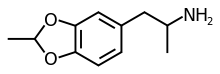
3,4-Ethylidenedioxyamphetamine
3,4-Ethylidenedioxyamphetamine (EIDA) is a substituted derivative of 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), which was developed by David Nichols and coworkers, in the course of research to determine the bulk tolerance around the benzodioxole portion of the MDA molecule. EIDA was found to produce similar effects to MDA in animals but with less than half the potency, while the isopropylidenedioxy derivative (IPIDA, IDA) did not substitute for MDA and instead had sedative and convulsant effects. This shows limited bulk tolerance at this position and (as with 2C-G-5) makes it likely the activity of EIDA will reside primarily in one enantiomer, although only the racemic mix has been studied as yet.[1][2][3]

Isopropylidenedioxyamphetamine (IDA)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15NO2 |
| Molar mass | 193.246 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
See also
References
- Nichols DE, Kostuba LJ (October 1979). "Steric effects of substituents on phenethylamine hallucinogens. 3,4-(Methylenedioxy)amphetamine analogues alkylated on the dioxole ring". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 22 (10): 1264–7. doi:10.1021/jm00196a022. PMID 513074.
- Nichols DE, Oberlender R, Burris K, Hoffman AJ, Johnson MP (November 1989). "Studies of dioxole ring substituted 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) analogues". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 34 (3): 571–6. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(89)90560-1. PMID 2623014. S2CID 7560526.
- Trachsel D, Hadorn M, Baumberger F (March 2006). "Synthesis of fluoro analogues of 3,4-(methylenedioxy)amphetamine (MDA) and its derivatives". Chemistry & Biodiversity. 3 (3): 326–36. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.688.5803. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200690035. PMID 17193269.
| Phenylalkyl- amines (other than cathinones) |
|
|---|---|
| Cyclized phenyl- alkylamines | |
| Cathinones | |
| Tryptamines | |
| Chemical classes | |
| Adamantanes | |
|---|---|
| Adenosine antagonists | |
| Alkylamines | |
| Ampakines | |
| Arylcyclohexylamines | |
| Benzazepines | |
| Cathinones |
|
| Cholinergics |
|
| Convulsants | |
| Eugeroics | |
| Oxazolines | |
| Phenethylamines |
|
| Phenylmorpholines | |
| Piperazines | |
| Piperidines |
|
| Pyrrolidines | |
| Racetams | |
| Tropanes |
|
| Tryptamines |
|
| Others |
|
| α1 |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α2 |
| ||||
| β |
| ||||
| See also | |||||
| D1-like |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-like |
| ||||
| |||||
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.