008". www.summitbucharest.ro. 3 April 2008. Archived from the original on 3 October 2011. Retrieved 27 August 2011.
- "2008/212/EC: Council Decision of 18 February 2008 on the principles, priorities and conditions contained in the Accession Partnership with the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia and repealing Decision 2006/57/EC". eur-lex.europa.eu. 18 February 2008. Retrieved 27 August 2011.
- "Conclusions on the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (PDF). ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 27 August 2011.
- "The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia institutes proceedings against Greece for a violation of Article 11 of the Interim Accord of 13 September 1995" (PDF). www.icj-cij.org. 17 November 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 December 2011. Retrieved 27 August 2011.
- "BBC News – ICJ rules Greece 'wrong' to block Macedonia's Nato bid". BBC News. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 20 January 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-47002865 BBC News Online. 25 January 2019. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- Country Studies US: Greeks and Other Minorities
- Madsen, Mikael Rask (2019). "Resistance to the European Court of Human Rights: The Institutional and Sociological Consequences of Principled Resistance". Principled Resistance to ECtHR Judgments - A New Paradigm?. Beiträge zum ausländischen öffentlichen Recht und Völkerrecht. 285. Springer. pp. 35–52. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-58986-1_2. ISBN 978-3-662-58986-1.
- Bates, Ed (2010). "The 'Greek' Case, 1967–1969". The Evolution of the European Convention on Human Rights: From Its Inception to the Creation of a Permanent Court of Human Rights. Oxford University Press. pp. 264–270. ISBN 978-0-19-920799-2.
Further reading
- Economides, Spyros (March 2005). "The Europeanisation of Greek Foreign Policy". West European Politics. 28 (2): 471–491. doi:10.1080/01402380500060528. S2CID 154004940.
External links
- Greece's foreign policy, via the Greek Ministry of Foreign affairs
- Ethnic groups in Albania, via CIA – The World Factbook
- Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Foreign relations of Greece. |
