Apple Maps
Apple Maps (or simply Maps) is a web mapping service developed by Apple Inc. It is the default map system of iOS, iPadOS, macOS, and watchOS. It provides directions and estimated times of arrival for automobile, pedestrian, and public transportation navigation. Apple Maps also features Flyover mode, a feature that enables a user to explore certain densely populated urban centers and other places of interest in a 3D landscape composed of models of buildings and structures.
 .svg.png.webp) | |||
| Developer(s) | Apple | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial release | September 19, 2012 | ||
| Stable release(s) | |||
| |||
| Operating system | iOS 6 and later, iPadOS, watchOS, and macOS | ||
| Type | Web mapping | ||
| Website | www | ||
On September 19, 2012, Apple released its mapping service in iOS, replacing Google Maps as the default mapping service for Apple operating systems.[2] In the initial launch, it received large amounts of criticism from users and newspapers for incorrect directions, a lack of support for public transportation users and various other bugs and errors. Since its introduction, further software development has addressed many of those criticisms.[3]
History

Initial release
On June 11, 2012, during the Apple Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC), Apple announced the initial release of Apple Maps and revealed that the application would replace Google Maps as the default web mapping service in iOS 6 and beyond. Apple also announced that the application would include turn-by-turn navigation, 3D maps, Flyovers, and the virtual assistant Siri. Furthermore, Apple stated that iPhone users would be able to navigate Apple Maps while in the locked screen.[4][5] The mapping service was released on September 19, 2012.[6] Following the launch, Apple Maps was heavily criticized, which resulted in a public apology by Apple CEO Tim Cook in late September and the departure of two key employees of Apple (see also §Early inaccuracy).[6][7]
Before Apple Maps launched as the default mapping application in iOS, Google Maps held this position since the first generation iPhone release in 2007. In late 2009, tensions between Google and Apple started to grow when the Android version of Google Maps featured turn-by-turn navigation, a feature which the iOS version lacked. At the time, Apple argued that Google collected too much user data.[8] When Apple made iOS 6 available, Google Maps could only be accessed by iOS 6 users via the web.[9] Although Google did not immediately launch a mapping application of its own, shortly after the announcement of Apple Maps, Google did add an equivalent of Apple Maps' Flyover feature to its virtual globe application Google Earth.[10] Three months later, in December 2012, Google Maps was released in the App Store. This version of Google Maps, unlike the previous version, featured turn-by-turn navigation. Shortly after it was launched, Google Maps was the most popular free application in the App Store.[11]
Speculation around Apple creating a mapping service of its own arose in 2009 after computer magazine Computerworld reported that Apple had acquired the company Placebase, an online mapping service, in July of that year.[12] Since then, the CEO of Placebase became a part of Apple's "Geo Team".[13][14] In the following two years, Apple acquired two more mapping related companies who specialized in 3D maps: Poly9 in 2010 and C3 Technologies in 2011.[15][16] C3 Technologies' imagery was later used for the Flyovers feature in Apple Maps.[17] Earlier in 2011, Apple indicated its plan for a mapping service when it stated on its website that it was collecting location data to create "an improved traffic service in the next couple of years" for iPhone users.[18] In September 2012, when Apple Maps was released, a source connected to both Google and Apple Maps claimed to technology website TechCrunch that Apple was recruiting Google employees that worked on Google Maps.[19]
2012–2015
In the first year after its release, Apple Maps received a number of improvements which solved various errors in the application.[20] Other changes included adding more satellite imagery and making the navigation available in more cities. In 2013, Apple also acquired a few companies to improve Apple Maps, namely HopStop, Embark, WifiSlam, and Locationary, as well as the team and the technology of the company BroadMap. HopStop and Embark both specialized in mapping public transportation, WifiSlam specialized in interior maps, Locationary provided accurate company data for mapping services, and BroadMap managed, sorted, and analyzed map data.[21][22][23]
During WWDC in June 2013, Apple announced the new version of Apple Maps in iOS 7. This new version had a new look and icon.[24] A number of new functions were also implemented, including full-screen mode, night mode, real-time traffic information, navigation for pedestrians, and the Frequent Locations feature. The latter feature, which can be switched on and off, was introduced to record the most frequently visited destinations by users in order to improve Apple Maps. In addition, new satellite imagery was added once again.[21][24] On September 18, 2013, Apple released iOS 7.[25] At that time, the new iPhone 5S included a new motion coprocessor, the M7, which can identify whether a user is walking or driving in order to adjust the navigation mode.[21]
During that same conference, Apple announced that a desktop version of the application would be made available for OS X Mavericks.[26] On October 22, 2013, Apple released OS X Mavericks and the desktop version of Apple Maps. The desktop version was similar to that in iOS 7, but it connected with the Contacts and Calendar applications. Additionally, the desktop version enabled users to send locations and directions to other devices with iOS.[27] In June of the following year, Apple acquired the company Spotsetter, a social search engine that gave personalized recommendations for places to visit. Since the acquisition, most of its employees now work at Apple.[28]
On September 17, 2014, the successor of iOS 7, iOS 8, became available. Later that year, on October, 16, Apple released OS X Yosemite.[29] Neither update brought any major modifications to Apple Maps. However, the feature "City Tours" was introduced to both iOS and OS X. This function made it possible for the user to be guided through locations with Flyovers.[30] Also, Apple Maps results were shown in the search feature Spotlight in OS X Yosemite.[31] Later in 2014, Apple news website 9to5Mac reported that in the previous months a number of Apple Maps employees, including a key employee, had left the company to work for Uber.[32] In the next year, Apple Maps was added to the operating system of the new Apple Watch, which was released on April 24, 2015.[33] The smartwatch version of Apple Maps features turn-by-turn navigation. The app indicates navigation instructions by taps on the user's wrist.[34]
2015–2018
During WWDC on June 8, 2015, Craig Federighi, Apple's senior vice president of Software Engineering, announced that the new version of Apple Maps in iOS 9 would have information about public transportation in a number of global cities.[35] The function also became available for OS X El Capitan and watchOS 2.[36][37] In addition, Apple added the function "Nearby", which shows nearby points of interest in several categories. With the update, the application chooses a detour in case of a traffic delay. The three new versions of the operating systems became available in September 2015. In addition to these new releases, Apple acquired a few companies in 2015 in order to improve the mapping application even further. In the spring, Apple also acquired Coherent Navigation, that provides precise location data through High Integrity GPS, and the startup company Mapsense later that year.[38][39] The latter had developed software to organize large amounts of location data.[40]
In 2016, Apple Maps opened a new development center and it was updated for watchOS and iOS. The application was improved when watchOS 2.2 came out in March 2016. Apple Maps was renewed in the new version of the operating system and received a number of new features, including "Nearby" which had previously been exclusive to iOS.[41] Four months later, Apple CEO Tim Cook inaugurated a new office in partnership with IT company RMSI, Noida, at the WaveRock campus in the Indian city Hyderabad. The development center focuses on the development of Apple Maps and employs 4,000 people.[42][43] According to ZDNet, the 250,000 square feet (23,000 square metres) office cost US$25 million.[44] In September, iOS 10 was released. The update of the Apple's mobile operating system was accompanied by a new design of Apple Maps. Moreover, the application was opened up to developers and gained a few features: it makes suggestions for places to go based on earlier usage of the app, it can remember the location where the user parked their vehicle, it allows a user to filter search suggestions, and the turn-by-turn navigation was improved.[45][46] The navigation automatically zooms in and out, shows traffic ahead, and allows users to search for points of interests along the route. These features are available for CarPlay as well.[45]
2018–present

In early 2018, Apple announced Maps can help users find bike-sharing stations in over 175 cities across 36 countries, for example: San Francisco (GoBike), New York (Citi Bike), Montreal (BIXI), London (Santander), Paris (Velib) and Brisbane (CityCycle).[47][48]
In summer 2018, Maps leader Eddy Cue announced an ambitious roll-out of Apple Maps, rebuilt "from the ground up" using map data Apple has been quietly gathering for the past four years. This new maps detail was originally only available in the San Francisco Bay area until it would be expanded to the entire United States and other countries.[49][50] The new maps data features outlines of buildings in all areas the new data is available (not just major cities as it was previously), more minor roads shown on the road map (for example, roads within parking lots), walking paths, and traffic lights and stop signs during navigation. One user noted "a staggering amount of vegetation detail" that displays strips of grass and vegetation between roads, outlines of holes on golf courses, baseball/football fields within parks, etc.
In November 2018, Apple revealed on its website that it will be sending its backpack-wearing team to different locations, including Los Angeles, San Francisco and Santa Clara County in an attempt to improve Apple Maps’ walking directions along footpaths and walkways. The company will also deploy its mapping cars throughout the US and the UK to gather its own data and add details to the maps.[51][52]
By the end of January 2020, Apple completed the rollout of their new maps detail in the United States, the District of Columbia, and most US territories.[53] Upon completion, Apple stated that Europe would receive updated maps later this year.[54] During WWDC on June 22, 2020, Apple announced that the UK, Ireland, and Canada would be the first places outside of the US to receive the updated maps.[55]
In September 2020, cycling directions were added to Maps alongside the public rollout of iOS 14, iPadOS 14, and watchOS 7. As of launch, cycling directions are only available in the cities of New York, Los Angeles, San Francisco, Shanghai, and Beijing, but Apple intends to add more over time.[56] Later the same month, Apple updated the United Kingdom and Ireland to include their new maps detail, Look Around, and cycling directions.[57] On October 19, 2020, Apple began testing their new maps for Canada and rolled the final version in early December.[58]
Features
Apple Maps started using vector graphics before competitor Google Maps, which allowed the application to use less data than Google Maps.[59] The map has four available layers: regular map, satellite view, hybrid view (a combination of regular and satellite view), and public transit view.[24] The main provider of map data is TomTom, but data is also supplied by Automotive Navigation Data, Getchee, Hexagon AB, IGN, Increment P, Intermap Technologies, LeadDog, MDA Information Systems, OpenStreetMap, and Waze.[60] Apple renewed their agreement with TomTom in 2015.[61] TomTom is the parent company of Tele Atlas, which is also used by Apple Maps' competitor, Google Maps.[21] The satellite imagery comes from DigitalGlobe.[60] iPhones located in China use data from AutoNavi instead.
Apple Maps can be used to plan routes. The navigation service features turn-by-turn navigation with spoken instructions for vehicles, pedestrians, and public transportation.[62] According to Apple, the navigation function is available in 56 countries worldwide.[63] Apple Maps can also be used to see real-time traffic information. In addition, Apple's virtual assistant, Siri, is integrated into Apple Maps. The map displays points of interest provided by approximately twenty companies, including Booking.com, Foursquare, TripAdvisor, and Yelp. The data from Foursquare was added in late 2015.[60][64] Users can drop pins on the map to save places for later retrieval. The satellite view features Flyovers, three-dimensional satellite views, in designated locations.[65]
Flyover and 3D maps
With Flyover, certain locations — mainly the big cities and landmarks — can be seen from a bird's-eye perspective.[24] The three-dimensional views are photo-realistic and users can change the perspective.[62] Flyover has been available since the first release of Apple Maps. A number of cities with Flyovers also have "City Tours". With this feature, the user is guided in the Flyover view along landmarks in that location. "City Tours" was added to Apple Maps in iOS 8 (released on September 17, 2014) and in OS X Yosemite (released on October 16, 2014).[29][30][31] In addition to Flyovers, around fifty cities also feature 3D maps. This feature enables the user to see three-dimensional models of structures in the map view. These models, which are not photo-realistic, can also be seen when using the turn-by-turn navigation.[24][62]
Flyovers are available at the following locations:[63]
Nearby
The feature "Nearby" is exclusive to iOS 9 and watchOS 2.2. It shows icons of different categories like "food" and "transportation" in the search menu.[66] After clicking each icon, nearby points of interest in that category are shown with their names, distances, and reviews on Yelp. Additionally, pins appear at the locations of these places on the map. The turn-by-turn navigation can be activated with Nearby as well.[67][68] When iOS 9 was launched on September 16, 2015, the function was only available in the United States and China, but had expanded to include Australia, Canada, Germany, and France by the end of October 2015.[69][70] In 2016, Nearby was added to Austria, Denmark, Finland, Japan, the Netherlands, Switzerland and the United Kingdom.[63] On June 12, 2020, Apple added support for Nearby to 31 new countries (Argentina, Belgium, Brazil, Croatia, Czech Republic, El Salvador, Greece, Hong Kong, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Ireland, Italy, Macau, Mexico, Montserrat, New Zealand, Norway, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Republic of Korea, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Africa, Spain, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey and Vietnam).
Transit
The function "Transit" shows the public transport networks on the map in a number of cities and their surroundings. The functionality was added to iOS 9 (released on September 16, 2015), OS X El Capitan (released on September 30), and watchOS 2 (released on September 21).[36][37][69] Apple Maps displays the networks of buses, subways, trains, and ferries in these cities.[35] Additionally, the mapping service includes public transit schedules and shows the locations of the entries and exits of the subway and train stations.[71] "Transit" is available in the following locations and metropolitan areas:
| Country | Locations |
|---|---|
| Full coverage, Real-Time Transit in Sydney | |
| Vienna, Salzburg, ÖBB | |
| Full coverage | |
| States of Rio de Janeiro & São Paulo | |
| Full coverage, Real-Time Transit | |
| Full coverage, Real-Time Transit in Beijing, Guangzhou and Shenzhen (only available when viewed inside China) | |
| Prague | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage in the states of Baden-Württemberg, Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Niedersachsen, NRW, Saxony, Thuringia. Partial coverage in the states of Bavaria, Hesse, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland, Saxony-Anhalt, Schleswig-Holstein | |
| Full coverage | |
| Budapest, MÁV | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Mexico City | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage, Real-Time Transit | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Lisbon | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage, Real-Time Transit | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage | |
| Full coverage, Real-Time Transit in England and Scotland | |
| Full coverage, Real-Time Transit in the states of Alaska, California, Colorado, Florida, Illinois, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Michigan, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Wisconsin, and the cities of Austin, Burlington, Dallas, Houston, Las Vegas, Miami, San Antonio, St. Louis, and Washington DC. |
Support for all the routes of Amtrak in the United States has been added as of October 2, 2016. The routes of NSW TrainLink in New South Wales were added in April 2016. The routes of V/Line (Regional Rail) in Victoria (Australia) were added on October 9, 2016. Transit directions were expanded across the United Kingdom, excluding Northern Ireland, on December 19, 2016. Ireland (Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland) was added on October 16, 2017.[73][74][75]
Apple's transit directions are not available in third party apps.
Indoor airport and shopping mall maps
iOS 11 introduced indoor maps for airports and shopping malls.
Traffic information
Apple Maps shows real-time traffic information on the map. In addition, the turn-by-turn navigation takes delays into account when calculating the estimated time of arrival and will occasionally choose a detour in case of traffic.[62] Apple introduced this function in iOS 7 (released on September 18, 2013) and it is available in 75 countries as of June 2019.[24][25][63] In the beginning of 2015, Consumentenbond, a Dutch organization promoting consumer rights, researched the traffic information of various navigation applications and concluded that Apple Maps gave the most false responses of all seven applications that were tested.[77]
Live traffic information is available at the following locations:[63]
 Andorra
Andorra Argentina
Argentina.svg.png.webp) Australia
Australia Austria
Austria Bahrain
Bahrain.svg.png.webp) Belgium
Belgium Brazil
Brazil Brunei
Brunei Bulgaria
Bulgaria.svg.png.webp) Canada
Canada Chile
Chile China
China Colombia
Colombia Croatia
Croatia Czech Republic
Czech Republic Denmark
Denmark Egypt
Egypt Estonia
Estonia Finland
Finland France
France Germany
Germany Gibraltar
Gibraltar Greece
Greece Hong Kong
Hong Kong Hungary
Hungary Iceland
Iceland India
India Ireland
Ireland Israel
Israel Italy
Italy Japan
Japan Kenya
Kenya Kuwait
Kuwait Latvia
Latvia Lesotho
Lesotho Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein Lithuania
Lithuania Luxembourg
Luxembourg Macau
Macau Malaysia
Malaysia Malta
Malta Mexico
Mexico Monaco
Monaco Morocco
Morocco Mozambique
Mozambique Netherlands
Netherlands New Zealand
New Zealand Nigeria
Nigeria Norway
Norway Oman
Oman Peru
Peru Philippines
Philippines Poland
Poland Portugal
Portugal Qatar
Qatar Romania
Romania Russia
Russia San Marino
San Marino Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Singapore
Singapore Slovakia
Slovakia Slovenia
Slovenia South Africa
South Africa Spain
Spain Sweden
Sweden Switzerland
Switzerland Taiwan
Taiwan Thailand
Thailand Turkey
Turkey United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates United Kingdom
United Kingdom Ukraine
Ukraine Uruguay
Uruguay United States
United States Vatican City
Vatican City Vietnam
Vietnam
Look Around
Look Around allows the user to view 360° street-level imagery, with smooth transitions as the scene is navigated. Look Around was introduced with iOS 13 at Apple Worldwide Developers Conference in June 2019. It was publicly released as part of iOS 13, with additional areas to be covered as time goes on.[78]
Apple Maps Connect
In October 2014, Apple introduced a service dubbed Apple Maps Connect.[79] It allows small business owners to claim their business listing and edit business information, such as location and open hours. After the user logs in with their Apple ID, they are given a prompt to claim and link an Apple Maps listing to their account. The user can search through Apple's database to either locate their listing or add a missing listing to Apple's database.[80]
Market share
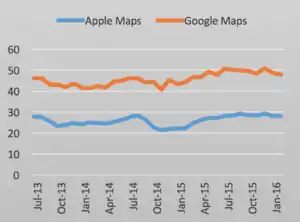
ComScore investigated the market shares of different web mapping services in the United States using polls. Prior to the launch of Apple Maps in September 2012, there were 103.6 million Americans with iOS or Android, 81 million of which used Google Maps. According to comScore, the latter figure had dropped to 58.7 million in September 2013, a year after the release of Apple Maps. At the same time, there were 35 million American Apple Maps users and a total of 136.7 million people with iOS or Android in the United States. Out of the 60.1 million iPhone users, 8.3 million used Google Maps. However, some of those iPhone users were not able to use Apple Maps, since their devices were not updated to iOS 6.[8] In addition, research by comScore conducted between July 2013 and February 2016 revealed that between 20% and 30% of all American smartphone users used Apple Maps — this includes users with operating systems for which Apple Maps was not compatible. During the same period, it was concluded that between 40% and 51% of American smartphone owners used the application Google Maps.[81]
Furthermore, comScore studied the market share of Apple Maps on iPhones in the United Kingdom. In September 2013, one year after its launch, more than 6.2 million of the total 10.35 million British iPhone owners used Apple Maps. Google Maps had the second largest market share on British iPhones with over 1.8 million British iPhone users.[82]
In the second half of 2013, British Internet service provider EE Limited concluded that Apple Maps had a market share in the UK of 64% of 4G network users and 57% of 3G network users.[83] The research involved comparing the data of the internet provider and the results of an investigation by Taylor Nelson Sofres among 1,000 users of the 4G network. However, EE Limited did not indicate how many of its users had an iPhone.[84] According to subsequent research by EE Limited, in the first half of 2014, the market share of Apple Maps increased among iPhone users: 70% of the 4G network and 76% of the 3G network.[85] At the turn of the year, the same values amounted to 73% and 82% respectively.[86]
Early inaccuracy
Apple Maps received considerable criticism after its launch on September 19, 2012, due to wrong and inaccurate information about places and points of interests. Many of these errors are now fixed.[6][21][87]
Some places were misspelled, were displayed with the wrong name, or were missing entirely.[6][9] Examples of those mistakes included the Ukrainian capital Kyiv, which was incorrectly spelled as "Kylv", the Welsh town Pontypridd, whose label was shown 6 miles (10 kilometres) northeast of its actual location, and the English town Stratford-upon-Avon, which was missing altogether in Apple Maps. Also, when users looked up "London" they were directed to the Canadian city London, Ontario, instead of its namesake, the capital of the United Kingdom.[9] Many complained about outdated or inaccurate data about companies and places of interest. For example, in the United Kingdom, chains that no longer exist were still on the maps and large stores were accidentally mapped in backyards.[21] Furthermore, in the United States, the label of the Willis Tower was displayed in the wrong location.[9] Apple Maps was sometimes inadequate to find companies or other points of interest at all.[21] For instance, the London train and underground station Paddington and Tokyo Station were missing, and the Helsinki Central railway station was shown as a park.[8][9] Also, parks were occasionally displayed as airports.[6]
On several occasions, government authorities and politicians warned citizens of errors with Apple Maps. In early December 2012, the police department of the Australian city Mildura alerted people who planned to reach the city using Apple Maps, because Mildura was shown in the middle of Murray-Sunset National Park, 40 miles (64 kilometres) from its actual location. The police department stated that the error was potentially life-threatening, as national park temperatures could rise to 114 °F (46 °C) and those traveling would be without water supplies. The police rescued at least four people, one of whom was stranded for 24 hours. After that, the police department tried to contact Apple to solve the problem. Apple fixed the error in December 2012.[88][89][90] Alan Shatter, the Minister for Justice and Equality and Minister of Defense of Ireland at the time, issued a warning because of a mistake in Apple Maps: a non-existent airport was shown near the Irish capital Dublin. This location was in reality a public farm called "Airfield". Shatter wrote in his statement that the mistake was dangerous, because a pilot could try to make an emergency landing there.[91]
If the phone is located within mainland China, it can result in all geo-tagged photos taken in Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Arunachal Pradesh, or disputed South China Sea islands being applied with incorrect location, or displaying the area as part of China (such as "Des Voeux Road Central" erroneously displayed as "Defudaozhong", as in pinyin, or photos taken in Taipei or Itanagar will display the location respectively as "Taiwan Province, China"[92] or "Tibet Autonomous Region, China").[93] As of 2020, this issue still persists.
Apple's response
As a result of the criticism, Tim Cook, CEO of Apple Inc., published a letter of apology on Apple's website on September 28, 2012, in which he apologized for the "frustrations" experienced by users. He said that Apple fell short and that the company was making every effort to improve the mapping service. Cook also suggested that dissatisfied users could use rival mapping applications like Bing Maps, MapQuest, Waze, Google Maps, and Nokia Maps.[94] Steve Jobs, former CEO of Apple Inc., had used this way of apologizing in the past.[6] A week before the release of the letter of apology, just after the launch of Apple Maps, spokesperson Trudy Miller had stated to technology news website All Things Digital that Apple Maps was a major initiative and that they "were just getting started with it." Miller also said the application would improve as more people used it.[95][96]
In the aftermath of the criticism, two key employees left the company due to the problems associated with Apple Maps. The departure of Scott Forstall, senior vice president of iOS, was announced in October 2012.[7] Sources told technology news website The Verge that he had been fired for refusing to sign Tim Cook's letter of apology.[97] According to business magazine Bloomberg Businessweek, Richard Williamson, the person responsible for the mapping team at Apple, left the following month. He was succeeded by Eddy Cue.[7]
In June 2016, Eddy Cue said in an interview with Fast Company that Apple "had completely underestimated the product, the complexity of it." He also said the problems with Apple Maps led to "significant changes to all of our development processes." After the launch of Maps, Apple started offering public betas of new versions of iOS and OS X. Furthermore, Cue commented that before Maps was launched Apple's executive team long discussed if Apple should have its own mapping service.[98] One month later, Tim Cook looked back to the launch of Apple Maps in an interview with The Washington Post and said "Maps was a mistake." He added that the company admitted its mistake and that Maps is something the company is now proud of because of the improvements.[99]
TomTom's response
As the primary provider of map data, TomTom has received criticism as well. Cees van Dok, TomTom's head of user experience design, in April 2013 told technology news website TechRadar that Apple was the problem. According to him, Apple was trying to combine too many sources of data to create Apple Maps.[100]
Modern reception
Despite fixing preliminary issues, Apple Maps has received mixed reviews, with some critics complimenting its "Flyover" feature and appearance of the street map,[101] while others are criticizing its lack of features similar to those in Google Maps. ZDNet said "[Apple Maps] had its share of problems, but Apple Maps is back with a vengeance. Powered by some jaw-dropping 3D graphics and enjoying an aggressive multi-platform strategy, Apple is finally set to redefine our geospatial expectations – and take Google down a few notches."[101] An editor of The Street wrote "But, today, and presumably after the iOS 7 update, Apple Maps has come into its own. Despite the lingering absence of transit directions (at last check, Apple still suggests Google Maps and other "routing" apps), I now prefer to Apple over Google."[102] Macworld wrote "Apple Maps has vastly improved since it was first launched and now we conclude the turn-by-turn navigation is a lot better than Google's offering. While there are areas that both Google and Apple can improve on, we’re certain that using Apple Maps won’t direct you to drive into the Thames and that most of the initial issues have been fixed."[103] Thrillist wrote an article about "Things Apple Maps Does Better Than Google Maps," praising its ability to let the user "send directions instantly from your computer to your phone," "see turn-by-turn directions from the lock screen," "get more specific recommendations for nearby attractions," "know which subway car to get on and which exit to use," "see true-to-life details," and "get seamless directions from Siri."[104]
Taiwan (Republic of China) was classified as a province of the People's Republic of China in the application in 2013; searches for "Taiwan" were changed automatically to "China Taiwan province" in Simplified Chinese, prompting the Ministry of Foreign Affairs to demand a correction from Apple.[105] [106]
References
- "Maps". App Store Preview. Archived from the original on October 2, 2019. Retrieved October 2, 2019.
- Oreskovic, Alex (2013-04-29). "Google Now comes to iPhone, challenging Siri". Reuters.
- Barbee, Brie (July 10, 2018). "Apple Maps vs. Google Maps: Which is better at helping you find your way?". Digital Trends. Retrieved October 2, 2018.
- Vroegop, B. (June 11, 2012). "WWDC 2012: Apple kondigt eigen kaartendienst Maps met volledige navigatie aan" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Zwaag, G. van der (June 11, 2012). "WWDC 2012: iOS 6 aangekondigd, iPad 1 krijgt geen update #WWDC" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Arthur, C. (September 28, 2012). "Apple Maps: Tim Cook says he is 'extremely sorry'". The Guardian. Retrieved October 22, 2015.
- Satariano, A. (November 28, 2012). "Apple's Cue Seeks Overhaul of Maps Amid Duel With Google". Bloomberg Businessweek. Retrieved October 24, 2015.
- Arthur, C. (November 11, 2013). "Apple maps: how Google lost when everyone thought it had won". The Guardian. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- Garside, J. (September 20, 2012). "Apple Maps service loses train stations, shrinks tower and creates new airport". The Guardian. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- Zwaag, G. van der (July 27, 2012). "Google Earth of Apple Kaarten: wie heeft de beste 3D-beelden?" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Whitney, L. (December 13, 2012). "Google Maps already No. 1 among free iPhone apps". CNET. Retrieved December 1, 2015.
- Weintraub, Seth (October 2009). "Apple purchased Placebase in July to replace Google Maps?". Computerworld. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- Weintraub, S. (October 1, 2009). "Apple purchased Placebase in July to replace Google Maps?". Computerworld. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Zwaag, G. van der (October 1, 2009). "Apple neemt kaartleverancier Placebase over en richt Geo Team op" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Bertolucci, J. (2010-07-14). "Why Apple Bought Poly9: And What Is Poly9?". PCWorld. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Gurman, M. (October 29, 2011). "Apple acquired mind-blowing 3D mapping company C3 Technologies, looking to take iOS Maps to the next level". 9to5Mac. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Gurman, M. (July 19, 2012). "Apple's iOS 6 3D Maps are straight from C3 Technologies, some interesting notes". 9to5Mac. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- "Apple Q&A on Location Data". Apple Press Info. April 27, 2011. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Etherington, D. (September 23, 2012). "Source: Apple Aggressively Recruiting Ex-Google Maps Staff To Build Out iOS Maps". TechCrunch. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Zwaag, G. van der (October 6, 2012). "Apple verbetert eigen Maps: meer 3D-gebouwen, minder fouten" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved December 1, 2015.
- Marshall, G. (September 21, 2013). "Apple Maps: one year on". TechRadar. Retrieved October 22, 2015.
- Gurman, M. (December 23, 2013). "Apple acquired mapping firm BroadMap's talent, location-infused Evernote competitor Catch". 9to5Mac. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Fried, I. (December 23, 2013). "Apple Did Indeed Acquire BroadMap and Catch Earlier This Year". All Things Digital. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- "Dossier: Apple Maps" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- Haslam, K. (September 18, 2013). "iOS 7 available to download now. How to download iOS 7 and update your iPhone and iPad". Macworld. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- "Apple Maps coming to OS X Mavericks". The Verge. June 10, 2013. Retrieved October 24, 2015.
- Goodwin, A. (October 22, 2013). "Walk with us through OS X Mavericks' new Maps app". CNET. Retrieved October 24, 2015.
- Perez, S. (June 6, 2014). "Apple Acquires Spotsetter, A Social Search Engine For Places". TechCrunch. Retrieved December 6, 2015.
- "Apple Announces iOS 8 Available September 17". Apple Press Info. September 9, 2014. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- Slivka, E. (September 7, 2014). "Apple Filling Out Flyover City Tours Ahead of iOS 8 and OS X Yosemite Launches". MacRumors. Retrieved December 6, 2015.
- "OS X Yosemite Available Today as a Free Upgrade". Apple Press Info. October 16, 2014. Retrieved October 24, 2015.
- Gurman, M. (November 25, 2014). "Top Apple Maps app manager for Watch, iOS & OS X exits for Uber". 9to5Mac. Retrieved December 7, 2015.
- "Apple Watch Available in Nine Countries on April 24". Apple Press Info. March 9, 2015. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Allsopp, A. (April 28, 2015). "How to use Maps to navigate from your Apple Watch". Macworld. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- Pino, N. (June 8, 2015). "Apple Maps finally adds public transit info". TechRadar. Retrieved October 22, 2015.
- Haslam K. (October 23, 2015). "Mac OS X 10.11 El Capitan updates, issues and fixes: 10.11.1 update released, addresses Mail, Office 2016 and more". Macworld. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- "Dossier: watchOS" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- Fingas, J. (May 17, 2015). "Apple bought a company focused on super-accurate GPS". Engadget. Retrieved December 25, 2015.
- Zwaag, G. van der (May 17, 2015). "Apple nam navigatiebedrijf Coherent over" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- Tung, L. (September 17, 2015). "Apple acquires mapping visualisation startup Mapsense". ZDNet. Retrieved December 25, 2015.
- "Apple brengt watchOS 2.2 voor Apple Watch met verbeterde Kaarten-app uit" (in Dutch). iCulture. March 21, 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- Kulshrestha, Ashish (May 19, 2016). "Apple opens development office in Hyderabad" (PDF). The Economic Times. Retrieved October 15, 2016.
- "Apple Opens Development Office in Hyderabad". Apple Press Info. May 19, 2016. Retrieved October 15, 2016.
- Srinivasan, V. L. (February 11, 2016). "Apple to open first offshore technology development centre in India". ZDNet. Retrieved October 16, 2016.
- Meijer, Eveline (June 13, 2016). "Apple Maps krijgt nieuw design: alle vernieuwingen op een rij" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- Zwaag, Gonny van der (September 15, 2016). "Twintig kleine iOS 10-verbeteringen die je zeker even moet proberen" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- Dillet, Romain. "Apple Maps shows you the nearest bike-sharing stations – TechCrunch". techcrunch.com. Retrieved July 2, 2018.
- Estrada, Zac. "Apple Maps gets upgraded bike-sharing information". The Verge. Retrieved July 2, 2018.
- Panzarino, Matthew. "Apple is rebuilding Maps from the ground up – TechCrunch". techcrunch.com. Retrieved July 2, 2018.
- Panzarino, Matthew. "Questions about Apple's new Maps, answered – TechCrunch". techcrunch.com. Retrieved July 2, 2018.
- "Apple Maps vehicles". Retrieved November 12, 2018.
- "Apple confirms it's collecting data on foot to improve its Maps app". Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- Leswing, Kif (2020-01-30). "Apple's new and improved maps that cost 'billions' are now out across the U.S." CNBC. Retrieved 2020-01-31.
- "Apple delivers a new redesigned Maps for all users in the United States". Apple Newsroom. Retrieved 2020-10-03.
- "Revamped Apple Maps App Expanding to UK, Ireland, and Canada Later This Year". MacRumors. Retrieved 2020-10-03.
- "iOS 14: How to Get Cycling Directions in Apple Maps". MacRumors. Retrieved 2020-09-17.
- "UK, Ireland get Apple Maps Look Around, cycling directions". AppleInsider. Retrieved 2020-10-02.
- "Redesigned Apple Maps Expanding to Canada Soon". MacRumors. Retrieved 2020-11-16.
- Vroegop, B. (October 2, 2012). "Apple Maps efficiënter met data dan Google Maps" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved December 1, 2015.
- "Apple: Acknowledgements". Archived from the original on January 18, 2016. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- "TomTom extends Apple agreement". TomTom. May 19, 2015. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- "Apple: Maps". Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- "Apple: iOS Feature Availability". Retrieved June 11, 2017.
- Kahn, J. (November 16, 2015). "Apple adds Foursquare business listings to Apple Maps". 9to5Mac. Retrieved December 25, 2015.
- Zwaag, G. van der (June 12, 2012). "iOS 6 uitgelicht: Apple Maps-kaartendienst met grote Nederlandse invloed" (in Dutch). Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Hall, Z. (January 16, 2016). "watchOS 2.2 adds Nearby search to Maps for Apple Watch". 9to5Mac. Retrieved January 23, 2015.
- Painter, L. (September 15, 2015). "How to use Proactive in iOS 9: How Siri is becoming more proactive and smart in iOS 9". Macworld. Retrieved November 1, 2015.
- Rossignol, J. (September 16, 2015). "Inside iOS 9: Apple Maps Gains Transit Mode and Nearby Search". MacRumors. Retrieved November 1, 2015.
- "iOS 9 Available as a Free Update for iPhone, iPad & iPod touch Users September 16". Apple Press Info. September 9, 2015. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- "Apple activates 'Nearby' Maps search results in 4 countries, expands Flyover support". AppleInsider. October 26, 2015. Retrieved November 1, 2015.
- "Apple Previews iOS 9". Apple Press Info. June 8, 2015. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- "iOS - Feature Availbility - Apple". Retrieved March 20, 2018.
- McGarry, C. (October 19, 2015). "Apple Maps gets a boost with Boston transit and Amtrak routes". Macworld. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- Broussard, M. (April 28, 2016). "Apple Maps Expands Transit Data in New South Wales, Australia With TrainLink and Bus Routes". MacRumors. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- Rossignol, J. (December 19, 2016). "Apple Maps Expands Transit Directions Across the United Kingdom". MacRumors. Retrieved December 19, 2016.
- "iOS - Feature Availbility - Apple". Retrieved November 23, 2018.
- Wokke, A. (January 27, 2015). "Consumentenbond: verkeersinfo in Apple Maps scoort dikke onvoldoende" (in Dutch). Tweakers. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- "iOS 13 Preview - Features". Apple. Apple. Retrieved June 26, 2019.
- "Apple Launches "Maps Connect" Self-Service Local Listings Portal". Search Engine Land. October 21, 2014. Retrieved May 27, 2016.
- "Maps Connect". mapsconnect.apple.com. Retrieved May 27, 2016.
- "comScore: Market Rankings". Retrieved November 3, 2015.
- Arthur, C. (November 26, 2013). "How Apple Maps won on UK iPhones over Google Maps - despite Waze". The Guardian. Retrieved November 3, 2015.
- "4GEE MOBILE LIVING INDEX: Second half 2013 report" (PDF). December 2013. Retrieved October 22, 2015.
- Rogerson, J. (August 12, 2014). "Apple Maps surging back in fight against Google". TechRadar. Retrieved October 22, 2015.
- "4GEE MOBILE LIVING INDEX: First half report 2014" (PDF). Retrieved October 22, 2015.
- "4GEE MOBILE LIVING INDEX: First half report 2015" (PDF). Retrieved October 22, 2015.
- Zwaag, G. van der (June 23, 2011). "Google belooft 'geweldige Google Maps-ervaring' op iOS" (in Dutch). iCulture. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Thompson, N. (December 11, 2012). "Apple Maps flaw could be deadly, warn Australian police". CNN. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- Musil, S. (December 9, 2012). "Australia police discourage use of Apple maps app after rescues". CNET. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- Arthur, C. (December 10, 2012). "Apple redraws maps after Australian drivers led astray in the bush". The Guardian. Retrieved October 24, 2015.
- "'Alan Shatter concerned over fake Apple airport' Statement of the Day". The Journal. September 20, 2012. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- "Taiwan protests Apple maps that show island as province of China".
- "Why You Can't Trust GPS in China".
- Cook, T. (September 28, 2012). "Apple: A letter from Tim Cook on Maps". Archived from the original on September 28, 2012. Retrieved October 22, 2015.
- Yarow, J. (September 20, 2012). "Apple Responds To The Maps Backlash: 'We Are Just Getting Started With It'". Business Insider. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- Paczkowski, J. (September 20, 2012). "Apple Maps App Takes Reality Distortion to a Whole New Level". All Things Digital. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
- Ziegler, C. (October 29, 2012). "Apple's Scott Forstall's fatal mistake was not signing iOS 6 Maps apology letter: sources". The Verge. Retrieved October 24, 2015.
- Tetzeli, Rick (August 8, 2016). "Playing The Long Game Inside Tim Cook's Apple". Fast Company. Retrieved October 16, 2016.
- McGregor, Jena (August 12, 2016). "Tim Cook, the interview: Running Apple 'is sort of a lonely job'". The Washington Post. Retrieved October 16, 2016.
- Langley, H. (April 22, 2013). "TomTom still defensive over Apple Maps, says smartphones not a threat". TechRadar. Retrieved October 22, 2015.
- Braue, David. "Apple Maps' worldview is now better than Google Maps'". ZDNet. Retrieved January 31, 2016.
- Rocco Pendola. "Google Maps No Longer Embarrass Apple Maps". TheStreet.
- Lewis Painter. "Apple Maps vs Google Maps comparison review: is Google still on top? - Review - Macworld UK". Macworld UK.
- Joe McGauley (January 31, 2016). "Things Apple Maps Does Better Than Google Maps". thrillist.
- https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/taiwan/10413744/Taiwan-demands-Apple-change-map-that-shows-it-as-part-of-China.html
- Prankur Haldiya (July 24, 2019). "Apple Maps Vs Google Maps: Which one navigates precisely?". RipenApps Technologies.

