Pennington County, Minnesota
Pennington County is a county in the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of the 2010 United States Census, the population was 13,930.[1] Its county seat is Thief River Falls.[2]
Pennington County | |
|---|---|
 Old Carnegie Library, downtown Thief River Falls, Minnesota. | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Minnesota | |
 Minnesota's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 48°04′N 96°02′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | November 23, 1910 |
| Named for | Edmund Pennington |
| Seat | Thief River Falls |
| Largest city | Thief River Falls |
| Area | |
| • Total | 618 sq mi (1,600 km2) |
| • Land | 617 sq mi (1,600 km2) |
| • Water | 1.7 sq mi (4 km2) 0.3% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 13,930 |
| • Estimate (2019) | 14,119 |
| • Density | 23.0/sq mi (8.9/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 7th |
| Website | co |
History
The Wisconsin Territory was established by the federal government effective 3 July 1836, and existed until its eastern portion was granted statehood (as Wisconsin) in 1848. The federal government set up the Minnesota Territory in the remaining territory, effective 3 March 1849. The newly organized territorial legislature created nine counties across the territory in October of that year. One of those original counties, Pembina, had its lower portion partitioned in 1858 by the newly organized Minnesota State legislature to create Polk County. On 24 December 1896, the legislature partitioned the northern portion of Polk to create Red Lake County. Then on 23 November 1910,[3] the northern part of Red Lake was sectioned off to create Pennington County, the penultimate Minnesota county to be created (followed by Lake of the Woods in 1922). The county was named for Edmund Pennington (1848-1926), a longtime Minnesota railroad executive, who was serving as president of the Minneapolis, St. Paul, and Sault Ste. Marie Railway when the county was formed. Thief River Falls, the area's major settlement (platted in 1887), was specified as the county seat.[4]
Geography
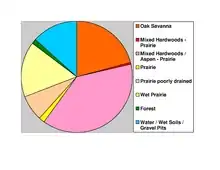
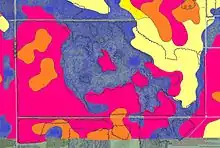
The Red Lake River flows westward into the county from Beltrami County through Pennington's central portion. Near Thief River Falls it is joined by the Thief River, flowing southward into the county from Marshall County. The combined flow exits Pennington County toward the south, then swings west- and northwestward as it moves to its confluence with the Red River near Grand Forks, North Dakota. The county terrain consists of low rolling hills, lightly wooded, with all available areas devoted to agriculture.[6] The terrain slopes to the west and south,[7] with its highest point near the lower east border, at 1,186' (361m) ASL.[8] The county has a total area of 618 square miles (1,600 km2), of which 617 square miles (1,600 km2) is land and 1.7 square miles (4.4 km2) (0.3%) is water.[9] Pennington is one of 17 Minnesota savanna region counties with more savanna soils than either prairie or forest soils.
Major highways
 U.S. Highway 59
U.S. Highway 59 Minnesota State Highway 1
Minnesota State Highway 1 Minnesota State Highway 32
Minnesota State Highway 32 Minnesota State Highway 219
Minnesota State Highway 219.svg.png.webp) Pennington County State-Aid Highway 3: Major connector between Pennington County and Grand Forks. Connects with Polk County State-Aid Highway 21.
Pennington County State-Aid Highway 3: Major connector between Pennington County and Grand Forks. Connects with Polk County State-Aid Highway 21..svg.png.webp) Pennington County State-Aid Highway 17: Connects Thief River Falls to the Airport
Pennington County State-Aid Highway 17: Connects Thief River Falls to the Airport.svg.png.webp) Pennington County State-Aid Highway 10: Major route, also known as Pembina Trail
Pennington County State-Aid Highway 10: Major route, also known as Pembina Trail.svg.png.webp) Pennington County State-Aid Highway 16: US 59 Truck Bypass of Thief River Falls, connects US 59 / MN 1 on the west side of town to MN 32 on the south side of town
Pennington County State-Aid Highway 16: US 59 Truck Bypass of Thief River Falls, connects US 59 / MN 1 on the west side of town to MN 32 on the south side of town.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp) Pennington County State-Aid Highways 27 & 28: Designated and designed for heavy truck traffic connecting US 2 to Roseau County and Marshall County
Pennington County State-Aid Highways 27 & 28: Designated and designed for heavy truck traffic connecting US 2 to Roseau County and Marshall County
Airports
Adjacent counties
- Marshall County - north
- Beltrami County - east
- Clearwater County - southeast
- Red Lake County - south
- Polk County - west
Protected areas
- Higinbotham State Wildlife Management Area
- Pembina State Wildlife Management Area
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1910 | 9,376 | — | |
| 1920 | 12,091 | 29.0% | |
| 1930 | 10,487 | −13.3% | |
| 1940 | 12,913 | 23.1% | |
| 1950 | 12,965 | 0.4% | |
| 1960 | 12,468 | −3.8% | |
| 1970 | 13,266 | 6.4% | |
| 1980 | 15,258 | 15.0% | |
| 1990 | 13,306 | −12.8% | |
| 2000 | 13,584 | 2.1% | |
| 2010 | 13,930 | 2.5% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 14,119 | [10] | 1.4% |
| US Decennial Census[11] 1790-1960[12] 1900-1990[13] 1990-2000[14] 2010-2019[1] | |||
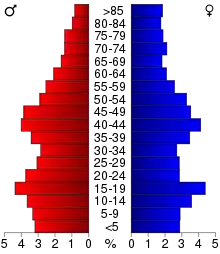
2000 census
As of the 2000 United States Census, there were 13,584 people, 5,525 households, and 3,552 families in the county. The population density was 22.0/sqmi (8.50/km2). There were 6,033 housing units at an average density of 9.78.sqmi (3.78/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 97.02% White, 0.21% Black or African American, 0.82% Native American, 0.59% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 0.51% from other races, and 0.81% from two or more races. 1.24% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 49.0% were of Norwegian, 15.4% German and 7.2% Swedish ancestry.
There were 5,525 households, out of which 30.60% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 51.70% were married couples living together, 9.10% had a female householder with no husband present, and 35.70% were non-families. 29.50% of all households were made up of individuals, and 12.60% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.38 and the average family size was 2.95.
The county population contained 24.50% under the age of 18, 10.30% from 18 to 24, 26.50% from 25 to 44, 22.90% from 45 to 64, and 15.80% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females there were 97.50 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 94.60 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $34,216, and the median income for a family was $43,936. Males had a median income of $30,771 versus $21,078 for females. The per capita income for the county was $17,346. About 7.70% of families and 11.10% of the population were below the poverty line, including 10.70% of those under age 18 and 14.80% of those age 65 or over.
Communities
Cities
- Goodridge
- St. Hilaire
- Thief River Falls (county seat)
Unincorporated communities
Townships
- Black River Township
- Bray Township
- Clover Leaf Township
- Deer Park Township
- Goodridge Township
- Hickory Township
- Highlanding Township
- Kratka Township
- Mayfield Township
- Norden Township
- North Township
- Numedal Township
- Polk Centre Township
- Reiner Township
- River Falls Township
- Rocksbury Township
- Sanders Township
- Silverton Township
- Smiley Township
- Star Township
- Wyandotte Township
Politics
Pennington County has a fairly balanced voting record but has tended to vote Republican in recent decades. In 60% of national elections since 1980 the county selected the Republican Party candidate (as of 2016).
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 59.6% 4,000 | 32.0% 2,147 | 8.5% 568 |
| 2012 | 50.7% 3,305 | 46.4% 3,024 | 2.9% 188 |
| 2008 | 47.6% 3,248 | 49.8% 3,394 | 2.6% 180 |
| 2004 | 53.7% 3,767 | 44.4% 3,117 | 1.9% 133 |
| 2000 | 53.5% 3,380 | 38.9% 2,458 | 7.6% 482 |
| 1996 | 36.0% 2,129 | 47.6% 2,814 | 16.4% 972 |
| 1992 | 33.9% 2,155 | 40.5% 2,578 | 25.6% 1,626 |
| 1988 | 48.1% 2,920 | 51.1% 3,105 | 0.8% 46 |
| 1984 | 54.5% 3,536 | 44.9% 2,913 | 0.6% 40 |
| 1980 | 50.1% 3,715 | 41.8% 3,101 | 8.1% 600 |
| 1976 | 43.5% 3,023 | 54.5% 3,787 | 2.0% 138 |
| 1972 | 53.8% 3,548 | 43.8% 2,892 | 2.4% 160 |
| 1968 | 41.1% 2,247 | 54.9% 2,998 | 4.0% 220 |
| 1964 | 29.5% 1,630 | 70.4% 3,894 | 0.2% 10 |
| 1960 | 44.1% 2,537 | 55.6% 3,204 | 0.3% 18 |
| 1956 | 44.9% 2,408 | 55.0% 2,947 | 0.1% 4 |
| 1952 | 48.6% 2,726 | 49.9% 2,802 | 1.6% 87 |
| 1948 | 31.4% 1,759 | 60.7% 3,402 | 8.0% 447 |
| 1944 | 31.1% 1,525 | 67.9% 3,330 | 1.0% 50 |
| 1940 | 31.8% 1,857 | 66.5% 3,886 | 1.7% 98 |
| 1936 | 24.4% 1,258 | 72.5% 3,736 | 3.1% 161 |
| 1932 | 28.1% 1,212 | 63.6% 2,743 | 8.2% 355 |
| 1928 | 65.3% 2,506 | 31.2% 1,198 | 3.5% 134 |
| 1924 | 31.2% 1,126 | 4.1% 146 | 64.8% 2,337 |
| 1920 | 60.7% 2,320 | 20.1% 768 | 19.2% 734 |
| 1916 | 40.5% 868 | 46.8% 1,004 | 12.7% 273 |
| 1912 | 13.0% 244 | 22.6% 423 | 64.4% 1,205 |
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved September 1, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved 7 June 2011.
- "Minnesota Place Names". Minnesota Historical Society. Archived from the original on June 20, 2012. Retrieved March 18, 2014.
- Upham, Warren. Minnesota Geographic Names (1920), pp. 406-408 (accessed April 29, 2019)
- Nelson, Steven (2011). Savanna Soils of Minnesota. Minnesota: Self. pp. 57-60. ISBN 978-0-615-50320-2.
- Pennington County MN Google Maps (accessed 29 April 2019)
- ""Find an Altitude/Pennington County MN" Google Maps (accessed 29 April 2019)". Archived from the original on 21 May 2019. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- High Point of Pennington County, Minnesota. PeakBagger.com (accessed 29 April 2019)
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". US Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved March 26, 2020.
- "US Decennial Census". US Census Bureau. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". US Census Bureau. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). US Census Bureau. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- Leip, David. "Atlas of US Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved October 10, 2018.
