RAR-related orphan receptor beta
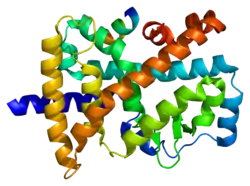
RAR-related orphan receptor beta (ROR-beta), also known as NR1F2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group F, member 2) is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RORB gene.[5]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the NR1 subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors. It is a DNA-binding protein that can bind as a monomer or as a homodimer to hormone response elements upstream of several genes to enhance the expression of those genes. The specific functions of this protein are not known, but it has been shown to interact with NM23-2, a nucleoside-diphosphate kinase involved in organogenesis and differentiation.[6]
In the brain, ROR-beta is concentrated in layer 4 of the cerebral cortex, where it plays a role in the development of structures such as barrel columns.[7]
See also
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000198963 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000036192 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Giguère V, Tini M, Flock G, Ong E, Evans RM, Otulakowski G (March 1994). "Isoform-specific amino-terminal domains dictate DNA-binding properties of ROR alpha, a novel family of orphan hormone nuclear receptors". Genes Dev. 8 (5): 538–53. doi:10.1101/gad.8.5.538. PMID 7926749.
- "Entrez Gene: RORB RAR-related orphan receptor B".
- Jabaudon D, Shnider SJ, Tischfield DJ, Galazo MJ, Macklis JD (May 2012). "RORβ induces barrel-like neuronal clusters in the developing neocortex". Cereb. Cortex. 22 (5): 996–1006. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhr182. PMC 3328343. PMID 21799210.
- Paravicini G, Steinmayr M, André E, Becker-André M (October 1996). "The metastasis suppressor candidate nucleotide diphosphate kinase NM23 specifically interacts with members of the ROR/RZR nuclear orphan receptor subfamily". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 227 (1): 82–7. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1996.1471. PMID 8858107.
Further reading
- Beeson WM, Perry TW, Zurcher TD (1977). "Effect of supplemental zinc on growth and on hair and blood serum levels of beef cattle". J. Anim. Sci. 45 (1): 160–5. doi:10.2527/jas1977.451160x. PMID 885817.
- Carlberg C, Hooft van Huijsduijnen R, Staple JK, DeLamarter JF, Becker-André M (1994). "RZRs, a new family of retinoid-related orphan receptors that function as both monomers and homodimers". Mol. Endocrinol. 8 (6): 757–70. doi:10.1210/me.8.6.757. PMID 7935491.
- Greiner EF, Kirfel J, Greschik H, Dörflinger U, Becker P, Mercep A, Schüle R (1996). "Functional analysis of retinoid Z receptor beta, a brain-specific nuclear orphan receptor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (19): 10105–10. Bibcode:1996PNAS...9310105G. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.19.10105. PMC 38344. PMID 8816759.
- Paravicini G, Steinmayr M, André E, Becker-André M (1996). "The metastasis suppressor candidate nucleotide diphosphate kinase NM23 specifically interacts with members of the ROR/RZR nuclear orphan receptor subfamily". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 227 (1): 82–7. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1996.1471. PMID 8858107.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1996). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Park HT, Baek SY, Kim BS, Kim JB, Kim JJ (1996). "Developmental expression of 'RZR beta, a putative nuclear-melatonin receptor' mRNA in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the rat". Neurosci. Lett. 217 (1): 17–20. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(96)13060-3. PMID 8905729.
- André E, Conquet F, Steinmayr M, Stratton SC, Porciatti V, Becker-André M (1998). "Disruption of retinoid-related orphan receptor beta changes circadian behavior, causes retinal degeneration and leads to vacillans phenotype in mice". EMBO J. 17 (14): 3867–77. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.14.3867. PMC 1170722. PMID 9670004.
- Greiner EF, Kirfel J, Greschik H, Huang D, Becker P, Kapfhammer JP, Schüle R (2000). "Differential ligand-dependent protein-protein interactions between nuclear receptors and a neuronal-specific cofactor". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (13): 7160–5. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.7160G. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.13.7160. PMC 16516. PMID 10860982.
- Gawlas K, Stunnenberg HG (2000). "Differential binding and transcriptional behaviour of two highly related orphan receptors, ROR alpha(4) and ROR beta(1)". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1494 (3): 236–41. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(00)00237-2. PMID 11121580.
- Gawlas K, Stunnenberg HG (2001). "Differential transcription of the orphan receptor RORbeta in nuclear extracts derived from Neuro2A and HeLa cells". Nucleic Acids Res. 29 (16): 3424–32. doi:10.1093/nar/29.16.3424. PMC 55847. PMID 11504880.
- Stehlin C, Wurtz JM, Steinmetz A, Greiner E, Schüle R, Moras D, Renaud JP (2001). "X-ray structure of the orphan nuclear receptor RORbeta ligand-binding domain in the active conformation". EMBO J. 20 (21): 5822–31. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.21.5822. PMC 125710. PMID 11689423.
- Sumi Y, Yagita K, Yamaguchi S, Ishida Y, Kuroda Y, Okamura H (2002). "Rhythmic expression of ROR beta mRNA in the mice suprachiasmatic nucleus". Neurosci. Lett. 320 (1–2): 13–6. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(02)00011-3. PMID 11849752. S2CID 54411407.
- Stehlin-Gaon C, Willmann D, Zeyer D, Sanglier S, Van Dorsselaer A, Renaud JP, Moras D, Schüle R (2003). "All-trans retinoic acid is a ligand for the orphan nuclear receptor ROR beta". Nat. Struct. Biol. 10 (10): 820–5. doi:10.1038/nsb979. PMID 12958591. S2CID 10108247.
External links
- orphan+nuclear+receptor+ROR-beta at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)