COVID-19 pandemic in Latvia
The COVID-19 pandemic in Latvia is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The virus was confirmed to have reached Latvia on 2 March 2020, having been brought along with people returning from abroad.
| COVID-19 pandemic in Latvia | |
|---|---|
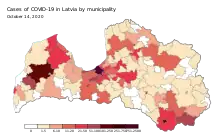 Confirmed cases of COVID-19 in Latvia by municipalities. | |
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | Latvia |
| First outbreak | Wuhan, Hubei, China |
| Index case | Riga |
| Arrival date | 2 March 2020 (11 months and 5 days) |
| Confirmed cases | 71,320[1][2] |
| Active cases | 10,594[1][2] |
| Severe cases | 4[1][2] |
| Recovered | 59,399[1][2] |
Deaths | 1,327[1][2] |
| Fatality rate | 1.86% |
| Government website | |
| COVID-19 News (in Latvian) | |
The government declared a state of emergency on 13 March with a number of epidemiological safety measures and restrictions, primarily limiting gatherings, travel, most public venues, and educational institutions. As the new confirmed cases stayed in the low two-digit range per day, the emergency was periodically extended until mid-2020, when the confirmed infection case dropped to almost 0 and the state of emergency ended on 9 June. Most restrictions were lifted.
The rates spiked again by the end of September, from a few dozen per day to low hundreds by November, and many of the restrictions were restored and tightened, including a range of new ones. Eventually, a new state of emergency was reinstated on 9 November with increased rules and restrictions, while the daily cases reached close to one thousand by the end of November.
Background
On 12 January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed that a novel coronavirus was the cause of a respiratory illness in a cluster of people in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China, which was reported to the WHO on 31 December 2019.[3][4]
The case fatality ratio for COVID-19 has been much lower than SARS of 2003,[5][6] but the transmission has been significantly greater, with a significant total death toll.[7][5]
Timeline

January 2020
On 31 January 2020, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Latvia updated their travel advice, calling on travellers not to travel to Hubei and assess the need to travel to China in general. It also recommended everyone returning from China and experiencing symptoms of the coronavirus infection to seek medical advice and information about their travel and contacts.[8]
February 2020
On 3 February, a Latvian citizen living in Wuhan was evacuated with a French government plane and taken to Paris, where she was quarantined for 14 days before being allowed to depart to Riga.[9][10] On 11 February, Latvia donated protective clothing, masks, respirators and other epidemic prevention and control supplies to China.[11]
On 27 February, Estonia confirmed the first COVID-19 case, an Iranian citizen fell ill on board a bus from Riga to Tallinn and called himself an ambulance from Tallinn bus station. He had originally departed from Iran, and flown from Turkey to Riga, spending at least 2.5 hours in Riga and using public transport.[12][13] By 2 March, 114 people had been tested for COVID-19, all tests coming out negative.[14]
March 2020

_in_Latvia.jpg.webp)
On 2 March, the Latvian Ministry of Health confirmed the first positive case of COVID-19 in Latvia. The infected person was a woman who had flown from Milan to Riga through Munich.[15][16] The day after her condition had improved considerably and a repeated test came out negative she was discharged from the Latvian Center of Infectious Diseases with instructions to remain in self-insolation for 14 days.[17][18] The same day the Latvian government allocated an additional 2.6 million euros to the Ministry of Health for various anti-coronavirus measures.[19] Minister of Health Ilze Viņķele rated country's preparedness for coronavirus 8 out of 10.[20] Between 8 and 10 March, Latvian Centre for Disease Prevention and Control has carried out 274 tests and confirmed seven more cases for people who had recently returned from Northern Italy.[21][22][23][24][25]
On 12 March, Prime Minister Krišjānis Kariņš announced that the government had declared a state of emergency and that starting 13 March and until 14 April large public gatherings with over 200 people were banned and schools would conduct distance learning, along with other safety recommendations.[26]
On 13 March, the government announced a billion euro support for businesses affected by coronavirus provided as "financial instruments" (such as tax holidays or sick leave pay) via the state-owned ALTUM development bank.[27]
A list of emergency measures took effect on 14 March.[28] On 14 March, Kariņš announced that starting 17 March international travel would be halted, however, this would not affect private travel within the European Union, returning citizens or flow of goods. Furthermore, organised public events are banned and other gatherings may not exceed 50 participants.[29][30]
In preparation of a possible COVID-19 patient influx most of the hospitals began reducing or stopping most unrelated scheduled and outpatient treatment, with the exception of critical operations.[31] On March 25 the Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Infectious Disease Risk Analysis and Prevention Department director Jurijs Perevoščikovs reported the first COVID-19 patients with no clear epidemiological links to any other infection cases or trips abroad, pointing to the start of COVID-19 transmission within the Latvian society.[32][33][34]
On 29 March, the government adopted a number of stricter regulations. Foremost, everyone had to maintain a 2-metre distance and observe epidemiological safety measures in private and public events, as well as during public indoor and outdoor activities. Exceptions were given for 2 people, those living in the same household or parents and their minor children if they didn't live in the same household. New restrictions also prohibited all private arrangements (except funerals), public events, meetings, processions, pickets, indoor sports and religious activities. Trading and public catering venues were still allowed to hold more people while maintaining the 2-metre distance and observing safety measures. Various other measures were also adopted, such as prioritisation of medical item supply for national purposes or the government's right to request information from electronic communications operators on specific persons for epidemiological investigation.[35][36]
Mid 2020
On 7 April, The Cabinet of Ministers decided to extend the state of emergency by another month until 12 May with the same restrictions in place.[37]
On 7 May, The Cabinet of Ministers extended the state of emergency until 9 June, but eased some of the restrictions. Notably, starting 12 May, outdoor and up to 3-hour indoor gatherings of up to 25 people would be allowed while observing the two-metre distancing and providing disinfectants. A mouth and nose cover would be required in public transport. Travel and tourism would also be allowed within the three Baltic states.[38] By 22 May, travel from the EU was reopened.[39] On 22 May, the contact-tracing app "Apturi Covid" (lit. Stop Covid) was released that could be voluntarily downloaded and followed Google and Apple API standards.[40]
The state of emergency ended on 10 June, while restrictions remained in effect -- face cover in public transport, 2-metre distancing, as well as various restrictions on gatherings and public events.[41] On 16 June, the government met with various experts to discuss the possible second wave.[42] Dumpis warned that the pandemic was not over and that the situation had to be closely monitored.[43] State-paid test availability was extended from end of June until the end of summer.[44]
At the start of July, Dumpis remarked that the greatest risk of new cases came from travel and import of the virus from other countries.[45] The small outbreaks observed the following week were attributed to personal gatherings.[46] Due to the case increase, some restrictions were restored for catering facilities.[47] On 15 July, penalties for not observing the self-isolation rules were approved.[48] By the end of July, epidemiologist Jurijs Perevošcikovs, director of the SPKC's Department for Risk Analysis and Prevention of Infectious Diseases, said that stricter restrictions were not needed at the time.[49] On 20 July, testing was made mandatory for guest workers,[50] Perevošcikovs remarked that guest workers would not significantly increase the risk of infection.[51]
After a regular weekly meeting, Levits and Karinš stated that various contingency plans being made for the likely second wave of the virus.[52]
Dumpis argued that keeping the rates low in Latvia relied heavily upon measures and stricter rules in other countries.[53] By 25 September, arrival from all EU countries (except The Vatican) required self-isolation upon arrival in Latvia.[54]
October 2020
In October, the infection rates increased 11-fold from September.[55] Use of face covers became mandatory in public transport on 7 October,[56] and other public places on 14 October, along with other restrictions.[57] Dumpis urged to prioritize social distancing over masks.[58] Rural areas saw a reusable mask deficit.[59] By 19 October, Latvia saw a record number of confirmed cases,[60] and restrictions on gatherings and remote study were further tightened by 24 October.[61] On 29 October, fines were introduced for not wearing a face cover in enclosed public places.[62]
Testing also saw long queues in October due to lack of personnel with up to 11 days in rural areas.[63][64] Voluntary tests were suspended,[65] and new testing locations were planned.[66]
November 2020
At the start of November, the Cabinet of Ministers was divided on instating a new state of emergency,[67] while Levits supported it.[68] Dumpis explained that travel and mobility has been the cause of rapidly rising case numbers and that stricter restrictions were necessary because society had not fully followed even the light restrictions before.[69] The SPKC reported that 50% of new cases could not be tracked to a source,[70] and infected persons have many contact persons, which suggests that restrictions are not being observed.[69] A study showed that social activity had returned to a level before the pandemic linking the decrease in social distancing with the rise of new cases.[71][72] On 6 November, the government declared a second state of emergency to begin on 9 November. The restrictions on gatherings, events, sport activities, catering and education were further tightened.[73] Following local outbreaks, municipalities and regions were faced with additional tighter restrictions,[74] and the government announced that the list of affected regions would be reviewed every week based on the infection rate.[75] Overall, the infection rates doubled in November.[76] Dumpis had remarked that distancing restrictions were still likely not being observed as evident by the increasing case rates.[77]
By mid-November, the testing queue waiting time had significantly decreased, following an earlier change in application procedures.[78][79] As the case rate doubled in November, the testing only increased by 10%.[76]
December 2020
At the start of December the state of emergency was extended until 11 January and a broader range of restriction came into force.[80] The government aimed to have 10,000 tests per day, which primarily meant having the testing sites open on weekends and holiday.[81]
Following a further increase in daily cases and hospitals approaching capacity, a range of new restriction are expected to come into effect on 21 December.[82]
Vinkele stated that various restrictions are likely to remain throughout 2021, while vaccines would be state-funded and voluntary.[83] The first batch arrived on 26 December.[84]
On 29 December 2020, the government introduced a curfew for New Year's holidays and weekend from December 30 until January 4, and the weekend following Orthodox Christmas on January 8 and 9, during which individuals must stay at their place of residence between 22:00 and 5:00 except for emergencies and work-related matters.[85]
January 2021
Karins expressed mistrust in Minister of Health Vinkele due to the lack of a vaccination plan and requested her demission. Vinkele disagreed that the plan was not sufficient, but resigned.[86] On 7 January, Daniels Pavļuts was confirmed as the new Minister of Health.[87]
The earlier restrictions, including the weekend curfew, were extended until 25 January,[88] and later to February 7.[89] Pavļuts proposed that the restrictions could be lifted only if the cumulative number of new cases per capita would fall trifold.[90]
February 2021
At the start of February, Latvia had a death rate 32% higher than EU average and being the third most frequent cause of death in the country.[91]
The government approved a "Covid warning system" based on 14-day cumulative new case count. The system aims to inform the public about the current levels of risk of the epidemiological situation and set the restriction accordingly.[92] On 5 February, the State of Emergency was extended to until April 6 with mostly the same the restriction in place, although it is to be decided whether the weekend curfew will remain in effect.[93] Notably, additional travel restrictions were also instated for two weeks.[94] The State voluntary vaccination registration website also began operating on 5 February.[95]
Statistics
| Date | Confirmed | Deaths | Recoveries | Tested | Sources | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New | Total | New | Total | Total | New | Total | ||
| 2020-03-02 | 1 | 1 | 17 | 131 | [96][15] | |||
| 2020-03-03 | 1 | 1 | 21 | 152 | [97][98] | |||
| 2020-03-04 | 1 | 1 | 17 | 170 | [99][18] | |||
| 2020-03-05 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 186 | [100] | |||
| 2020-03-06 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 200 | [101][102] | |||
| 2020-03-07 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 22 | 222 | [103][21] | ||
| 2020-03-08 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 22 | 244 | [104][22] | ||
| 2020-03-09 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 30 | 274 | [105][24] | ||
| 2020-03-10 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 17 | 291 | [106][107] | ||
| 2020-03-11 | 6 | 16 | 1 | 41 | 332 | [108][109] | ||
| 2020-03-12 | 1 | 17 | 1 | 76 | 408 | [110][111] | ||
| 2020-03-13 | 9 | 26 | 1 | 258 | 666 | [112][113] | ||
| 2020-03-14 | 4 | 30 | 1 | 244 | 910 | [114][115] | ||
| 2020-03-15 | 4 | 34 | 1 | 237 | 1,147 | [116][117] | ||
| 2020-03-16 | 15 | 49 | 1 | 391 | 1,538 | [118][119] | ||
| 2020-03-17 | 22 | 71 | 1 | 604 | 2,144 | [120][121] | ||
| 2020-03-18 | 15 | 86 | 1 | 533 | 2,677 | [122][123] | ||
| 2020-03-19 | 25 | 111 | 1 | 528 | 3,205 | [124][125] | ||
| 2020-03-20 | 13 | 124 | 1 | 1,241 | 4,446 | [126][127] | ||
| 2020-03-21 | 15 | 139 | 1 | 681 | 5,127 | [128][129] | ||
| 2020-03-22 | 41 | 180 | 1 | 987 | 6,114 | [130][131] | ||
| 2020-03-23 | 17 | 197 | 1 | 692 | 6,806 | [132][133] | ||
| 2020-03-24 | 24 | 221 | 1 | 1,151 | 9,796 | [134][135] | ||
| 2020-03-25 | 23 | 244 | 1 | 817 | 10,613 | [136][137] | ||
| 2020-03-26 | 36 | 280 | 1 | 1,089 | 11,702 | [138][139] | ||
| 2020-03-27 | 25 | 305 | 1 | 1,046 | 12,748 | [140][141] | ||
| 2020-03-28 | 42 | 347 | 1 | 1,057 | 13,805 | [142][143] | ||
| 2020-03-29 | 29 | 376 | 1 | 502 | 14,307 | [144][145] | ||
| 2020-03-30 | 22 | 398 | 1 | 500 | 14,807 | [146][147] | ||
| 2020-03-31 | 48 | 446 | 1 | 1,003 | 15,810 | [148][149] | ||
| 2020-04-01 | 12 | 458 | 1 | 1,024 | 16,834 | [150][151] | ||
| 2020-04-02 | 35 | 493 | 1 | 1,364 | 18,198 | [152][153] | ||
| 2020-04-03 | 16 | 509 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1,182 | 19,380 | [154][155][156] |
| 2020-04-04 | 24 | 533 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1,300 | 20,680 | [157][158][159] |
| 2020-04-05 | 9 | 542 | 2 | 1 | 773 | 21,453 | [160][161] | |
| 2020-04-06 | 6 | 548 | 2 | 16 | 1,122 | 22,575 | [162][161][163] | |
| 2020-04-07 | 29 | 577 | 2 | 16 | 1,461 | 24,036 | [164][165] | |
| 2020-04-08 | 12 | 589 | 2 | 16 | 1,422 | 25,458 | [166][167] | |
| 2020-04-09 | 23 | 612 | 2 | 16 | 1,198 | 26,656 | [168][169] | |
| 2020-04-10 | 18 | 630 | 1 | 3 | 16 | 1,140 | 27,796 | [170][171][172][173] |
| 2020-04-11 | 21 | 651 | 2 | 5 | 16 | 418 | 28,214 | [174][175][176][177] |
| 2020-04-12 | 4 | 655 | 5 | 16 | 562 | 28,776 | [178][179][180] | |
| 2020-04-13 | 2 | 657 | 5 | 16 | 242 | 29,018 | [181] | |
| 2020-04-14 | 9 | 666 | 5 | 16 | 878 | 29,896 | [182][183] | |
| 2020-04-15 | 9 | 675 | 5 | 16 | 1,406 | 31,302 | [184][185] | |
| 2020-04-16 | 7 | 682 | 5 | 88 | 1,535 | 32,837 | [186][187][188][189] | |
| 2020-04-17 | 30 | 712 | 5 | 88 | 1,860 | 34,697 | [190][191] | |
| 2020-04-18 | 15 | 727 | 5 | 88 | 1,184 | 35,881 | [192][193] | |
| 2020-04-19 | 12 | 739 | 5 | 88 | 787 | 36,668 | [194] | |
| 2020-04-20 | 9 | 748 | 4 | 9 | 133 | 1,304 | 37,972 | [195] |
| 2020-04-21 | 13 | 761 | 2 | 11 | 133 | 1,364 | 39,336 | [196] |
| 2020-04-22 | 17 | 778 | 11 | 133 | 1,705 | 41,041 | [197] | |
| 2020-04-23 | 6 | 784 | 1 | 12 | 133 | 2,039 | 43,080 | [198] |
| 2020-04-24 | 20 | 804 | 12 | 267 | 2,663 | 45,743 | [199] | |
| 2020-04-25 | 8 | 812 | 12 | 267 | 1,874 | 47,617 | [200] | |
| 2020-04-26 | 6 | 818 | 1 | 13 | 267 | 1,564 | 49,235 | [201] |
| 2020-04-27 | 18 | 836 | 13 | 267 | 2,380 | 51,561 | [202] | |
| 2020-04-28 | 13 | 849 | 2 | 15 | 348 | 3,250 | 54,811 | [203] |
| 2020-04-29 | 9 | 858 | 15 | 348 | 3,075 | 57,886 | [204] | |
| 2020-04-30 | 12 | 870 | 1 | 16 | 348 | 3,234 | 61,120 | [205] |
| 2020-05-01 | 1 | 871 | 16 | 348 | 1,982 | 63,102 | [206] | |
| 2020-05-02 | 8 | 879 | 16 | 348 | 1,143 | 64,245 | [207] | |
| 2020-05-03 | 17 | 896 | 16 | 348 | 1,219 | 65,464 | [208] | |
| 2020-05-04 | 896 | 1 | 17 | 348 | 686 | 66,150 | [209] | |
| 2020-05-05 | 4 | 900 | 17 | 464 | 2,477 | 68,627 | [210] | |
| 2020-05-06 | 9 | 909 | 1 | 18 | 464 | 2,442 | 71,069 | [211] |
| 2020-05-07 | 19 | 928 | 18 | 464 | 1,947 | 73,016 | [212] | |
| 2020-05-08 | 2 | 930 | 18 | 464 | 2,555 | 75,571 | [213] | |
| 2020-05-09 | 9 | 939 | 18 | 464 | 1,021 | 76,592 | [214] | |
| 2020-05-10 | 7 | 946 | 18 | 464 | 555 | 77,147 | [215] | |
| 2020-05-11 | 4 | 950 | 18 | 627 | 1,900 | 79,047 | [216] | |
| 2020-05-12 | 1 | 951 | 1 | 19 | 627 | 2,199 | 81,246 | [217] |
| 2020-05-13 | 11 | 962 | 19 | 627 | 2,029 | 83,275 | [218] | |
| 2020-05-14 | 8 | 970 | 19 | 662 | 2,156 | 85,431 | [219][220] | |
| 2020-05-15 | 27 | 997 | 19 | 662 | 1,946 | 87,377 | [221] | |
| 2020-05-16 | 11 | 1,008 | 19 | 662 | 1,028 | 88,405 | [222] | |
| 2020-05-17 | 1 | 1,009 | 19 | 662 | 718 | 89,123 | [223] | |
| 2020-05-18 | 3 | 1,012 | 2 | 21 | 694 | 1,845 | 90,968 | [224] |
| 2020-05-19 | 4 | 1,016 | 21 | 694 | 1,783 | 92,751 | [225] | |
| 2020-05-20 | 9 | 1,025 | 1 | 22 | 694 | 1,870 | 94,621 | [226] |
| 2020-05-21 | 5 | 1,030 | 22 | 712 | 1,745 | 96,366 | [227] | |
Notes:
1.^ Number of new tested does not sum to total tested reported (1 missing).
2.^ Number of new tested does not sum to total tested reported (2 missing).
3.^ Number of people tested includes those who paid for the test themselves, not government sponsored from 25 March.
4.^ The original new confirmed case number of 2 was later revised to 4. | ||||||||
References
- "Aktualitātes par COVID-19 (News about COVID-19)" (in Latvian). Latvijas Slimību profilakses un kontroles centrs. Retrieved 16 January 2021.
- "Covid-19 izplatība Latvijā". covid19.gov.lv (in Latvian). 6 February 2021. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- Elsevier. "Novel Coronavirus Information Center". Elsevier Connect. Archived from the original on 30 January 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- Reynolds, Matt (4 March 2020). "What is coronavirus and how close is it to becoming a pandemic?". Wired UK. ISSN 1357-0978. Archived from the original on 5 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- "Crunching the numbers for coronavirus". Imperial News. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "High consequence infectious diseases (HCID); Guidance and information about high consequence infectious diseases and their management in England". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 3 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- "World Federation Of Societies of Anaesthesiologists – Coronavirus". www.wfsahq.org. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "Avoid travel to China's Hubei province, says Latvian Foreign Ministry". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 31 January 2020. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "France helps evacuate Latvian citizen from China's coronovirus city". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 3 February 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2020.
- "Latvian citizen evacuated to France from coronavirus-affected region in China". Baltic News Network. LETA. 3 February 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2020.
- "Latvia extends its assistance to fight against coronavirus". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Latvia. 11 February 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- "First Coronavirus case found in Estonia". ERR. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- "Coronavirus appears in Baltic states". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 27 February 2020. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- "All Latvian coronavirus tests negative so far". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 2 March 2020. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- "First case of COVID-19 coronavirus confirmed in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 3 March 2020. Retrieved 3 March 2020.
- "Coronavirus makes its way to Latvia". Baltic News Network. LETA. 3 February 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2020.
- "Latvia's first coronavirus patient to be discharged from hospital Tuesday". Baltic Times. 3 February 2020. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- "More coronavirus tests come up negative in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 4 March 2020. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- "Latvian government allocates additional funding to measures against Covid-19". Baltic News Network. LETA. 3 February 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2020.
- "Latvian Health Minister: We score 8 out of 10 for coronavirus preparedness". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 3 March 2020. Retrieved 3 March 2020.
- "Second case of coronavirus confirmed in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 8 March 2020. Retrieved 8 March 2020.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia rises to six". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 9 March 2020. Retrieved 9 March 2020.
- "Three more Covid-19 cases confirmed in Latvia, total number reaching 6". The Baltic Course. 9 March 2020. Retrieved 9 March 2020.
- "Number of COVID-19 coronavirus cases in Latvia rises to eight". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 10 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- "Two more confirmed coronavirus cases in Latvia; both returned from Italy". The Baltic Course. 10 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- "Latvian government announces widespread measures to contain coronavirus". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 12 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- "Latvian government announces billion-euro support for businesses hit by coronavirus". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 13 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- "COVID-19 emergency measures in English". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 13 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- "Latvia to close borders to passenger traffic on Tuesday 17 March". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 14 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- "Stay home. Latvian government shuts down all international passenger services". Baltic News Network. 14 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- "Hospitals cut services bracing for patient influx". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 17 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- "First untraceable Covid-19 cases in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- "Covid-19 transmission in society has begun in Latvia". Baltic News Network. LETA. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- "Community spread of Covid-19 has begun in Latvia". The Baltic Times. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- "Latvian government steps up restrictions with two-person, two-meter rule". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 30 March 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- State Chancellery (29 March 2020). "Stricter rules for physical distancing of persons are introduced to limit the spread of Covid-19". Cabinet of Ministers. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- "Latvia extends state of emergency by one month". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 7 April 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- "Latvia's state of emergency extended until June 9, some restrictions eased". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 7 May 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- "European Union citizens can travel to Latvia again". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Latvian 'Stop Covid' app first of its kind in the world". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Latvia's state of emergency comes to an end on June 10". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Possible second wave of COVID-19 to be discussed". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Infectologist: Nothing is really over". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "State-paid COVID-19 tests available until end of summer". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Epidemiologist Dumpis: main worry is importing new cases from abroad". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Coronavirus loves company, says epidemiologist". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Some COVID-19 restrictions restored in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Latvian government approves penalties for quarantine rule-breakers". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Stricter COVID-19 restrictions not needed in Latvia, epidemiologist says". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "COVID-19 testing made mandatory for guest workers in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Guest workers not a COVID-19 threat, says epidemiologist". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "President and PM say preparations being made for COVID-19 second wave". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Infectologist: Latvia's hope is restrictions in other countries". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "All European countries (except the Vatican) now require self-isolation upon arrival in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Kopš septembra vidus inficēšanās ar Covid-19 pieaugusi 11 reizes". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Face masks now required on all public transport in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 7 October 2020. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- "Face masks compulsory in public places in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 13 October 2020. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- "Infectologist: Distancing is a stronger weapon against COVID-19 than masks". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 14 October 2020. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- "Laukos daudzkārt lietojamās sejas maskas – deficīts". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Latvia saw record COVID-19 cases last week". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "New restrictions come into force in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- "Saeima okays fines for not using a mask in public places". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/covid-19-test-queues-grow-in-latvia.a376896/
- "Workers lack for COVID-19 testing in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/voluntary-sign-up-for-covid-19-tests-suspended-in-latvia.a379077/
- "Latvia to have more COVID-19 testing locations". Public Broadcasting of Latvia.
- https://www.lsm.lv/raksts/zinas/latvija/ministriem-nav-vienpratibas-par-arkartejas-situacijas-nepieciesamibu.a380542/
- https://www.lsm.lv/raksts/zinas/latvija/prezidents-atbalsta-arkartejas-situacijas-izsludinasanu-covid-19-ierobezosanai.a380480/
- https://www.lsm.lv/raksts/zinas/latvija/dumpis-ar-visiem-lidzekliem-jasamazina-covid-19-gadijumu-skaits.a380686/
- https://www.lsm.lv/raksts/zinas/latvija/spkc-50-inficetajiem-nevar-noteikt-inficesanos-avotu.a380828/
- https://www.lsm.lv/raksts/zinas/latvija/petijums-cilveki-parvietojas-aktivak-salidzinajuma-ar-arkartas-situaciju-pavasari.a381079/
- https://www.bvef.lu.lv/par-mums/zinas/zina/t/61977/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/society/second-state-of-emergency-declared-in-latvia.a380742/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/twelve-municipalities-to-have-additional-rules-imposed.a382909/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/regional-rules-to-be-determined-every-week-in-latvia.a383227/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/covid-19-infection-rates-doubled-in-november-in-latvia.a383879/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/infectologist-dumpis-many-rules-are-being-breached-in-latvia.a382651/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/queues-for-covid-19-tests-have-shrunk-in-latvia.a381282/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/new-covid-19-test-queue-system-comes-into-force-in-latvia.a379270/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/politics/politics/state-of-emergency-extended-until-january-11-in-latvia.a383783/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/latvia-aims-for-10000-covid-19-tests-a-day.a383933/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/politics/politics/new-covid-19-rules-will-take-effect-from-december-21.a385567/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/restrictions-likely-to-remain-throughout-2021-says-health-minister.a385063/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/first-coronavirus-vaccines-delivered-to-latvia.a386775/
- https://www.leta.lv/eng/home/important/A03FBBAA-9095-47D4-BF51-5F47761F0ED7/
- https://www.lsm.lv/raksts/zinas/latvija/premjers-izsaka-neuzticibu-veselibas-ministrei-vinkelei.a387740/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/politics/politics/pavluts-confirmed-as-new-health-minister.a388080/
- https://www.lsm.lv/raksts/zinas/latvija/lidz-25-janvarim-bus-lidzsinejie-covid-19-ierobezojumi-un-majsede-nedelas-nogale.a388042/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/society/latvias-covid-19-restrictions-to-be-extended-until-february-7.a389515/
- https://www.lsm.lv/raksts/zinas/latvija/vm-piedava-covid-19-ierobezojumus-vares-mikstinat-saslimstibai-samazinoties-tris-reizes.a389524/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/latvian-covid-19-death-rate-32-higher-than-eu-average.a391586/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/new-covid-warning-system-gets-the-green-light-from-government.a391670/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/politics/politics/state-of-emergency-extended-until-april-6-in-latvia.a391766/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/economy/transport/unnecessary-entry-to-latvia-banned-from-february-11-until-february-25.a391745/
- https://eng.lsm.lv/article/society/health/vaccination-signup-website-starts-working-friday.a391694/
- @SPKCentrs (3 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (4 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvia's first coronavirus patient to be discharged from hospital Tuesday". Baltic Times. 3 February 2020. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (5 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (6 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (7 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "No new cases of coronavirus registered in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. Retrieved 6 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (8 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (9 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (10 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (11 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Confirmed COVID-19 coronavirus cases into double figures in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 11 March 2020. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (12 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia climbs to 16". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 12 March 2020. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (13 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "One more case of coronavirus confirmed in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 13 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (14 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvia's coronavirus case count reaches 26". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 14 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (15 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Coronavirus case count reaches 30 in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 15 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (16 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvian coronavirus case count stands at 34". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 16 March 2020. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (17 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia rises to 49". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 17 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (18 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "71 cases of COVID-19 coronavirus confirmed in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 18 March 2020. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (19 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvia coronavirus case total reaches 86". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 19 March 2020. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- "Aktualitātes - Slimību profilakses un kontroles centrs". arkartassituacija.gov.lv. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia rises to 111". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 20 March 2020. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (21 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvia reaches total of 124 cases of COVID-19 coronavirus". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 21 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- "Aktualitātes - Slimību profilakses un kontroles centrs". web.archive.org. 22 March 2020. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia rises to 139". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 22 March 2020. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (23 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia rises to 180". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 23 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (24 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvia's number of confirmed coronavirus cases reaches 197". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 24 March 2020. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (25 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Coronavirus case total rises to 221 in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (26 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia increases to 244". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 26 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (27 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "COVID-19 case total for Latvia increases to 280". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 27 March 2020. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (28 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia increases to 305". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (29 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia increases to 347". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (30 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Coronavirus cases in Latvia now number 376". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 30 March 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (31 March 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia rises to 398". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 31 March 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (1 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvia coronavirus case total reaches 446". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 1 April 2020. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (2 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Coronavirus case total reaches 458 in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 2 April 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (3 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of COVID-19 cases in Latvia rises to 493". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 3 April 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (4 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia passes 500 mark". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 4 April 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- "Latvia records first coronavirus-linked death". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 3 April 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (5 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Coronavirus cases in Latvia now number 533". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 5 April 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- "Second COVID-19 related death confirmed in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 5 April 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (6 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "COVID-19 case total for Latvia increases to 542". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 6 April 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (7 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Recovery from COVID-19 confirmed for 16 people in Latvia". Baltic News Network. LETA. 7 April 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (8 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of COVID-19 cases in Latvia reaches 577". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 8 April 2020. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (9 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Coronavirus case count reaches 589 in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 9 April 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (10 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Coronavirus case total reaches 612 in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 10 April 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (11 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "COVID-19 case total for Latvia increases to 630". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (11 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 death statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvijā miris Covid-19 slimnieks, kuram bija smaga slimības gaita" [First Covid-19 patient who was in severe condition dies in Latvia] (in Latvian). Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (12 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvia coronavirus case total reaches 651". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 12 April 2020. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (12 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 death statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvijā miruši vēl divi Covid-19 slimnieki" [Two more Covid-19 patients die in Latvia] (in Latvian). Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 12 April 2020. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (13 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (13 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "More cases takes Latvia's coronavirus case total to 655". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 13 April 2020. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (14 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (15 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia rises to 666". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 15 April 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (16 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Latvia's coronavirus case count reaches 675". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 16 April 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (17 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "COVID-19 case total for Latvia increases to 682". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 17 April 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (17 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 recovery statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Covid-19 saslimšana Latvijā fiksēta septiņiem cilvēkiem; atveseļojušies 88" [Covid-19 in Latvia confirmed for seven people; 88 recovered] (in Latvian). Delfi. 17 April 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (18 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Number of coronavirus cases in Latvia passes 700". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 18 April 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (19 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "Coronavirus case total rises to 727 in Latvia". Public Broadcasting of Latvia. 19 April 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- @SPKCentrs (20 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (21 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (22 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (23 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (24 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (25 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (26 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (27 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (28 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (29 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (30 April 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (1 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (2 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (3 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (4 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (5 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (6 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (7 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (8 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (9 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (10 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (11 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (12 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (13 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (14 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (15 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (15 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (16 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (17 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (18 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (19 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (20 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (21 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- @SPKCentrs (22 May 2020). "SPKC.gov.lv COVID-19 testing statistics" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
External links
- Worldwide Coronavirus Map, confirmed Cases – Map the route paths of coronavirus confirmed cases.
- Novel Coronavirus COVID-19 advice for the public. Ministry of Health of Latvia
- COVID-19. Regarding the Declation of Emergency Situation. Latvian Centre for Disease Prevention and Control