Augusta, Georgia
Augusta (/əˈɡʌstə/), officially Augusta–Richmond County, is a consolidated city-county on the central eastern border of the U.S. state of Georgia. The city lies across the Savannah River from South Carolina at the head of its navigable portion. Georgia's second-largest city after Atlanta, Augusta is located in the Fall Line section of the state.
Augusta, Georgia | |
|---|---|
| Augusta–Richmond County | |
 .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp)     Clockwise from top: Downtown Augusta on Broad Street, Riverwalk Augusta on the Savannah River, Sacred Heart Cultural Center, Old Government House, Augusta Canal with the Enterprise Mill in the background, Augusta University, Augusta National Golf Club | |
 | |
| Nickname(s): "The Garden City" | |
| Motto(s): | |
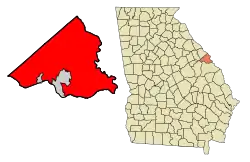 Location within Richmond County | |
| Coordinates: 33°28′N 81°58′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Counties | Richmond |
| Established | 1736[1] |
| City-county consolidation | 1996[1] |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Hardie Davis (D) |
| Area | |
| • Consolidated city-county | 306.5 sq mi (793 km2) |
| • Land | 302.1 sq mi (782 km2) |
| • Water | 4.3 sq mi (11.3 km2) |
| • Urban | 259.52 sq mi (672.2 km2) |
| Elevation | 136 ft (45 m) |
| Population | |
| • Consolidated city-county | 195,844 |
| • Estimate (2019)[4] | 197,888 |
| • Rank | US: 122nd |
| • Density | 654.2/sq mi (252.6/km2) |
| • Urban | 386,787 (US: 98th) |
| • Urban density | 1,490.4/sq mi (575.4/km2) |
| • Metro | 600,151 (US: 93rd) |
| • CSRA | 709,433 |
| • Change 2011–2014 | |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| ZIP codes | 30901, 30904, 30906, 30907, 30909, 30912,[5] 30815 |
| Area codes | 706, 762[6][7] |
| Website | AugustaGA.gov |
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Augusta–Richmond County had a 2019 estimated population of 197,888, not counting the unconsolidated cities of Blythe and Hephzibah.[3] It is the 123rd largest city in the United States. The process of consolidation between the City of Augusta and Richmond County began with a 1995 referendum in the two jurisdictions. The merger was completed on July 1, 1996. Augusta is the principal city of the Augusta metropolitan area. In 2017 it had an estimated population of 600,151, making it the second-largest metro area in the state. It is the 93rd largest metropolitan area in the United States.
Augusta was established in 1736 and is named in honor of Princess Augusta of Saxe-Gotha (1719–1772), the bride of Frederick, Prince of Wales and the mother of the British monarch George III.[1] During the American Civil War, Augusta housed the principal Confederate powder works.[8] Augusta's warm climate made it a major resort town of the Eastern United States in the early and mid-20th century. Internationally, Augusta is best known for hosting The Masters golf tournament each spring. The Masters brings over 200,000 visitors from across the world to the Augusta National Golf Club. Membership at Augusta National is widely considered to be the most exclusive in the sport of golf across the world.
Augusta lies approximately two hours east of downtown Atlanta by car via I-20. The city is home to Fort Gordon, a major U.S. Army base. In 2016, it was announced that the new National Cyber Security Headquarters would be based in Augusta.
The area along the river was long inhabited by varying cultures of indigenous peoples, who relied on the river for fish, water and transportation. The site of Augusta was used by Native Americans as a place to cross the Savannah River, because of its location on the fall line.
In 1735, two years after James Oglethorpe founded Savannah, he sent a detachment of troops to explore the upper Savannah River. He gave them an order to build a fort at the head of the navigable part of the river. The expedition was led by Noble Jones, who created a settlement as a first line of defense for coastal areas against potential Spanish or French invasion from the interior.[9] Oglethorpe named the town in honor of Princess Augusta, the mother of King George III and the wife of Frederick, Prince of Wales. Oglethorpe visited Augusta in September 1739 on his return to Savannah from a perilous visit to Coweta Town, near present-day Phenix City, Alabama.[10] There, he had met with a convention of 7,000 Native American warriors and concluded a peace treaty with them in their territories in northern and western Georgia.[11] Augusta was the second state capital of Georgia from 1785 until 1795 (alternating for a period with Savannah, the first).
Augusta developed rapidly as a market town as the Black Belt in the Piedmont was developed for cotton cultivation. Invention of the cotton gin made processing of short-staple cotton profitable, and this type of cotton was well-suited to the upland areas. Cotton plantations were worked by slave labor, with hundreds of thousands of slaves shipped from the Upper South to the Deep South in the domestic slave trade. Many of the slaves were brought from the Lowcountry, where their Gullah culture had developed on the large Sea Island cotton and rice plantations.
The city experienced the Augusta Fire of 1916, which damaged 25 blocks of the town and many buildings of historical significance.
As a major city in the area, Augusta was a center of activities during Reconstruction and after. In the mid-20th century, it was a site of civil rights demonstrations. In 1970 Charles Oatman, a mentally disabled teenager, was killed by his cellmates in an Augusta jail. A protest against his death broke out in a riot involving 500 people, after six black men were killed by police,[12] each found to have been shot in the back.[13] The noted singer and entertainer James Brown was called in to help quell lingering tensions, which he succeeded in doing.[12]
Geography

Augusta is located near the Georgia/South Carolina border, about 150 miles (240 km) east of Atlanta and 70 miles (110 km) west of Columbia. The city is located at 33°28′12″N 81°58′30″W (33.470, −81.975).[14]
According to the United States Census Bureau, the Augusta–Richmond County balance has a total area of 306.5 square miles (793.8 km2), of which 302.1 square miles (782.4 km2) is land and 4.3 square miles (11.1 km2) (1.42%) is water.

Augusta is located about halfway up the Savannah River on the fall line, which creates a number of small falls on the river. The city marks the end of a navigable waterway for the river and the entry to the Georgia Piedmont area.
The Clarks Hill Dam is built on the fall line near Augusta, forming Clarks Hill Lake. Farther downstream, near the border of Columbia County, is the Stevens Creek Dam, which generates hydroelectric power. Even farther downstream is the Augusta Diversion Dam, which marks the beginning of the Augusta Canal and channels Savannah River waters into the canal.[15]
Climate
As with the rest of the state, Augusta has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa), with short, mild winters, very hot, humid summers, and a wide diurnal temperature variation throughout much of the year, despite its low elevation and moisture. The monthly daily average temperature ranges from 45.4 °F (7.4 °C) in January to 81.6 °F (27.6 °C) in July; there are 53 nights with the low reaching the freezing mark, 82 days reaching or exceeding 90 °F (32 °C), and 5.5 days reaching 100 °F (38 °C) annually. Extreme temperatures range from −1 °F (−18 °C) on January 21, 1985 up to 108 °F (42 °C) on August 10, 2007 and August 21, 1983. Snowfall is not nearly as common as in Atlanta, due largely to Augusta's elevation, with downtown Augusta being about 900 ft (270 m) lower than downtown Atlanta. Freezing rain is also a threat in wintertime.
| Climate data for Augusta Regional Airport, Georgia (1981–2010 normals,[lower-alpha 1] extremes 1871–present[lower-alpha 2]) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 84 (29) |
86 (30) |
93 (34) |
96 (36) |
101 (38) |
106 (41) |
107 (42) |
108 (42) |
106 (41) |
101 (38) |
90 (32) |
84 (29) |
108 (42) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 74.8 (23.8) |
78.1 (25.6) |
84.4 (29.1) |
88.8 (31.6) |
93.9 (34.4) |
98.3 (36.8) |
100.1 (37.8) |
99.2 (37.3) |
94.9 (34.9) |
88.5 (31.4) |
81.6 (27.6) |
76.5 (24.7) |
101.3 (38.5) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 57.9 (14.4) |
62.3 (16.8) |
69.9 (21.1) |
77.3 (25.2) |
85.0 (29.4) |
91.0 (32.8) |
93.4 (34.1) |
91.8 (33.2) |
86.7 (30.4) |
77.7 (25.4) |
69.1 (20.6) |
60.0 (15.6) |
76.9 (24.9) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 32.8 (0.4) |
35.9 (2.2) |
42.0 (5.6) |
48.1 (8.9) |
57.3 (14.1) |
66.2 (19.0) |
69.8 (21.0) |
69.3 (20.7) |
62.6 (17.0) |
51.0 (10.6) |
41.4 (5.2) |
34.5 (1.4) |
51.0 (10.6) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 16.4 (−8.7) |
20.5 (−6.4) |
25.8 (−3.4) |
32.6 (0.3) |
43.6 (6.4) |
55.6 (13.1) |
62.5 (16.9) |
61.2 (16.2) |
49.0 (9.4) |
34.6 (1.4) |
26.1 (−3.3) |
18.5 (−7.5) |
13.9 (−10.1) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −1 (−18) |
3 (−16) |
12 (−11) |
26 (−3) |
35 (2) |
46 (8) |
54 (12) |
52 (11) |
36 (2) |
22 (−6) |
11 (−12) |
5 (−15) |
−1 (−18) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.91 (99) |
3.92 (100) |
4.18 (106) |
2.84 (72) |
2.65 (67) |
4.72 (120) |
4.33 (110) |
4.32 (110) |
3.22 (82) |
3.27 (83) |
2.82 (72) |
3.39 (86) |
43.57 (1,107) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 0.4 (1.0) |
0.4 (1.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.9 (2.3) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 9.8 | 8.8 | 8.6 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 7.1 | 6.5 | 6.9 | 9.2 | 104.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 69.8 | 65.8 | 65.0 | 64.5 | 69.6 | 71.3 | 73.9 | 76.5 | 76.2 | 73.3 | 71.9 | 71.6 | 70.8 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity 1961–1990)[16][17][18] | |||||||||||||
Historic districts
Augusta Downtown Historic District is a historic district that encompasses most of downtown Augusta and its pre-Civil War area. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2004.[19]
Augusta also includes the:
- Bethlehem Historic District
- Broad Street Historic District
- Greene Street Historic District
- Harrisburg–West End Historic District
- Laney–Walker North Historic District
- Paine College Historic District
- Pinched Gut Historic District
- Sand Hills Historic District
- Summerville Historic District
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1800 | 2,215 | — | |
| 1810 | 2,476 | 11.8% | |
| 1830 | 6,710 | — | |
| 1840 | 6,403 | −4.6% | |
| 1850 | 9,448 | 47.6% | |
| 1860 | 12,493 | 32.2% | |
| 1870 | 15,389 | 23.2% | |
| 1880 | 21,891 | 42.3% | |
| 1890 | 33,300 | 52.1% | |
| 1900 | 39,441 | 18.4% | |
| 1910 | 41,040 | 4.1% | |
| 1920 | 52,548 | 28.0% | |
| 1930 | 60,342 | 14.8% | |
| 1940 | 65,919 | 9.2% | |
| 1950 | 71,508 | 8.5% | |
| 1960 | 70,626 | −1.2% | |
| 1970 | 59,864 | −15.2% | |
| 1980 | 47,532 | −20.6% | |
| 1990 | 44,639 | −6.1% | |
| 2000 | 195,182 | 337.2% | |
| 2010 | 195,844 | 0.3% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 197,888 | [4] | 1.0% |
| Population 1800–2010.[23][24] | |||
According to 2013 US Census estimates, the Augusta–Richmond County population was 197,350[25] not counting the unconsolidated cities of Hephzibah and Blythe. In the 2010 census, Augusta–Richmond County had 195,844 residents. The population density was 647.5 people per square mile (250/km2).[26] There were 84,427 housing units at an average density of 279.5 per square mile (782/km2). The racial makeup of the city-county area was 64.7% Black or African American, 29.1% White, 0.3% Native American, 1.7% Asian, 0.2% Pacific Islander, 1.3% some other race, and 2.6% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino people of any race were 4.1% of the population.[27]
There were 75,208 households, out of which 28.0% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 35.2% were headed by married couples living together, 22.7% had a female householder with no husband present, and 37.1% were non-families. 30.7% of all households were made up of individuals, and 8.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.46 and the average family size was 3.09.[27]
In the city-county consolidated area the population was spread out, with 24.6% under the age of 18, 12.6% from 18 to 24, 26.7% from 25 to 44, 24.8% from 45 to 64, and 11.3% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 33.0 years. For every 100 females, there were 93.8 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 90.7 males.[27]
As of the 2000 census, the median income for a household in the city-county area was $37,231, and the median income for a family was $45,372. Males had a median income of $32,008 versus $23,988 for females. The per capita income for the balance was $19,558. About 13.2% of families and 16.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 24.1% of those under age 18 and 12.5% of those age 65 or over.
Religion
The most-attended church is the Southern Baptist Convention, with 221 congregations with 114,351 members. The Catholic Church has 13 congregations and 31,687 members, while the United Methodist Church has 83 churches and 30,722 members. The National Baptist Convention had 26,671 members. The Presbyterian Church (USA) has 14 congregations and 4,500 members, the Presbyterian Church in America has 4,396 members in 14 churches.[28]
The Jewish community in Augusta dates back to the early 19th century. Today, there are two congregations, Congregation Children of Israel (Reform) and Adas Yeshurun (Conservative). There is also a Chabad-Lubavitch house. Around 1,300 Jews currently live in Augusta, who collectively support a Jewish Community Center.
Economy
Augusta is a regional center of medicine, biotechnology, and cyber security. Augusta University, the state's only public health sciences graduate university, employs over 7,000 people. Along with University Hospital, the Medical District of Augusta employs over 25,000 people and has an economic impact of over $1.8 billion.[29]
The city's three largest employers are Augusta University, the Savannah River Site (a Department of Energy nuclear facility) and the U.S. Army Cyber Center of Excellence at Fort Gordon, which oversees training for Cyber, Signal Corps, and Electronic Warfare. Despite layoffs from several companies during the U.S. economic recession and a relatively high state unemployment rate,[30] the Augusta community has experienced a decrease in bankruptcy filings[31] and saw a slight decrease in the unemployment rate from late 2009 to March 2011. However, these unemployment numbers are misleading as spring brings lower unemployment rates due to the Masters Golf Tournament. While unemployment fell to a two-year low of 8.3% in April 2011, unemployment rates have since risen to 9.9% as of July 2011.[32]
Companies that have facilities, headquarters or distribution centers in the Augusta metro area include CareSouth, NutraSweet, T-Mobile, Covidien, Solo Cup Company, Automatic Data Processing, Graphic Packaging International, Solvay S.A., Bridgestone, Teleperformance, Olin Corporation, Sitel, E-Z-GO, Taxslayer, Elanco, KSB Company (Georgia Iron Works), Club Car (Worldwide Headquarters), Halocarbon, MTU Friedrichshafen (subsidiary of Tognum), Kimberly Clark Corporation, Nutrien (formerly PotashCorp), John Deere, Kellogg's and Delta Air Lines' baggage call center.[33]
Top employers
According to the Augusta Economic Development Authority,[34] the top manufacturing employers in the city are:
| # | Employer | # of employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Textron Specialized Vehicles | 1000 |
| 2 | Covidien | 850 |
| 3 | Graphic Packaging International | 820 |
| 4 | Kellogg's | 535 |
| 5 | FPL Food | 500 |
| 6 | Procter & Gamble | 450 |
| 7 | Thermal Ceramics | 444 |
| 8 | Resolute Forest Products | 374 |
| 9 | Boral Brick | 363 |
| 10 | Nutrien | 350 |
The top public sector employers are:
| # | Employer | # of employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fort Gordon | 19,884 |
| 2 | Augusta University | 4,656 |
| 3 | Richmond County School System | 4,418 |
| 4 | University Hospital | 3,200 |
| 5 | Augusta University Health System | 3,054 |
| 6 | Augusta–Richmond County | 4,418 |
| 7 | Charlie Norwood VA Medical Center | 2,082 |
| 8 | East Central Regional Hospital | 1,488 |
| 9 | Doctors Hospital | 1,210 |
| 10 | Doctors Hospital | 270 |
Sports
Teams
The Augusta GreenJackets minor league baseball club, formerly located at Lake Olmstead Stadium in Augusta, now play at SRP Park along the Savannah River in North Augusta, South Carolina. The team began to play in 1988 as the Augusta Pirates, affiliated with the Pittsburgh Pirates. Later affiliated with the Boston Red Sox, the GreenJackets are with the San Francisco Giants.[35]
The Augusta Lynx were a minor-league professional ice hockey team based in Augusta, Georgia. The Lynx played their home games at the James Brown Arena from 1998 until 2008. The Lynx, who played in the ECHL, had affiliations with the Tampa Bay Lightning of the NHL and the Norfolk Admirals of the AHL.
The Augusta RiverHawks were a professional minor league ice hockey team. They played in the Southern Professional Hockey League (SPHL) from 2010 to 2013. They played their home games at the James Brown Arena.
The Augusta Stallions were a professional Arena football team founded in 1999. They were one of the 15 original teams to join the inaugural 2000 AF2 season. They started off in the American Conference, before switching to the Southeast Division in 2001, and then the Eastern Division in 2002. The team folded in 2002.
The Augusta Rugby Football Club (ARFC)[36] is a division 2 men's club competing in the Palmetto Rugby Union,[37] part of the USA Rugby South Conference.[38]
Augusta has an all-female flat track roller derby team, the Soul City Sirens. Founded in 2008, this league is all-volunteer and skater-owned.[39]
Augusta is also home to the former Augusta 706ers, a minor league professional basketball team in the American Basketball Association. The team was founded in 2017 and stopped operations in December 2018 because of a lack of funds. The team played all home games at the James Brown Arena.
| Club | Sport | League | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Augusta GreenJackets | Baseball | South Atlantic League | SRP Park |
| Augusta Stallions | Arena football | AF2 | James Brown Arena |
| Augusta RiverHawks | Minor league hockey | Southern Professional Hockey League | James Brown Arena |
| Augusta Mad Dogs | Rugby | Palmetto Rugby Union | Larry Bray Memorial |
| Soul City Sirens | Roller derby | WFTDA | Red Wing Rollerway |
| Augusta 706ers | Basketball | American Basketball Association | James Brown Arena |
Tournaments

The city's famous golf course, the Augusta National Golf Club, hosts the first major golf tournament of each year, The Masters. This tournament is the most prestigious in the sport[40] and is one of the four major championships. The best professional and amateur golfers in the world come to Augusta during the first full week of April every year. The grounds of Augusta National are known for being pristine, and the course was ranked in 2009 as the third best golf course in the world by Golf Magazine.[41]
The city also has several disc golf facilities. The Augusta Top Gun Series is a series of tournaments sanctioned by the Professional Disc Golf Association. These tournaments are held at various venues in Augusta, including Pendleton King Park and Lake Olmstead.[42] Also, Augusta hosted the 2006 Professional Disc Golf World Championships. Along with Pendleton King and Lake Olmstead, two courses in North Augusta, SC was used for the tournament. 299 disc golfers from around the world attended the event, with Ken Climo winning the tournament and his 12th world championship.
Augusta hosted the Augusta Southern Nationals billed as "World's Richest Drag Boat Race" for 30 consecutive years. The event was held on the Savannah River near downtown in July until 2016. The race was part of the Lucas Oil Drag Boat Racing Series and was sanctioned by the International Hot Boat Association. The event benefited the Augusta Chapter of the Georgia Special Olympics with over 100 racing teams from 25 states competed annually for $140,000 in purse and prizes while trying to beat the course record of 252.94 miles per hour (407.07 km/h).
Augusta is the site of the Head of the South Regatta. The youth rowing regatta is held on the Savannah River and is usually scheduled for early November.
Parks and recreation
- Riverwalk Augusta – riverfront park along and on top of the city's levee
- Augusta Common – green space linking Broad Street to Reynolds Street, with statue of James Oglethorpe
- Augusta Canal – historic canal with bike/pedestrian path
- Phinizy Swamp Nature Park – wetlands park with pedestrian/bike paths and boardwalks
- Diamond Lakes Regional Park – in south Richmond County
- Brookfield Park – public park featuring a playground, putting green, pedestrian/bike path, and a fountain in which children can play
- Pendleton King – public park featuring a disc golf course, dog park, amphitheater, bike and running paths, and gardens
Government
In 1995, citizens of Augusta and unincorporated parts of Richmond County voted to consolidate their city and county governments. Citizens of Hephzibah and Blythe, also located in Richmond County, voted against joining in the merger, which took effect January 1, 1996. The unified government consists of a mayor and ten commissioners. Eight commissioners represent single-member districts, while two are elected at-large, each to represent a super district that encompasses half of Augusta-Richmond's population.[43]
Education

Colleges and universities
- Main campuses
- Augusta Technical College (state technical college)
- Augusta University (public research university)
- Paine College (private, Methodist historically black college)
- Satellite campuses
- East Georgia State College (state four-year college), main campus located in Swainsboro
- Georgia Military College (state funded military college), main campus located in Milledgeville
- Brenau University (private, not-for-profit, undergraduate and graduate-level higher education), main campus located in Gainesville, Georgia
K–12 schools

Public K–12 schools in Augusta are managed by the Richmond County School System. The school system contains 36 elementary schools, 10 middle schools, and the following eight high schools: Glenn Hills, Butler, Westside, Hephzibah, T. W. Josey, A.R.C. (Academy of Richmond County), Lucy Craft Laney, and Cross Creek. There are four magnet schools: C. T. Walker Traditional Magnet School, A. R. Johnson Health Science and Engineering Magnet High School, Davidson Fine Arts, and the Richmond County Technical Career Magnet School.
Private schools in Augusta include Aquinas High School, Episcopal Day School, Saint Mary on the Hill Catholic School, Immaculate Conception School, Hillcrest Baptist Church School, Curtis Baptist High School, Gracewood Baptist First Academy, Alleluia Community School, New Life Christian Academy, Charles Henry Terrell Academy, Heritage Academy, and Westminster Schools of Augusta. Augusta Christian Schools, Augusta First Seventh-day Adventist School, and Augusta Preparatory Day School serve Augusta, but are located in neighboring Martinez.
Transportation
Augusta is linked to Atlanta to the west and Columbia, South Carolina, to the east by Interstate 20 (I-20). I-520 (Bobby Jones Expressway) extends from I-20 exit 196 through Augusta's western and southern suburban areas, eventually crossing the Savannah River to South Carolina, in which it is known as Palmetto Parkway.
U.S. Route 1 (US 1), along with State Route 4 (SR 4), connects Wrens. US 1 also links Augusta with Aiken, South Carolina. US 25 and SR 121 connects Waynesboro with Augusta; across the state line, US 25 and South Carolina Highway 121 (SC 121) links Augusta with Edgefield, South Carolina. US 78/US 278/SR 10, known locally as Gordon Highway, connects Thomson with Augusta. In South Carolina, US 1 and US 78 go through Aiken, South Carolina. US 78 further connects with Charleston, South Carolina. US 278 bypasses Aiken and serves as a connecting route to Hilton Head Island, South Carolina.
Major roads and expressways
 I-20 (Carl Sanders Highway)
I-20 (Carl Sanders Highway) I-520 (Bobby Jones Expressway / Deputy James D. Paugh Memorial Highway)
I-520 (Bobby Jones Expressway / Deputy James D. Paugh Memorial Highway) US 1 (Deans Bridge Road (from Jefferson County line to Gordon Highway); Gordon Highway (from Deans Bridge Road to South Carolina state line); Fall Line Freeway (from Jefferson County line to I-520))
US 1 (Deans Bridge Road (from Jefferson County line to Gordon Highway); Gordon Highway (from Deans Bridge Road to South Carolina state line); Fall Line Freeway (from Jefferson County line to I-520)) US 25 (Peach Orchard Road (entire length); Gordon Highway (from Peach Orchard Road to South Carolina state line))
US 25 (Peach Orchard Road (entire length); Gordon Highway (from Peach Orchard Road to South Carolina state line))

 US 78 / US 278 / SR 10 (Gordon Highway)
US 78 / US 278 / SR 10 (Gordon Highway) SR 4 (follows US 1 from Jefferson County line to Gordon Highway; leaves Georgia at James U. Jackson Memorial Bridge)
SR 4 (follows US 1 from Jefferson County line to Gordon Highway; leaves Georgia at James U. Jackson Memorial Bridge) SR 28 (various roads, including John C. Calhoun Expressway and Washington Road)
SR 28 (various roads, including John C. Calhoun Expressway and Washington Road) SR 56 (Mike Padgett Highway)
SR 56 (Mike Padgett Highway) SR 88 in southern Richmond County
SR 88 in southern Richmond County SR 104 (Washington Road; Pleasant Home Road; River Watch Parkway)
SR 104 (Washington Road; Pleasant Home Road; River Watch Parkway) SR 104 Conn. (Washington Road)
SR 104 Conn. (Washington Road) SR 232 (Columbia Road / Bobby Jones Expressway)
SR 232 (Columbia Road / Bobby Jones Expressway) SR 383 (Jimmie Dyess Parkway)
SR 383 (Jimmie Dyess Parkway) SR 540 (Fall Line Freeway (Deans Bridge Road from Jefferson County line to I-520))[44]
SR 540 (Fall Line Freeway (Deans Bridge Road from Jefferson County line to I-520))[44]
 SR 555 / SR 565 (Savannah River Parkway) (Peach Orchard Road from Burke County line to I-520)
SR 555 / SR 565 (Savannah River Parkway) (Peach Orchard Road from Burke County line to I-520)
Parts of Augusta are served by city transit service Augusta Public Transit (APT), but the main mode of transportation within the city is by car. The city has two airports: Augusta Regional Airport and Daniel Field. Augusta is also served by a number of taxi companies.
Rail
Until the 1960s the city's Augusta Union Station was a passenger rail hub, with trains arriving from the Atlantic Coast Line (as spur sections from Florence, South Carolina from trains such as the Champion, Everglades and Palmetto), Georgia Railroad and Southern Railway (for example, the Aiken-Augusta Special from New York City). The last Seaboard Coast Line (the successor to the ACL) train was a Florence-Augusta section of the Champion; this section ended in 1970.[45][46] The last train to the city was the unnamed daily in-state Georgia Railroad train between Atlanta and Augusta. This latter train, unofficially called The Georgia Cannonball, ran as a mixed train, until May 6, 1983.[47] Most trains went to the Union Station at Barrett Square. The Southern Railway trains went to the Southern Railway depot at Fifth and Reynolds Street. Today freight service is handled by Norfolk Southern Railway's Georgia Division and Piedmont Division through their Augusta Yard and Nixon Yard located near the city. Norfolk Southern Trains such as the NS 191 and 192 pass through Augusta's downtown as they "street run" at 5 mph down 6th street. They also cross the old Trestle over the Savannah River in and out of South Carolina. CSX Transportation Atlanta Division and Florence Division Trains serve the Augusta, Georgia area too from the CSX Augusta Yard near Gordon Highway southwest of the city.
Pedestrians and cycling
- Augusta Canal Historic Trail
- New Bartram Trail
- Phinizy Swamp Constructed Wetlands Trail
- River Levee Trail
- Riverwalk Augusta Trail
Notable people
Sister cities
Augusta is twinned with:
 Biarritz, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France[48]
Biarritz, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France[48] Takarazuka, Hyōgo, Japan
Takarazuka, Hyōgo, Japan
See also
Notes
- Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the expected highest and lowest temperature readings at any point during the year or given month) calculated based on data at said location from 1981 to 2010.
- Official records for Augusta were kept at downtown from February 1871 to March 1944, Daniel Field from April 1944 to June 1950, and at Bush Field / Augusta Regional Airport since July 1950. For more information, see Threadex
References
- "History". Archived from the original on May 27, 2010. Retrieved December 22, 2009.
- "Augusta Facts". Archived from the original on May 27, 2010. Retrieved December 22, 2009.
- "2017 U.S. Census Estimates–List of Places". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on September 22, 2018. Retrieved May 24, 2018.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved May 21, 2020.
- "USPS.com® – ZIP Code Lookup". Archived from the original on November 4, 2010.
- "Get your digits straight - chronicle.augusta.com". chronicle.augusta.com. Archived from the original on September 24, 2009. Retrieved May 28, 2008.
- "762 on way to phone near you". Archived from the original on September 27, 2009. Retrieved May 28, 2008.
- "Augusta", in The Concise Columbia Encyclopedia (New York: Columbia Univ. Press, 1994), p. 56.
- Robertson Jr., Thomas Heard (2002). "The Colonial Plan of Augusta". Georgia Historical Quarterly. 86 (4): 511.
- "Coweta Town historical marker". KVWE-TV. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- Memorial History of Augusta, Georgia: from Its Settlement in 1735 to the Close of the Eighteenth Century by Charles Colcock Jones, Salem Dutcher (Augusta, GA: D. Mason, 1890) page 31
- "Freedom On Film: Civil Rights In Georgia". Archived from the original on September 23, 2015. Retrieved June 20, 2015.
- "Baltimore is Everywhere," New York Magazine, May 18–31, 2015, p. 33.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "Officials consider relicensing Augusta Canal" Archived October 17, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Augusta Chronicle, June 29, 2003
- "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on July 2, 2017. Retrieved October 9, 2019.
- "Station Name: GA AUGUSTA BUSH FLD AP". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved September 4, 2016.
- "WMO Climate Normals for COLUMBIA/METRO ARPT SC 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved September 4, 2016.
- "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- Emporis.com. Retrieved 2017-06-12.
- Emporis.com. Retrieved 2017-06-12.
- Emporis.com. Retrieved 2017-06-12.
- "Census Of Population And Housing". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved February 3, 2015.
- "Population of the 100 Largest Cities and Other Urban Places in the United States: 1790 to 1990". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on January 2, 2011. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- Data Access and Dissemination Systems (DADS). "U.S. Census website".
- Data Access and Dissemination Systems (DADS). "American FactFinder – Results". Archived from the original on February 12, 2020.
- "Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (DP-1): Augusta–Richmond County consolidated government (balance), Georgia". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 6, 2012.
- "The Association of Religion Data Archives – Maps & Reports". Archived from the original on April 29, 2014. Retrieved May 15, 2014.
- HOME | AugustaTomorrow.com Archived July 7, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- Department of Labor – State of Georgia – http://www.dol.state.ga.us/ Archived March 17, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- Seymour & Associates | The Bankruptcy Lawyers Archived June 24, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Augustageorgialawyer.org (July 1, 2013). Retrieved on August 9, 2013.
- Unemployment Rate in Augusta–Richmond County, GA-SC (MSA) (AUGU213URN) – FRED – St. Louis Fed Archived April 3, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. Research.stlouisfed.org (July 30, 2013). Retrieved on August 9, 2013.
- "Delta closing two U.S. call centers". USA Today. September 8, 2010. Archived from the original on June 22, 2006.
- City of Augusta Largest Employers Archived November 24, 2013, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved November 14, 2013
- "About Greenjackets Baseball". The official site of the Augusta Greenjackets. Archived from the original on November 11, 2011. Retrieved May 21, 2011.
- Augusta Rugby Football Club (ARFC) Archived November 10, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- Palmetto Rugby Union Archived September 29, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- USA Rugby South Conference Archived April 8, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- Fans Vote Augusta River Hawks As Hockey Team's Name Archived March 17, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Thesphl.com (March 13, 2010). Retrieved on August 9, 2013.
- Super Bowl, World Series, NBA Finals: None say 'class' like the Masters Archived May 26, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Worldgolf.com (February 25, 2008). Retrieved on August 9, 2013.
- Archived January 21, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- Augusta Disc Golf Archived September 4, 2011, at the Wayback Machine Augusta Disc Golf Association
- "Maps". Archived from the original on May 27, 2010. Retrieved December 22, 2009.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 4, 2011. Retrieved April 9, 2011.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Seaboard Coast Line timetable, April 26, 1970, Table 3
- Seaboard Coast Line timetable, December 1, 1970, Table 4
- 1939–, Cox, Jim (2011). Rails across dixie : a history of passenger trains in the American South. Jefferson, N.C.: McFarland. p. 246. ISBN 9780786445288. OCLC 609716000.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- "Twin towns, Biarritz official website". Biarritz.fr. Archived from the original on July 29, 2013. Retrieved May 11, 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Augusta, Georgia. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Augusta, Georgia. |
| Wikisource has the text of a 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article about Augusta, Georgia. |
- Official website
- Augusta Metropolitan Convention and Visitors Bureau
- Augusta Economic Development Authority homepage
- Augusta Tomorrow
- Downtown Development Authority
- Robert E. Williams Photographic Collection: African-Americans in the Augusta, Ga. Vicinity (Richmond Co.), ca. 1872–1898 from the Digital Library of Georgia
- Picturing Augusta: Historic Postcards from the Collection of the East Central Georgia Regional Library
- . The American Cyclopædia. 1879.



%252C_May_2017_1.jpg.webp)